Angiogenesis
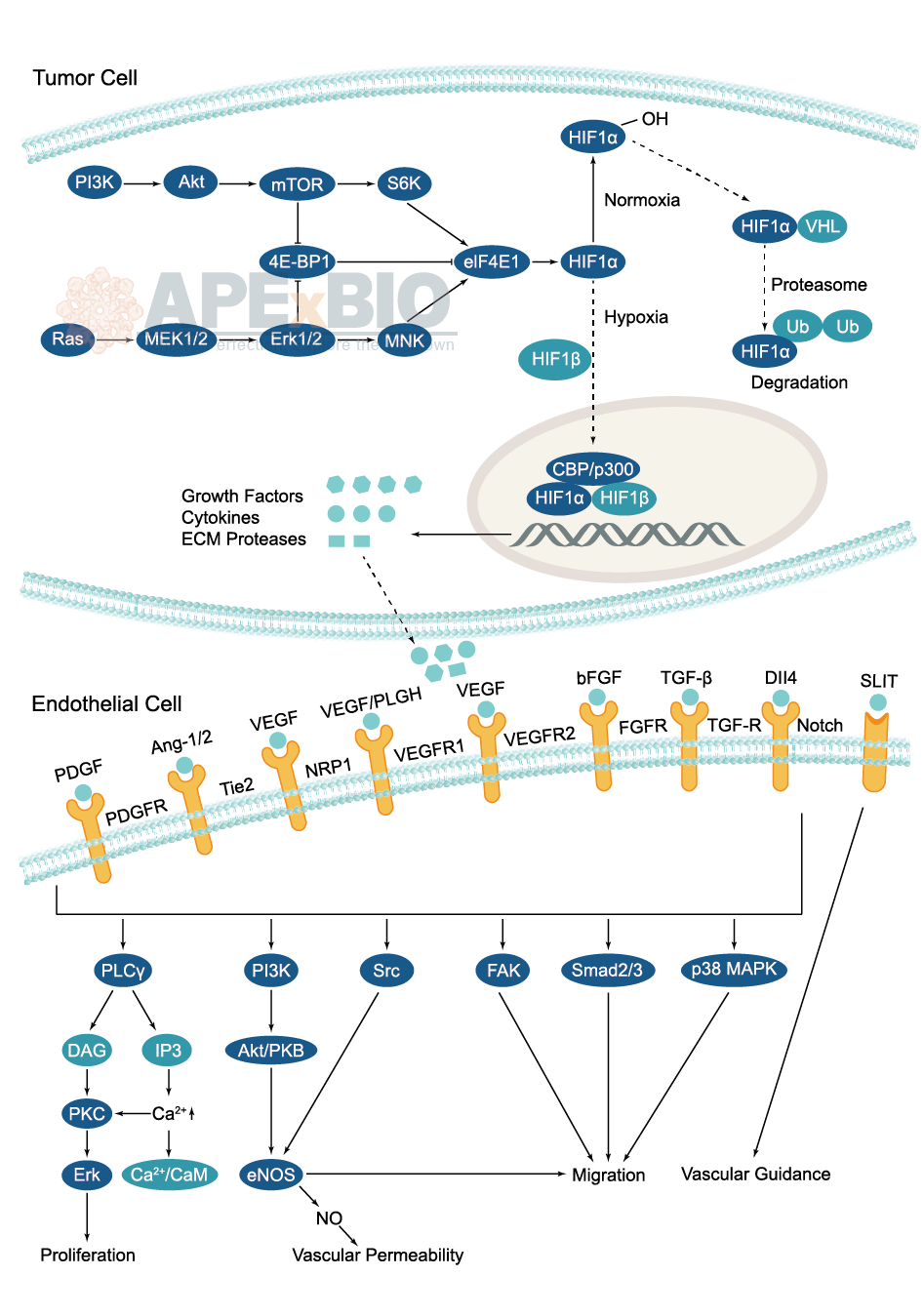

During tumor angiogenesis, cancer cells stimulate formation of new blood vessel for delivering oxygen and nutrients to a tumor. As the tumor grows, cells at the center of the mass become starved of oxygen, causing hypoxia. It stabilizes the expression of a transcription factor, HIF-1α (hypoxia inducible factor-1), which binds HIF-1β to upregulate the expression of several angiogenesis-promoting genes. Moreover, growth factor signaling also stimulates HIF-1 activity in order to maintain oxygen homeostasis for growing cells.
