Isotope-Labeled Compounds

Isotope-labeled compounds are enriched specific compounds incorporated with stable isotopes, whose core function is to achieve accurate quantification in mass spectrometry (MS), particularly in isotope dilution mass spectrometry (IDMS). Quantitative analysis is accomplished by determining the concentration ratio of unlabeled to labeled analytes, which constitutes the key distinction from traditional analytical methods. As molecular probes amenable to specific detection, isotope-labeled compounds address the critical challenges in conventional research, namely the inability to track the dynamic changes of molecules and to distinguish between endogenous and exogenous molecules.
¹³C and deuterium (D, ²H) labeled compounds represent the most widely used stable isotope-labeled agents at present. They refer to enriched labeled products prepared by the precise incorporation of ¹³C or deuterium atoms into organic molecules, biological macromolecules or metabolites via chemical synthesis, microbial fermentation and other approaches. Their core characteristics include the retention of the physicochemical properties and biological activity of the parent molecules, with only subtle differences in atomic mass and nuclear spin. Moreover, they are free of radioactive contamination and can be safely used in various in vitro and in vivo experiments. Relying on techniques such as mass spectrometry (GC-MS/LC-MS, nano-SIMS, etc.), nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and Raman spectroscopy (micro-RS/SRS, etc.), these labeled compounds