Search results for: 'signaling pathways membrane transporter ion channel'
-
 L1030 DiscoveryProbe™ Ion Channel Compound LibrarySummary: A unique collection of 199 ion channel-related compounds for high throughput screening (HTS) and high content screening (HCS).
L1030 DiscoveryProbe™ Ion Channel Compound LibrarySummary: A unique collection of 199 ion channel-related compounds for high throughput screening (HTS) and high content screening (HCS). -
 L1030P DiscoveryProbe™ Ion Channel Compound Library Plus1 CitationSummary: A unique collection of 350 ion channel-related compounds for high throughput screening (HTS) and high content screening (HCS).
L1030P DiscoveryProbe™ Ion Channel Compound Library Plus1 CitationSummary: A unique collection of 350 ion channel-related compounds for high throughput screening (HTS) and high content screening (HCS). -
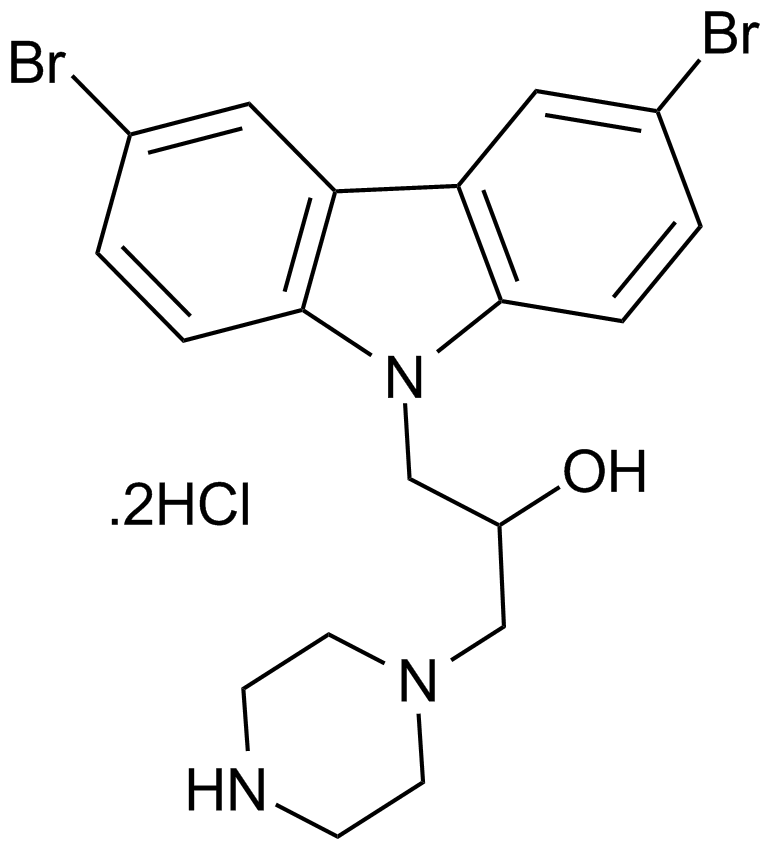 A4459 Bax channel blockerSummary: Inhibitor of Bax-mediated mitochondrial cytochrome c release
A4459 Bax channel blockerSummary: Inhibitor of Bax-mediated mitochondrial cytochrome c release -
 K2113 Membrane Protein Extraction KitSummary: Extracts membrane proteins within an hour
K2113 Membrane Protein Extraction KitSummary: Extracts membrane proteins within an hour -
 L1044 DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling LibrarySummary: A unique collection of 73 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research.
L1044 DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling LibrarySummary: A unique collection of 73 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research. -
 L1026 DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Library1 CitationSummary: A unique collection of 556 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch.
L1026 DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Library1 CitationSummary: A unique collection of 556 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch. -
 K2264 Mitochondrial Membrane Potential and Apoptosis Detection KitSummary: Detecting apoptosis and mitochondrial membrane potential by Annexin V-FITC and Mito-Tracker Red CMXRos
K2264 Mitochondrial Membrane Potential and Apoptosis Detection KitSummary: Detecting apoptosis and mitochondrial membrane potential by Annexin V-FITC and Mito-Tracker Red CMXRos -
 MA5080 Anti-Serotonin Transporter Rabbit Monoclonal AntibodySummary: Anti-Serotonin Transporter Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody
MA5080 Anti-Serotonin Transporter Rabbit Monoclonal AntibodySummary: Anti-Serotonin Transporter Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody -
 MA2325 Anti-Dopamine Transporter Rabbit Monoclonal AntibodySummary: Anti-Dopamine Transporter Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody
MA2325 Anti-Dopamine Transporter Rabbit Monoclonal AntibodySummary: Anti-Dopamine Transporter Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody -
 L1044P DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling Compound Library PlusSummary: A unique collection of 178 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research.
L1044P DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling Compound Library PlusSummary: A unique collection of 178 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research.