-
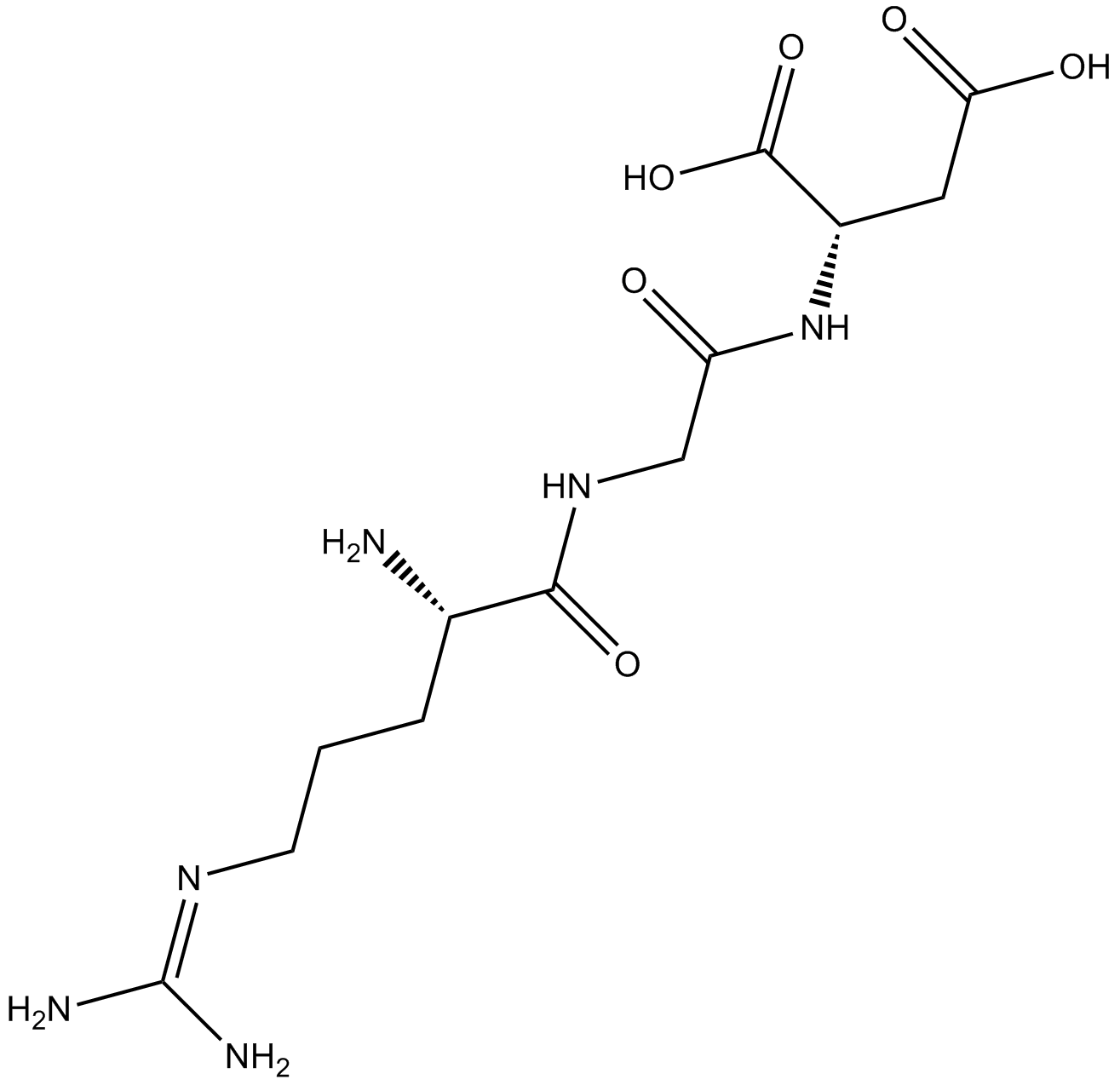 B3708 RGD (Arg-Gly-Asp) Peptides2 CitationTarget: Integrin-ligand interactionsSummary: Inhibits integrin binding to RGD motifs
B3708 RGD (Arg-Gly-Asp) Peptides2 CitationTarget: Integrin-ligand interactionsSummary: Inhibits integrin binding to RGD motifs -
 A4507 KC7F25 CitationSummary: HIF-1α inhibitor
