Search results for: 'signaling pathways apoptosis c ret'
-
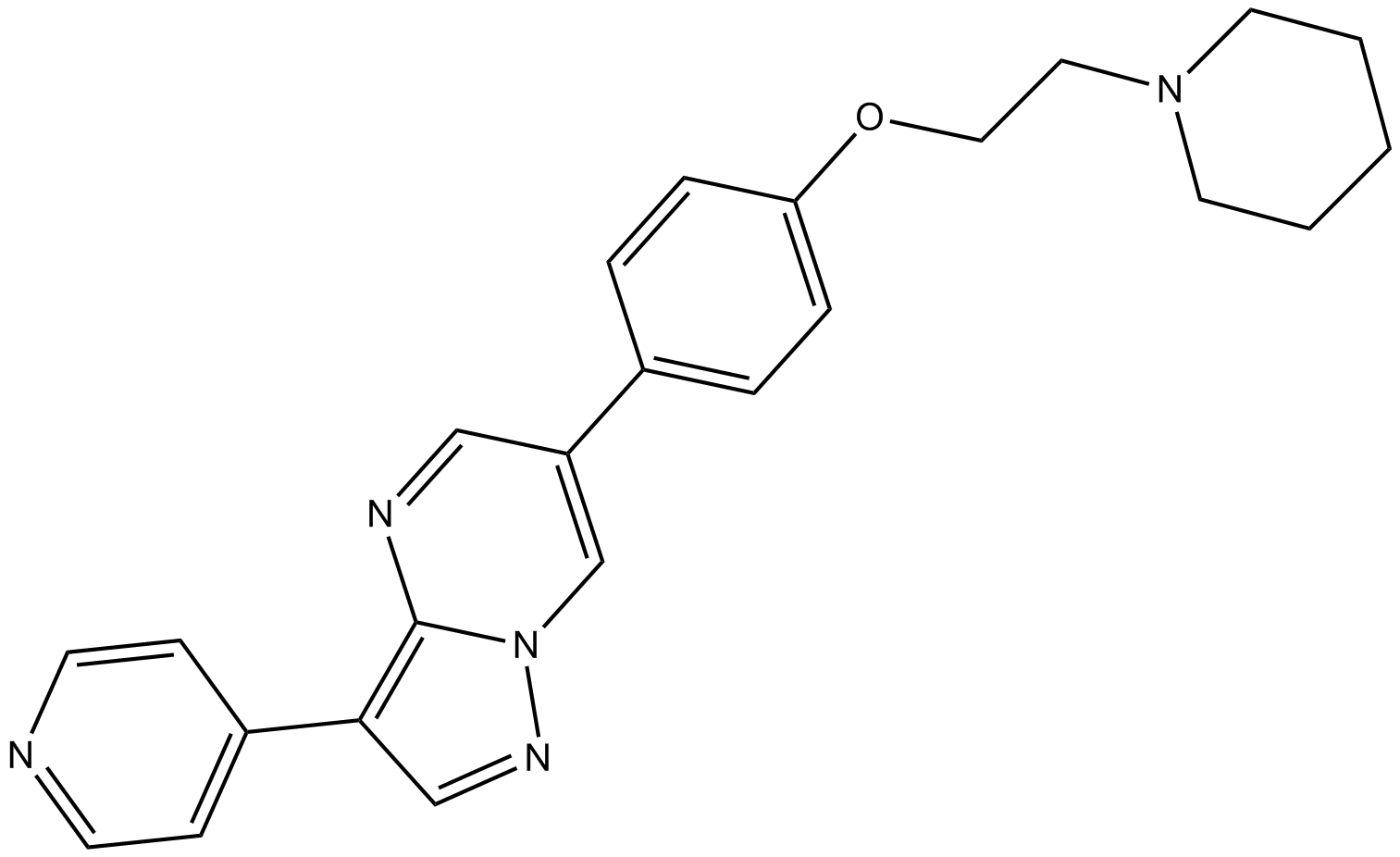 B3252 Dorsomorphin (Compound C)38 CitationTarget: AMPKSummary: AMPK inhibitor
B3252 Dorsomorphin (Compound C)38 CitationTarget: AMPKSummary: AMPK inhibitor -
