Sulforaphane
Sulforaphane (CAS 4478-93-7) is a naturally occurring isothiocyanate abundantly found in vegetables, especially broccoli. It acts primarily through activation of the Keap1-Nrf2 signaling pathway, enhancing cellular defense against oxidative and electrophilic stress. Sulforaphane has demonstrated antiproliferative activity in vitro, as shown by dose-dependent cell cycle arrest at G2/M and apoptosis induction in HT29 human colon carcinoma cells. Such effects involve elevated cyclin A and B1 levels, increased pro-apoptotic Bax expression, mitochondrial cytochrome c release, and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase cleavage. These properties make sulforaphane relevant for investigating cancer chemoprevention and cellular stress responses.
- 1. Zhongcheng Xie, Jiamin Guo, et al. "The suppression of FSP1 expression via NRF2 promotes ferroptosis induced by reactive oxygen species in vascular smooth muscle cells." Process Biochemistry. August 2024.
- 2. Fabian Szepanowski, Jaqueline Zipfel, et al. "Enhancement of Heme-Oxygenase 1 in the Injured Peripheral Nerve Following Sulforaphane Administration Fosters Regeneration via Proliferation and Maintenance of Repair Schwann Cells" Antioxidants 2024, 13(9), 1038
- 3. Folbergrová J, Ješina P, et al. "Protective Effect of Sulforaphane on Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Dysfunction Associated with Status Epilepticus in Immature Rats." Mol Neurobiol 2023 Jan 04 PMID: 36598650
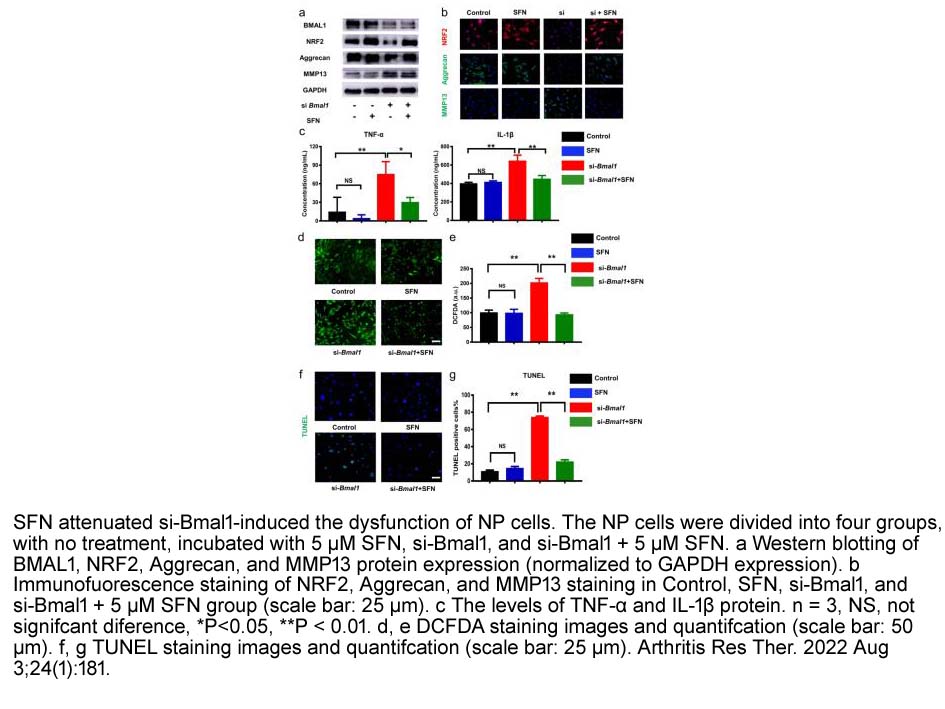
- 4. Pandi Peng, Dong Wang, et al. "Targeting clock-controlled gene Nrf2 ameliorates inflammation-induced intervertebral disc degeneration." Arthritis Res Ther. 2022 Aug 3;24(1):181. PMID: 35922862
- 5. Zheng K, Ma J, et al. "Sulforaphane Inhibits Autophagy and Induces Exosome-Mediated Paracrine Senescence via Regulating mTOR/TFE3." Mol Nutr Food Res. 2020;e1901231. PMID: 32476238
- 6. Junjun Yang, Xiongbo Song, et al. "Natural ingredients-derived antioxidants attenuate H2O2-induced oxidative stress and have chondroprotective effects on human osteoarthritic chondrocytes via Keap1/Nrf2 pathway." Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 28 January 2020. PII: S0891-5849(19)32431-1.
