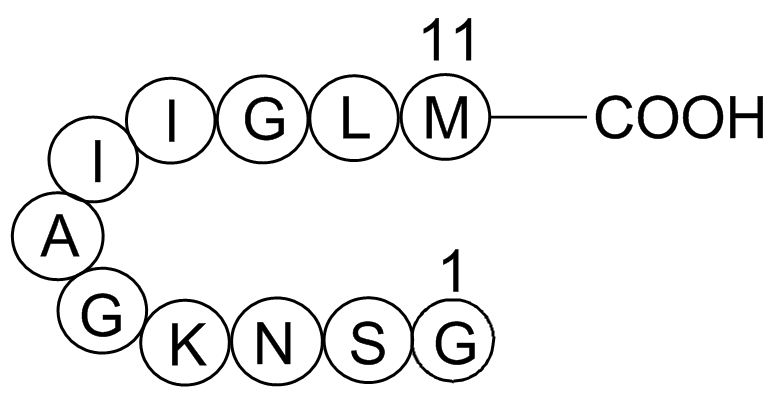
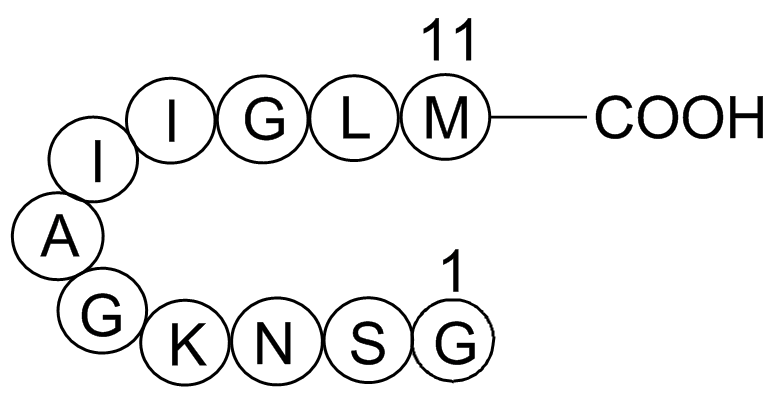
Amyloid Beta-peptide (25-35) (human)
β-Amyloid (25-35) (CAS 131602-53-4) is a synthetic peptide fragment corresponding to amino acids 25 to 35 of the full-length amyloid beta-protein, categorized within the amyloid peptide family. This peptide functions as a neurotoxic agent in neuronal cell cultures and exhibits pronounced neurotoxicity in various neural cell models. Additionally, it mimics the pathogenic activity associated with amyloid aggregation, which is a key feature of Alzheimer's disease-related neurodegeneration.
In experimental studies, β-Amyloid (25-35) induces significant cytotoxicity and neuronal cell death, demonstrated by decreased cell viability and increased apoptotic markers, tested against various neuronal cell lines such as PC12 and primary cortical neurons. It can also disrupt mitochondrial membrane potential, enhance oxidative stress, and promote reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, as well as facilitate the formation of amyloid fibrils and aggregates.
In neuroscience and neurodegenerative disease research, β-Amyloid (25-35) is widely used as a model compound for studying amyloid-induced neurotoxicity, cellular mechanisms underlying Alzheimer's disease, and for evaluating potential neuroprotective drugs and therapeutic strategies targeting amyloid aggregation and toxicity.