A4507 KC7F25 CitationSummary: HIF-1α inhibitor -
 A4509 PX 121 CitationTarget: TrxSummary: Trx-1 inhibitor
A4509 PX 121 CitationTarget: TrxSummary: Trx-1 inhibitor -
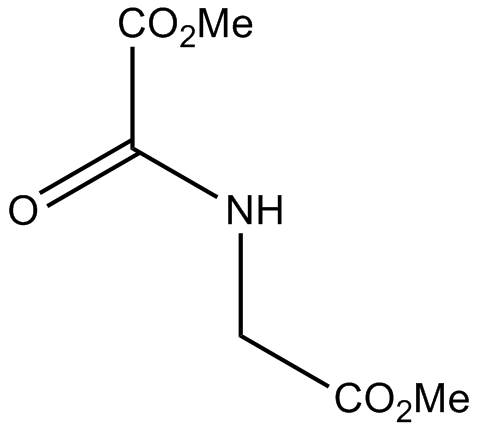 A4506 DMOG4 CitationTarget: Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitors (HIF-PHIs)Summary: Competitive HIF-PH inhibitor, cell-permeable
A4506 DMOG4 CitationTarget: Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitors (HIF-PHIs)Summary: Competitive HIF-PH inhibitor, cell-permeable -
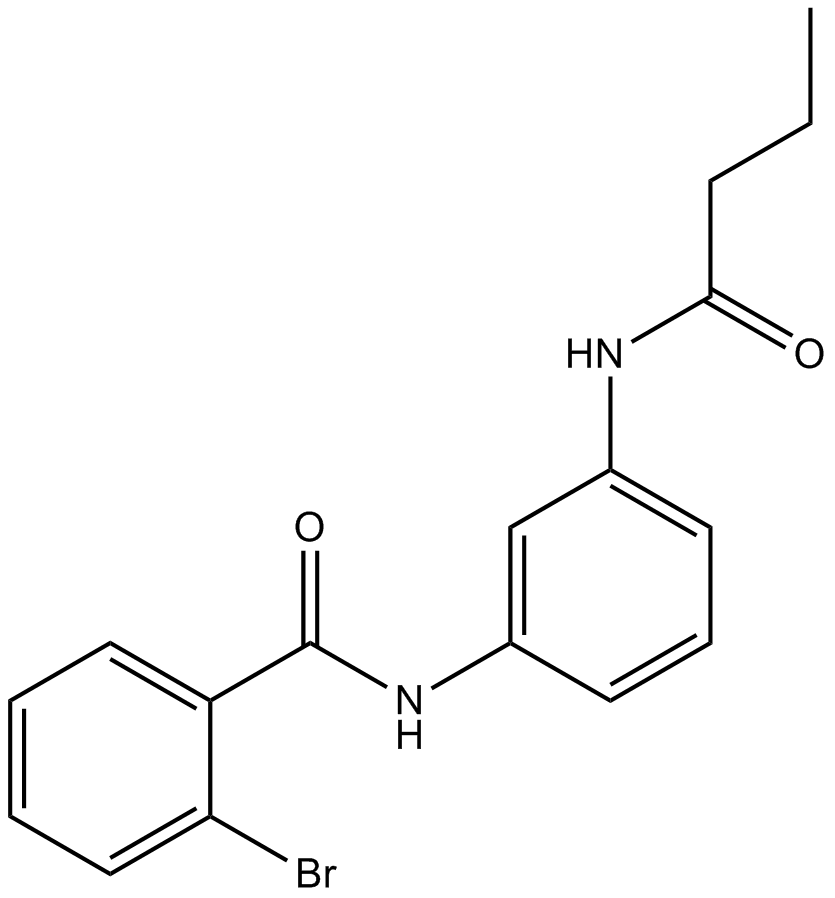 A8229 ML161Target: Protease-Activated ReceptorsSummary: PAR1 inhibitor
A8229 ML161Target: Protease-Activated ReceptorsSummary: PAR1 inhibitor -
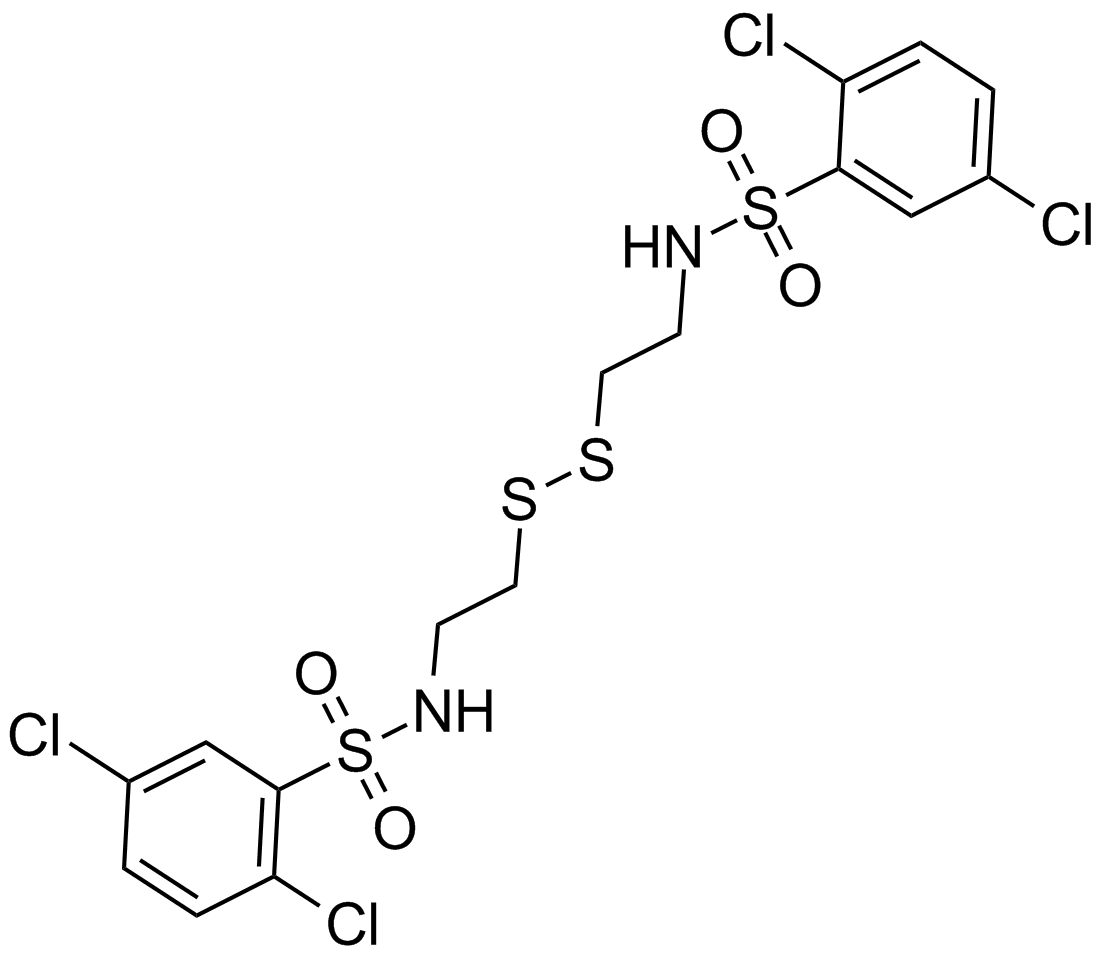
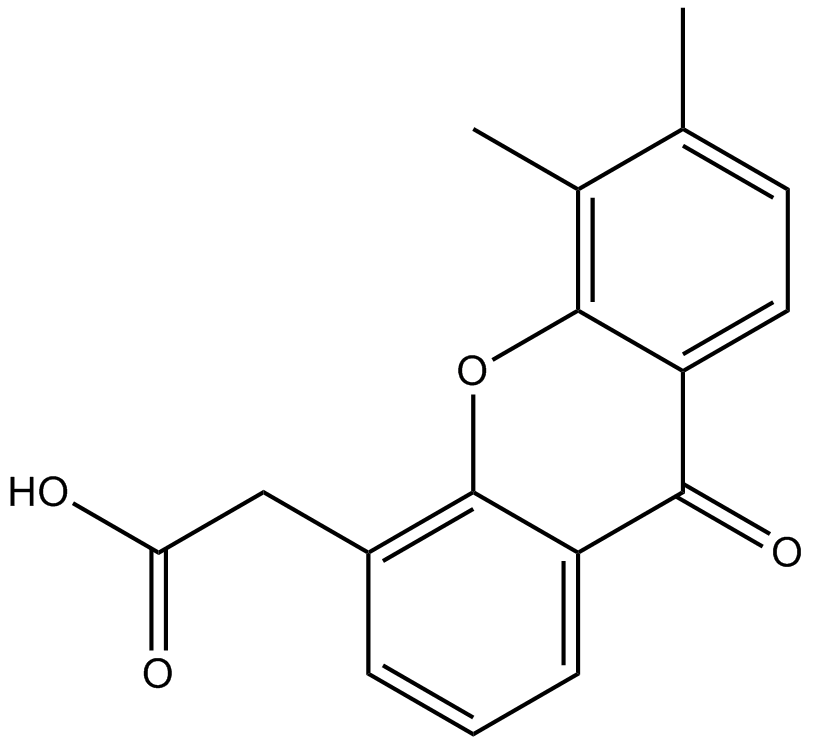 A8233 DMXAA (Vadimezan)2 CitationTarget: DT-diaphorasesSummary: Tumnor vascular disrupting agent, apoptosis inducer
A8233 DMXAA (Vadimezan)2 CitationTarget: DT-diaphorasesSummary: Tumnor vascular disrupting agent, apoptosis inducer -
