Search results for: 'signaling pathways proteases dpp 4'
-
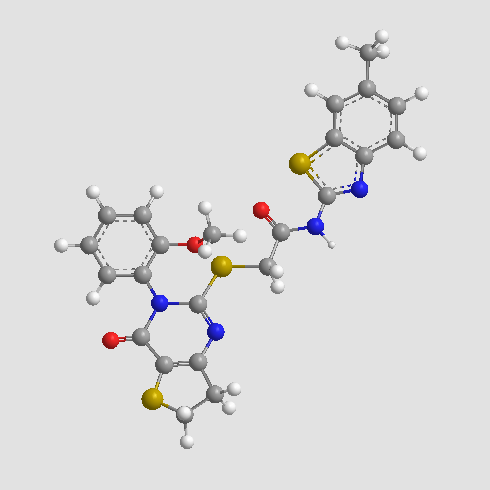 B4922 IWP 4Summary: A potent inhibitor of Wnt production
B4922 IWP 4Summary: A potent inhibitor of Wnt production -
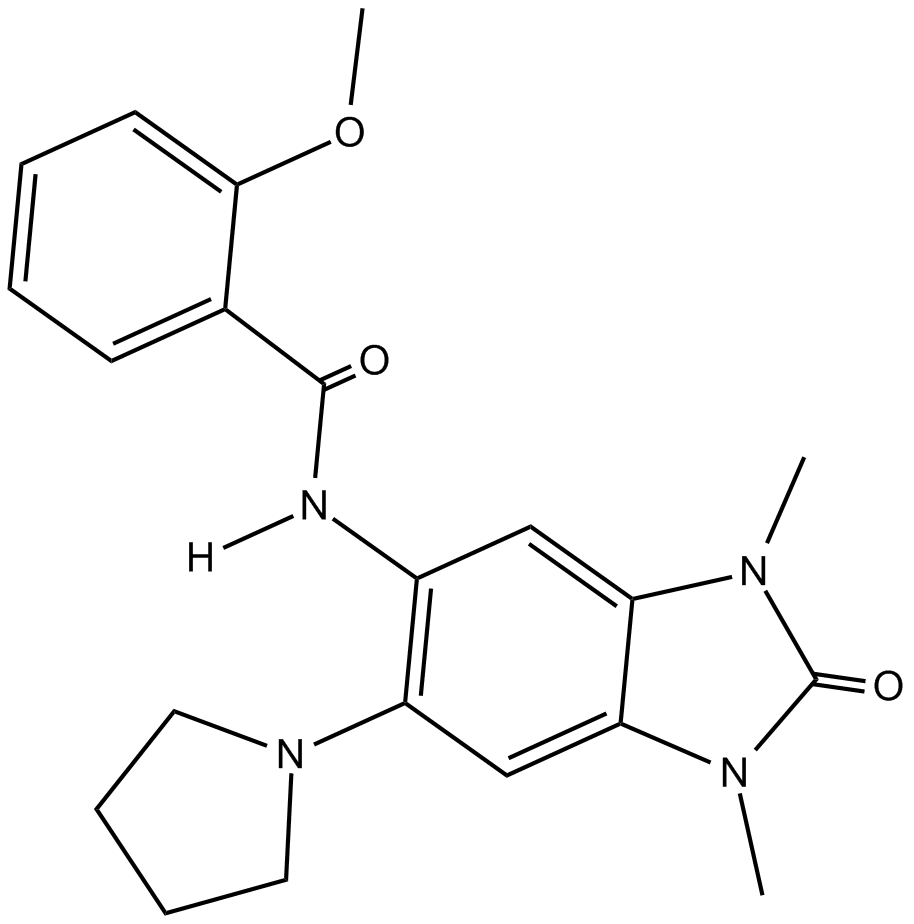 B5973 PFI 4Summary: Potent and selective BRPF1 Bromodomain inhibitor
B5973 PFI 4Summary: Potent and selective BRPF1 Bromodomain inhibitor -
