Search results for: 'signaling pathways proteases thrombin'
-
 A8668 Thrombin Receptor Agonist PeptideSummary: Protease-activated receptor agonist
A8668 Thrombin Receptor Agonist PeptideSummary: Protease-activated receptor agonist -
 L1044 DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling LibrarySummary: A unique collection of 73 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research.
L1044 DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling LibrarySummary: A unique collection of 73 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research. -
 L1026 DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Library1 CitationSummary: A unique collection of 556 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch.
L1026 DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Library1 CitationSummary: A unique collection of 556 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch. -
 A1036 Thrombin Receptor Activator for Peptide 5 (TRAP-5)Target: Thrombin ReceptorSummary: Thrombin Receptor Activator for Peptide 5
A1036 Thrombin Receptor Activator for Peptide 5 (TRAP-5)Target: Thrombin ReceptorSummary: Thrombin Receptor Activator for Peptide 5 -
 A2571 Pepstatin A9 CitationTarget: Cathepsins|Renin|HIV proteases|PepsinsSummary: aspartic proteases inhibitor
A2571 Pepstatin A9 CitationTarget: Cathepsins|Renin|HIV proteases|PepsinsSummary: aspartic proteases inhibitor -
 L1044P DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling Compound Library PlusSummary: A unique collection of 178 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research.
L1044P DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling Compound Library PlusSummary: A unique collection of 178 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research. -
 L1026P DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Compound Library PlusSummary: A unique collection of 948 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch.
L1026P DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Compound Library PlusSummary: A unique collection of 948 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch. -
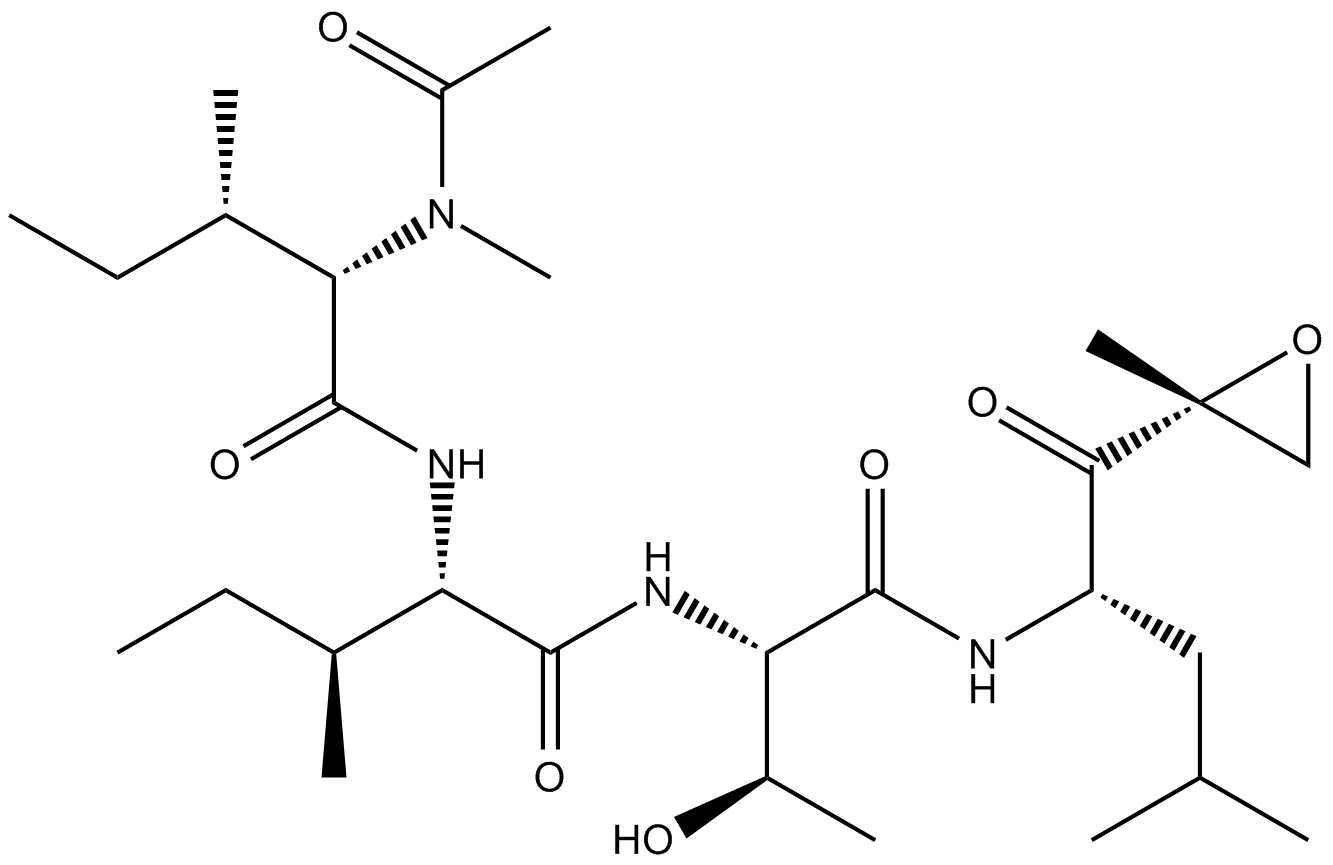 A2606 Epoxomicin35 CitationSummary: proteasome inhibitor
A2606 Epoxomicin35 CitationSummary: proteasome inhibitor -
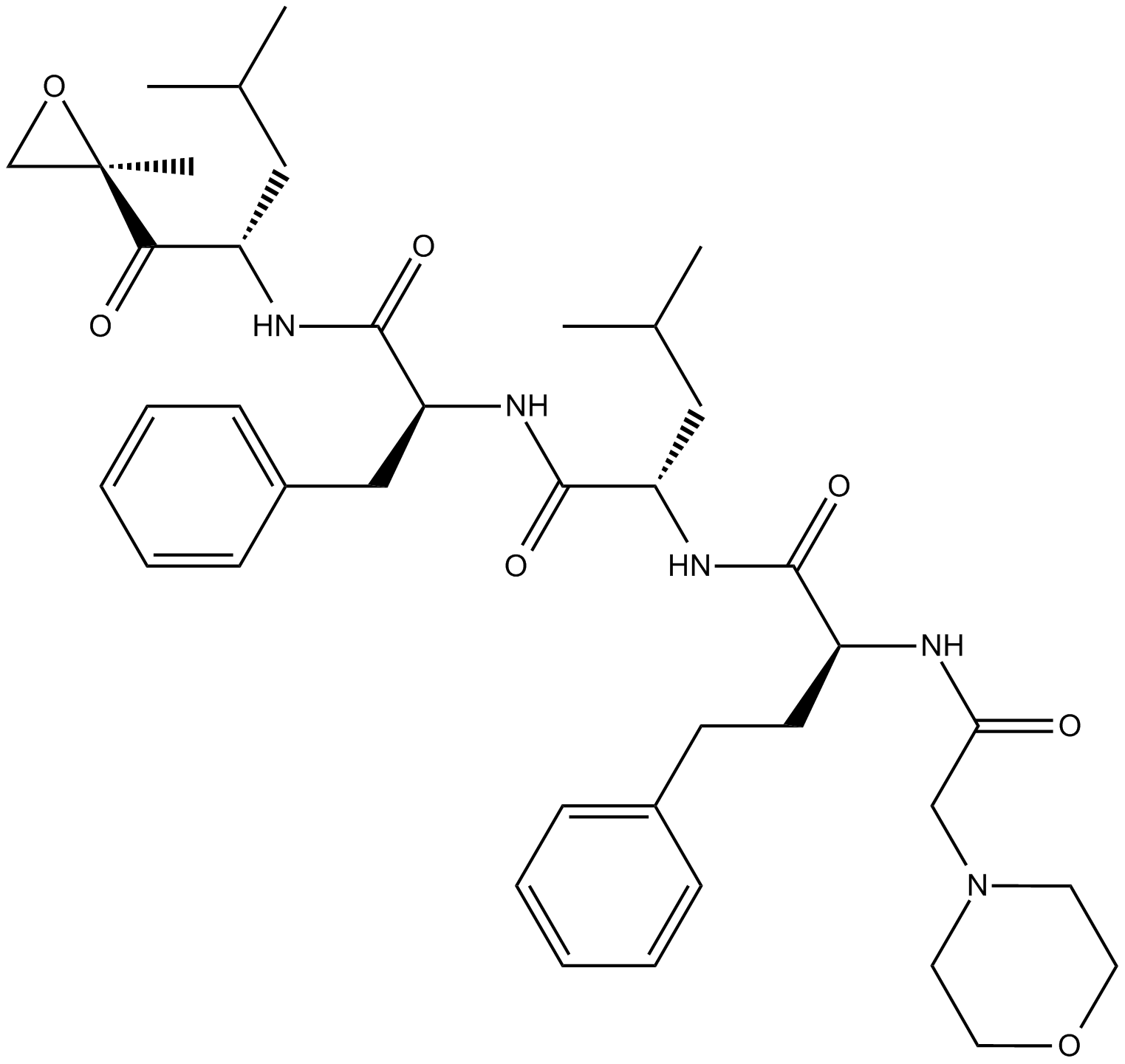 A1933 Carfilzomib (PR-171)10 CitationTarget: ProteasomeSummary: Proteasome inhibitor, epoxomicin analog
A1933 Carfilzomib (PR-171)10 CitationTarget: ProteasomeSummary: Proteasome inhibitor, epoxomicin analog -
![coagulation factor II (thrombin) B chain fragment [Homo sapiens]](/pub/media/prod_images/a/1/a1057.png) A1057 coagulation factor II (thrombin) B chain fragment [Homo sapiens]Summary: Trypsin-like serine protease
A1057 coagulation factor II (thrombin) B chain fragment [Homo sapiens]Summary: Trypsin-like serine protease