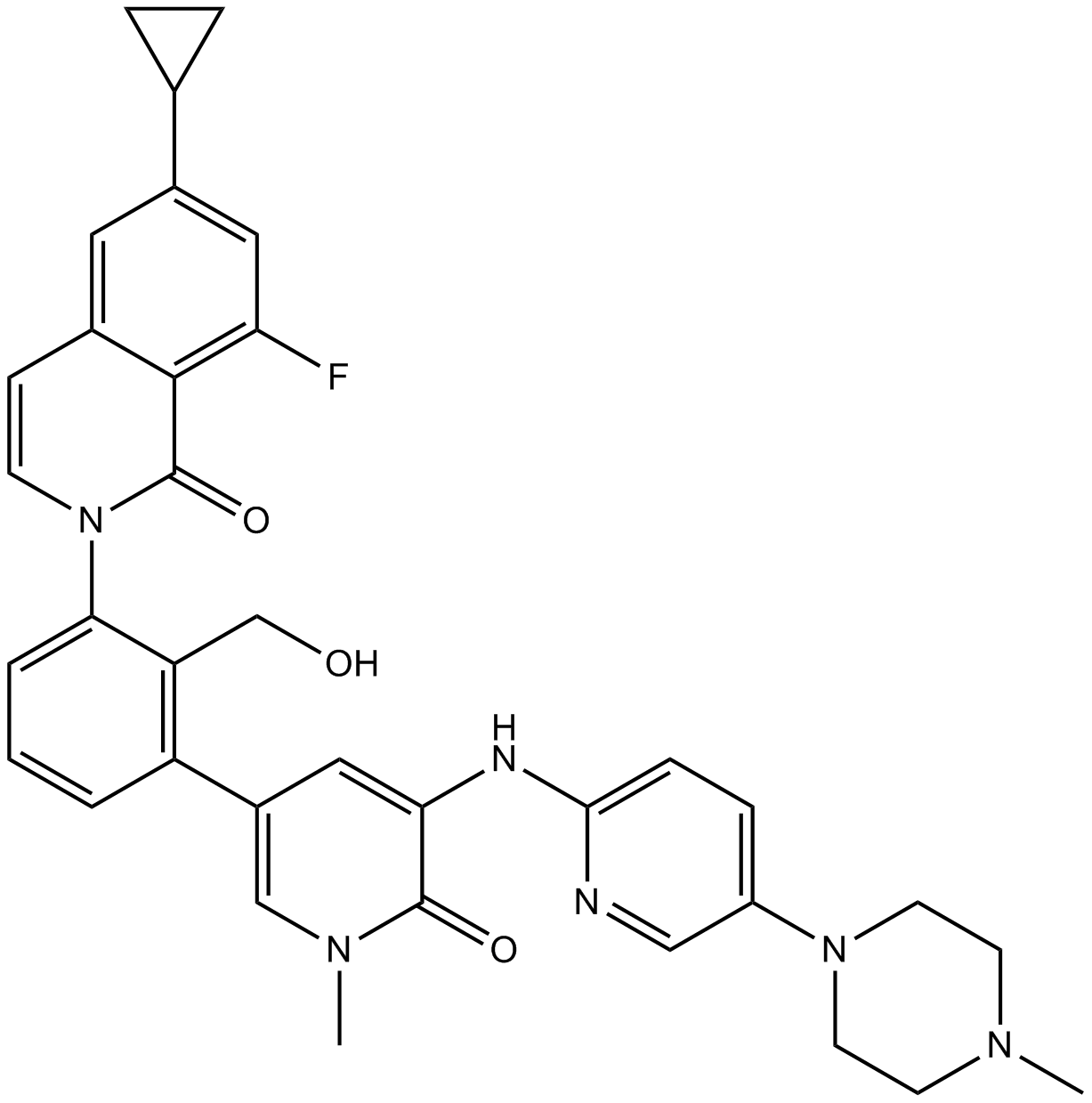 A8636 RN486Summary: Btk inhibitor,potent and selective
A8636 RN486Summary: Btk inhibitor,potent and selective -
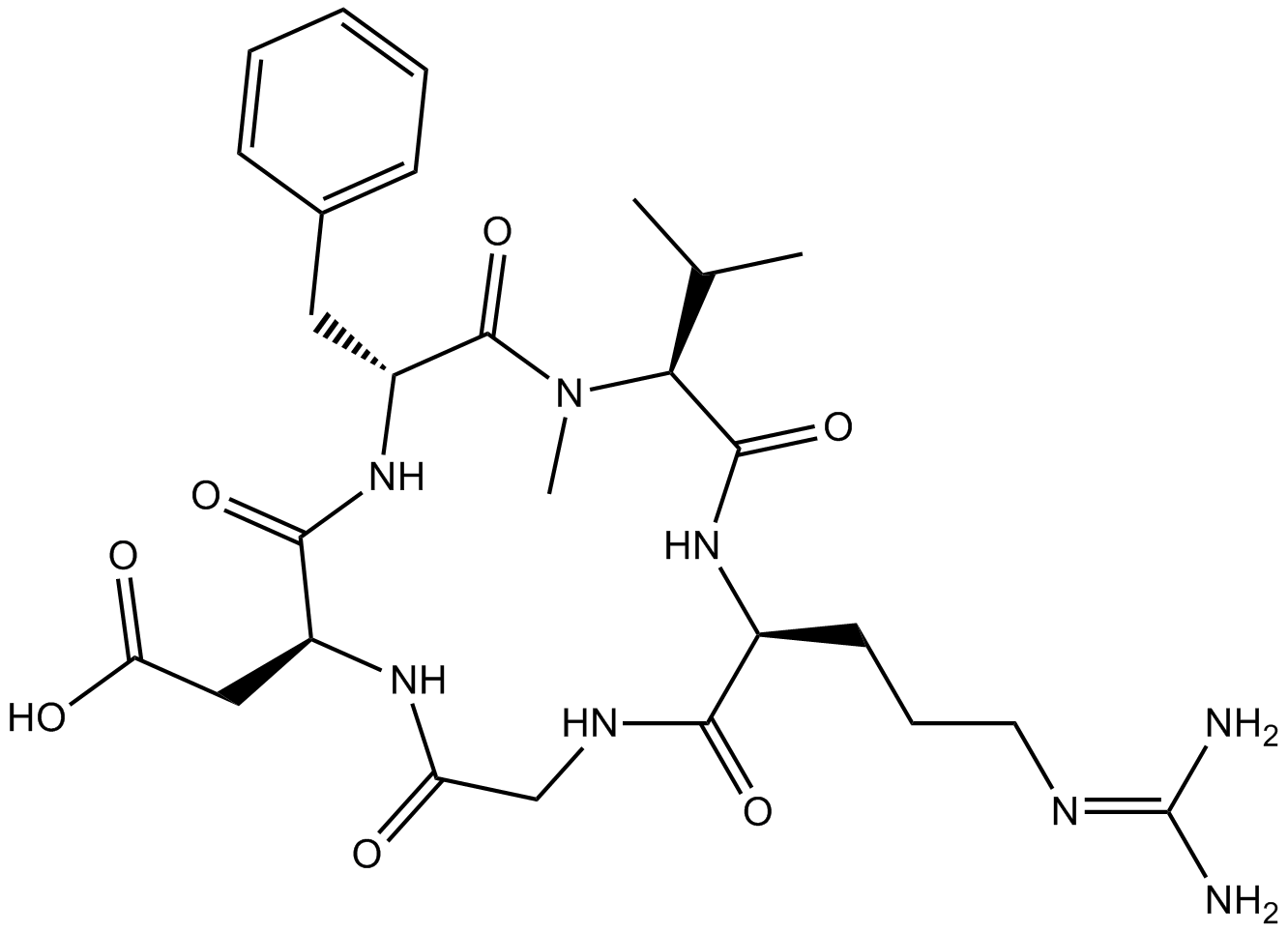 A8660 Cilengitide5 CitationTarget: IntegrinsSummary: Integrin inhibitor for αvβ3 and αvβ5
A8660 Cilengitide5 CitationTarget: IntegrinsSummary: Integrin inhibitor for αvβ3 and αvβ5 -
