Neuroscience Peptides

Neuroscience
Neurons communicate with each other, effector organs and sensory organs through the neurotransmitter – receptor pathway at synapses. Neurotransmitters can be divided into 4 major groups: 1. Amino acids (glumate, aspartate, serine, glycine and GABA); 2. Monoamines (norepinephrine, epinephrine, dopamine, histamine, and serotonin); 3. Peptides (opioid peptides, substance P, somatostatin); and 4. Others (acetylcholine, NO, nucleosides). read more
-
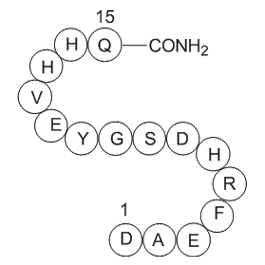 A1003 Amyloid β-Protein (1-15)Summary: Principal component of amyloid
A1003 Amyloid β-Protein (1-15)Summary: Principal component of amyloid -
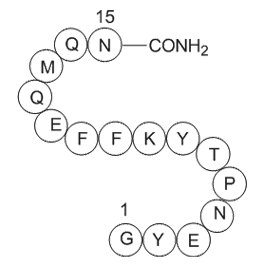 A1004 Amyloid Precursor C-Terminal PeptideSummary: For beta amyloid generation
A1004 Amyloid Precursor C-Terminal PeptideSummary: For beta amyloid generation -
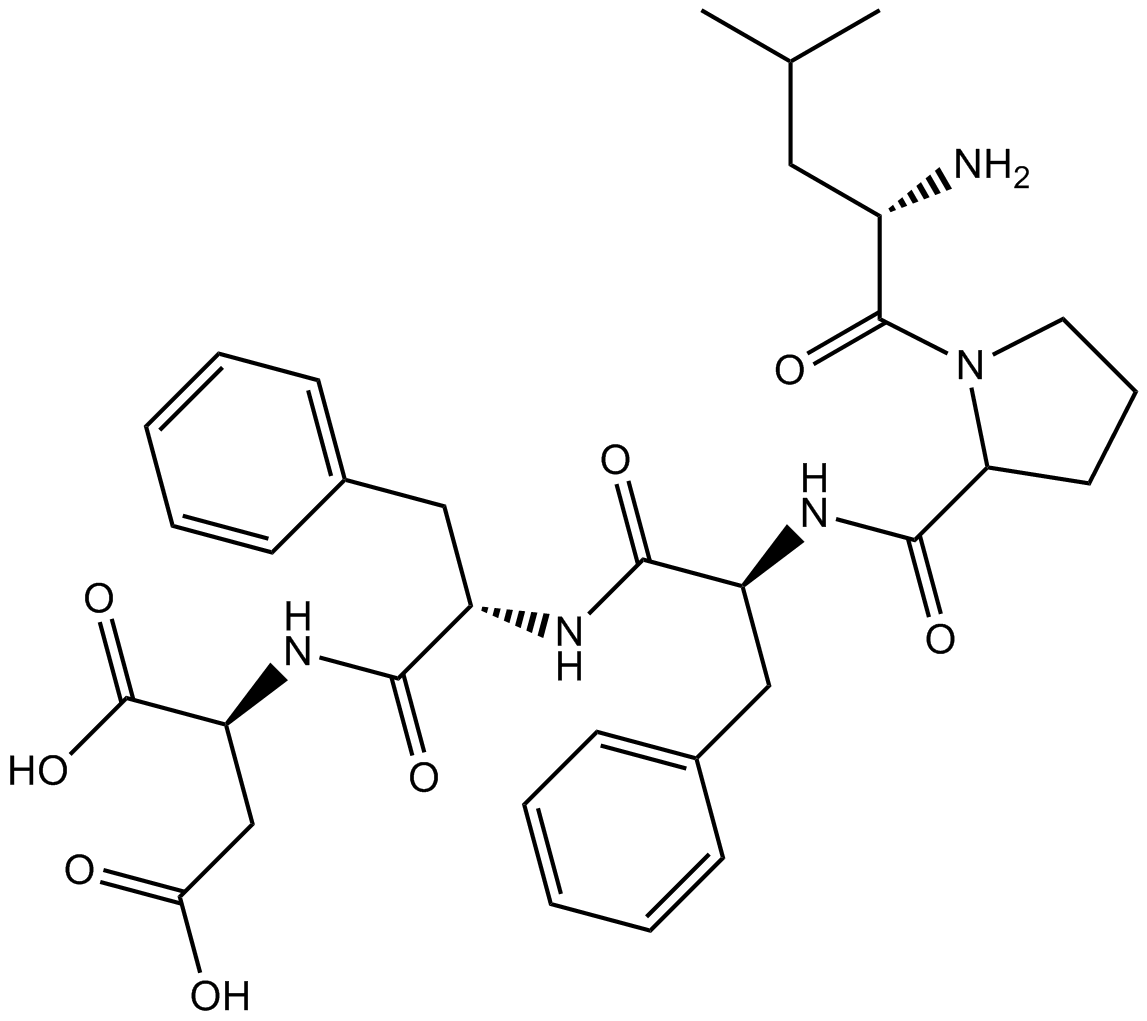 A1005 Beta-Sheet Breaker Peptide iAβ5Summary: Peptide which can inhibit amyloidogenesis
A1005 Beta-Sheet Breaker Peptide iAβ5Summary: Peptide which can inhibit amyloidogenesis -
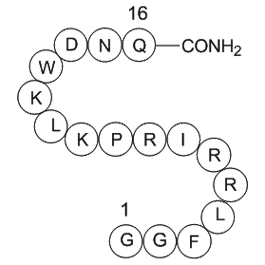 A1012 Dynorphin (2-17), amide, porcineSummary: A modulator of pain response
