Angiogenesis
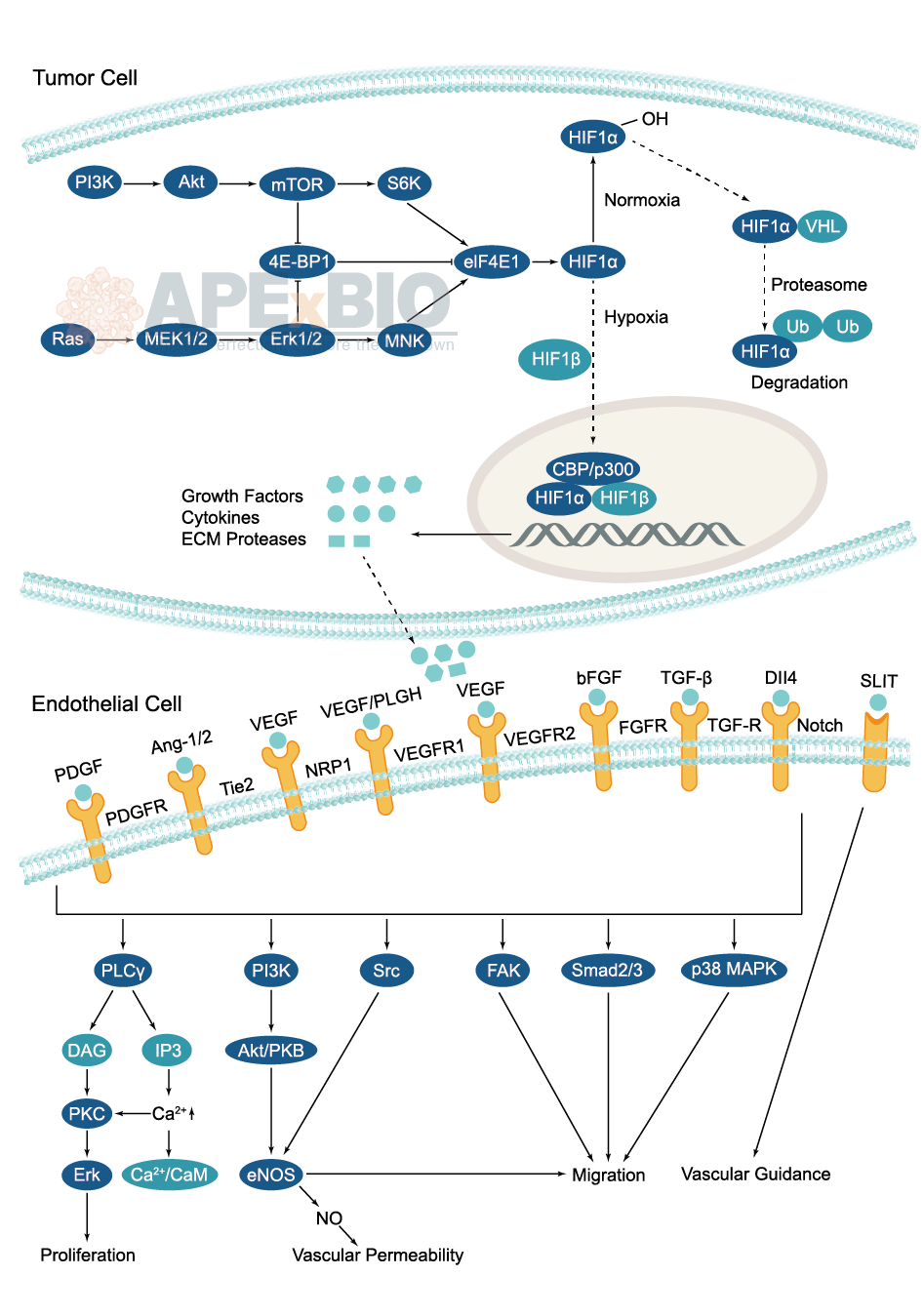

During tumor angiogenesis, cancer cells stimulate formation of new blood vessel for delivering oxygen and nutrients to a tumor. As the tumor grows, cells at the center of the mass become starved of oxygen, causing hypoxia. It stabilizes the expression of a transcription factor, HIF-1α (hypoxia inducible factor-1), which binds HIF-1β to upregulate the expression of several angiogenesis-promoting genes. Moreover, growth factor signaling also stimulates HIF-1 activity in order to maintain oxygen homeostasis for growing cells.
