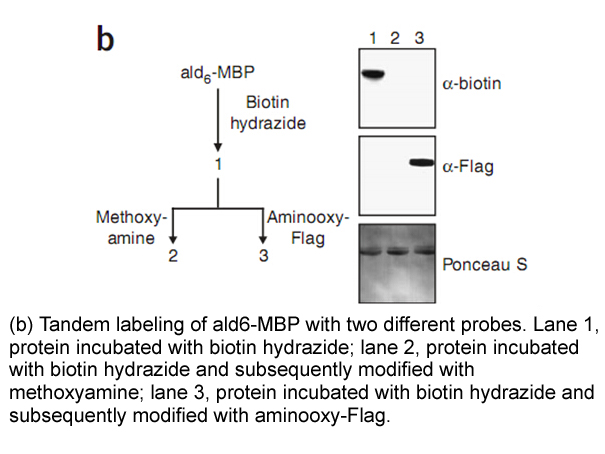
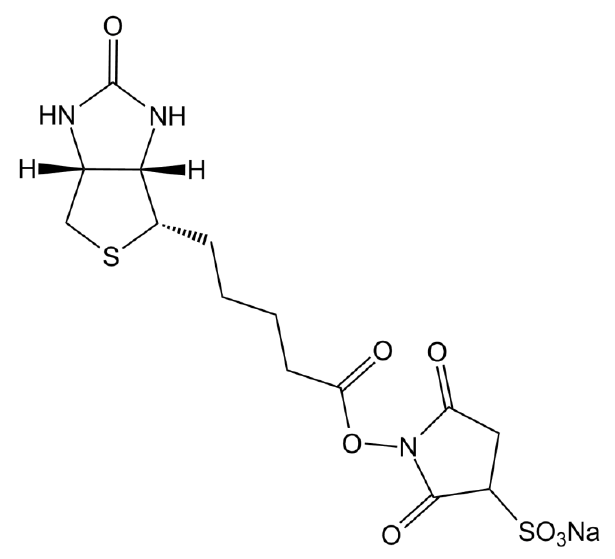
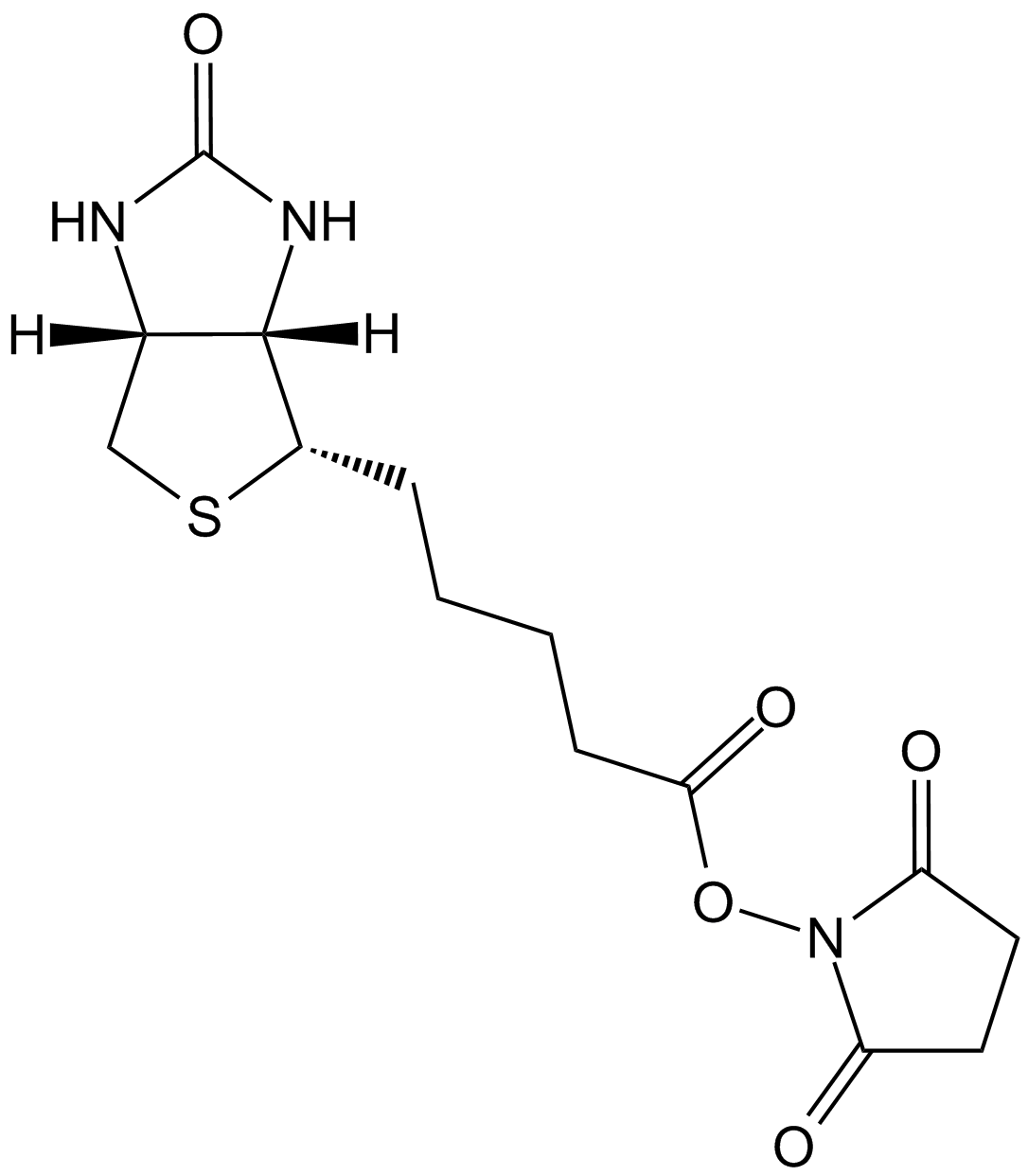
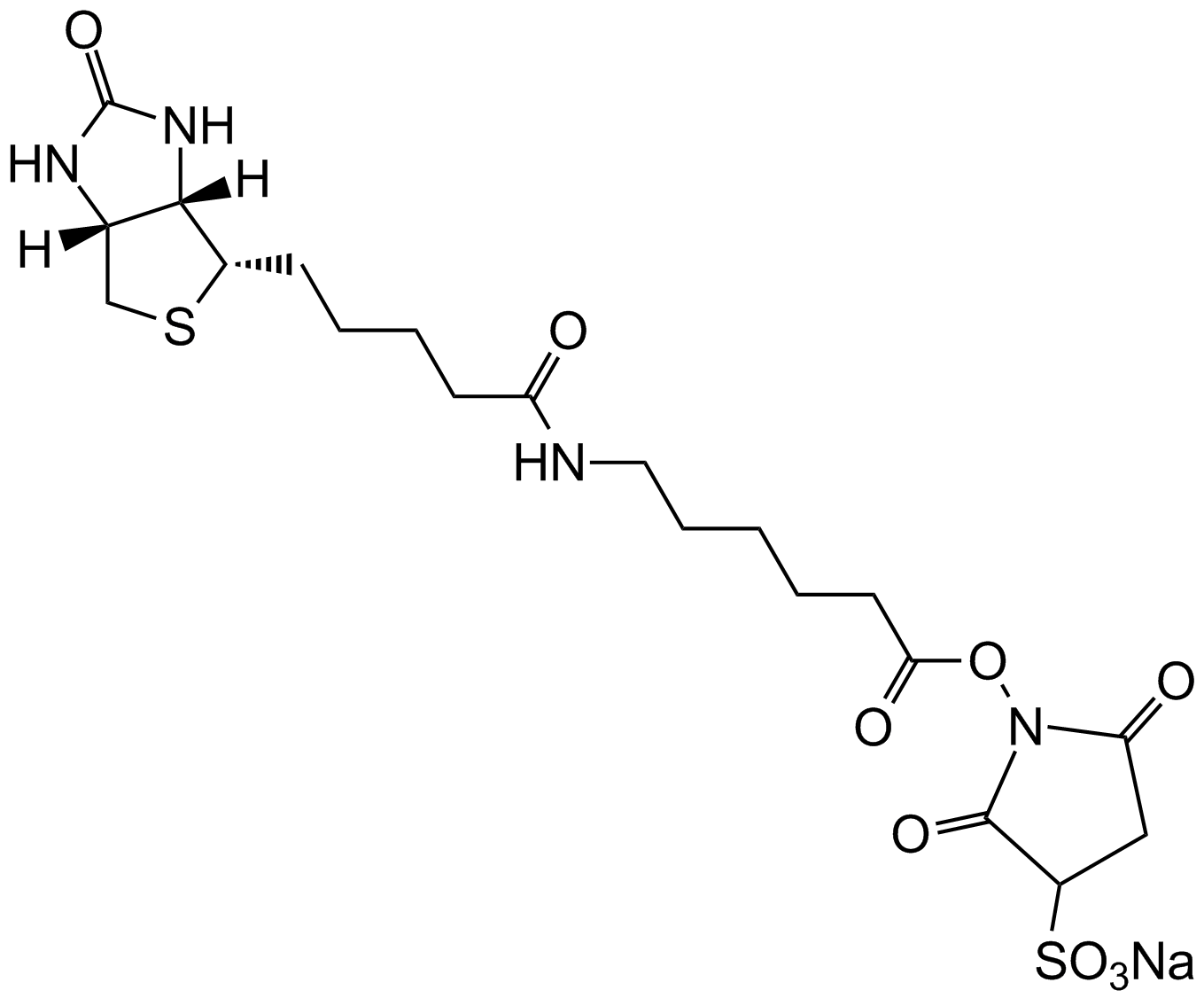
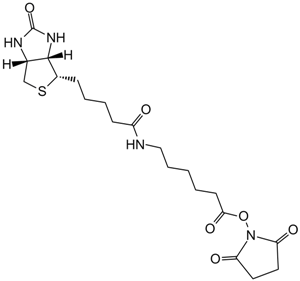
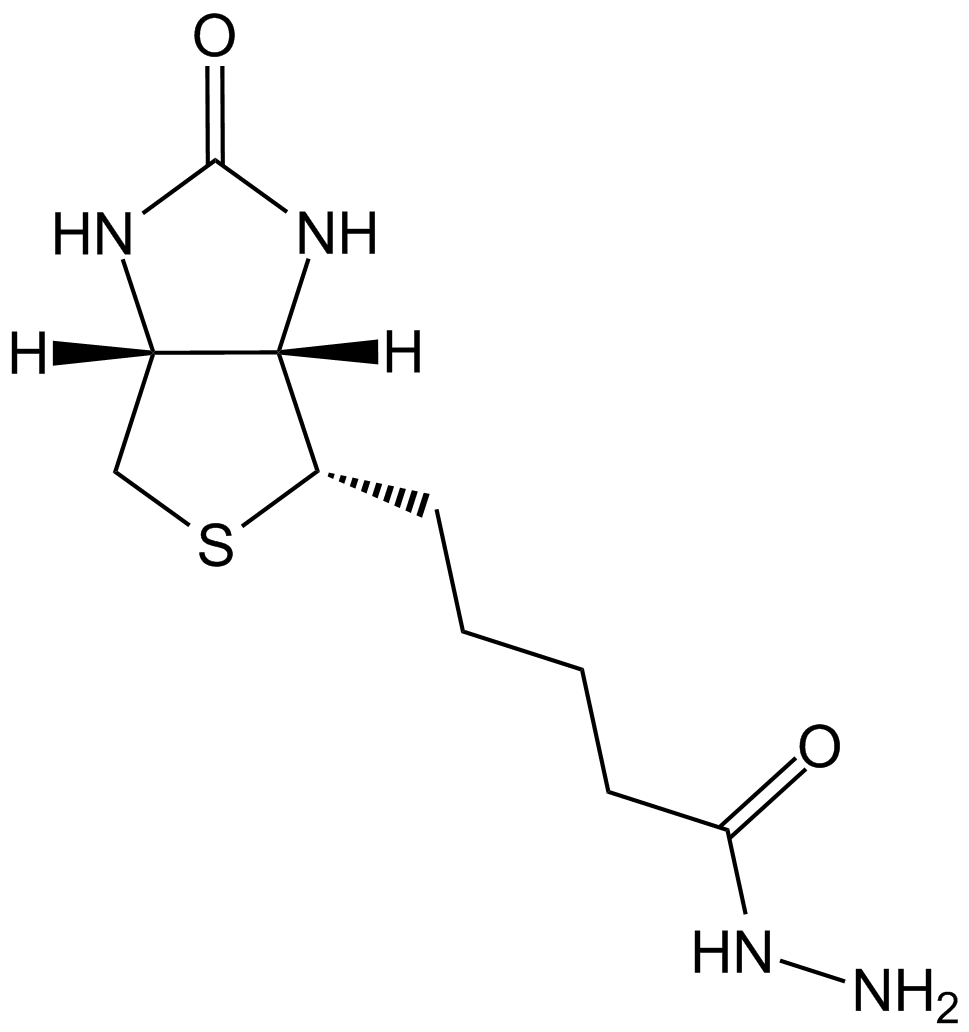
Biotin Hydrazide
Biotin hydrazide is a biotinyl derivative that can be used as a probe for the determination of protein carbonylation, which is a component of several diseases. Protein carbonylation, an irreversible post translational modification (PTM), is caused by attack of reactive oxygen species (ROS), numerous lipid oxidation products (such as α,β-unsaturated γ-hydroxyalkenals), or nonemzymatic glycation resulting in the loss of protein function. Biotin hydrazide is a preferred carbonyl-reactive probe for its direct reaction and chemistry and no requirement of additional catalysts or reducing agents. Biotin hydrazide exclusively and readily derivatizes carbonyl groups at pH 5.5, which facilitates its use to measure carbonylated proteins in biological samples.
Reference
Kenneth Hensley, Kelly S. Williamson. Protein Carbonyl Determination Using Biotin Hydrazide. Methods in Biological Oxidative Stress. Methods in Pharmacology and Toxicology 2003, pp 195-199
Madian AG, Regnier FE. Proteomic identification of carbonylated proteins and their oxidation sites. J Proteome Res. 2010;9(8):3766-3780.