A1012 Dynorphin (2-17), amide, porcineSummary: A modulator of pain response -
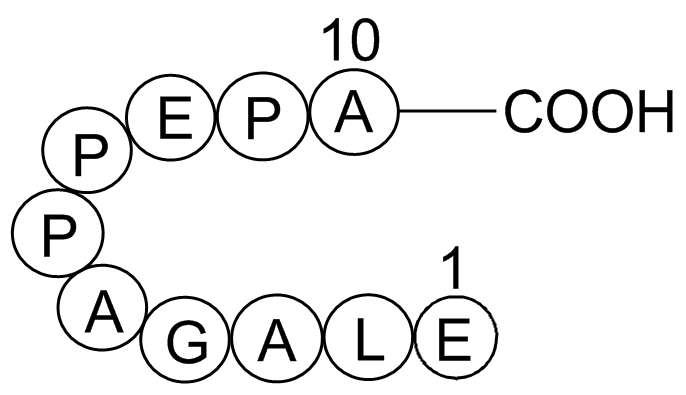 A1014 Beta-Lipotropin (1-10), porcineSummary: Morphine-like substance
A1014 Beta-Lipotropin (1-10), porcineSummary: Morphine-like substance -
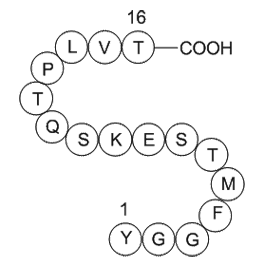 A1015 alpha-EndorphinSummary: Neurotransmitters
A1015 alpha-EndorphinSummary: Neurotransmitters -
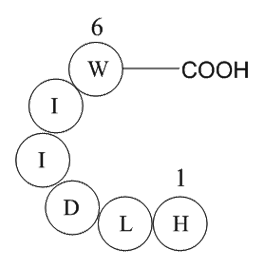 A1016 Ac-Endothelin-1 (16-21), humanSummary: ETA/ETB agonist,vasoconstrictor
A1016 Ac-Endothelin-1 (16-21), humanSummary: ETA/ETB agonist,vasoconstrictor -
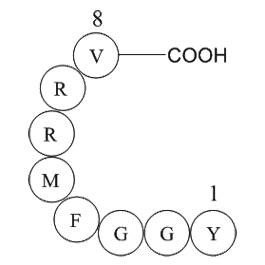 A1017 Adrenorphin, Free AcidSummary: μ/κ opioid receptor agonist
A1017 Adrenorphin, Free AcidSummary: μ/κ opioid receptor agonist -
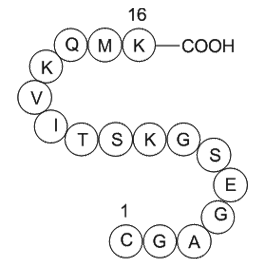 A1022 GTP-Binding Protein Fragment, G alphaSummary: Hydrolyzes GTP to GDP
A1022 GTP-Binding Protein Fragment, G alphaSummary: Hydrolyzes GTP to GDP -
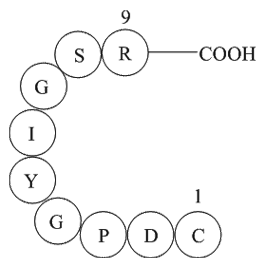 A1023 Laminin (925-933)2 CitationSummary: Extracellular matrix glycoprotein
A1023 Laminin (925-933)2 CitationSummary: Extracellular matrix glycoprotein