enable qualitative and quantitative analysis, spatial localization and dynamic tracking of target molecules by virtue of isotopic mass differences or characteristic molecular vibrational/nuclear spin signals. They also serve as core tools for isotope dilution mass spectrometry (IDMS), realizing accurate quantification through the ratio of labeled to unlabeled analytes and effectively distinguishing endogenous native molecules from exogenously introduced molecules in biological systems, thus acting as molecular probes with both high specificity and reliability.
-
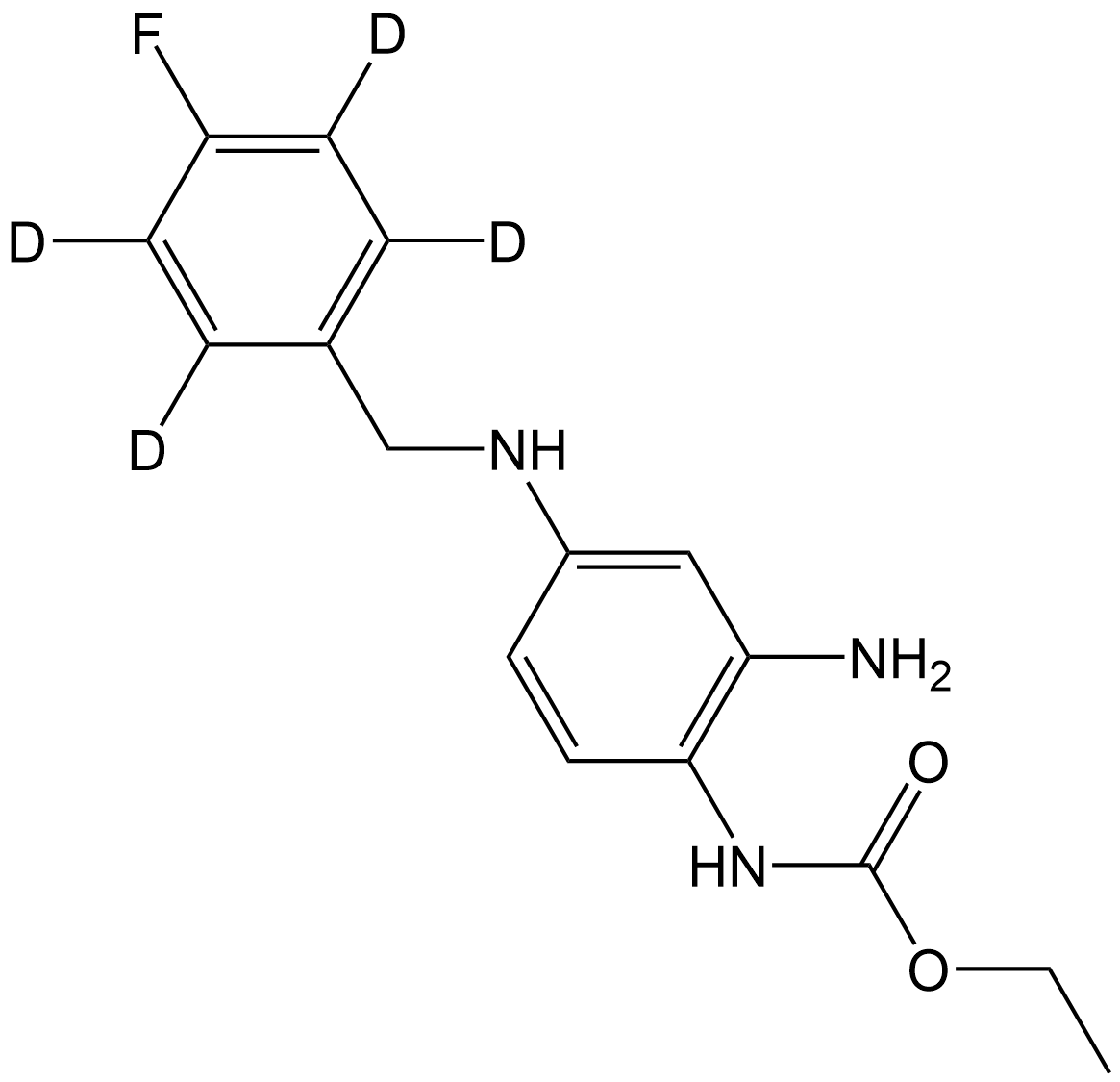 SL1071 Retigabine-d4Summary: A stable isotope deuterated compound of Retigabine
SL1071 Retigabine-d4Summary: A stable isotope deuterated compound of Retigabine -
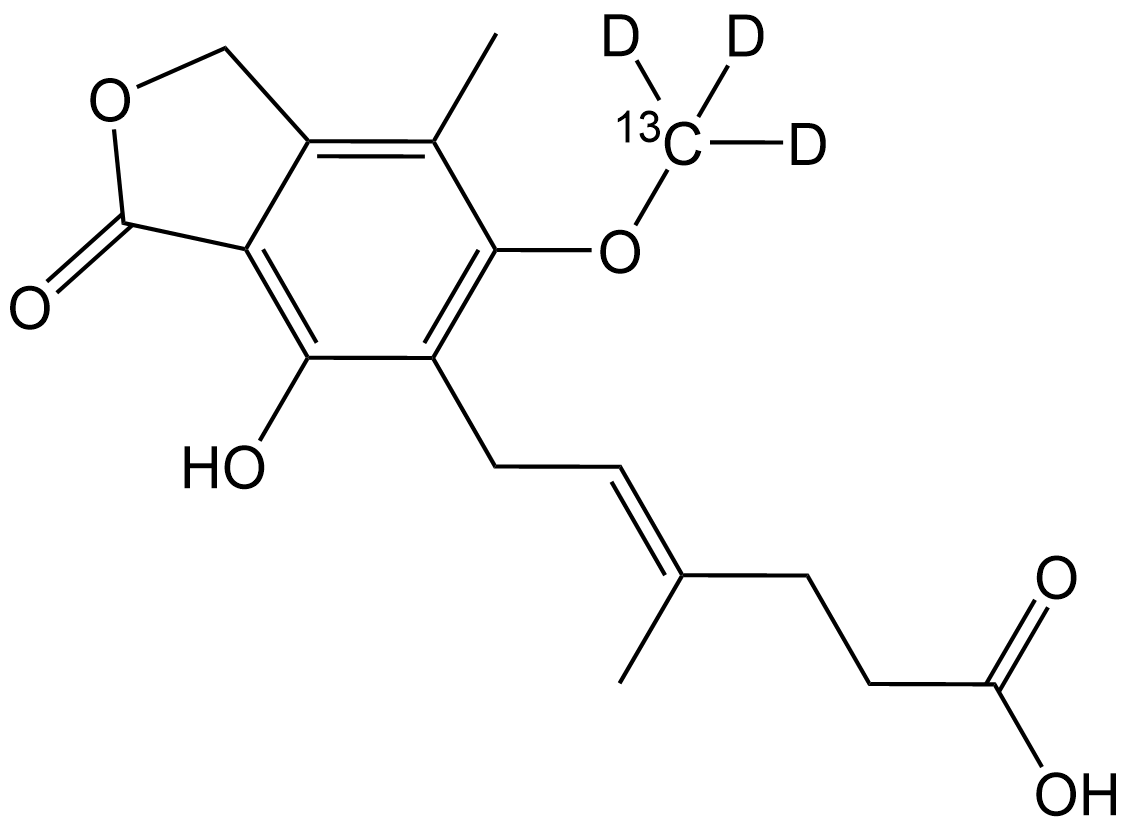 SL1070 Mycophenolic acid-13C,d3Summary: 13C- and deuterium-labeled Mycophenolic acid
SL1070 Mycophenolic acid-13C,d3Summary: 13C- and deuterium-labeled Mycophenolic acid -
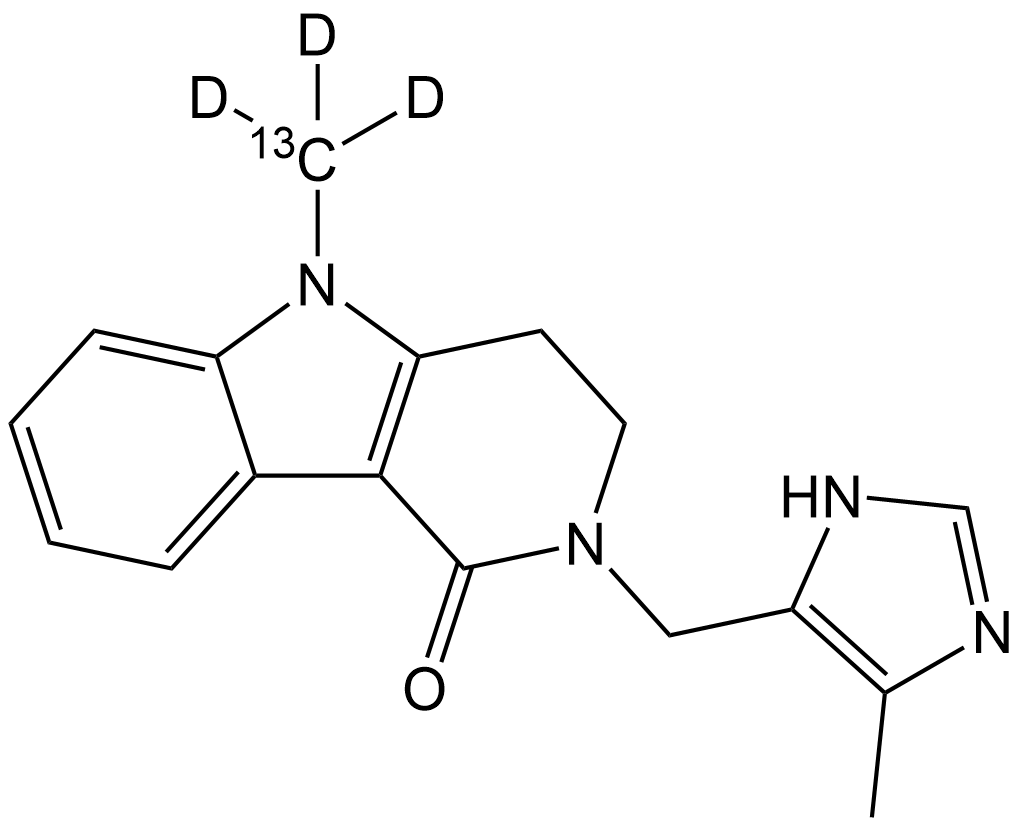 SL1069 Alosetron-13CD3Summary: 13C- and deuterium-labeled Alosetron