| Storage | Store at -20°C, Light exposure should be avoided |
| M.Wt | 177.3 |
| Cas No. | 4478-93-7 |
| Formula | C6H11NOS2 |
| Synonyms | SFN |
| Solubility | ≥51.6 mg/mL in H2O; ≥58.2 mg/mL in EtOH; ≥67.6 mg/mL in DMSO |
| Chemical Name | 1-isothiocyanato-4-(methylsulfinyl)-butane |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | CS(CCCCN=C=S)=O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment:[1] | |
|
Cell lines |
HT29 human colon cancer cells |
|
Reaction Conditions |
0 ~ 30 μM sulforaphane for 48 h incubation |
|
Applications |
Sulforaphane resulted in a net decrease in the total number of cells and an accumulation of cells floating in the culture medium. The inhibition of growth and the effect on the adherence were already important at 15 μM. Sulforaphane at 15 μM was able to inhibit cell growth and induce cell death. Cell mortality was already 75% at 24 h and almost total at 96 h. |
| Animal experiment:[2] | |
|
Animal models |
Female Sprague-Dawley rats, 40 days of age |
|
Dosage form |
75 or 150 μmol Once daily by gavage for 5 days |
|
Applications |
When sulforaphane was administered by gavage (75 or 150 μmol per day for 5 days) around the time of exposure to the 9,10-dimethyl-1,2-benzanthracene carcinogen, the incidence, multiplicity, and weight of mammary tumors were significantly reduced, and their development was delayed. Sulforaphane was able to protect against carcinogenesis. |
|
Note |
The technical data provided above is for reference only. |
|
References: 1. Gamet-Payrastre L, Li P, Lumeau S, et al. Sulforaphane, a naturally occurring isothiocyanate, induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in HT29 human colon cancer cells. Cancer Research, 2000, 60(5): 1426-1433. 2. Zhang Y, Kensler TW, Cho CG, et al. Anticarcinogenic activities of sulforaphane and structurally related synthetic norbornyl isothiocyanates. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1994, 91(8): 3147-3150. |
|
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure
Related Biological Data
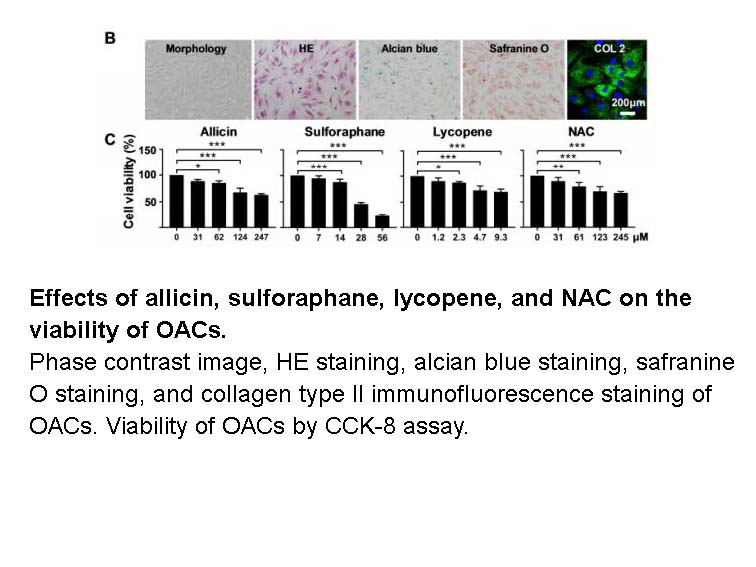
Related Biological Data