Search results for: 'signaling pathways stem cell'
-
 A9905 Stem Cell Set ISummary: For inhibiting HDAC/ GSK-3α/β /histone methyltransferase /ALK5
A9905 Stem Cell Set ISummary: For inhibiting HDAC/ GSK-3α/β /histone methyltransferase /ALK5 -
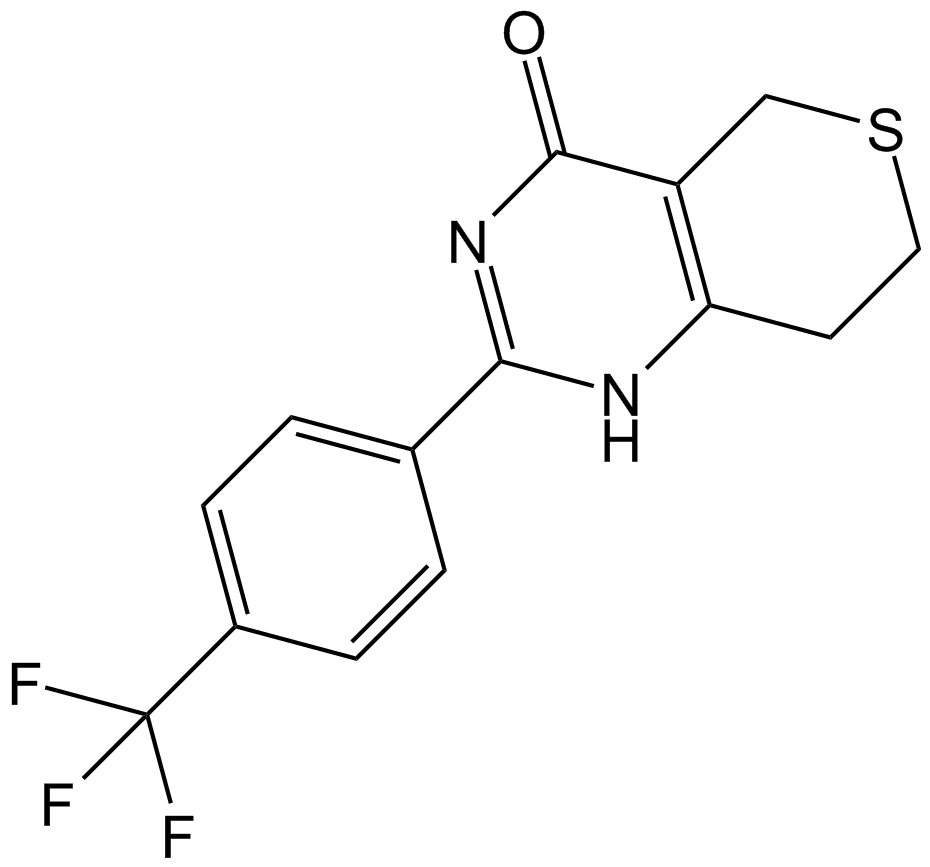 A1877 XAV-93916 CitationTarget: TNKSSummary: Tankyrase 1/2 (TNKS) inhibitor
A1877 XAV-93916 CitationTarget: TNKSSummary: Tankyrase 1/2 (TNKS) inhibitor -
 L1040 DiscoveryProbe™ Stem Cell Compound LibrarySummary: A unique collection of 169 stem cell-related compounds for stem cell research.
L1040 DiscoveryProbe™ Stem Cell Compound LibrarySummary: A unique collection of 169 stem cell-related compounds for stem cell research. -
 P1368 Recombinant Canine Stem Cell Factor
P1368 Recombinant Canine Stem Cell Factor -
 K1018 Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8)1010 CitationSummary: Cell Counting Kit-8 (Enter code “CCK8BOGO” at checkout to receive your “Buy 1 get 1 Free” offer)
K1018 Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8)1010 CitationSummary: Cell Counting Kit-8 (Enter code “CCK8BOGO” at checkout to receive your “Buy 1 get 1 Free” offer) -
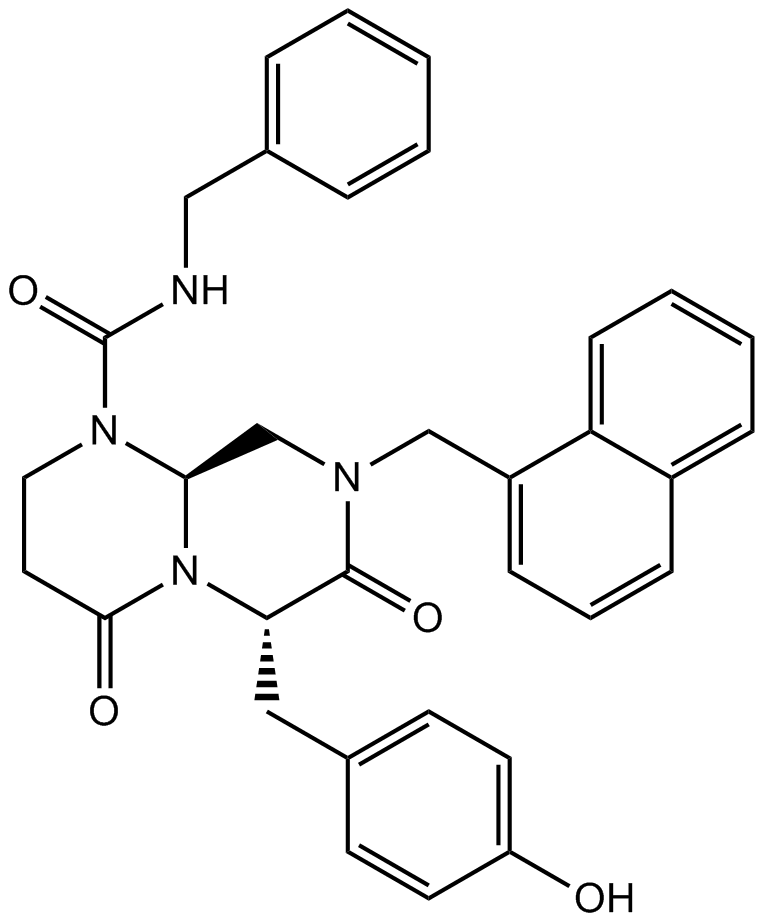 A8217 ICG 0011 CitationSummary: Wnt/β-catenin pathway inhibitor
A8217 ICG 0011 CitationSummary: Wnt/β-catenin pathway inhibitor -
 L1040P DiscoveryProbe™ Stem Cell Compound Library PlusSummary: A unique collection of 280 stem cell-related compounds for stem cell research.
L1040P DiscoveryProbe™ Stem Cell Compound Library PlusSummary: A unique collection of 280 stem cell-related compounds for stem cell research. -
 K2081 Live-Dead Cell Staining Kit12 CitationSummary: Live-Dead Cell Staining Kit
K2081 Live-Dead Cell Staining Kit12 CitationSummary: Live-Dead Cell Staining Kit -
 L1044 DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling LibrarySummary: A unique collection of 73 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research.
L1044 DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling LibrarySummary: A unique collection of 73 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research. -
 L1026 DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Library1 CitationSummary: A unique collection of 556 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch.
L1026 DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Library1 CitationSummary: A unique collection of 556 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch.