• Glycoprotein labeling—biotinylate glycosylated proteins at sialic acid residues for detection or purification using streptavidin probes or resins
• Cell surface labeling—biotinylate and isolate cell surface glycoproteins
• Aldehyde-reactive—reacts with aldehydes formed by periodate-oxidation of sugar groups
• Hydrazide-activated—perform reactions at pH 4 to 6 in buffers such as sodium acetate
• Irreversible—forms semi-permanent hydrazone bonds; spacer arm cannot be cleaved
• Solubility—water insoluble, usually dissolved in DMSO before further dilution in aqueous buffers
• Spacer arm length—15.7Å
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 258.3 |
| Cas No. | 66640-86-6 |
| Formula | C10H18N4O2S |
| Synonyms | (+)-Biotin Hydrazide; Biotin-Hz; Hydrazide Biotin; Biotine Hydrazide |
| Solubility | insoluble in EtOH; ≥12.9 mg/mL in DMSO with gentle warming; ≥2.98 mg/mL in H2O with ultrasonic |
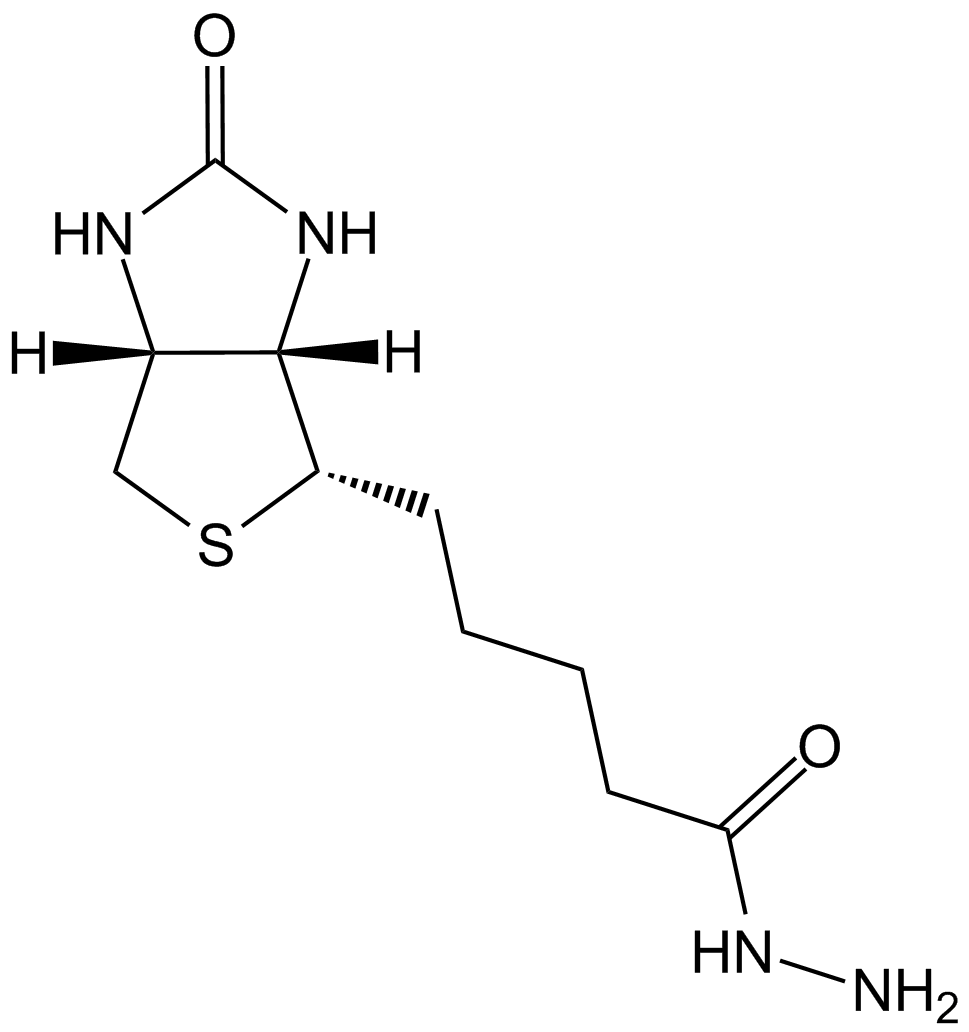
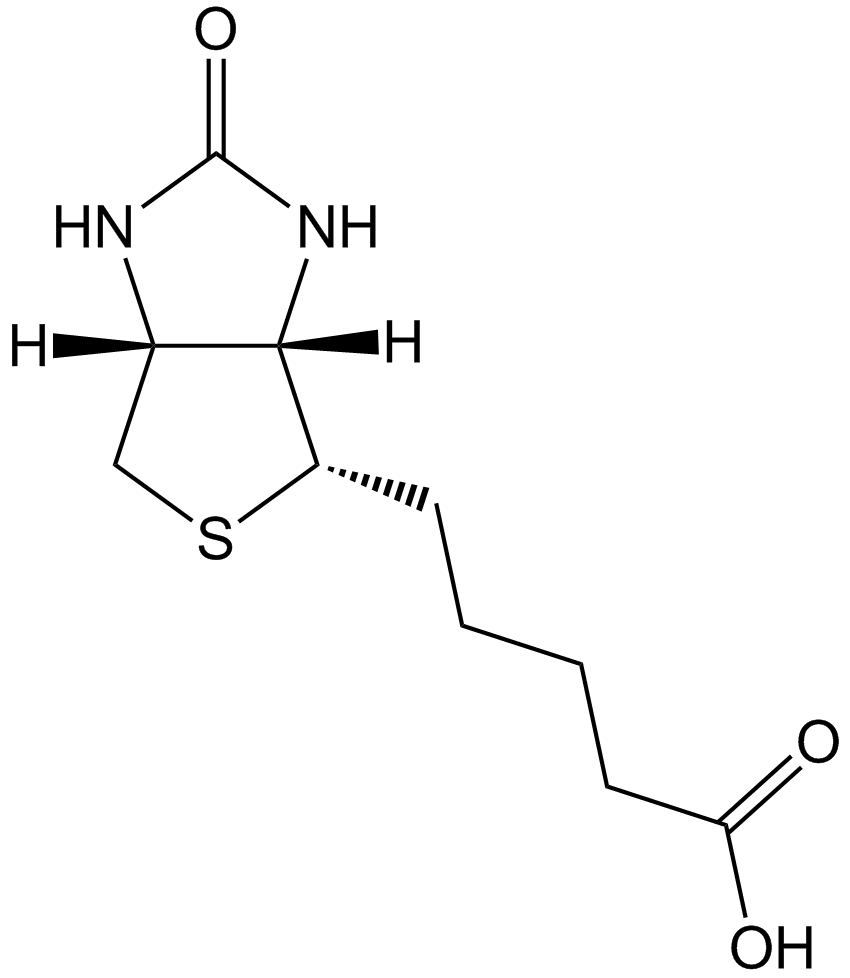
| Chemical Name | 5-[(3aS,4S,6aR)-2-oxo-1,3,3a,4,6,6a-hexahydrothieno[3,4-d]imidazol-4-yl]pentanehydrazide |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | NNC(CCCC[C@@H]([C@H]1N2)SC[C@@H]1NC2=O)=O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Biotinylation method [1]: | |
|
Sample |
human umbilical cord HA |
|
Preparation method |