 K2104 Cytochrome c Apoptosis Assay Kit
K2104 Cytochrome c Apoptosis Assay Kit -
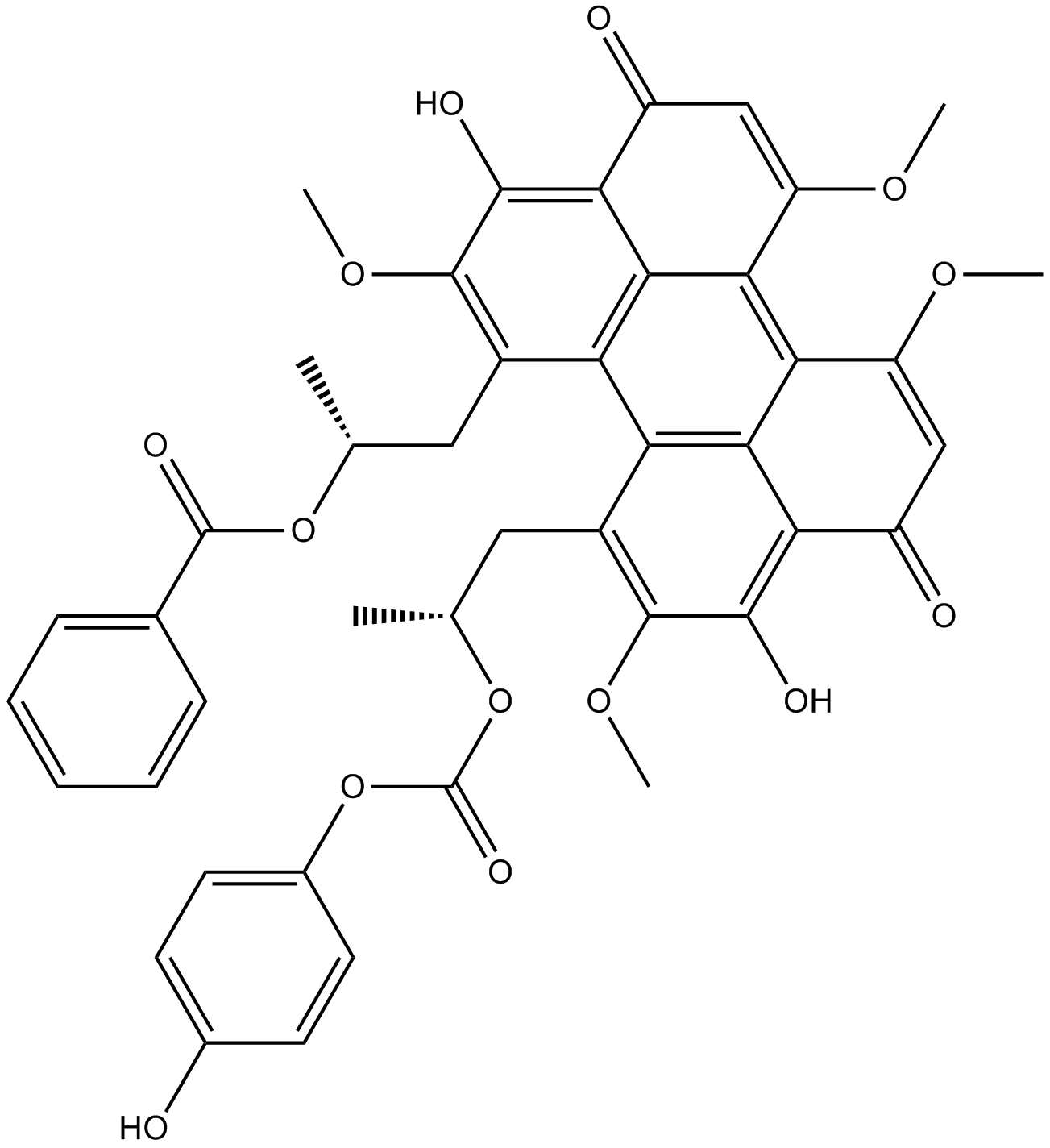 B6807 Calphostin CSummary: protein kinase C inhibitor
