Search results for: 'signaling pathways dna damage dna repair dna alkylating'
-
 L1033 DiscoveryProbe™ DNA Damage/DNA Repair LibrarySummary: A unique collection of 481 DNA Damage/DNA repair-related compounds for DNA damage/DNA repair research.
L1033 DiscoveryProbe™ DNA Damage/DNA Repair LibrarySummary: A unique collection of 481 DNA Damage/DNA repair-related compounds for DNA damage/DNA repair research. -
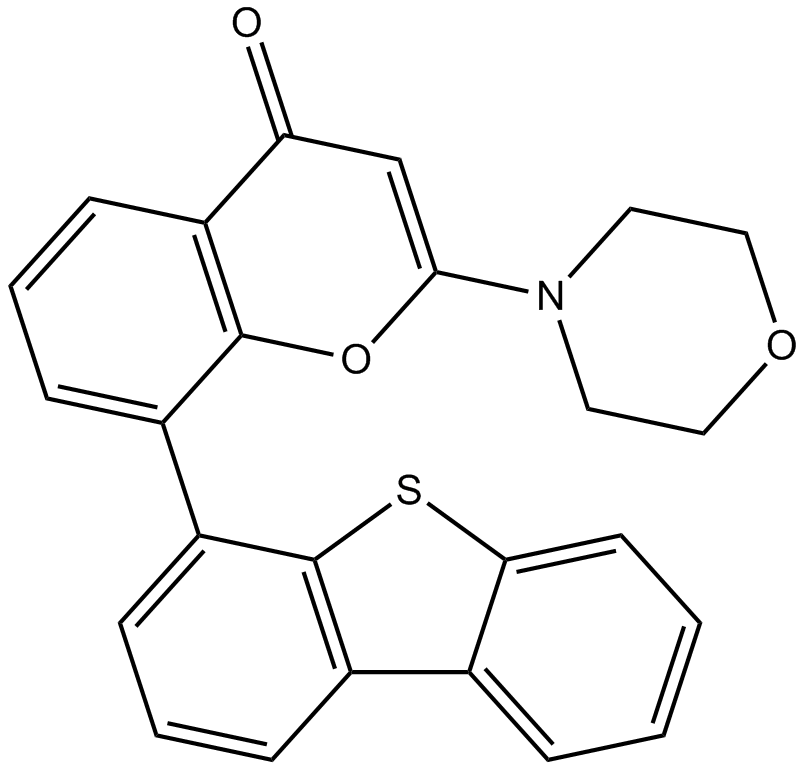 A8315 NU7441 (KU-57788)4 CitationTarget: PI3K|DNA-PKSummary: DNA-PK inhibitor
A8315 NU7441 (KU-57788)4 CitationTarget: PI3K|DNA-PKSummary: DNA-PK inhibitor -
 K1811 DNA Clean Beads1 CitationSummary: DNA Purification Sorting Magnetic Beads are suitable for DNA purification and fragment size sorting in NGS library construction and are a perfect alternative to AMPure XP Beads.
K1811 DNA Clean Beads1 CitationSummary: DNA Purification Sorting Magnetic Beads are suitable for DNA purification and fragment size sorting in NGS library construction and are a perfect alternative to AMPure XP Beads. -
 K3105 Bst DNA PolymeraseSummary: Bst DNA polymerase, an ideal choice for isothermal nucleic acid amplification.
K3105 Bst DNA PolymeraseSummary: Bst DNA polymerase, an ideal choice for isothermal nucleic acid amplification. -
 K3107 T4 DNA PolymeraseSummary: T4 DNA Polymerase,a template-dependent DNA polymerase.
K3107 T4 DNA PolymeraseSummary: T4 DNA Polymerase,a template-dependent DNA polymerase. -
 K3108 UltraFidelity™ DNA PolymeraseSummary: UltraFidelity DNA Polymerase
K3108 UltraFidelity™ DNA PolymeraseSummary: UltraFidelity DNA Polymerase -
 K3153 Taq DNA LigaseSummary: A heat-stable ligase, widely used in PCR amplification, gene cloning and genome sequencing, among others
K3153 Taq DNA LigaseSummary: A heat-stable ligase, widely used in PCR amplification, gene cloning and genome sequencing, among others -
 K2277 γH2AX DNA Damage Detection Kit (Rabbit mAb/Red)Summary: Detection of DNA damage by γ-H2AX immunofluorescence (rabbit mAb, red fluorescence)
K2277 γH2AX DNA Damage Detection Kit (Rabbit mAb/Red)Summary: Detection of DNA damage by γ-H2AX immunofluorescence (rabbit mAb, red fluorescence) -
 K2274 γH2AX DNA Damage Detection Kit (Mouse mAb/Green)Summary: Detection of DNA damage by γ-H2AX immunofluorescence (mouse mAb, green fluorescence)
K2274 γH2AX DNA Damage Detection Kit (Mouse mAb/Green)Summary: Detection of DNA damage by γ-H2AX immunofluorescence (mouse mAb, green fluorescence) -
 K2275 γH2AX DNA Damage Detection Kit (Mouse mAb/Red)Summary: Detection of DNA damage by γ-H2AX immunofluorescence (mouse mAb, red fluorescence)
K2275 γH2AX DNA Damage Detection Kit (Mouse mAb/Red)Summary: Detection of DNA damage by γ-H2AX immunofluorescence (mouse mAb, red fluorescence)