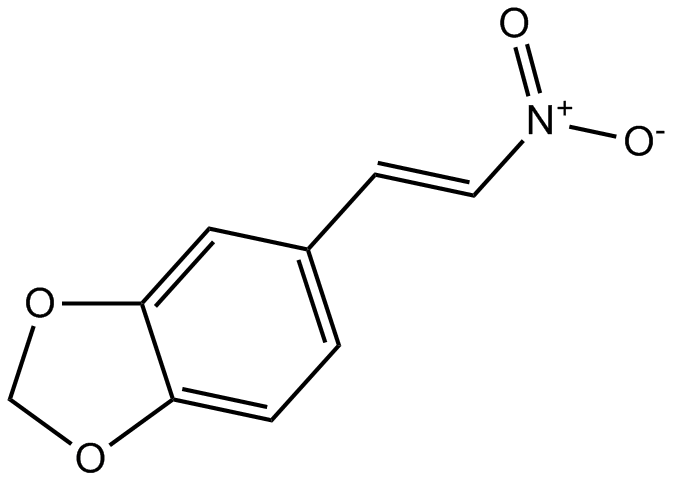 A8661 MNSSummary: Inhibitor of Src/Syk tyrosine kinases
A8661 MNSSummary: Inhibitor of Src/Syk tyrosine kinases -
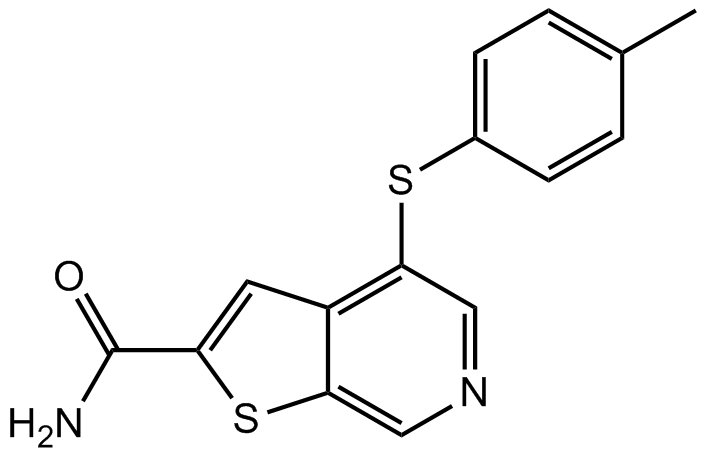 A8662 A 205804Summary: E-selectin/ICAM-1 expression inhibitor
A8662 A 205804Summary: E-selectin/ICAM-1 expression inhibitor


