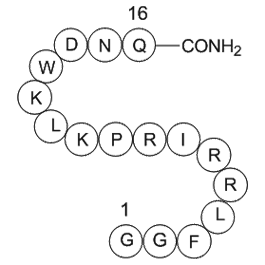
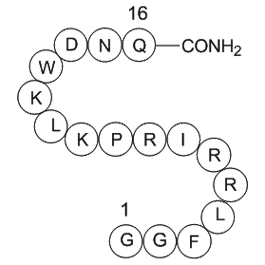
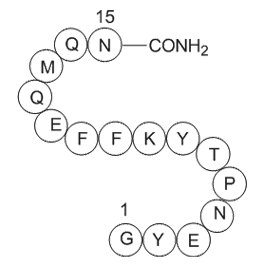
Dynorphin (2-17), amide, porcine
Dynorphins are a class of opioid peptides that arise from the precursor protein prodynorphin. When prodynorphin is cleaved during processing by proprotein convertase 2 (PC2), multiple active peptides are released: dynorphin A, dynorphin B, and α/β-neo-endorphin(1). Depolarization of a neuron containing prodynorphin stimulates PC2 processing, which occurs within synaptic vesicles in the presynaptic terminal(2). Dynorphin is produced in many different parts of the brain, including the hypothalamus, the striatum, the hippocampus and the spinal cord. Dynorphin has been shown to be a modulator of pain response. injecting dynorphin into the subarachnoid space of the rat spinal cord produced dose-dependent analgesia that was measured by tail-flick latency. Analgesia was partially eliminated by opioid antagonist naloxone. dynorphin activates bradykinin receptors, which triggers the release of calcium ions into the cell through voltage-sensitive channels in the cell membrane. Blocking bradykinin receptors in the lumbar region of the spinal cord reversed persistent pain(3). A multiple pathway system might help explain the conflicting effects of dynorphin in the CNS.
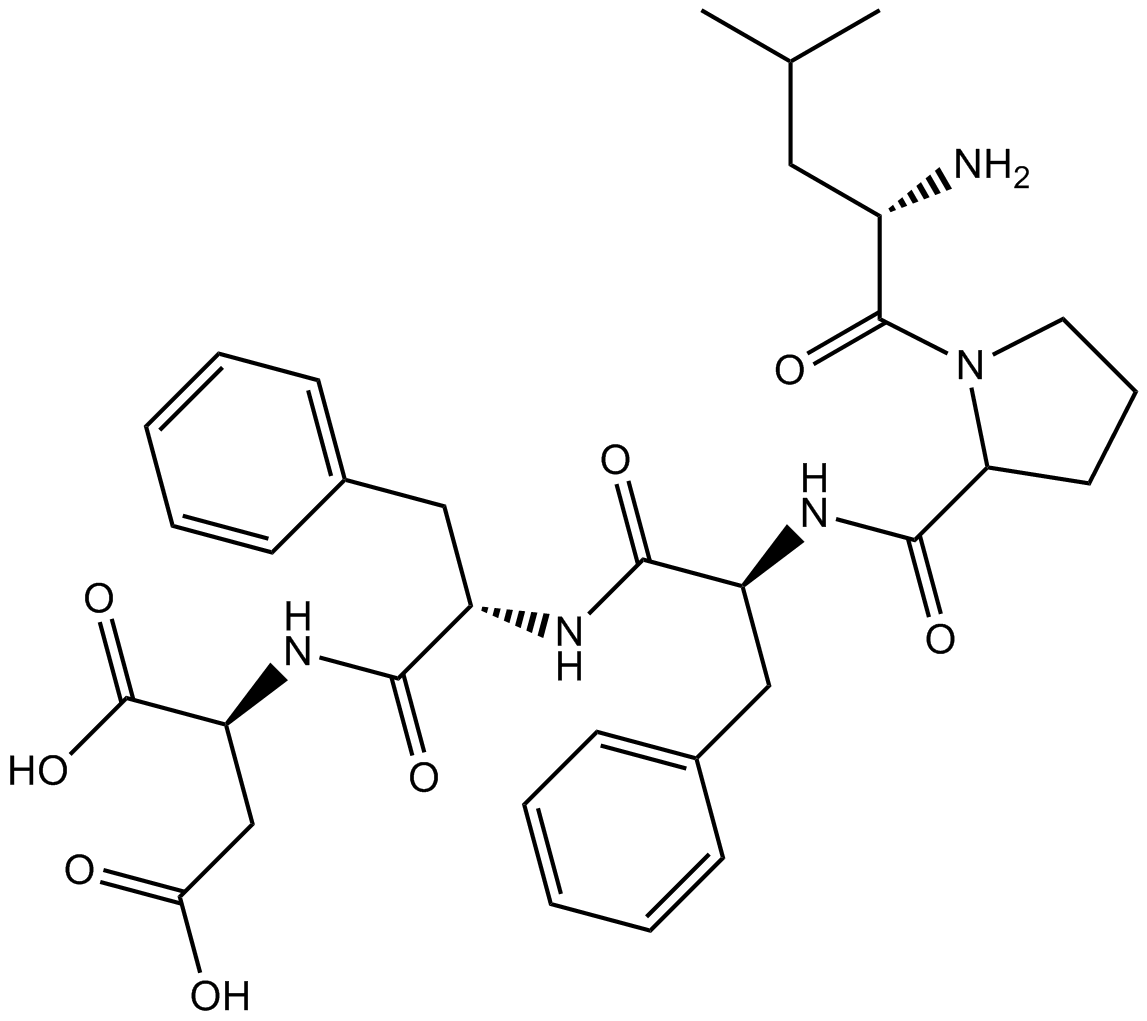
Figure1 Formula of b-Casomorphin (1-3)
Figure 2 role of dynorphin in the nucleus accumbens in depression
Ref:
1. Day R, Lazure C, Basak A, Boudreault A, Limperis P, Dong W, Lindberg I (January 1998). "Prodynorphin processing by proprotein convertase 2. Cleavage at single basic residues and enhanced processing in the presence of carboxypeptidase activity". J. Biol. Chem. 273 (2): 829–36.
2. Yakovleva T, Bazov I, Cebers G, Marinova Z, Hara Y, Ahmed A, Vlaskovska M, Johansson B, Hochgeschwender U, Singh IN, Bruce-Keller AJ, Hurd YL, Kaneko T, Terenius L, Ekström TJ, Hauser KF, Pickel VM, Bakalkin G (October 2006). "Prodynorphin storage and processing in axon terminals and dendrites". FASEB J. 20 (12): 2124–6.
3. Lai J, Luo MC, Chen Q, Ma S, Gardell LR, Ossipov MH, Porreca F (December 2006). "Dynorphin A activates bradykinin receptors to maintain neuropathic pain". Nat. Neurosci. 9 (12): 1534–40.
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 1983.33 |
| Formula | C90H147N31O20 |
| Synonyms | H2N-Gly-Gly-Phe-Leu-Arg-Arg-Ile-Arg-Pro-Lys-Leu-Lys-Trp-Asp-Asn-Gln-amide |
| Solubility | ≥198.3 mg/mL in DMSO; ≥14.02 mg/mL in EtOH; ≥23.13 mg/mL in H2O |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure