Search results for: 'signaling pathways apoptosis keap1 nrf2'
-
 L1044 DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling LibrarySummary: A unique collection of 73 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research.
L1044 DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling LibrarySummary: A unique collection of 73 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research. -
 L1026 DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Library1 CitationSummary: A unique collection of 556 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch.
L1026 DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Library1 CitationSummary: A unique collection of 556 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch. -
 K2711 Apoptosis Inducer KitSummary: A ready-to-use apoptosis inducer reagent, which consists of recombinant human TNF-α and SM-164
K2711 Apoptosis Inducer KitSummary: A ready-to-use apoptosis inducer reagent, which consists of recombinant human TNF-α and SM-164 -
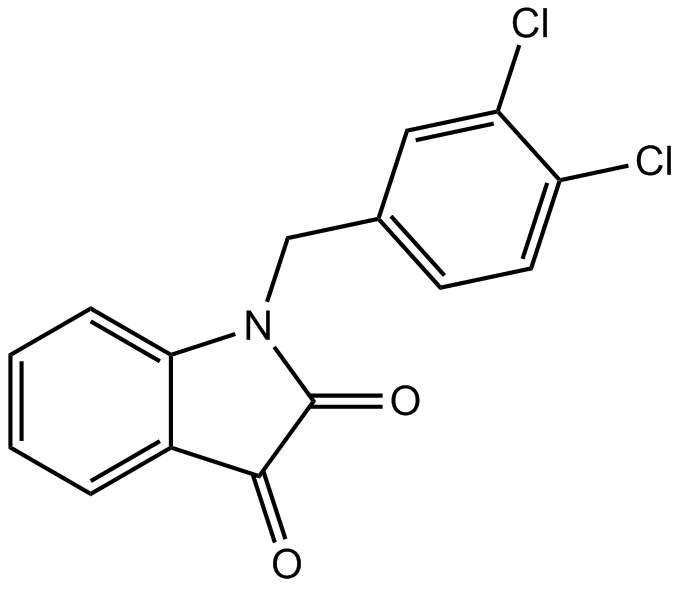 A4016 Apoptosis Activator 2Summary: Indoledione caspase activator, cell-permeable
A4016 Apoptosis Activator 2Summary: Indoledione caspase activator, cell-permeable -
 L1044P DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling Compound Library PlusSummary: A unique collection of 178 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research.
L1044P DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling Compound Library PlusSummary: A unique collection of 178 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research. -
 L1026P DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Compound Library PlusSummary: A unique collection of 948 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch.
L1026P DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Compound Library PlusSummary: A unique collection of 948 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch. -
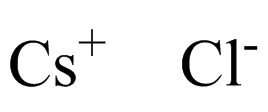 A4468 Cesium chlorideSummary: Potassium channel blocker
A4468 Cesium chlorideSummary: Potassium channel blocker -
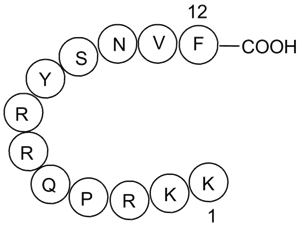 A4469 DAPK Substrate PeptideSummary: Synthetic peptide substrate for DAPK
A4469 DAPK Substrate PeptideSummary: Synthetic peptide substrate for DAPK -
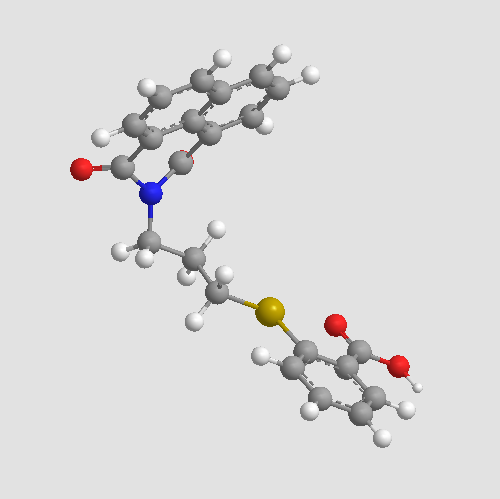 A4471 GRI 977143Summary: LPA2 receptor non-lipid agonist
A4471 GRI 977143Summary: LPA2 receptor non-lipid agonist -
 A4472 Mdivi 16 CitationSummary: Selective DRP1/Dnm1 inhibitor, cell-permeable
A4472 Mdivi 16 CitationSummary: Selective DRP1/Dnm1 inhibitor, cell-permeable