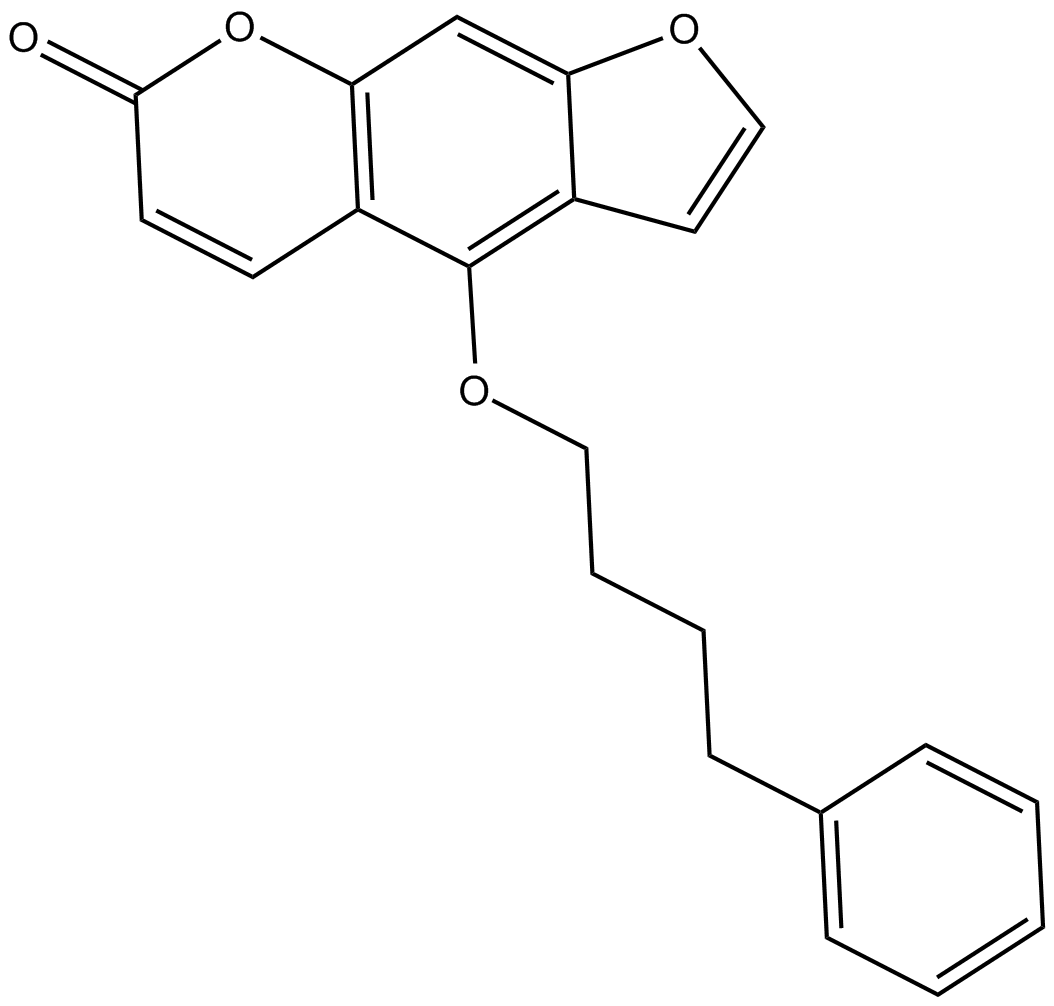 B7659 Psora 41 CitationTarget: Voltage-gated Potassium (KV) ChannelsSummary: Kv1.3 blocker
B7659 Psora 41 CitationTarget: Voltage-gated Potassium (KV) ChannelsSummary: Kv1.3 blocker -
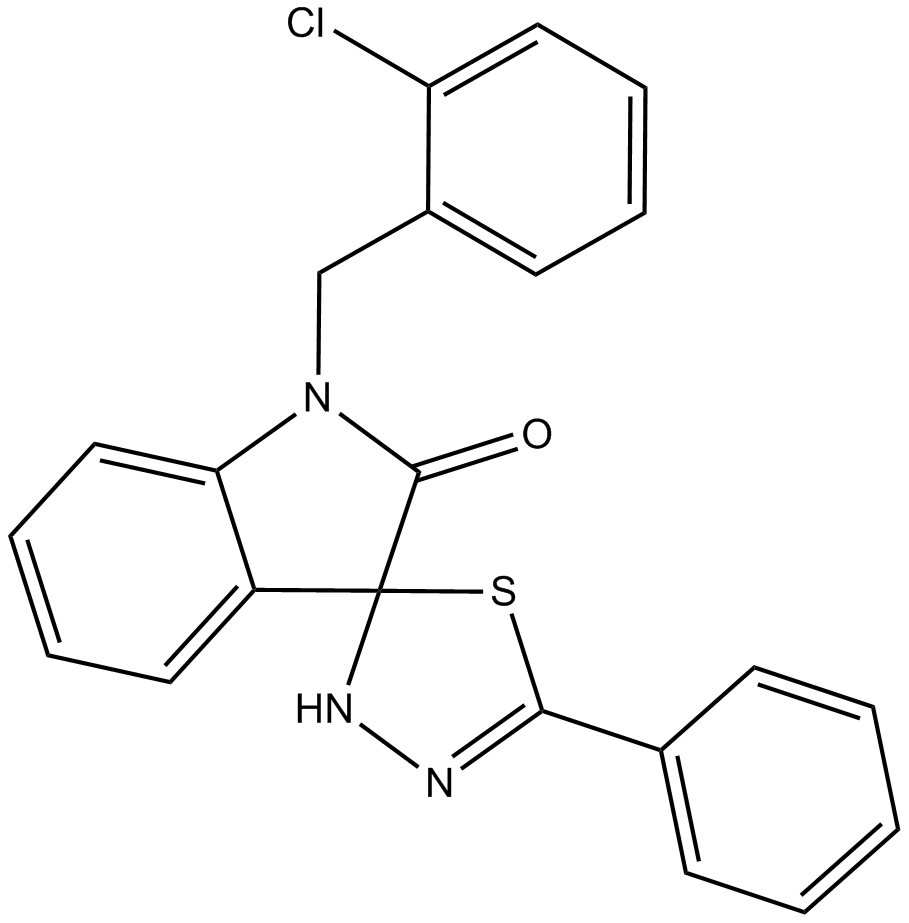 B7760 CFM 4Summary: Interferes with CARP-1 binding to APC-2
