ADC Linker
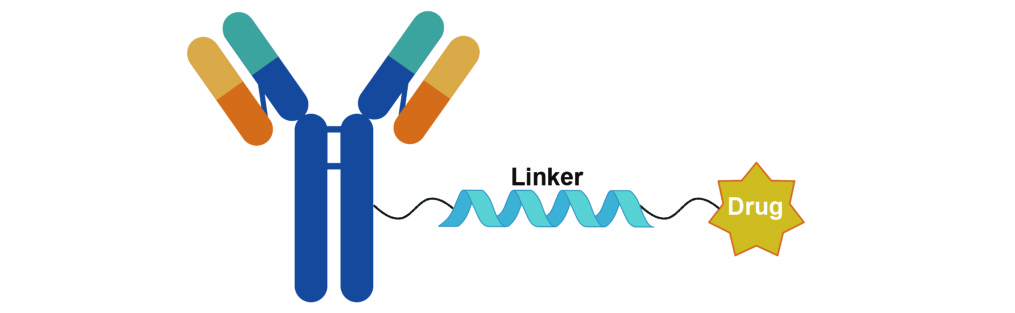

Antibody–drug conjugate (ADC) linkers are core functional components of ADCs, serving as covalent bridges that connect targeting antibodies to cytotoxic payloads. Their design is governed by the dual requirement of circulatory stability and efficient intracellular release. By employing specific chemical structures (such as peptide bonds, disulfide bonds, and acid-labile linkages), linkers enable precise control over ADC behavior: they preserve the integrity of the conjugate in the bloodstream to prevent premature payload release and off-target toxicity, while, after cellular uptake (e.g., via endocytosis and subsequent lysosomal degradation), they facilitate efficient payload liberation through enzymatic hydrolysis, reductive cleavage, or pH-responsive mechanisms. In this way, linkers form the molecular basis for both the targeting selectivity and safety profile of ADCs.