B6807 Calphostin CSummary: protein kinase C inhibitor -
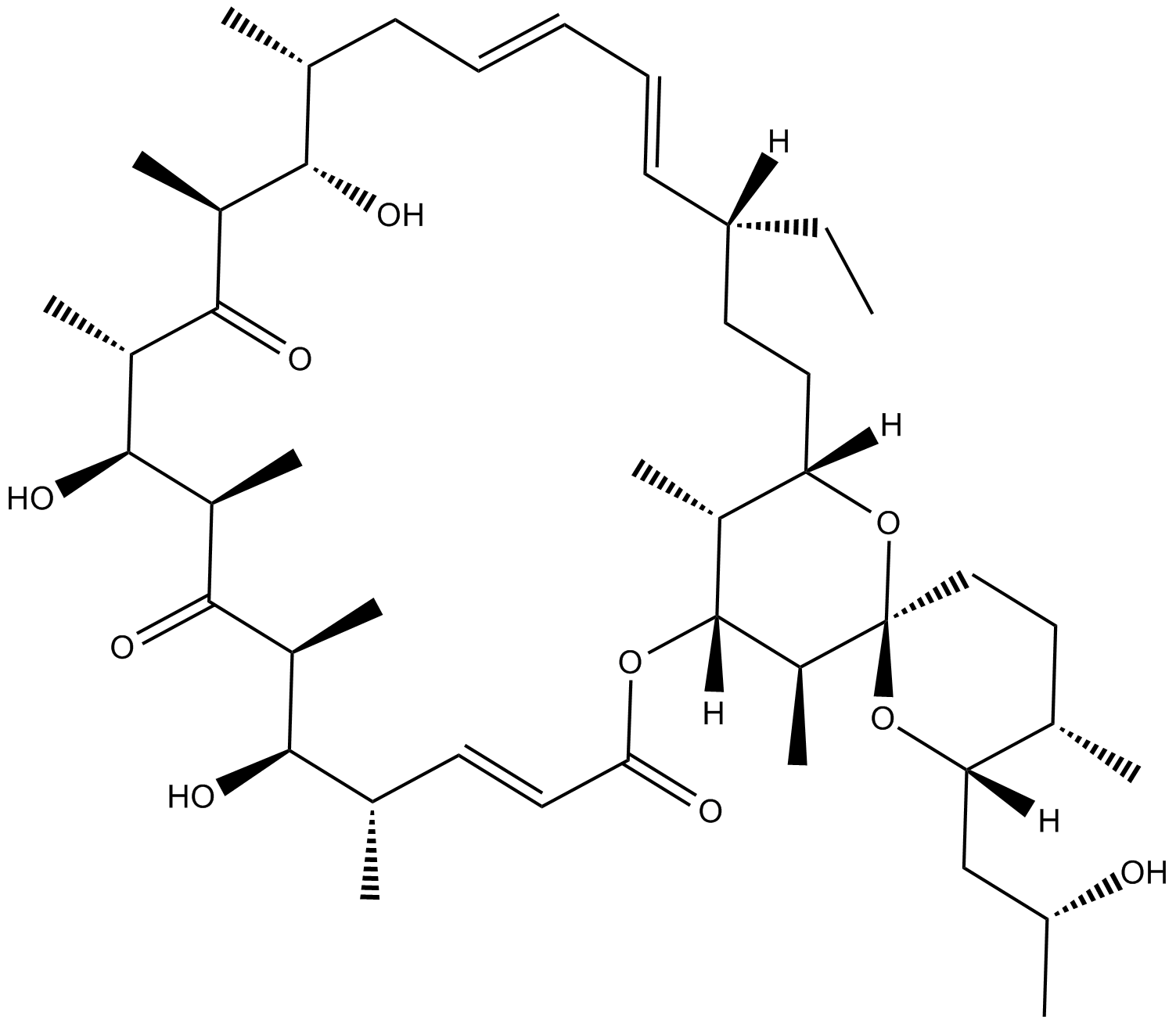 C3410 Oligomycin CSummary: mitochondrial F1FO-ATP synthase inhibitor
C3410 Oligomycin CSummary: mitochondrial F1FO-ATP synthase inhibitor -
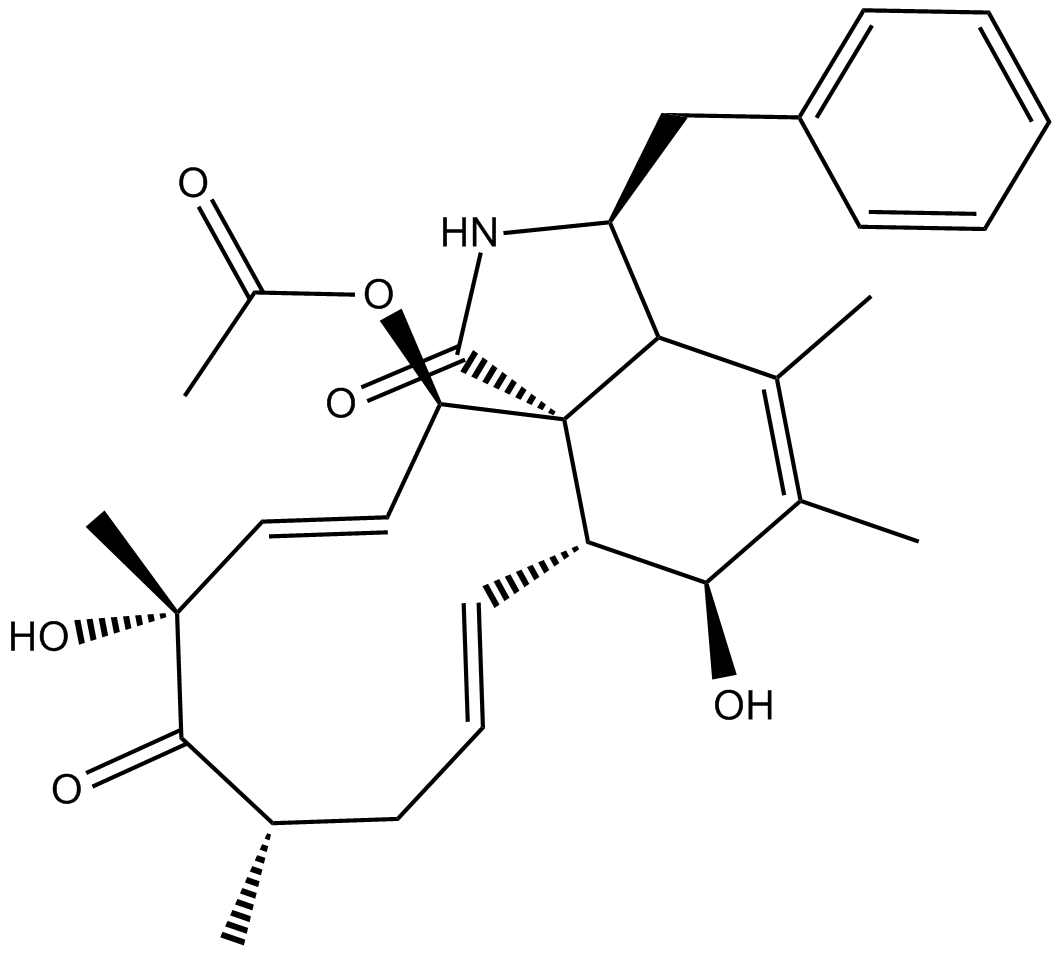 C4537 Cytochalasin CSummary: inhibits actin polymerization
C4537 Cytochalasin CSummary: inhibits actin polymerization -
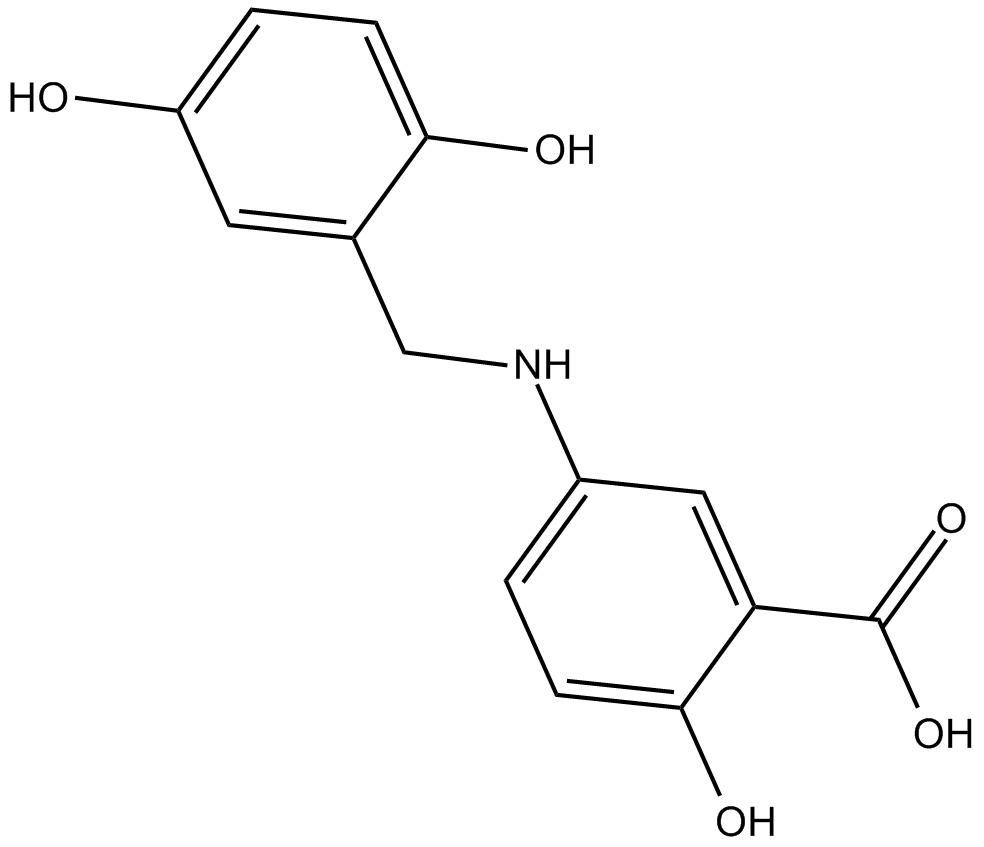 C4688 Lavendustin CSummary: inhibitor of Ca2+ calmodulin-dependent kinase II(CaMKII)
C4688 Lavendustin CSummary: inhibitor of Ca2+ calmodulin-dependent kinase II(CaMKII) -
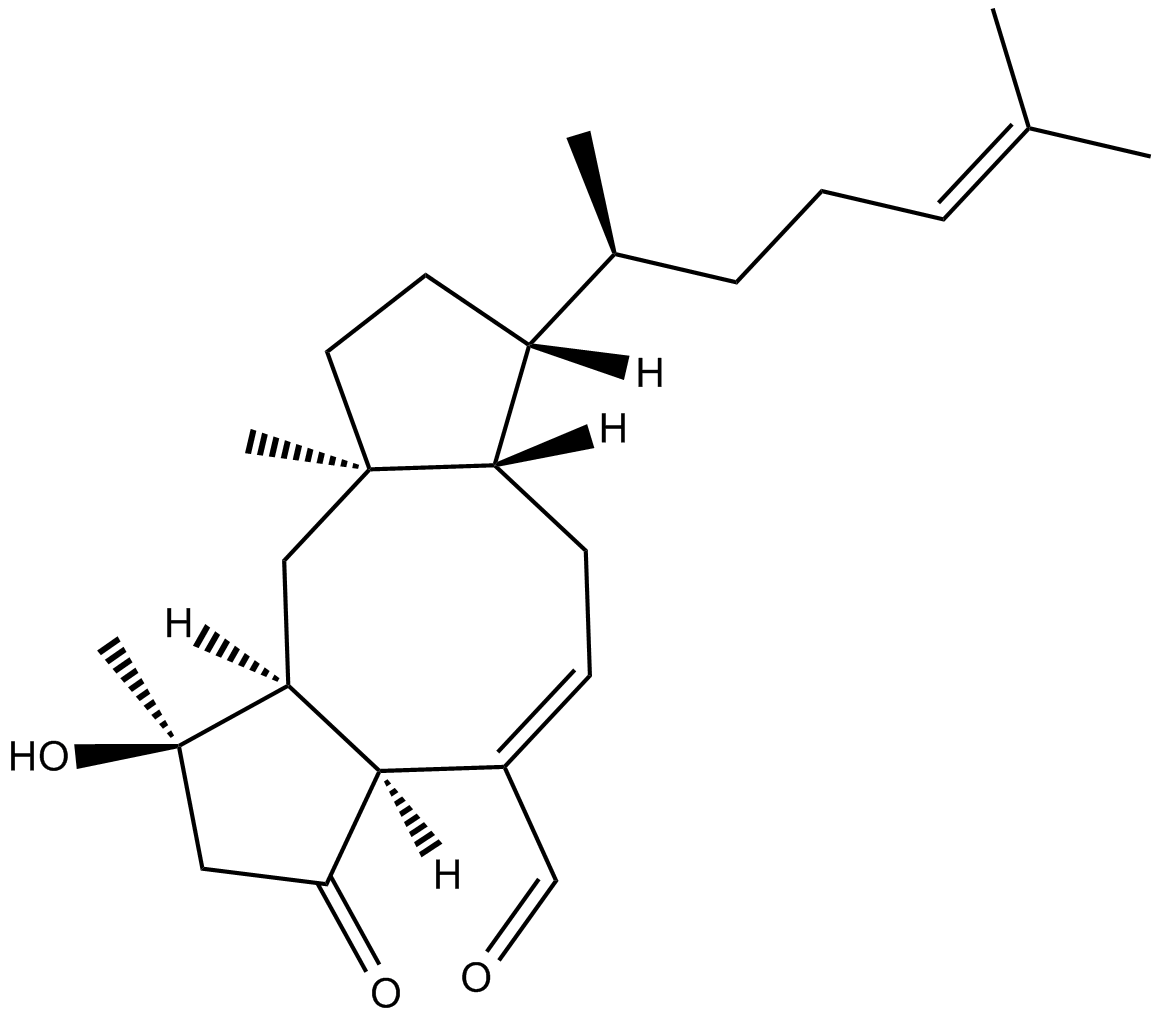 C4974 Ophiobolin CSummary: inhibitor