-
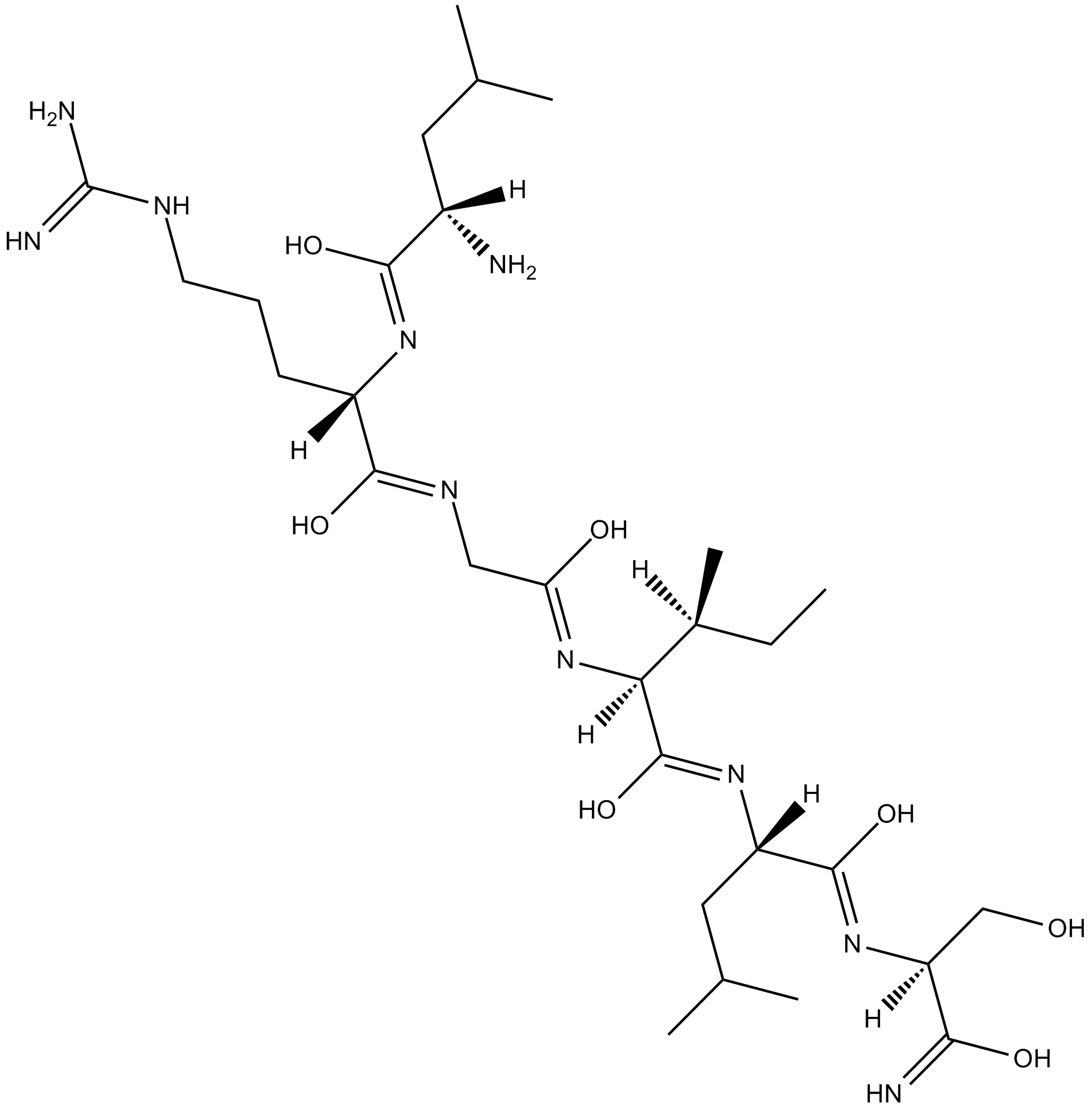 A8673 LRGILS-NH2Summary: Protease-activated receptor agonist
A8673 LRGILS-NH2Summary: Protease-activated receptor agonist -
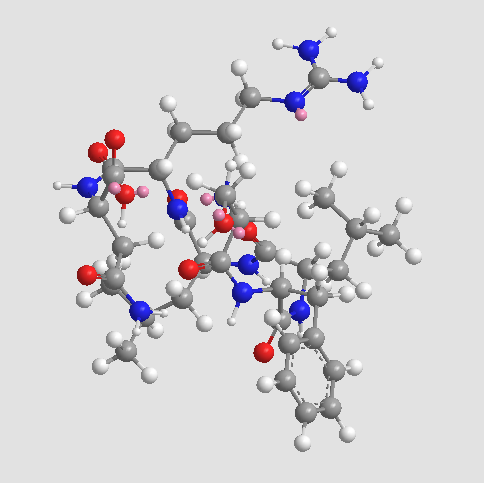 A8675 TRAP-6Target: PARSummary: PAR1 agonist
