Search results for: 'signaling pathways tyrosine kinase'
-
 L1028 DiscoveryProbe™ Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor LibrarySummary: A unique collection of 369 tyrosine kinase inhibitors for high throughput screening (HTS) and high content screening (HCS).
L1028 DiscoveryProbe™ Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor LibrarySummary: A unique collection of 369 tyrosine kinase inhibitors for high throughput screening (HTS) and high content screening (HCS). -
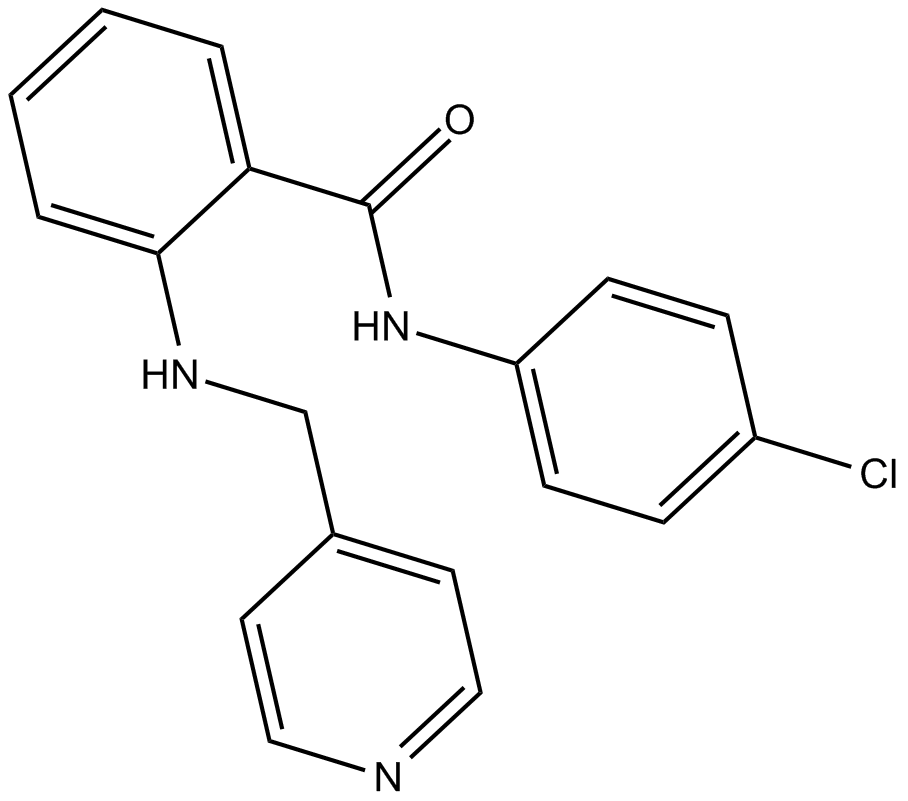 C4603 VEGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor II1 CitationSummary: VEGFR inhibitor
C4603 VEGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor II1 CitationSummary: VEGFR inhibitor -
 P1330 Recombinant Rhesus Macaque Fms-related Tyrosine Kinase 3 Ligand
P1330 Recombinant Rhesus Macaque Fms-related Tyrosine Kinase 3 Ligand -
 L1044 DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling LibrarySummary: A unique collection of 73 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research.
L1044 DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling LibrarySummary: A unique collection of 73 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research. -
 L1026 DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Library1 CitationSummary: A unique collection of 556 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch.