SL1069 Alosetron-13CD3Summary: 13C- and deuterium-labeled Alosetron -
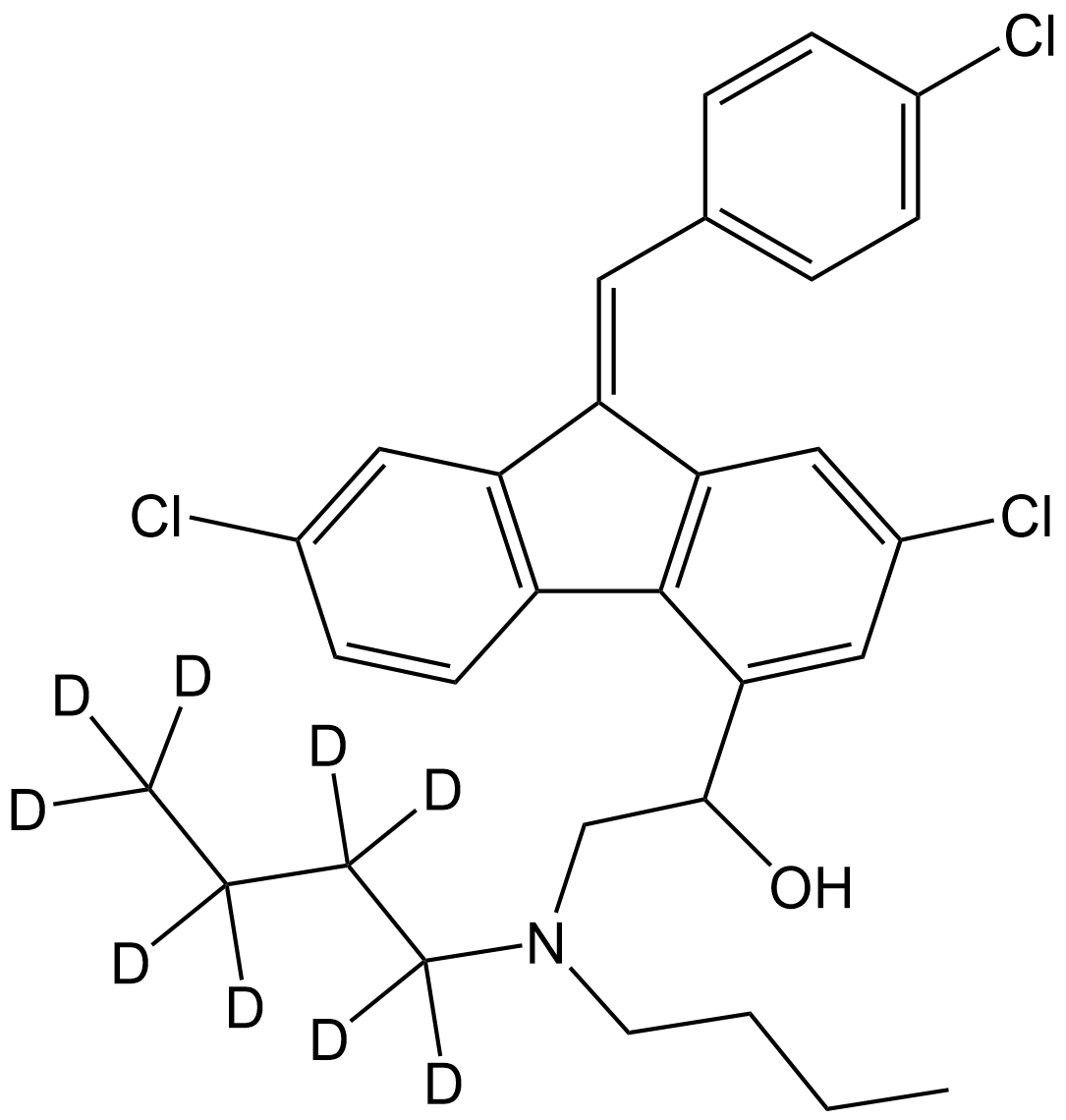 SL1068 Lumefantrine-d9Summary: A stable isotope deuterated compound of Lumefantrine
SL1068 Lumefantrine-d9Summary: A stable isotope deuterated compound of Lumefantrine -
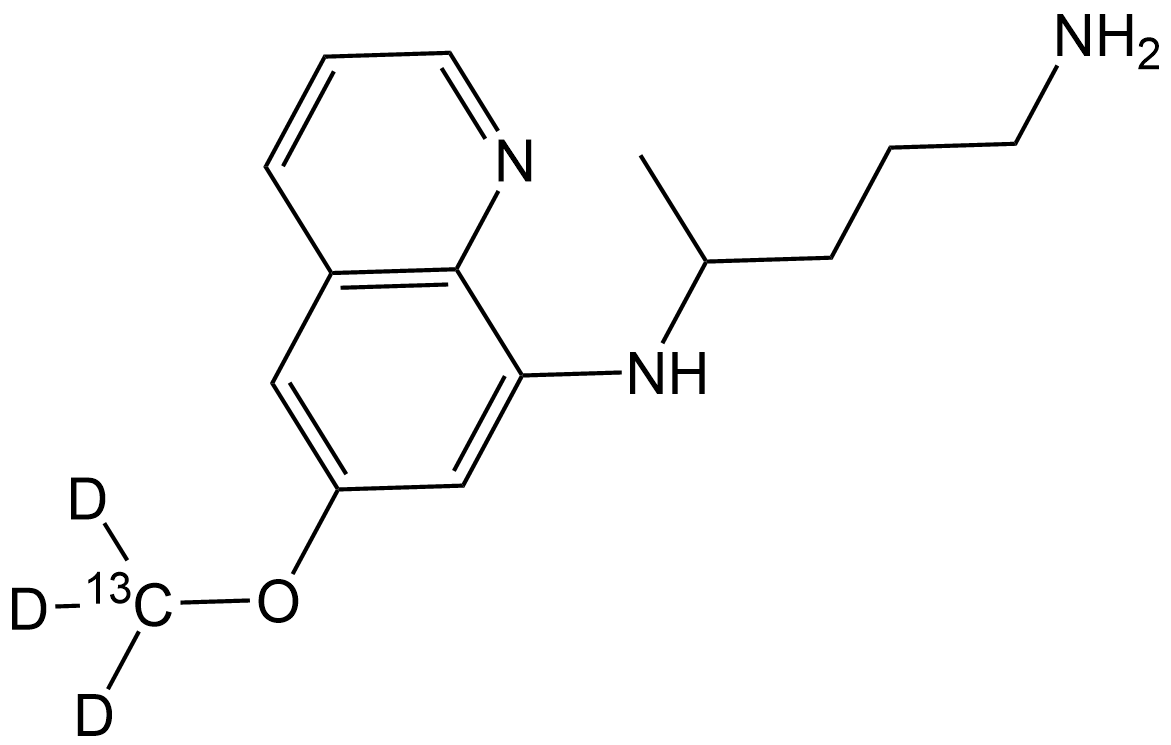 SL1067 Primaquine-13CD3Summary: 13C- and deuterium-labeled Primaquine
SL1067 Primaquine-13CD3Summary: 13C- and deuterium-labeled Primaquine -