of human CCR5 binding to HIV-1 gp120
C4974 Ophiobolin CSummary: inhibitor of human CCR5 binding to HIV-1 gp120 -
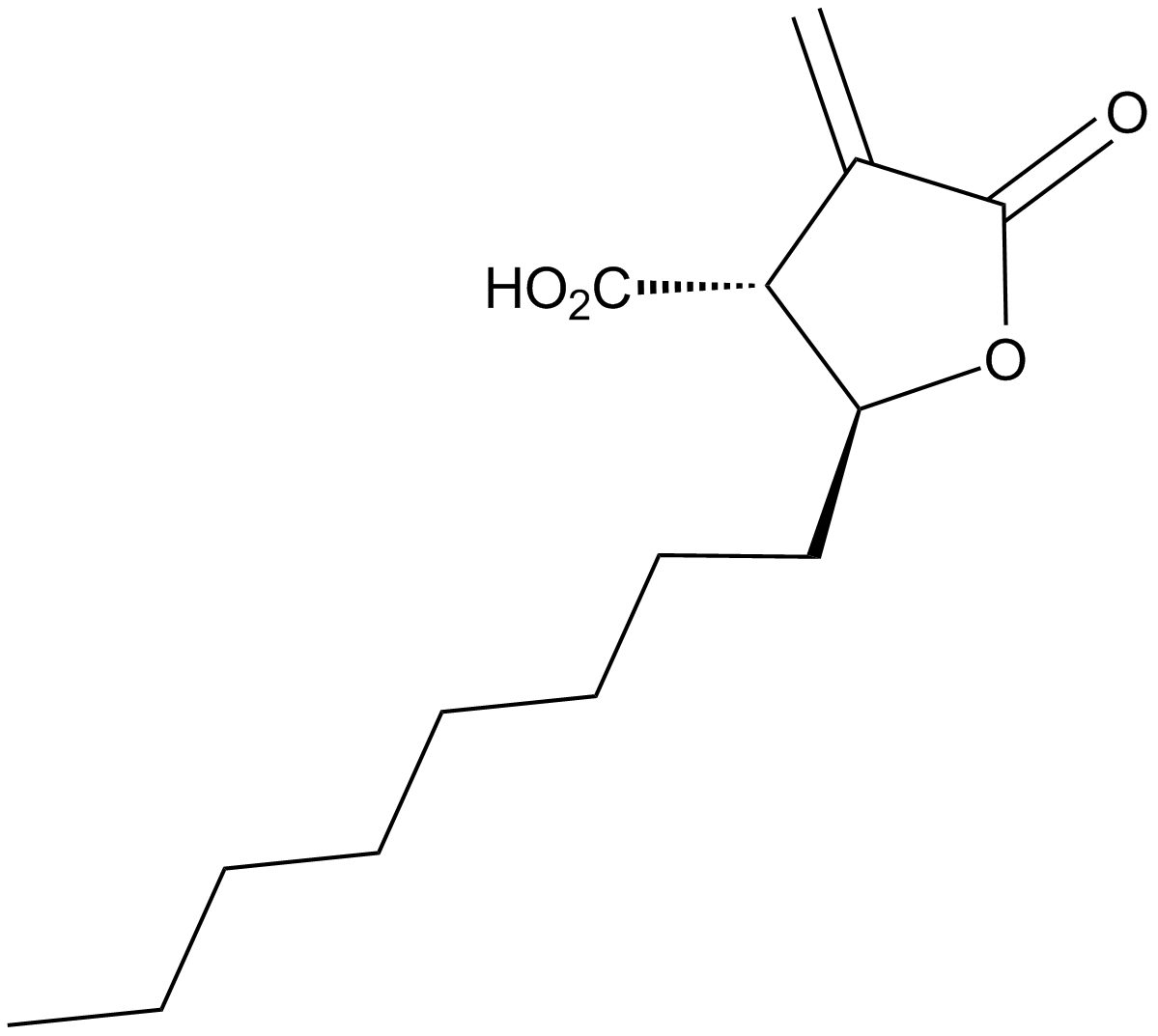 A4449 C 75Summary: Fatty acid synthase (FAS) inhibitor