A8675 TRAP-6Target: PARSummary: PAR1 agonist -
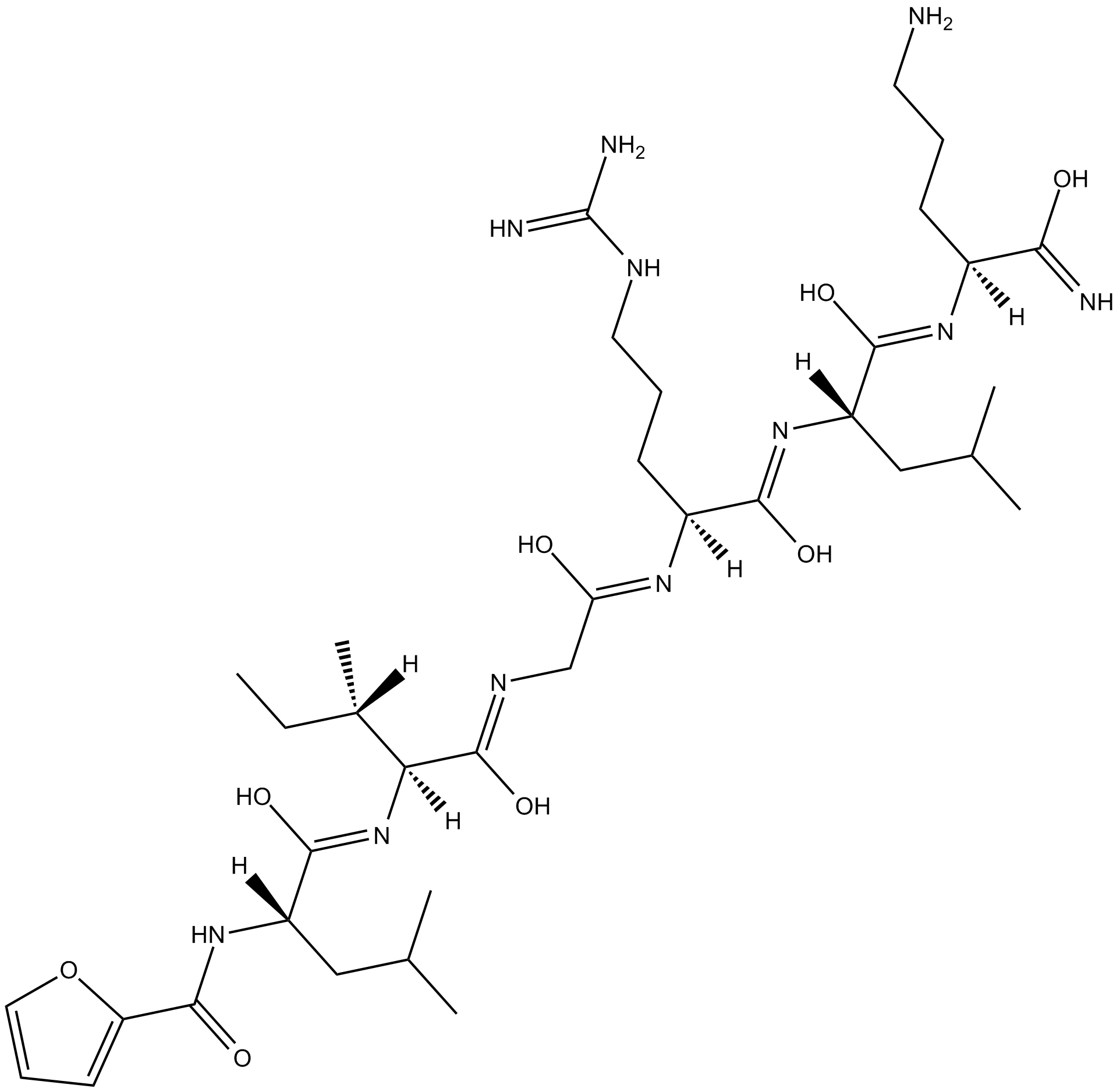 A8676 2-Furoyl-LIGRLO-amideSummary: Protease-activated receptor agonist
A8676 2-Furoyl-LIGRLO-amideSummary: Protease-activated receptor agonist -