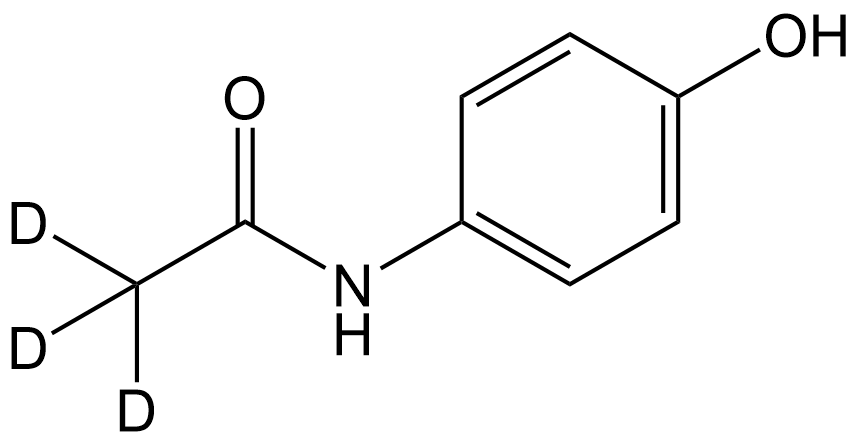 SL1066 Acetaminophen-d3Summary: A stable isotope deuterated compound of Acetaminophen
SL1066 Acetaminophen-d3Summary: A stable isotope deuterated compound of Acetaminophen -
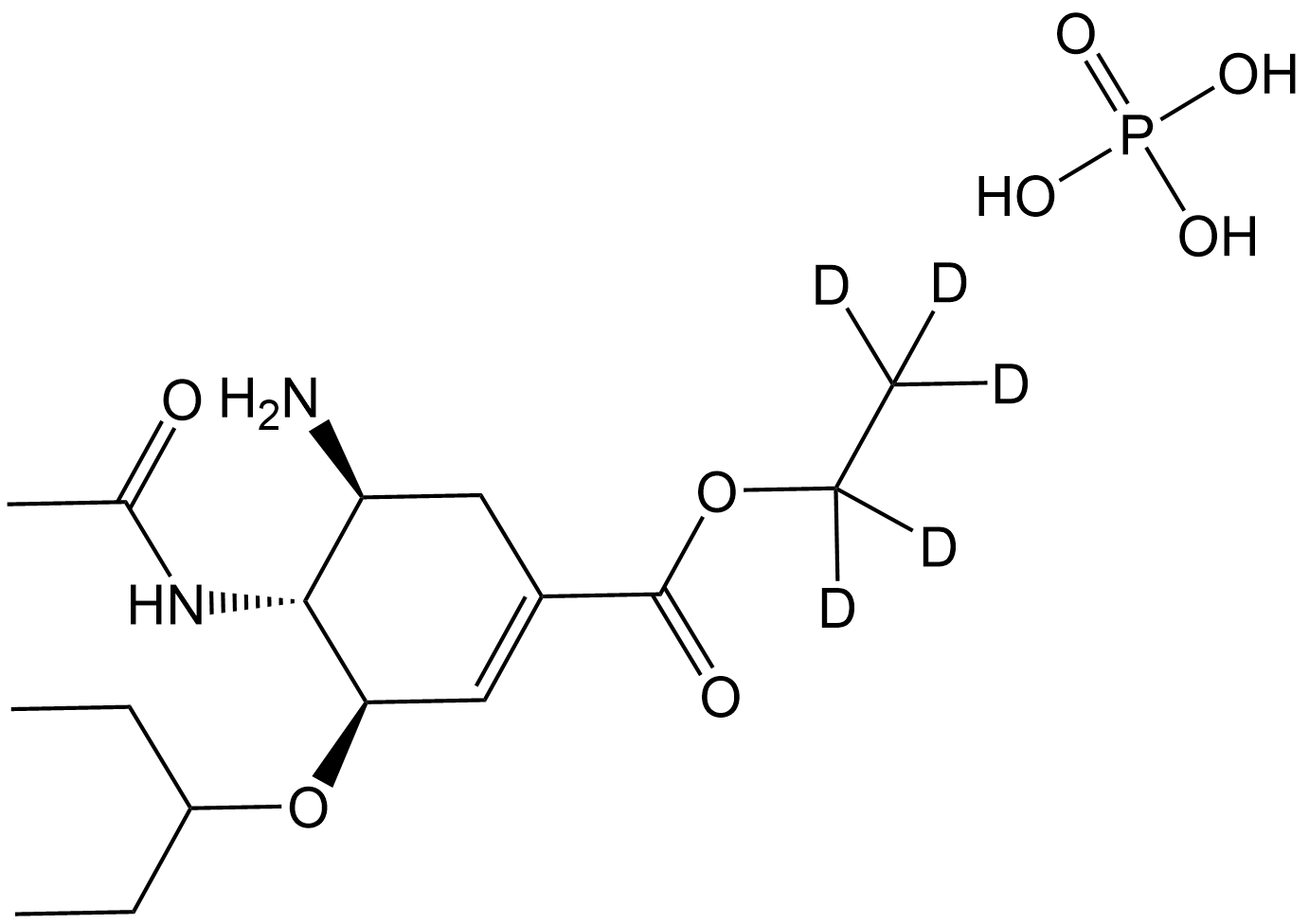 SL1065 Oseltamivir phosphate-d5Summary: A stable isotope deuterated compound of Oseltamivir phosphate
SL1065 Oseltamivir phosphate-d5Summary: A stable isotope deuterated compound of Oseltamivir phosphate -
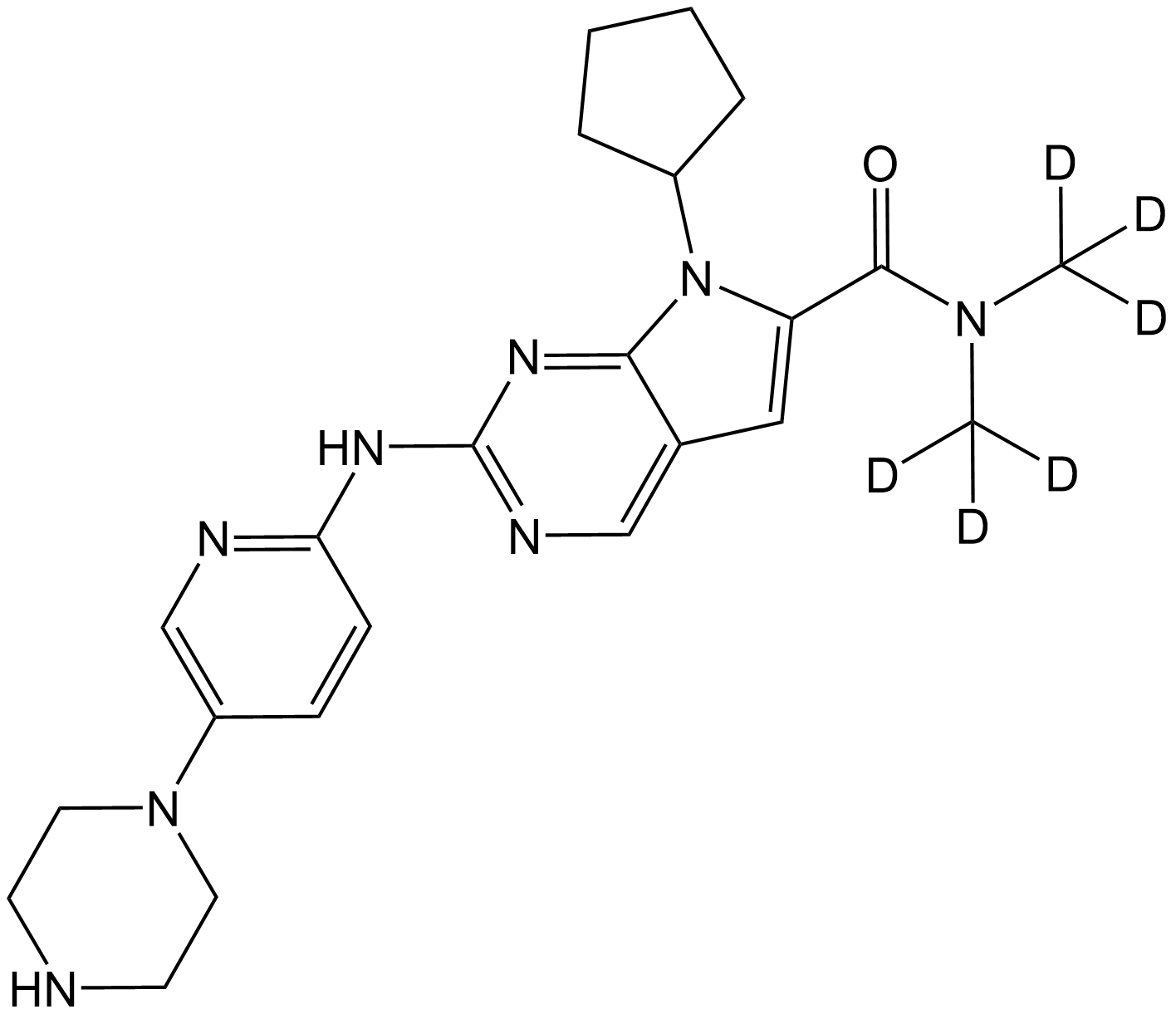 SL1064 Ribociclib-d6Summary: A stable isotope deuterated compound of Ribociclib