B7760 CFM 4Summary: Interferes with CARP-1 binding to APC-2 -
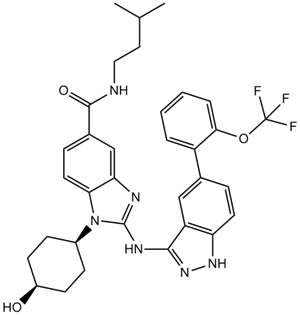 A3503 IRAK inhibitor 4Target: IRAKSummary: IRAK inhibitor
A3503 IRAK inhibitor 4Target: IRAKSummary: IRAK inhibitor -
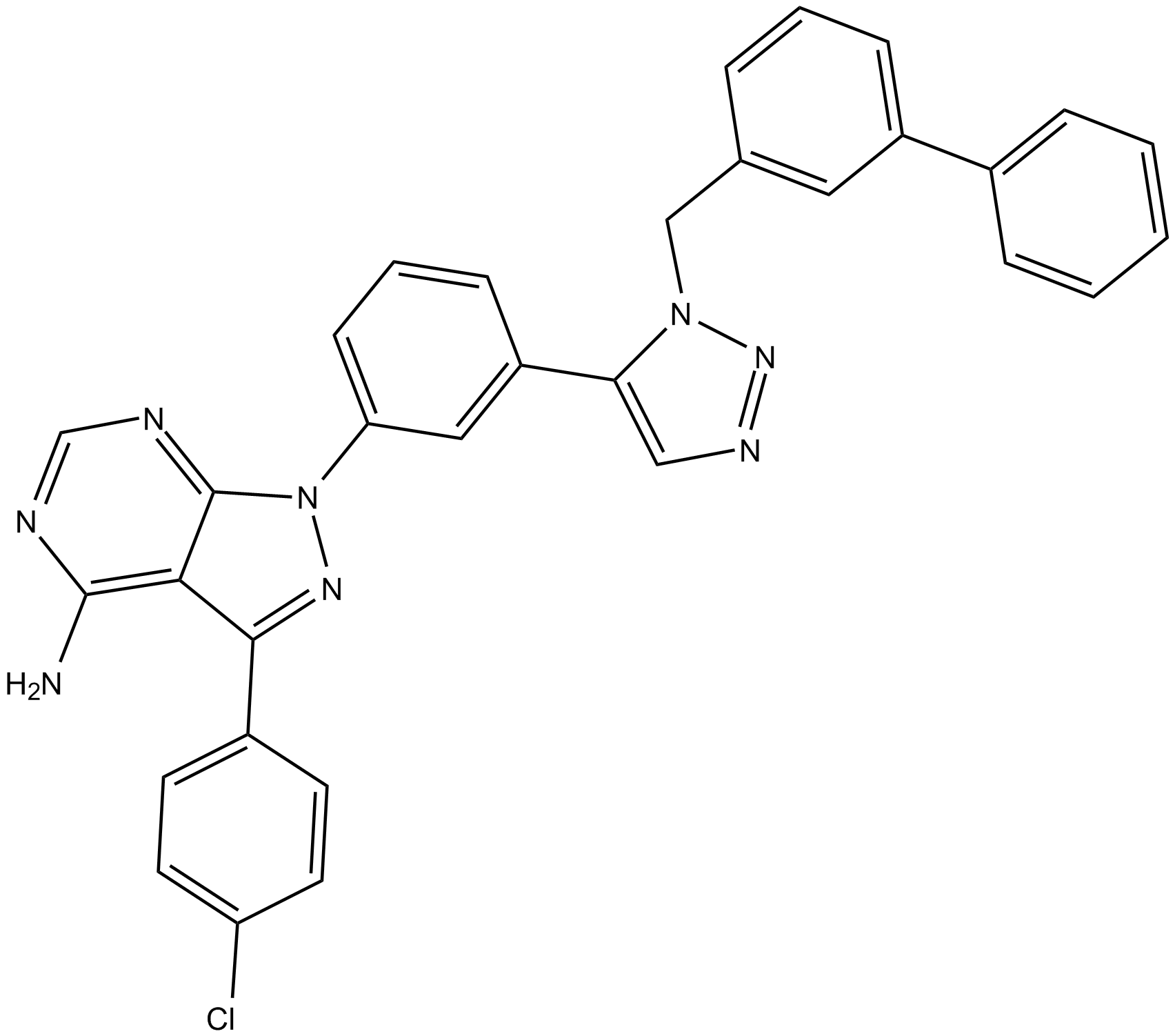 B5673 KB SRC 4Target: SrcSummary: c-Src inhibitor
B5673 KB SRC 4Target: SrcSummary: c-Src inhibitor -