L1026 DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Library1 CitationSummary: A unique collection of 556 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch. -
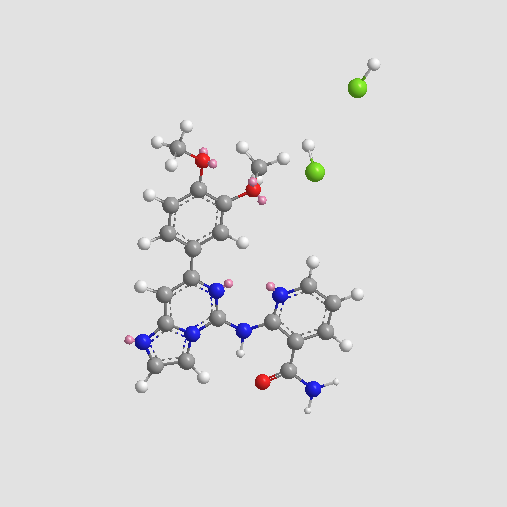 A3228 BAY 61-3606 dihydrochlorideSummary: Syk tyrosine kinase inhibitor
A3228 BAY 61-3606 dihydrochlorideSummary: Syk tyrosine kinase inhibitor -
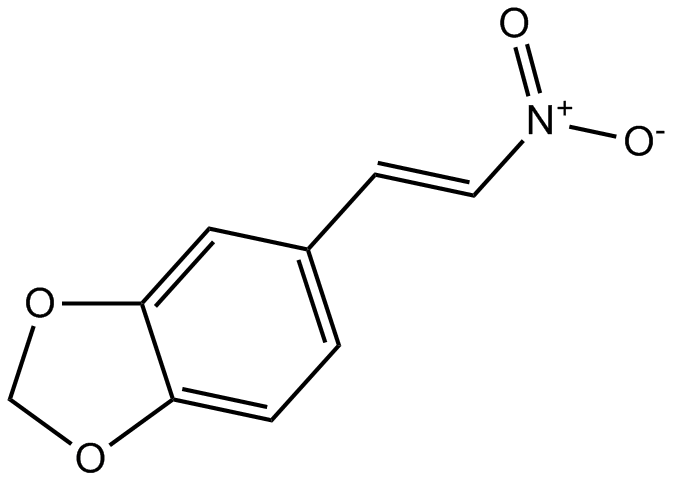 A8661 MNSSummary: Inhibitor of Src/Syk tyrosine kinases
A8661 MNSSummary: Inhibitor of Src/Syk tyrosine kinases -
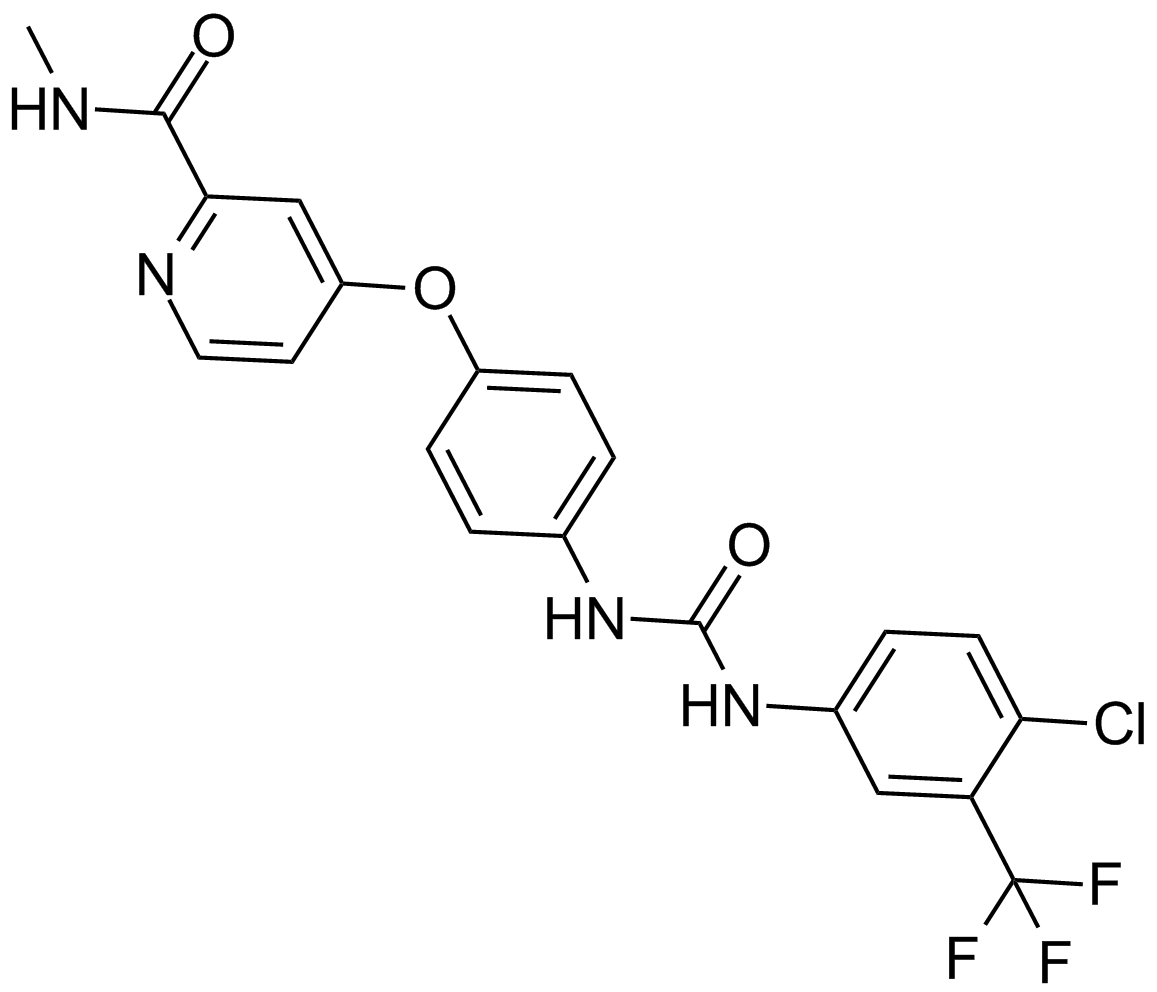 A3009 Sorafenib11 CitationTarget: Raf|VEGFRSummary: Raf kinases and tyrosine kinases inhibitor
A3009 Sorafenib11 CitationTarget: Raf|VEGFRSummary: Raf kinases and tyrosine kinases inhibitor -