As essential reagents for ADC research and development, structurally diverse linkers provide critical support for both basic research and translational drug discovery. Different linker types (including cleavable, non-cleavable, and hydrophilically modified linkers) can be tailored to a wide range of payloads, such as microtubule inhibitors and DNA-damaging agents, thereby accommodating diverse molecular targets and heterogeneous tumor microenvironments. Linker stability, intracellular release efficiency, and biocompatibility directly shape the therapeutic window of ADCs and contribute to overcoming the resistance and toxicity limitations associated with conventional chemotherapy. In target validation, structure–activity relationship studies of ADCs, and preclinical drug screening, linker reagents thus provide crucial technical leverage for the precise modulation of ADC performance and for expanding the therapeutic applications of ADCs in oncology.
-
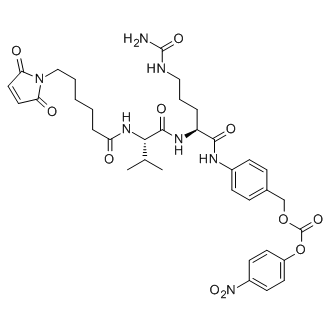 B1003 Mc-Val-Cit-PABC-PNPSummary: Cathepsin cleavable ADC peptide linker
B1003 Mc-Val-Cit-PABC-PNPSummary: Cathepsin cleavable ADC peptide linker -
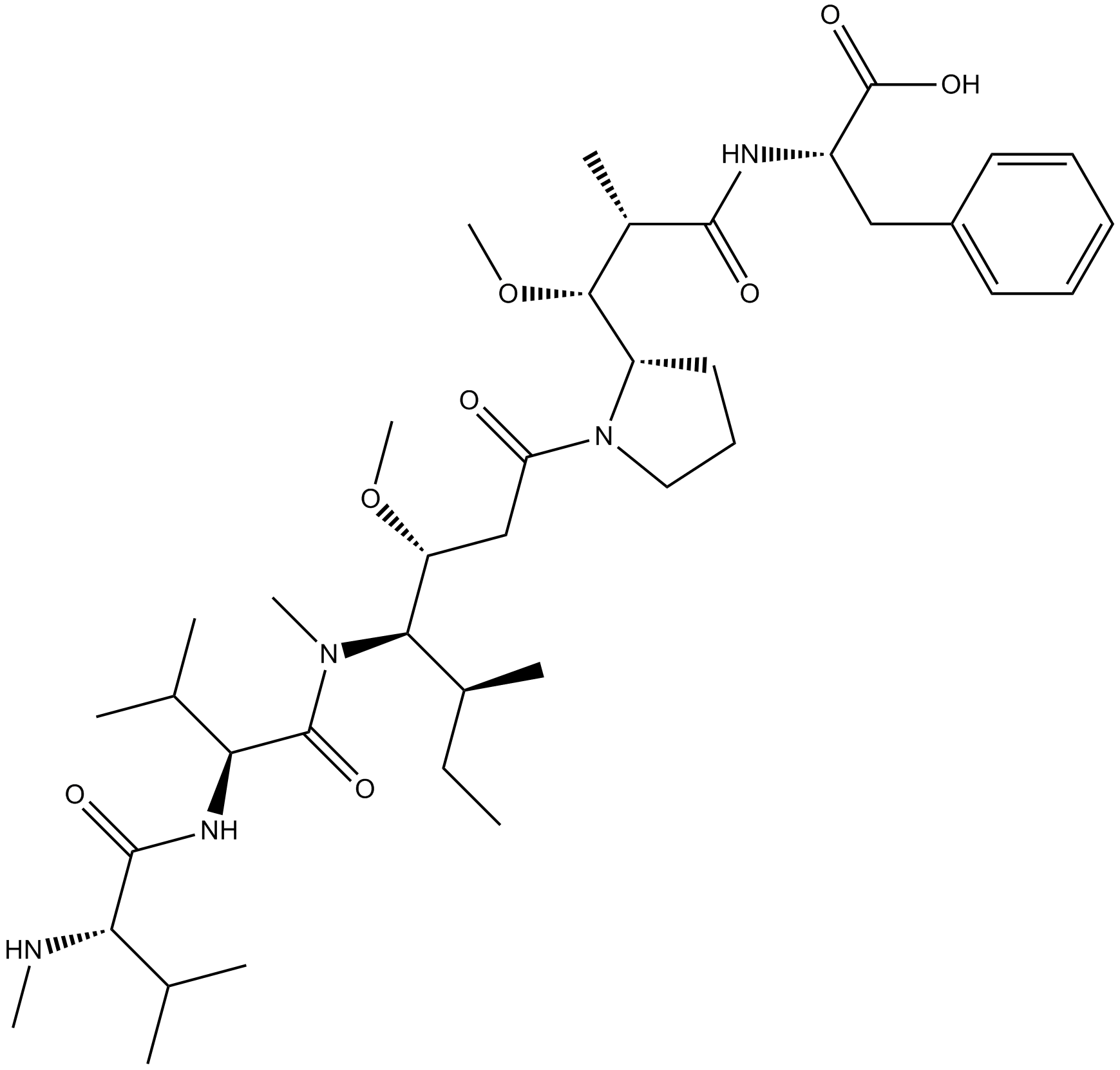 B3270 MMAFTarget: Microtubules/TubulinsSummary: Anti-mitotic/anti-tubulin/antineoplastic agent
B3270 MMAFTarget: Microtubules/TubulinsSummary: Anti-mitotic/anti-tubulin/antineoplastic agent -
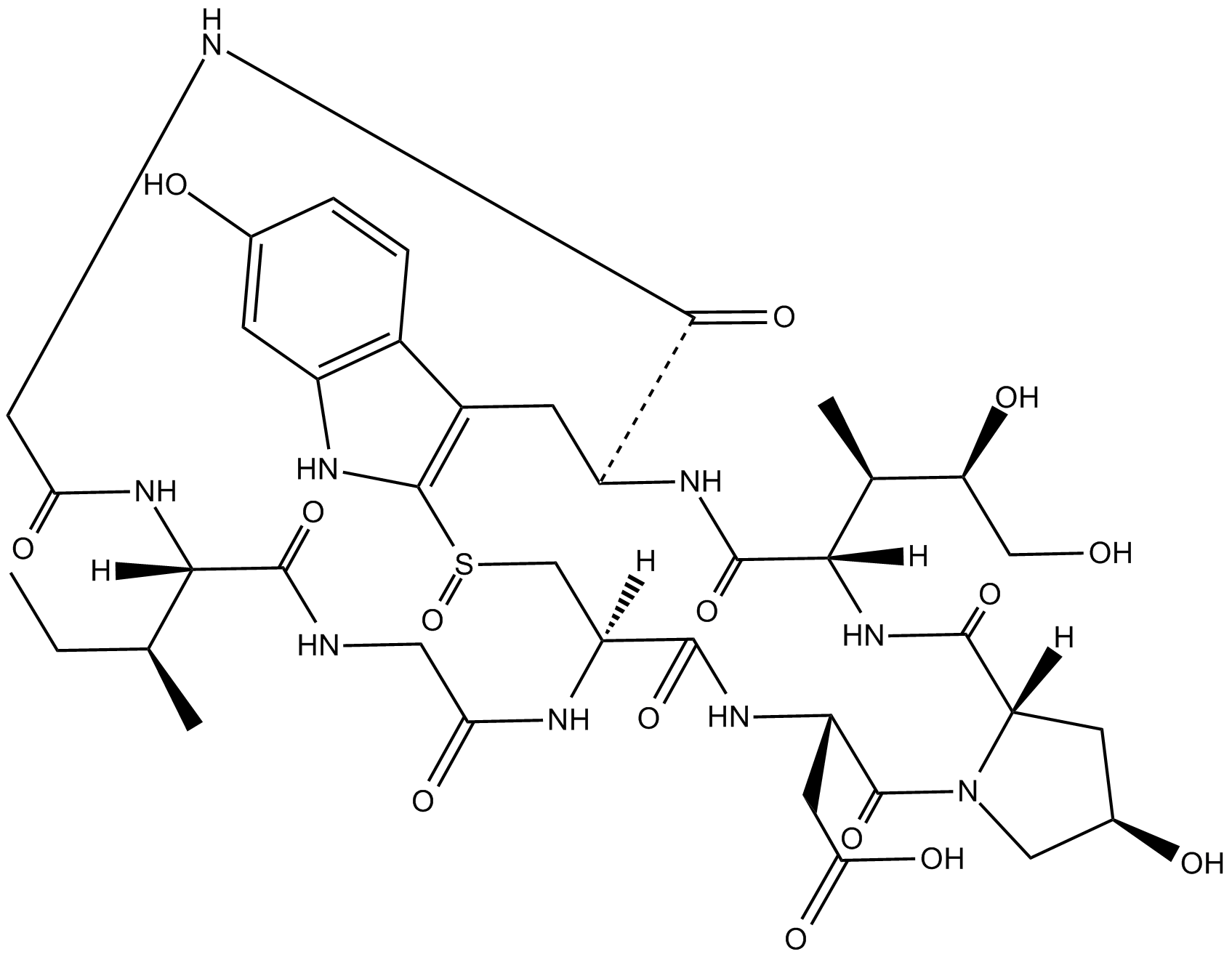 B8467 β-Amanitin
B8467 β-Amanitin -
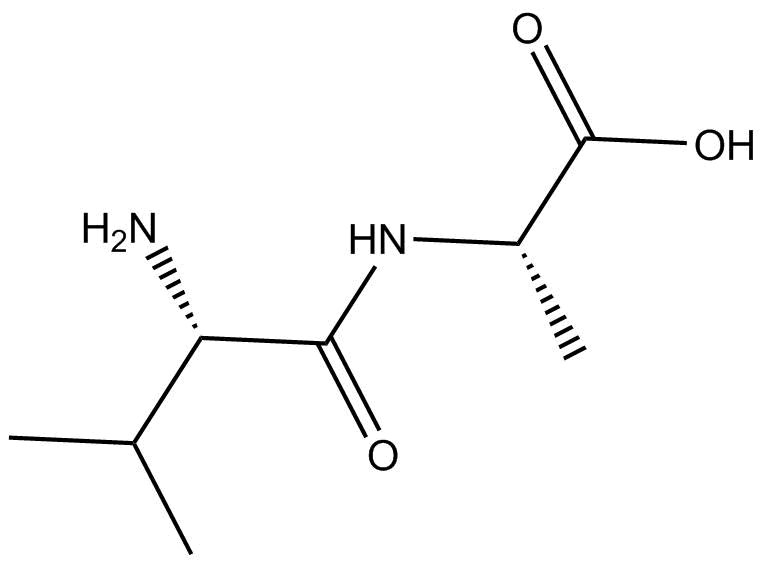 C6575 H-Val-Ala-OH
C6575 H-Val-Ala-OH -
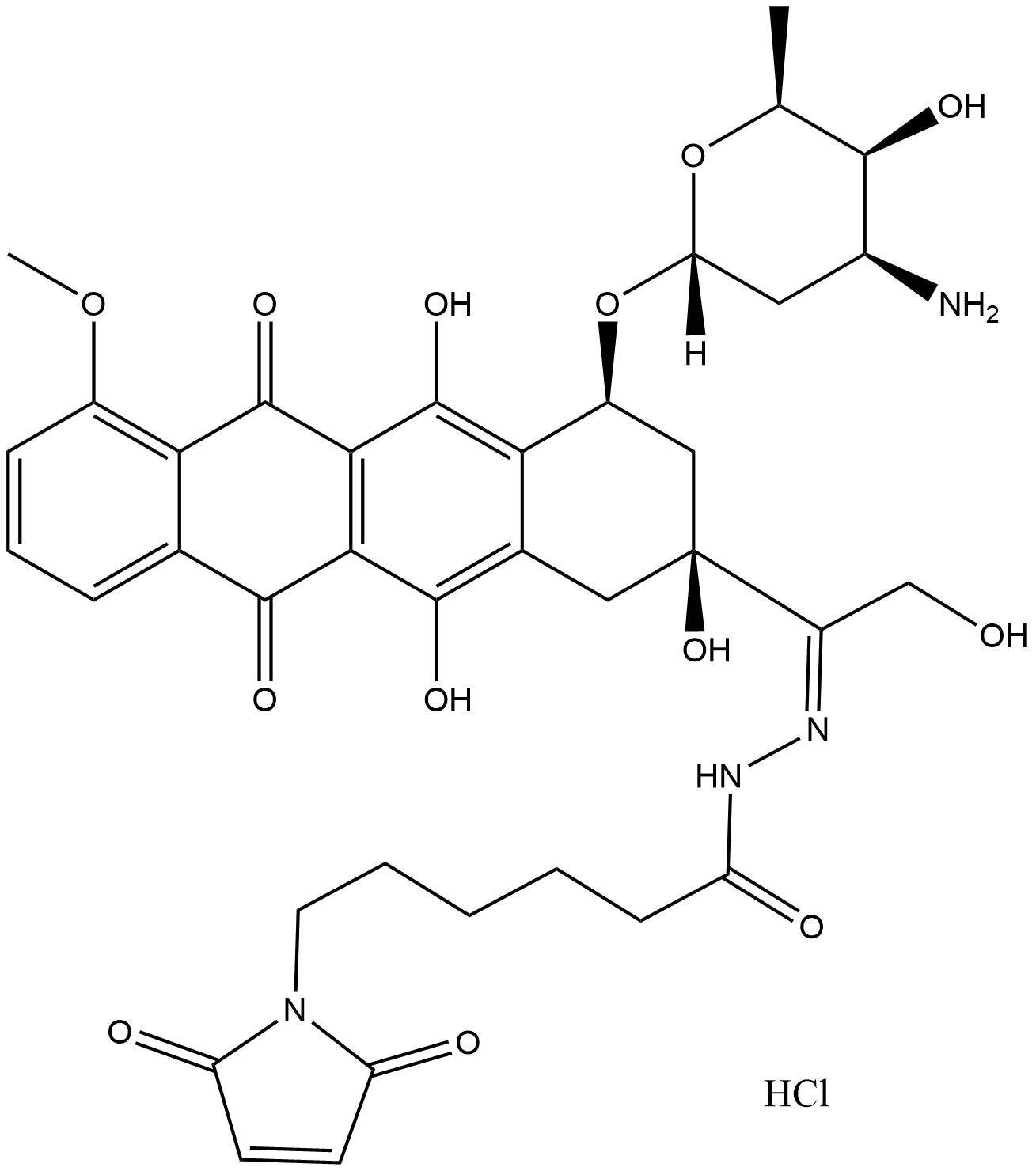 B8916 Aldoxorubicin (hydrochloride)
