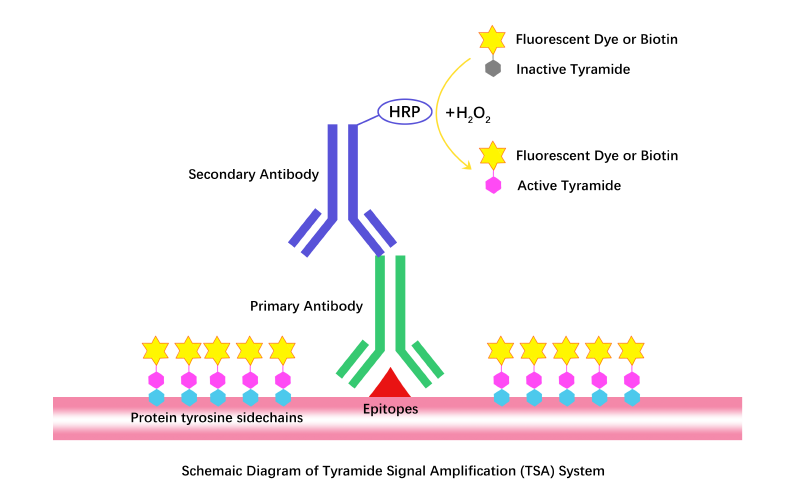
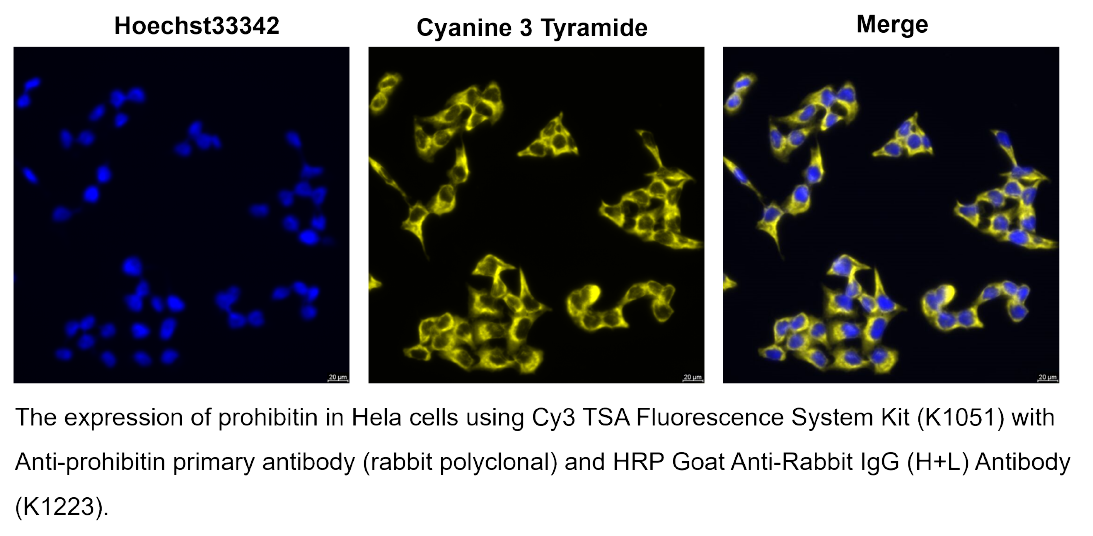
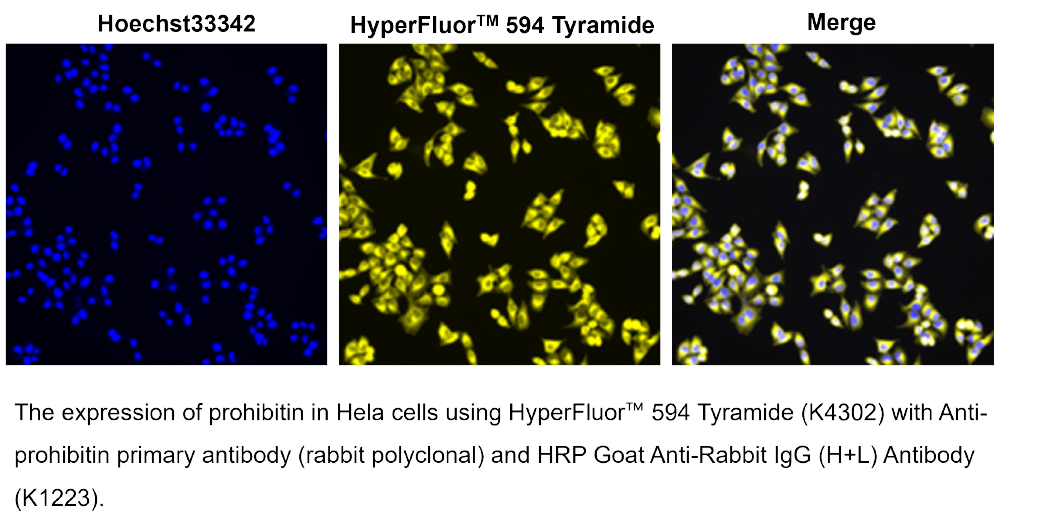
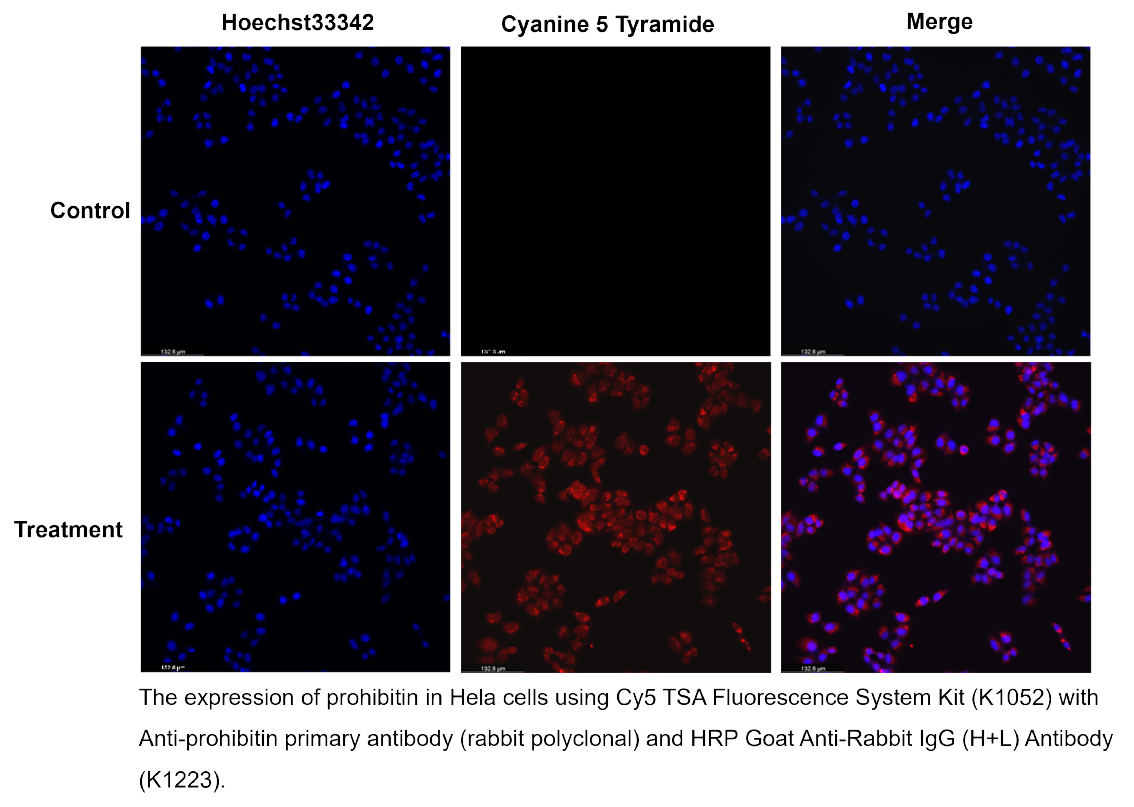
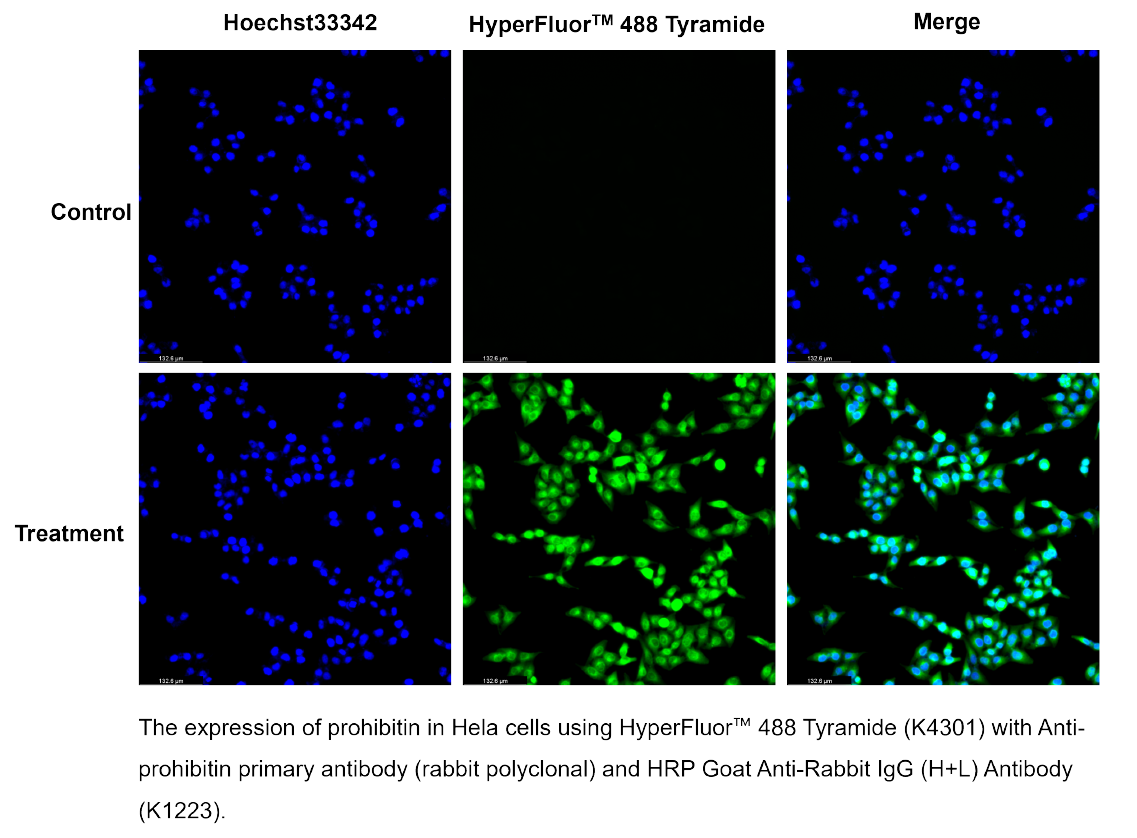
Tyramide Signal Amplification (TSA) is a highly sensitive, enzyme-mediated signal enhancement technique used to detect low-abundance proteins or nucleic acid sequences in situ. TSA relies on horseradish peroxidase (HRP) to catalyze the deposition of tyramide, a phenolic compound that covalently binds to electron-rich regions near the target site. This reaction results in high-density local labeling, producing strong fluorescent or chromogenic signals with minimal background.
TSA is widely applied in immunohistochemistry (IHC), immunocytochemistry (ICC), fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH/ISH), and other fluorescence imaging workflows, and is compatible with standard cell types and imaging systems.