Search results for: 'signaling pathways metabolism carbonic anhydrase'
-
 L1044 DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling LibrarySummary: A unique collection of 73 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research.
L1044 DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling LibrarySummary: A unique collection of 73 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research. -
 L1026 DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Library1 CitationSummary: A unique collection of 556 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch.
L1026 DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Library1 CitationSummary: A unique collection of 556 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch. -
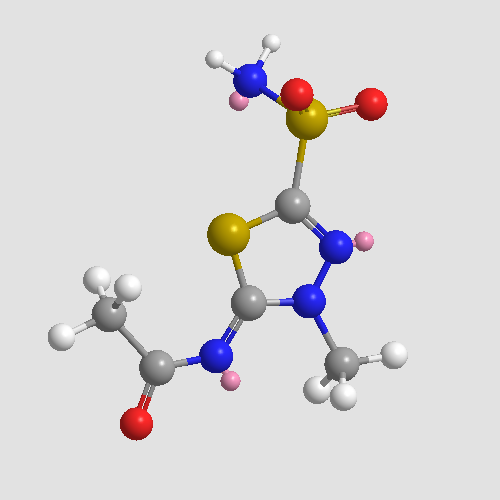 A4364 MethazolamideTarget: Carbonic AnhydrasesSummary: Carbonic anhydrase inhibitor
A4364 MethazolamideTarget: Carbonic AnhydrasesSummary: Carbonic anhydrase inhibitor -
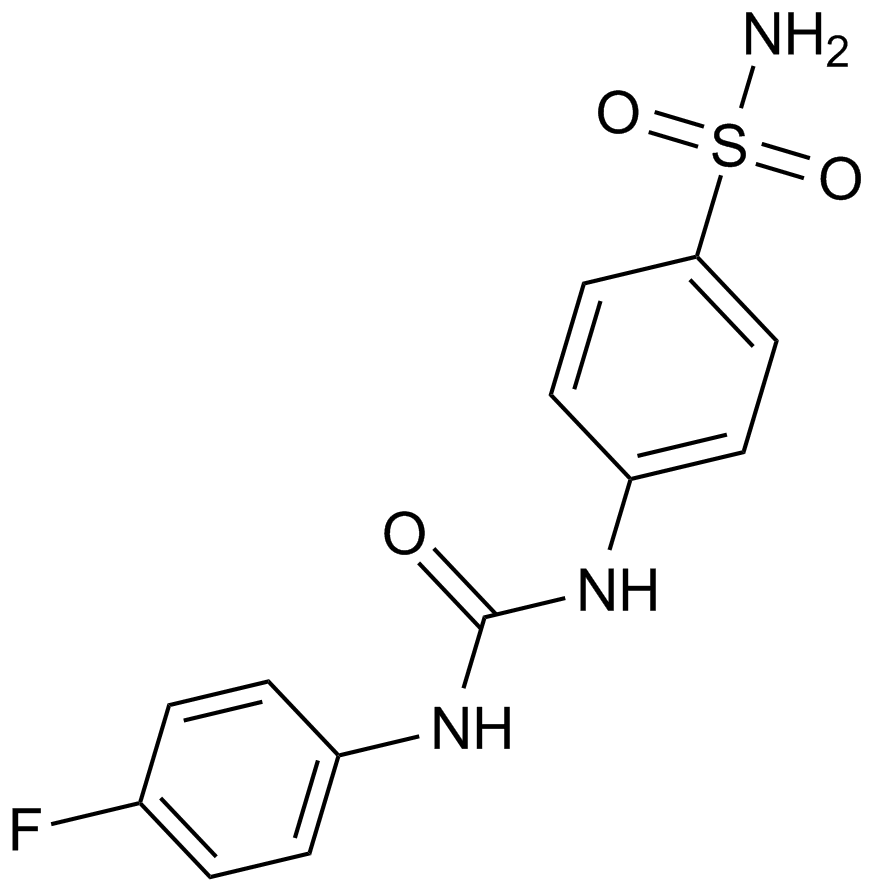 A4358 U-104Target: Carbonic AnhydrasesSummary: CAIX inhibitor
A4358 U-104Target: Carbonic AnhydrasesSummary: CAIX inhibitor -
 MA1585 Anti-Carbonic Anhydrase 1 Rabbit Monoclonal AntibodySummary: Anti-Carbonic Anhydrase 1 Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody
MA1585 Anti-Carbonic Anhydrase 1 Rabbit Monoclonal AntibodySummary: Anti-Carbonic Anhydrase 1 Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody -
 MA1586 Anti-Carbonic Anhydrase 1 Rabbit Monoclonal AntibodySummary: Anti-Carbonic Anhydrase 1 Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody
MA1586 Anti-Carbonic Anhydrase 1 Rabbit Monoclonal AntibodySummary: Anti-Carbonic Anhydrase 1 Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody -
 MA1587 Anti-Carbonic Anhydrase 2 Rabbit Monoclonal AntibodySummary: Anti-Carbonic Anhydrase 2 Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody
MA1587 Anti-Carbonic Anhydrase 2 Rabbit Monoclonal AntibodySummary: Anti-Carbonic Anhydrase 2 Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody -
 MA1588 Anti-Carbonic Anhydrase 9 Rabbit Monoclonal AntibodySummary: Anti-Carbonic Anhydrase 9 Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody
MA1588 Anti-Carbonic Anhydrase 9 Rabbit Monoclonal AntibodySummary: Anti-Carbonic Anhydrase 9 Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody -
 MA1589 Anti-Carbonic Anhydrase 9 Rabbit Monoclonal AntibodySummary: Anti-Carbonic Anhydrase 9 Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody
MA1589 Anti-Carbonic Anhydrase 9 Rabbit Monoclonal AntibodySummary: Anti-Carbonic Anhydrase 9 Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody -
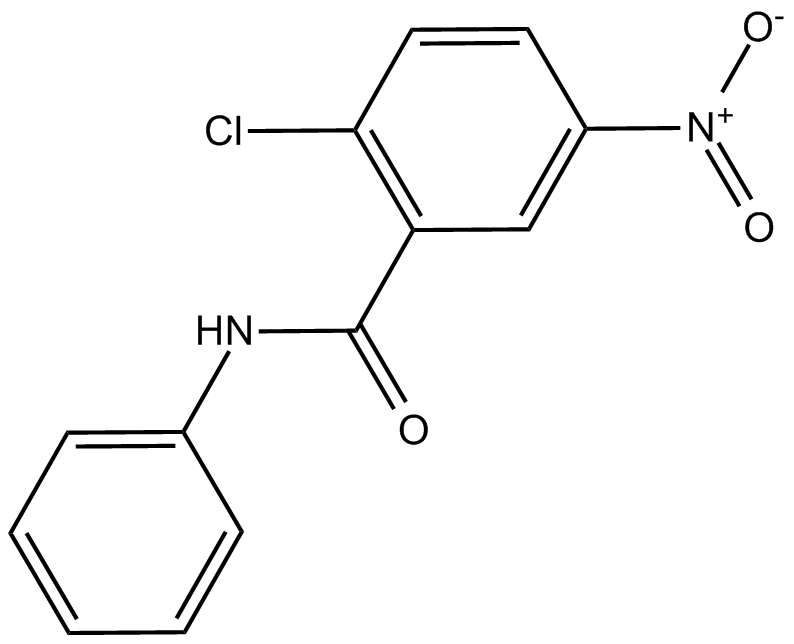 A4300 GW96627 CitationSummary: PPARγ antagonist
A4300 GW96627 CitationSummary: PPARγ antagonist