B8916 Aldoxorubicin (hydrochloride) -
 BA2651 MC-SN38Summary: MC-SN38 is an active molecular coupler consisting of SN38, a potent microtubule disruptor, and a non-cleavable MClinker for the synthesis of antibody active molecular couplers (ADCs).
BA2651 MC-SN38Summary: MC-SN38 is an active molecular coupler consisting of SN38, a potent microtubule disruptor, and a non-cleavable MClinker for the synthesis of antibody active molecular couplers (ADCs). -
 BA2667 Mal-PEG2-Gly-Gly-Phe-Gly-ExatecanSummary: Mal-PEG2-Gly-Gly-Phe-Gly-Exatecan is an ADC.
BA2667 Mal-PEG2-Gly-Gly-Phe-Gly-ExatecanSummary: Mal-PEG2-Gly-Gly-Phe-Gly-Exatecan is an ADC. -
 BA2681 GGFG-amide-glycol-amide-ExatecanSummary: GGFG-amide-glycol-amide-Exatecan (Intermediate2) is a derivative.
BA2681 GGFG-amide-glycol-amide-ExatecanSummary: GGFG-amide-glycol-amide-Exatecan (Intermediate2) is a derivative. -
 BA2688 MC-Gly-Gly-Phe-Gly-Cyclobutanecarboxylic-ExatecanSummary: MC-Gly-Gly-Phe-Gly-Cyclobutanecarboxylic-Exatecan is part of an antibody-coupled active molecule consisting of (MC-Gly-Gly-Phe-Gly-Cyclobutanecarboxylic) coupled to a DNA topoisomerase I inhibitor.
BA2688 MC-Gly-Gly-Phe-Gly-Cyclobutanecarboxylic-ExatecanSummary: MC-Gly-Gly-Phe-Gly-Cyclobutanecarboxylic-Exatecan is part of an antibody-coupled active molecule consisting of (MC-Gly-Gly-Phe-Gly-Cyclobutanecarboxylic) coupled to a DNA topoisomerase I inhibitor. -
 BA2707 MC-Gly-Gly-Phe-Gly-GABA-ExatecanSummary: MC-Gly-Gly-Phe-Gly-GABA-ExatecanADC is a drug-linker coupler containing 22 μM topoisomerase.
BA2707 MC-Gly-Gly-Phe-Gly-GABA-ExatecanSummary: MC-Gly-Gly-Phe-Gly-GABA-ExatecanADC is a drug-linker coupler containing 22 μM topoisomerase.