A4449 C 75Summary: Fatty acid synthase (FAS) inhibitor -
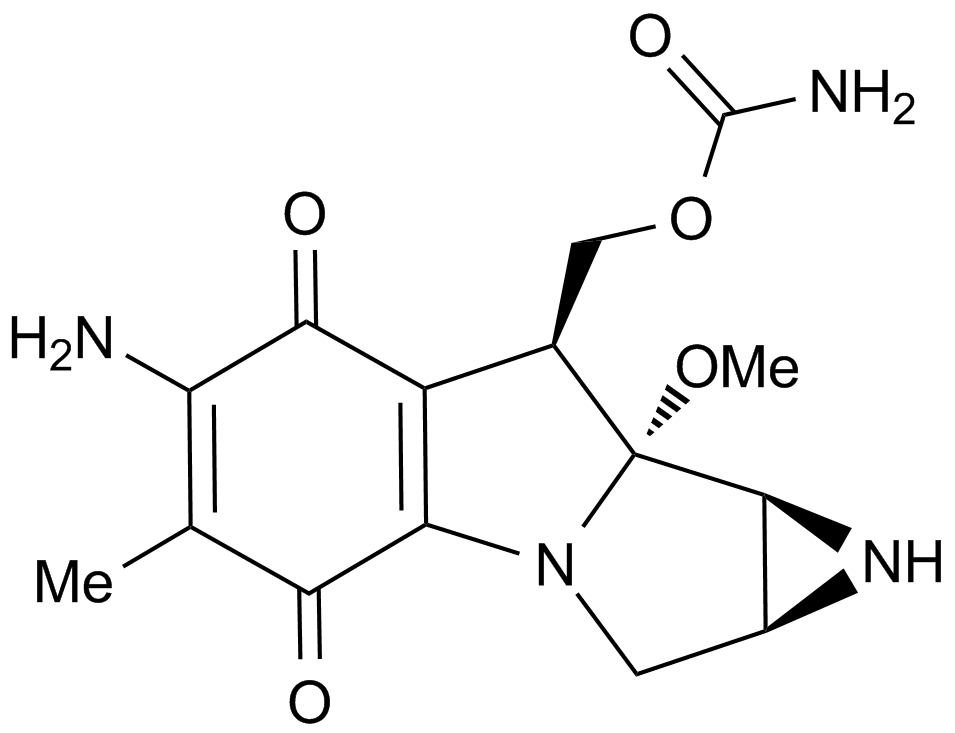 A4452 Mitomycin C8 CitationSummary: Inhibits DNA synthesis,antibiotic and antitumor agent
A4452 Mitomycin C8 CitationSummary: Inhibits DNA