- 1. Suman Manandhar, Prasada Chowdari Gurram, et al. "Voglibose Attenuates Amyloid Beta–Induced Memory Deficits in a Rodent Model: A Potential Alzheimer's Therapy via Wnt Signaling Modulation." Mol Neurobiol. 2025 May 17 PMID: 40381169
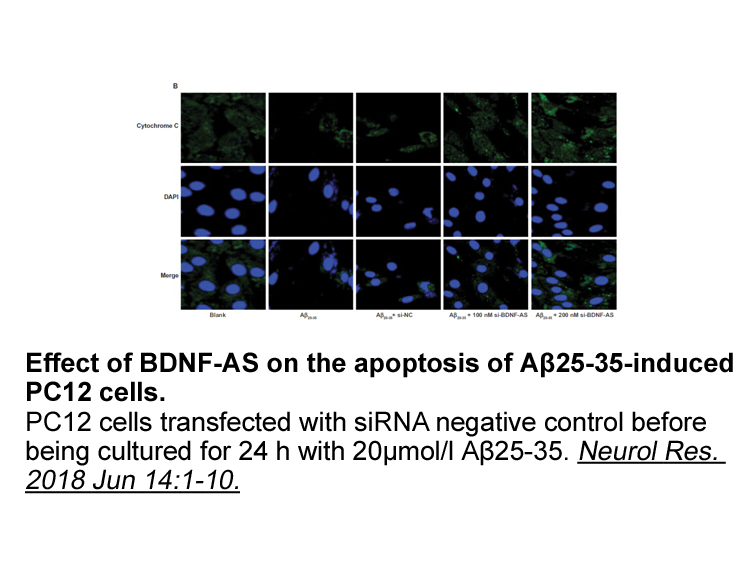
- 2. Guo CC, Jiao CH, et al. "Silencing of LncRNA BDNF-AS attenuates Aβ(25-35)-induced neurotoxicity in PC12 cells by suppressing cell apoptosis and oxidative stress." Neurol Res. 2018 Jun 14:1-10. PMID: 29902125
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 1060.27 |
| Cas No. | 131602-53-4 |
| Formula | C45H81N13O14S |
| Synonyms | Amyloid beta-peptide (25-35); Aβ25-35; β-Amyloid peptide (25-35) |
| Solubility | insoluble in EtOH; insoluble in H2O; ≥106 mg/mL in DMSO |
| Chemical Name | Amyloid Beta-peptide (25-35) (human) |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | CCC(C)C(C(=O)NC(C(C)CC)C(=O)NCC(=O)NC(CC(C)C)C(=O)NC(CCSC)C(=O)O)NC(=O)C(C)NC(=O)CNC(=O)C(CCCCN)NC(=O)C(CC(=O)N)NC(=O)C(CO)NC(=O)CN |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment: [1] | |
|
Cell lines |
Embryonic rat hippocampal cells |
|
Preparation method |
The solubility of this peptide in sterile water is >0.5mg/ml. Stock solution should be splited and stored at -80°C for several months. |
|
Reaction Conditions |
20 μM, 6 hours |
|
Applications |
To investigate the involvement of the tau phosphorylation kinases in Aβ (25–35)-induced tau phosphorylation, the level of each kinase was determined after Aβ (25–35) (20μM) exposure for various periods. GSK-3α did not show a significant change in response to Aβ (25–35), whereas MAP kinase decreased to ~ 60% of the control after 6h Aβ (25–35) exposure, when tau was phosphorylated maximally. TPK I/GSK-3βrapidly increased in response to Aβ (25–35), reaching a maximum (2.2-fold the control) at 6 h. |
| Animal experiment: [2] | |
|
Animal models |
Male Charles River Wistar rats |
|
Dosage form |
Intraperitoneal injection, 400 mg/kg |
|
Applications |
A statistically significant decrease in basal ACh release (-28%) was detected one week after the injection of Aβ (25–35). The effect persisted for only two week. K+-stimulated ACh release was similarly affected by the treatment. Aβ (25–35) treatment induced a statistically significant decrease in the stimulated release on day 14 after lesioning (-45%). |
|
Other notes |
Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
|
References: [1] Takashima A, Honda T, Yasutake K, et al. Activation of tau protein kinase I/glycogen synthase kinase-3 β by amyloid β peptide (25–35) enhances phosphorylation of tau in hippocampal neurons. Neuroscience research, 1998, 31(4): 317-323. [2] Giovannelli L, Casamenti F, Scali C, et al. Differential effects of amyloid peptides β-(1–40) and β-(25–35) injections into the rat nucleus basalis. Neuroscience, 1995, 66(4): 781-792. |
|
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data