Search results for: 'signaling pathways proteases elastase'
-
 P1057 Elastase, Human NeutrophilSummary: Elastase, biological active, isolated from human neutrophil.
P1057 Elastase, Human NeutrophilSummary: Elastase, biological active, isolated from human neutrophil. -
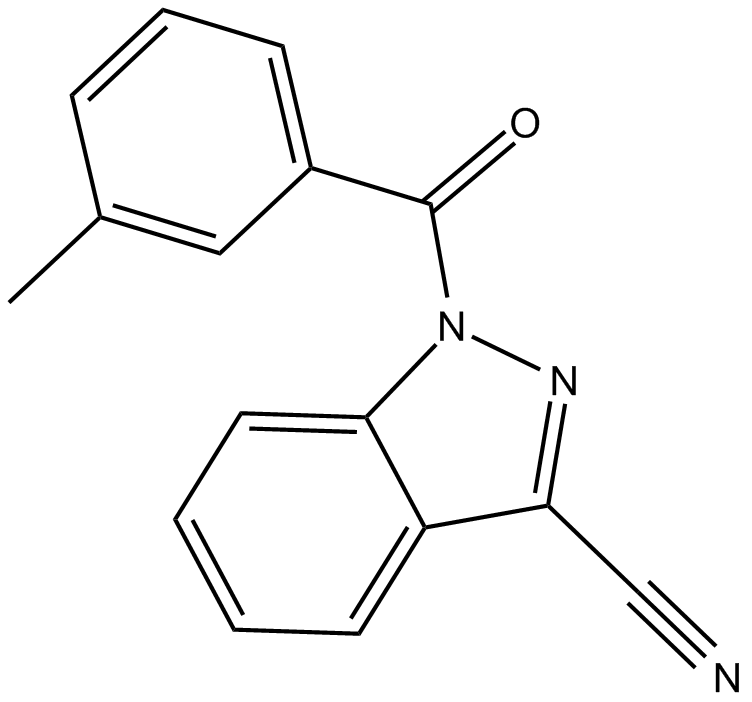 C3252 Neutrophil Elastase InhibitorSummary: neutrophil elastase inhibitor
C3252 Neutrophil Elastase InhibitorSummary: neutrophil elastase inhibitor -
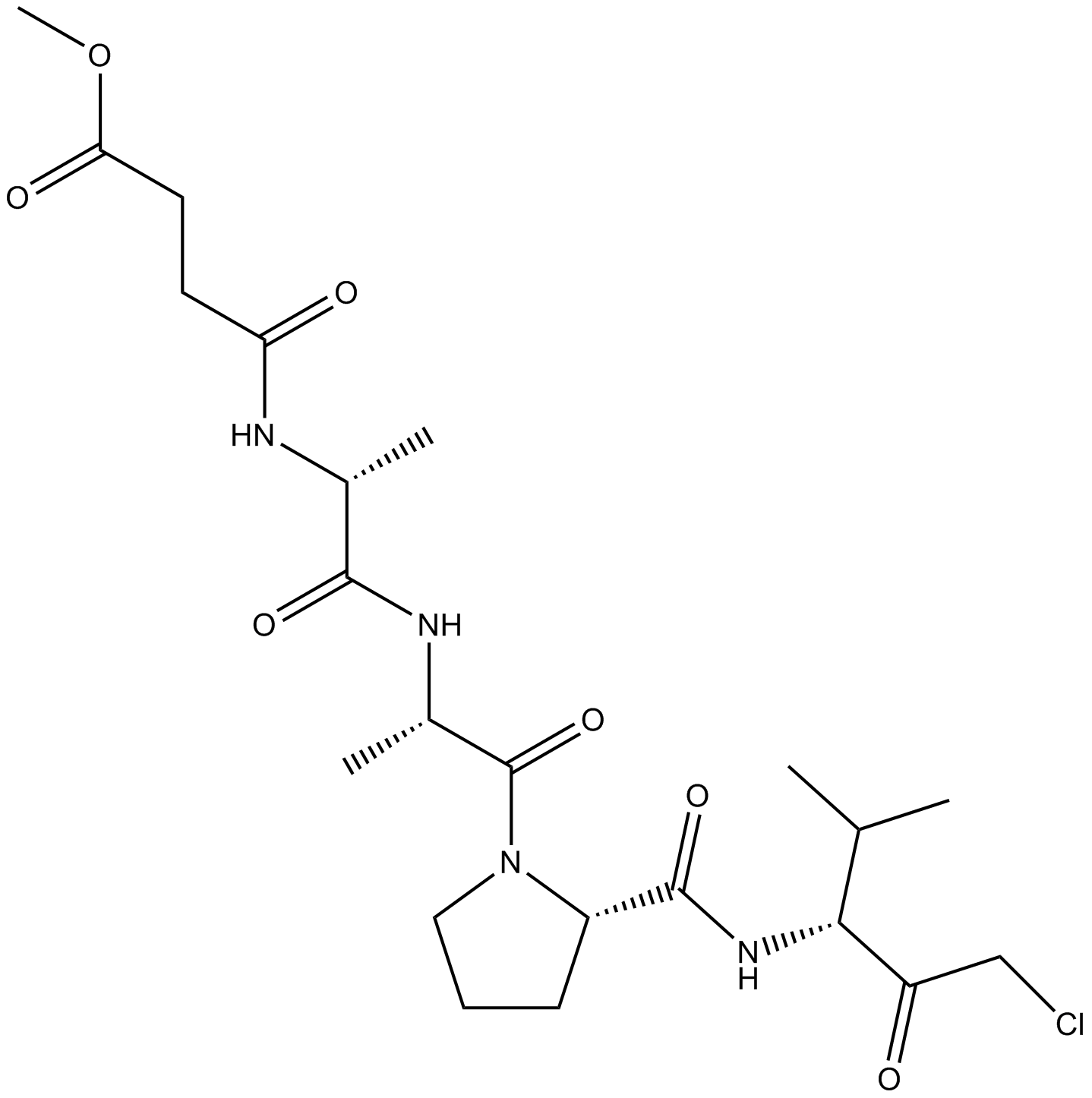 A2580 Elastase Inhibitor, SPCKSummary: HLE inhibitor
A2580 Elastase Inhibitor, SPCKSummary: HLE inhibitor -
 L1044 DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling LibrarySummary: A unique collection of 73 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research.
L1044 DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling LibrarySummary: A unique collection of 73 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research. -
 L1026 DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Library1 CitationSummary: A unique collection of 556 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch.
L1026 DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Library1 CitationSummary: A unique collection of 556 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch. -
 MA3962 Anti-Neutrophil Elastase Rabbit Monoclonal AntibodySummary: Anti-Neutrophil Elastase Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody
MA3962 Anti-Neutrophil Elastase Rabbit Monoclonal AntibodySummary: Anti-Neutrophil Elastase Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody -
 MA3963 Anti-Neutrophil Elastase Rabbit Monoclonal AntibodySummary: Anti-Neutrophil Elastase Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody
MA3963 Anti-Neutrophil Elastase Rabbit Monoclonal AntibodySummary: Anti-Neutrophil Elastase Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody -
 A2571 Pepstatin A9 CitationTarget: Cathepsins|Renin|HIV proteases|PepsinsSummary: aspartic proteases inhibitor
A2571 Pepstatin A9 CitationTarget: Cathepsins|Renin|HIV proteases|PepsinsSummary: aspartic proteases inhibitor -
 L1044P DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling Compound Library PlusSummary: A unique collection of 178 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research.
L1044P DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling Compound Library PlusSummary: A unique collection of 178 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research. -
 L1026P DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Compound Library PlusSummary: A unique collection of 948 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch.
L1026P DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Compound Library PlusSummary: A unique collection of 948 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch.


