Search results for: 'signaling pathways neuroscience neuroscience peptides'
-
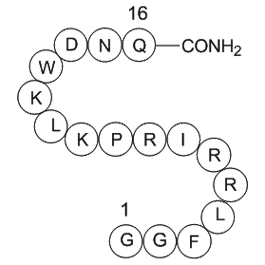 A1012 Dynorphin (2-17), amide, porcineSummary: A modulator of pain response
A1012 Dynorphin (2-17), amide, porcineSummary: A modulator of pain response -
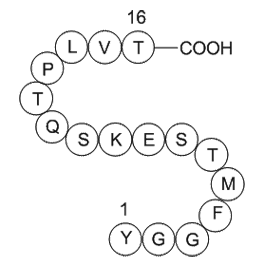 A1015 alpha-EndorphinSummary: Neurotransmitters
A1015 alpha-EndorphinSummary: Neurotransmitters -
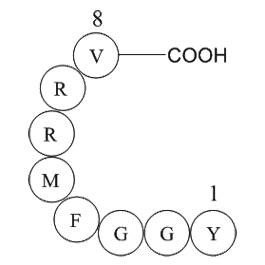 A1017 Adrenorphin, Free AcidSummary: μ/κ opioid receptor agonist
A1017 Adrenorphin, Free AcidSummary: μ/κ opioid receptor agonist -
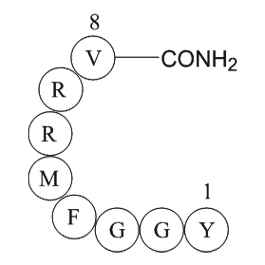 A1032 AdrenorphinSummary: Endogenous μ/κ opioid agonist,potent and selective
A1032 AdrenorphinSummary: Endogenous μ/κ opioid agonist,potent and selective -
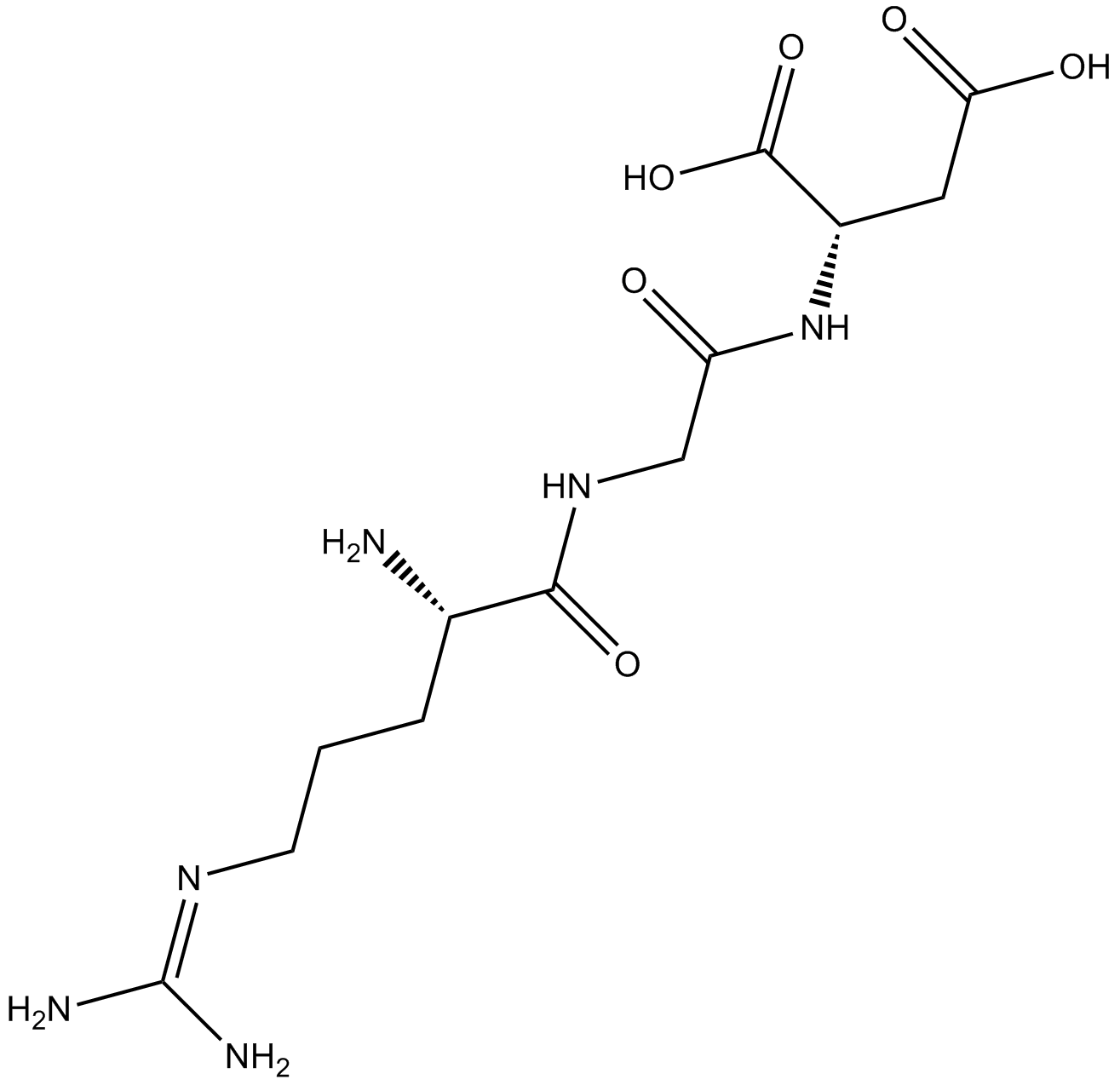 B3708 RGD (Arg-Gly-Asp) Peptides2 CitationTarget: Integrin-ligand interactionsSummary: Inhibits integrin binding to RGD motifs
B3708 RGD (Arg-Gly-Asp) Peptides2 CitationTarget: Integrin-ligand interactionsSummary: Inhibits integrin binding to RGD motifs -
 L1026 DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Library1 CitationSummary: A unique collection of 556 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch.
L1026 DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Library1 CitationSummary: A unique collection of 556 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch. -
 L1044 DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling LibrarySummary: A unique collection of 73 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research.
L1044 DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling LibrarySummary: A unique collection of 73 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research. -
 MA3880 Anti-Natriuretic Peptides A Rabbit Monoclonal AntibodySummary: Anti-Natriuretic Peptides A Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody
MA3880 Anti-Natriuretic Peptides A Rabbit Monoclonal AntibodySummary: Anti-Natriuretic Peptides A Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody -
 L1026P DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Compound Library PlusSummary: A unique collection of 948 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch.
L1026P DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Compound Library PlusSummary: A unique collection of 948 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch. -
 L1044P DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling Compound Library PlusSummary: A unique collection of 178 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research.
L1044P DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling Compound Library PlusSummary: A unique collection of 178 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research.


