Bioinformatics
Services
Professional bioinformatics analysis aiming at answering your research questions.
Microbial
Microorganisms are the most widespread organisms on the earth. Over 99% of them can not be isolated and cultured clonally, while traditional culture-dependent methods challenge the study of microorganisms in their natural environment . Based on microbial characteristics, researchers developed several culture-free ways to explore the diversity structure and functional genome of microorganisms. Now you can enjoy these services from APExBIO.
Transcriptomics
Transcriptomics is the study of the transcriptome—the complete set of RNA transcripts that are produced by the genome, under specific circumstances or in a specific cell—using high-throughput methods, such as next generation sequencing data analysis. Comparison of transcriptomes allows the identification of genes that are differentially expressed in distinct cell populations, or in response to different treatments.


Genomics
APExBIO’s whole genome sequencing (WGS) detects the complete genome sequence at one time and provides the most comprehensive collection of an individual’s genetic variation based on the reference genome, and analyzes the differences of individuals or groups.
Epigenomics
Epigenomics is the study of the complete set of epigenetic modifications on the genetic material of a cell, known as the epigenome. The field is analogous to genomics and proteomics, which are the study of the genome and proteome of a cell.

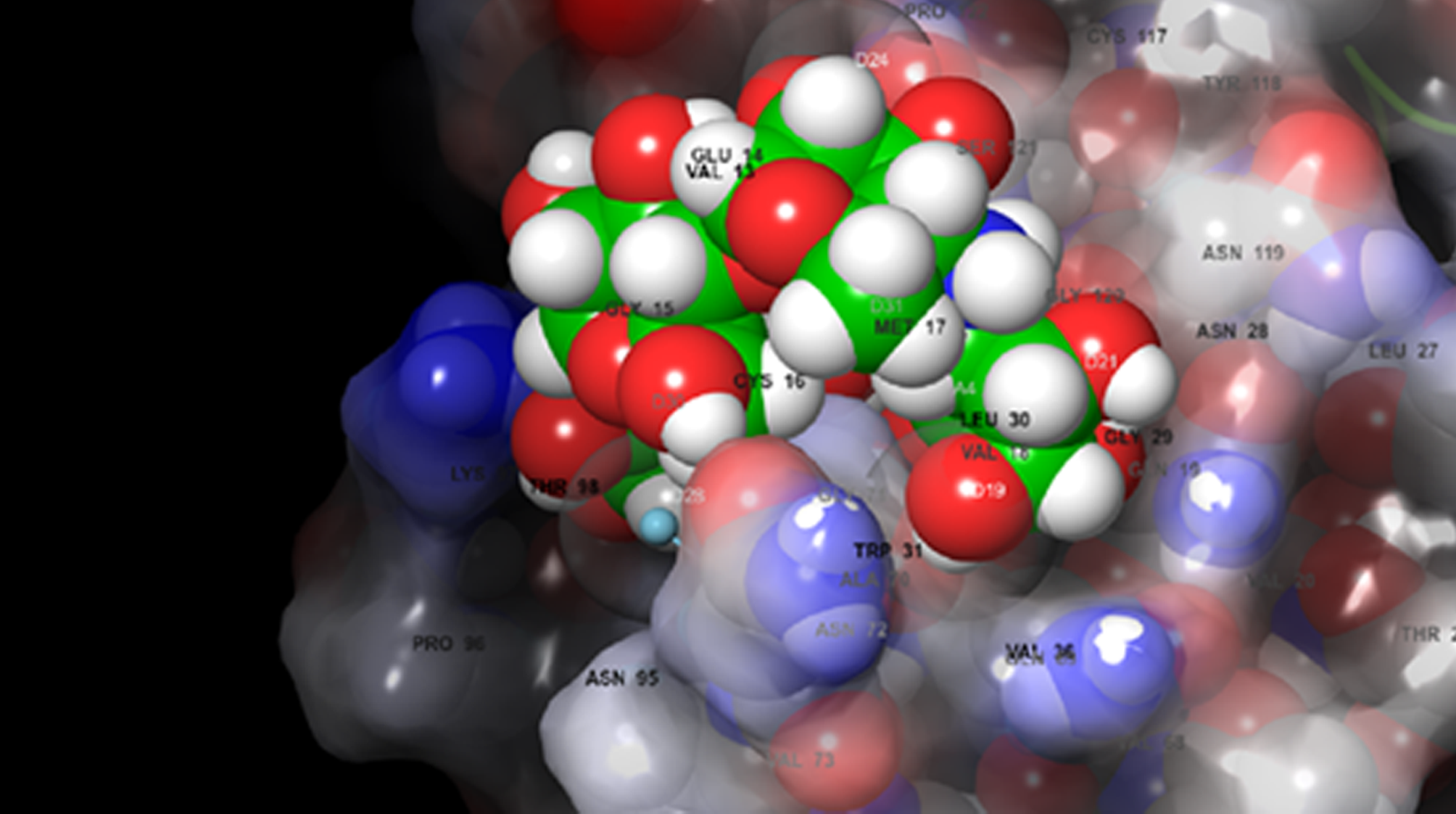
Virtual screening
Virtual screening (VS) is a computational technique used in drug discovery to search libraries of small molecules in order to identify those structures which are most likely to bind to a drug target, typically a protein receptor or enzyme. In nowadays, virtual screening has become the most promising drug development tool.
Metabolomics
Metabolomics/Metabolomics is a newly developed discipline following genomics and proteomics. Its main goal is to quantitatively study the multiple dynamic responses of living organisms to external stimuli, physiological and pathological changes, and genetic mutations in the level of metabolites in the body.