synthesis,antibiotic and antitumor agent -
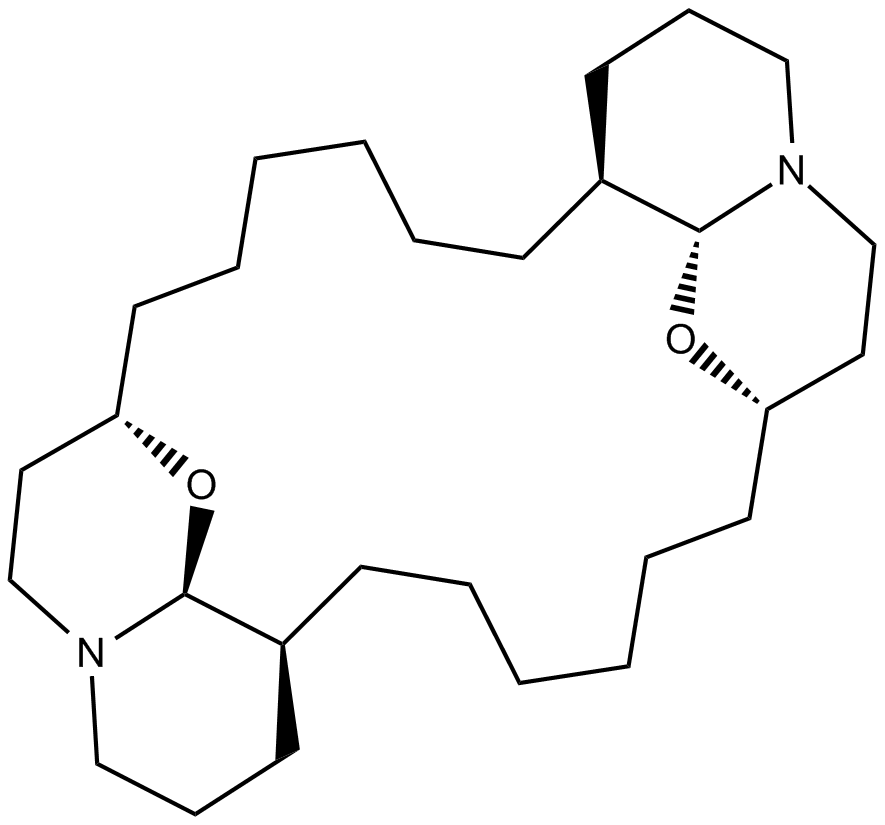 B6668 (-)-Xestospongin CSummary: IP3-dependent Ca2+ release inhibitor
B6668 (-)-Xestospongin CSummary: IP3-dependent Ca2+ release inhibitor