Soluble in DMSO. Dissolve glycoprotein at a concentration of 1-5 mg/mL in cold 100mM Sodium Acetate, pH 5.5. |
|
Reaction Conditions |
1 mM, overnight at 4℃ |
|
Applications |
One hundred milligrams of human umbilical cord HA was dissolved in 0.1 M Mes, pH 5.0, to a final concentration of 1 mg/ml and allowed to dissolve for at least 24 h at 4℃ prior to the coupling of biotin. Biotin hydrazide was dissolved in DMSO as a stock solution of 100 mM and added to the HA solution to a final concentration of 1 mM. A stock solution of 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylamin-opropyl) carbidodiimide (EDAC) was prepared as a 100 mM stock solution in dH2O and added to the HA–biotin solution at a final concentration of 30 mM. This solution was left stirred overnight at 4℃. Unlinked biotin and EDAC were removed after the addition of 4M guanidine–HCl. The dialyzed, biotinylated HA (bHA) was aliquoted and stored at 0207C for up to several months. |
|
References: [1]. Gregory I. Frost and Robert Stern. A Microtiter-Based Assay for Hyaluronidase Activity Not Requiring Specialized Reagents. ANALYTICAL BIOCHEMISTRY 251, 263–269 (1997). |
|
| Description | Biotin Hydrazide is a biotinylation reagent used to biotinylate glycoproteins and glycolipids. | |||||
| Targets | glycoproteins | glycolipids | ||||
| IC50 | ||||||
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure
Related Biological Data