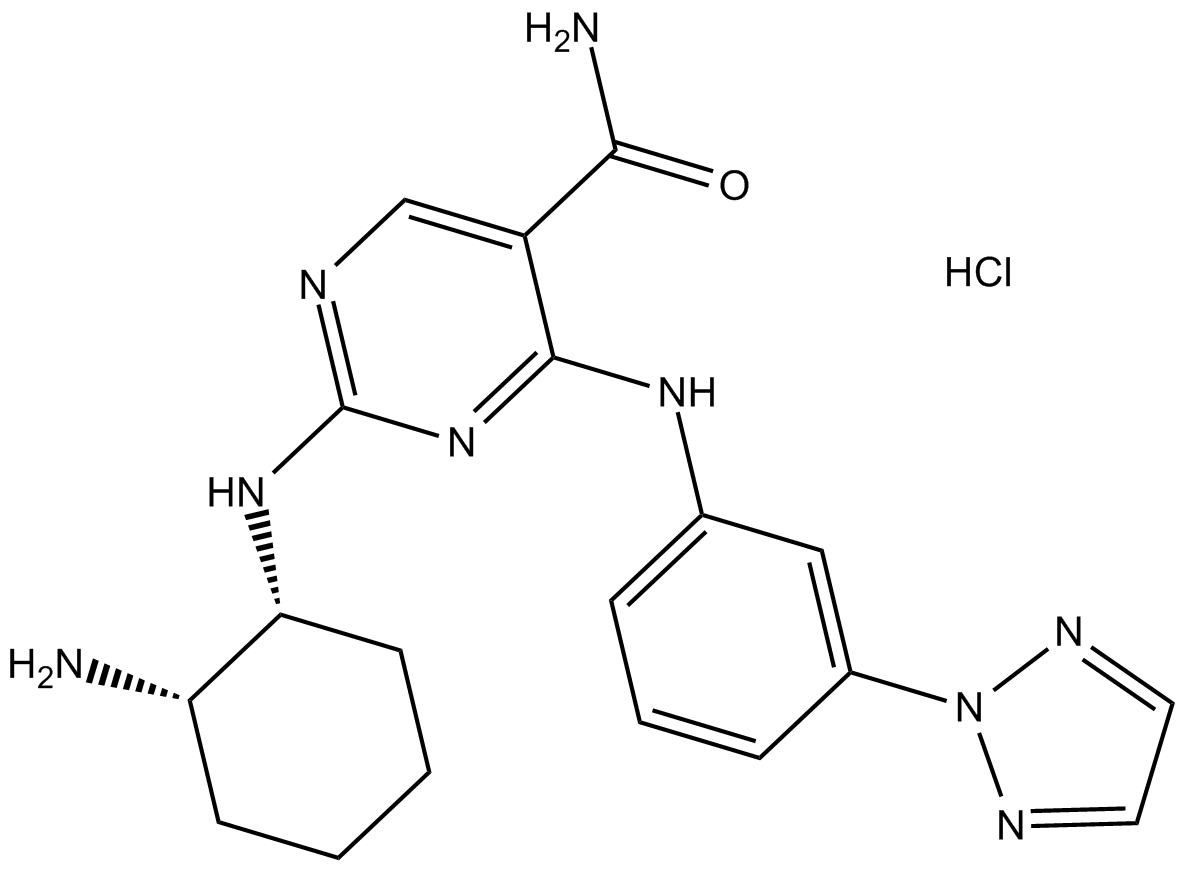 A3736 PRT062607 Hydrochloride1 CitationTarget: SykSummary: SYK inhibitor,potent and selective
A3736 PRT062607 Hydrochloride1 CitationTarget: SykSummary: SYK inhibitor,potent and selective -
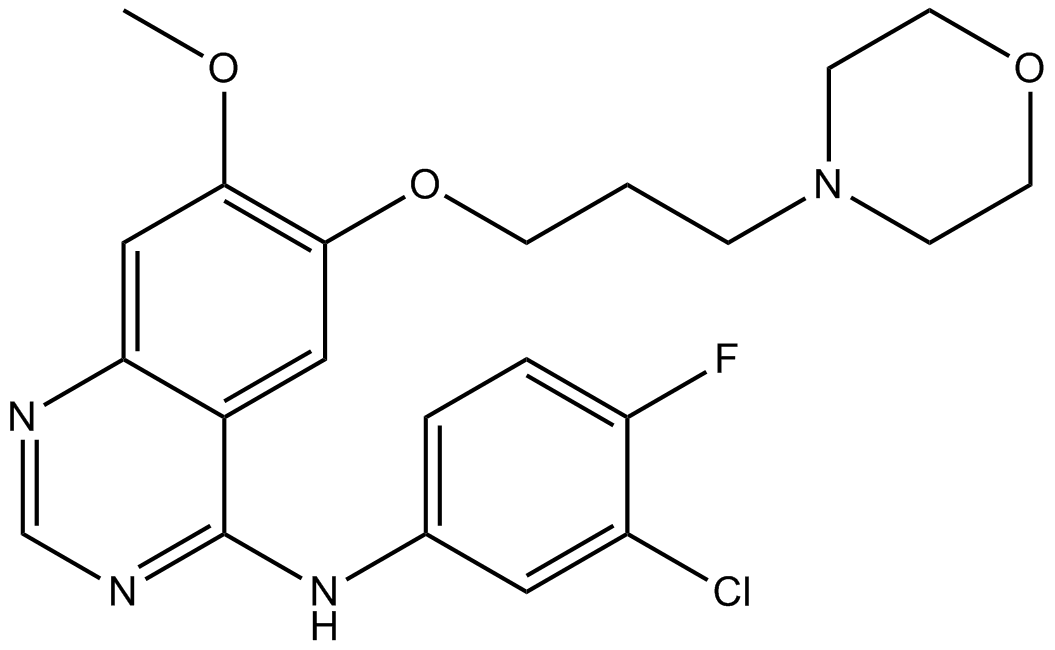 A8219 Gefitinib (ZD1839)15 CitationTarget: EGFRSummary: Selective EGFR inhibitor
A8219 Gefitinib (ZD1839)15 CitationTarget: EGFRSummary: Selective EGFR inhibitor