SL1064 Ribociclib-d6Summary: A stable isotope deuterated compound of Ribociclib -
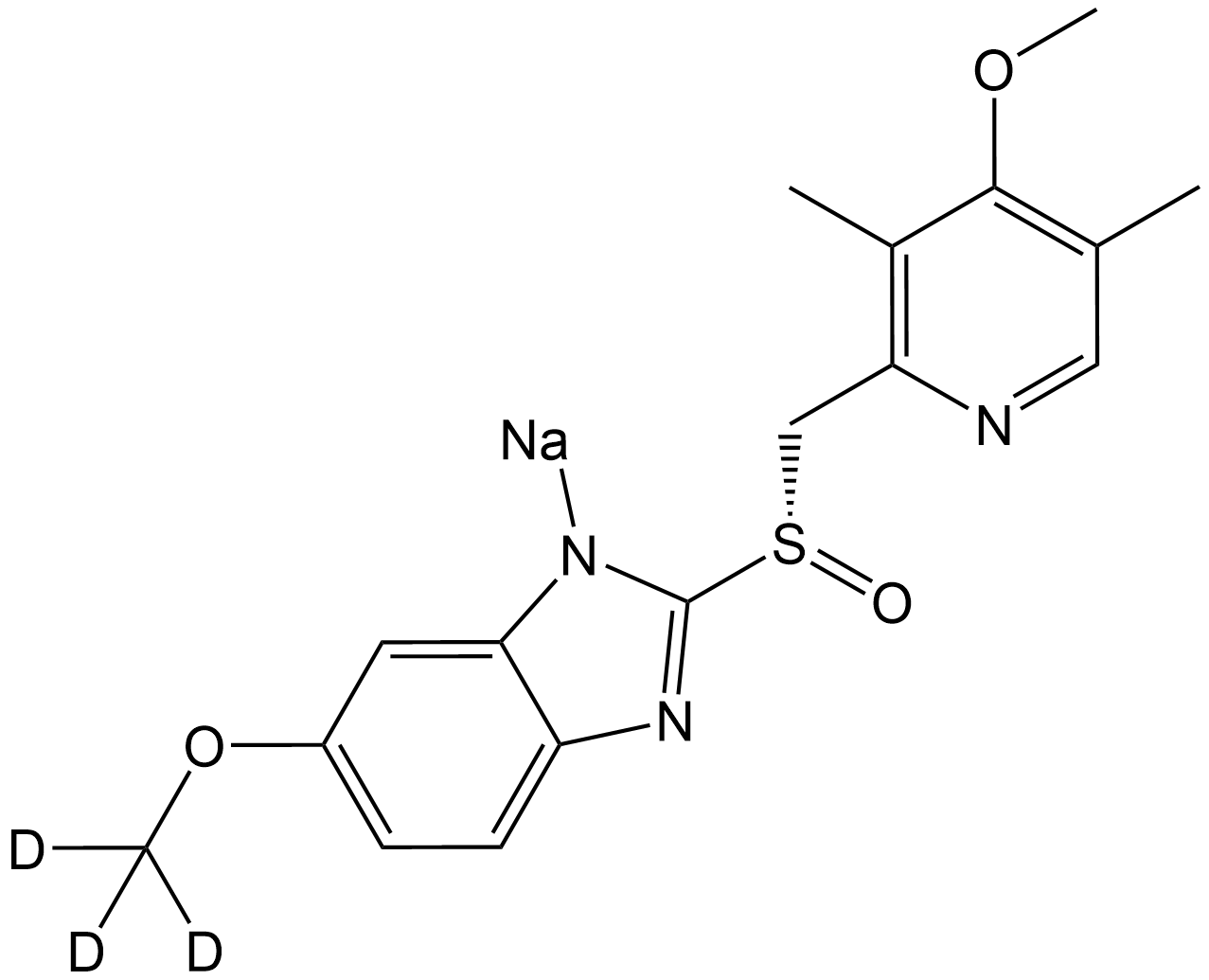 SL1063 Esomeprazole-d3 sodiumSummary: A stable isotope deuterated compound of Esomeprazole sodium
SL1063 Esomeprazole-d3 sodiumSummary: A stable isotope deuterated compound of Esomeprazole sodium -
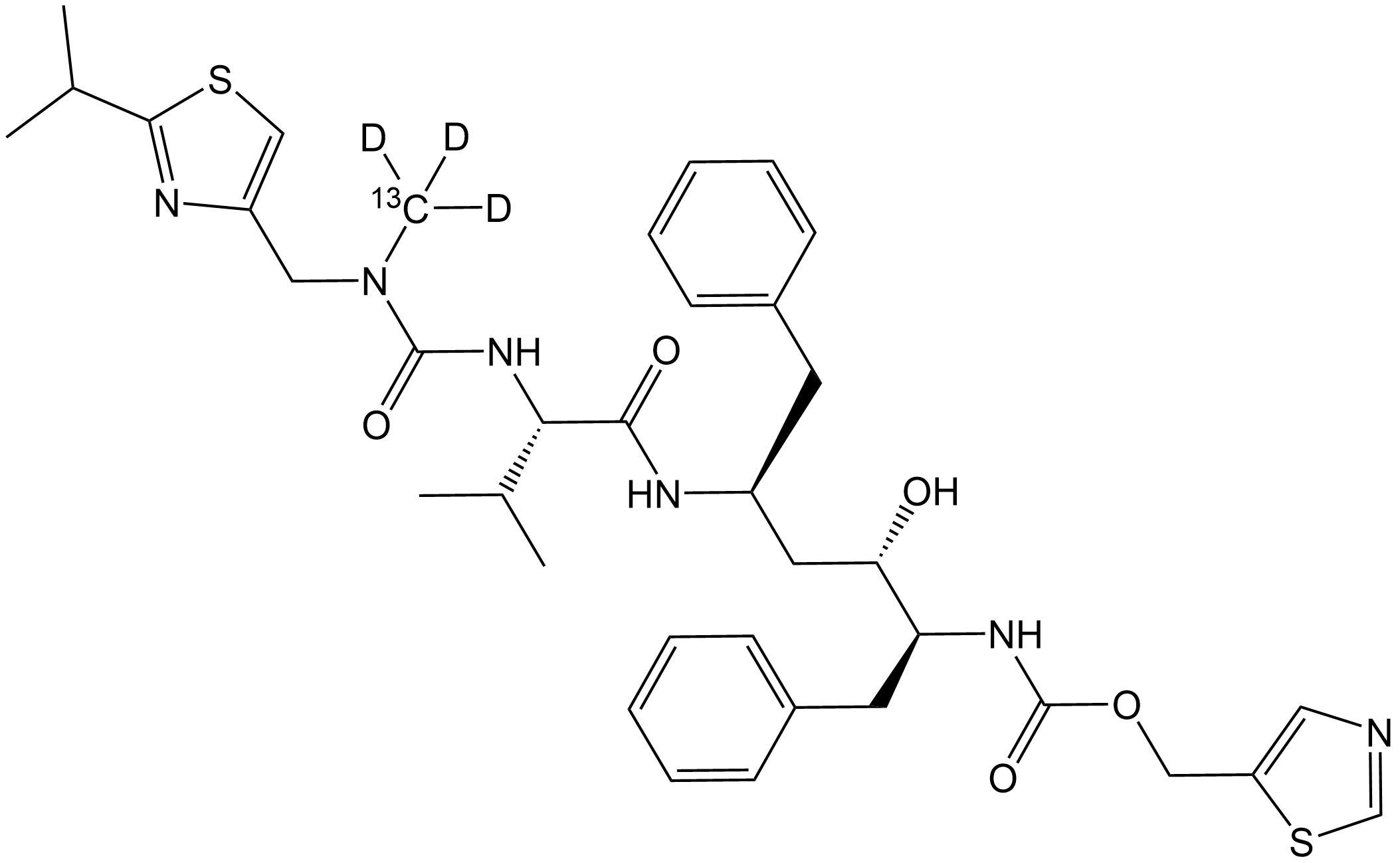 SL1062 Ritonavir-13CD3Summary: 13C- and deuterium-labeled Ritonavir
SL1062 Ritonavir-13CD3Summary: 13C- and deuterium-labeled Ritonavir