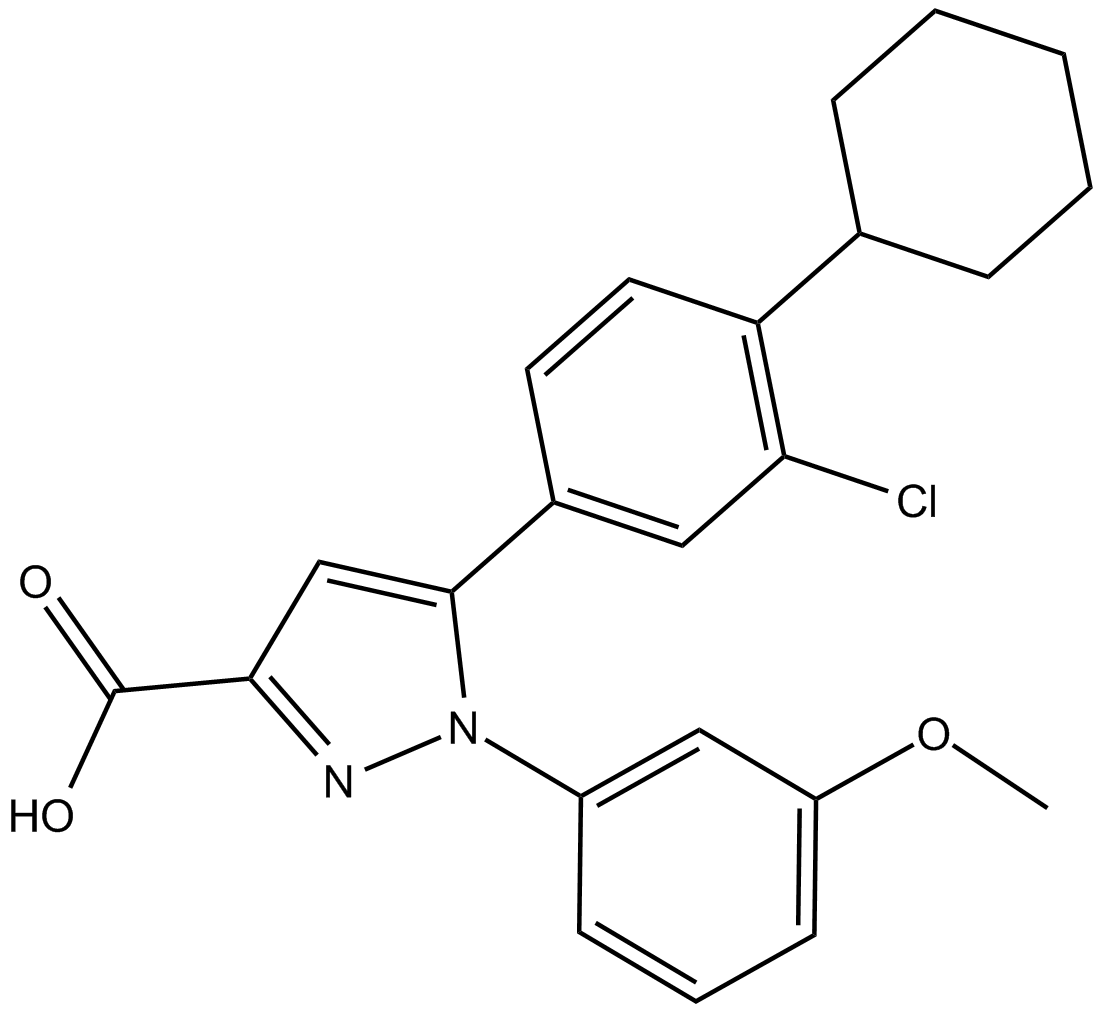 B5689 TC LPA5 4Summary: LPA5 receptor antagonist
B5689 TC LPA5 4Summary: LPA5 receptor antagonist -
 P1386 Recombinant Rat Beta-defensin 4
P1386 Recombinant Rat Beta-defensin 4 -
 MA1289 Anti-Aquaporin 4 Rabbit Monoclonal AntibodySummary: Anti-Aquaporin 4 Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody
MA1289 Anti-Aquaporin 4 Rabbit Monoclonal AntibodySummary: Anti-Aquaporin 4 Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody -
 MA3824 Anti-Mucin 4 Rabbit Monoclonal AntibodySummary: Anti-Mucin 4 Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody
MA3824 Anti-Mucin 4 Rabbit Monoclonal AntibodySummary: Anti-Mucin 4 Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody