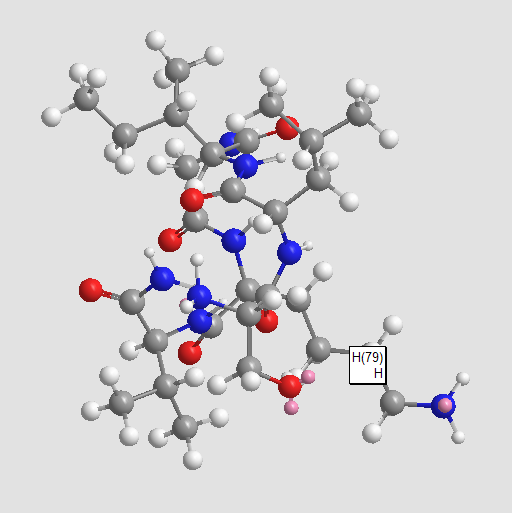 A8677 SLIGKV-NH2Summary: PAR2 agonist
A8677 SLIGKV-NH2Summary: PAR2 agonist -
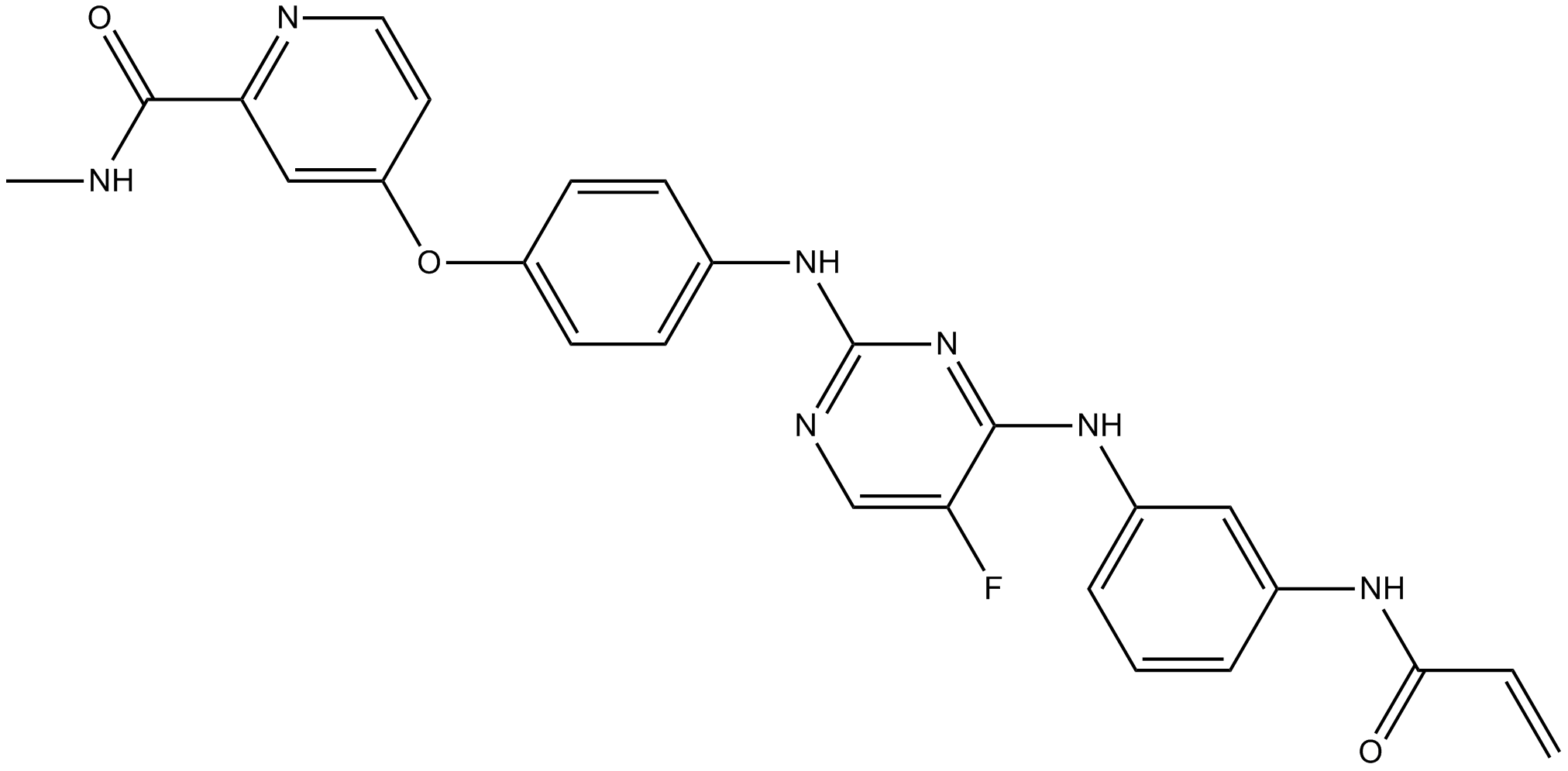 B1408 CNX-774Summary: BTK inhibitor, orally active, irreversible and selective
B1408 CNX-774Summary: BTK inhibitor, orally active, irreversible and selective -
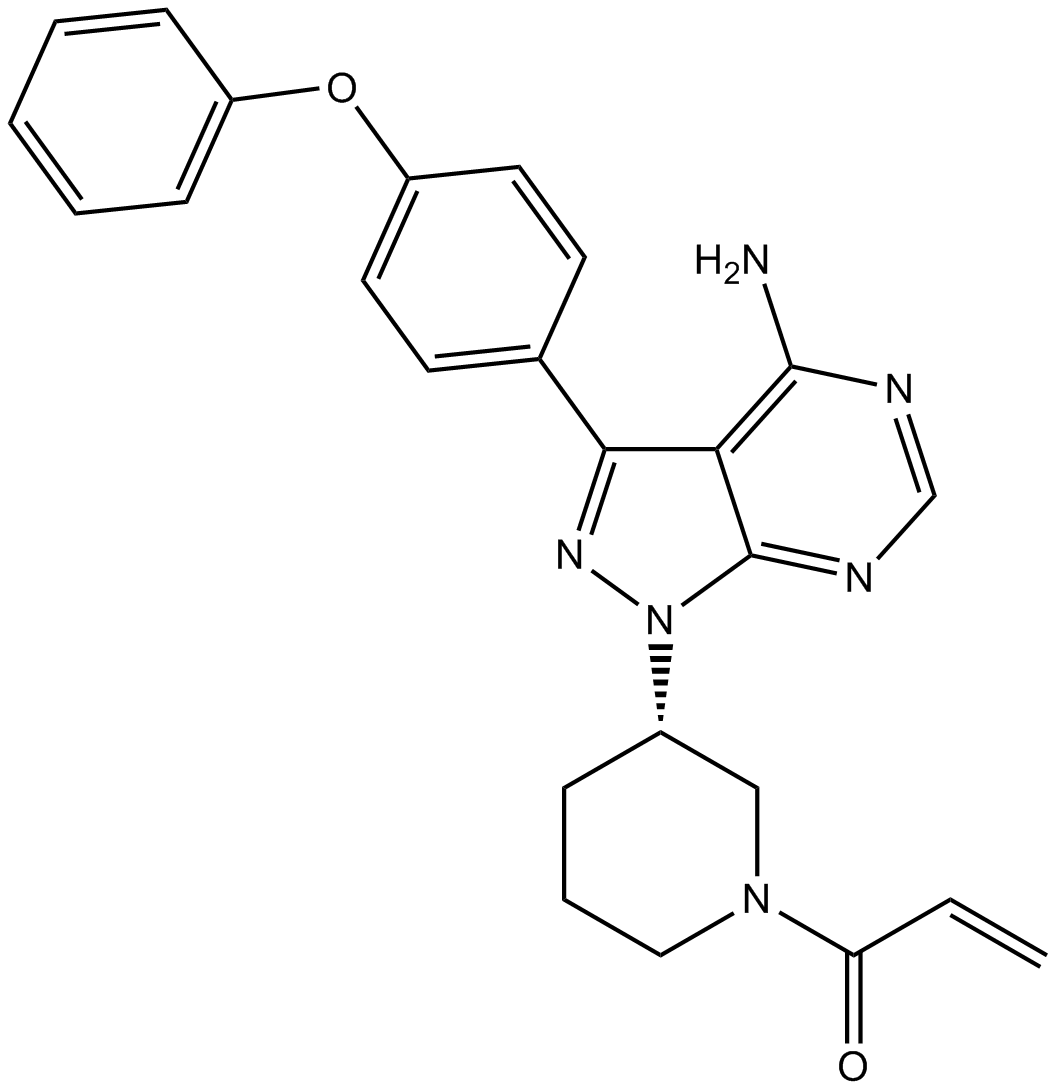 B3242 PCI-32765 RacemateSummary: BTK inhibitor
B3242 PCI-32765 RacemateSummary: BTK inhibitor -
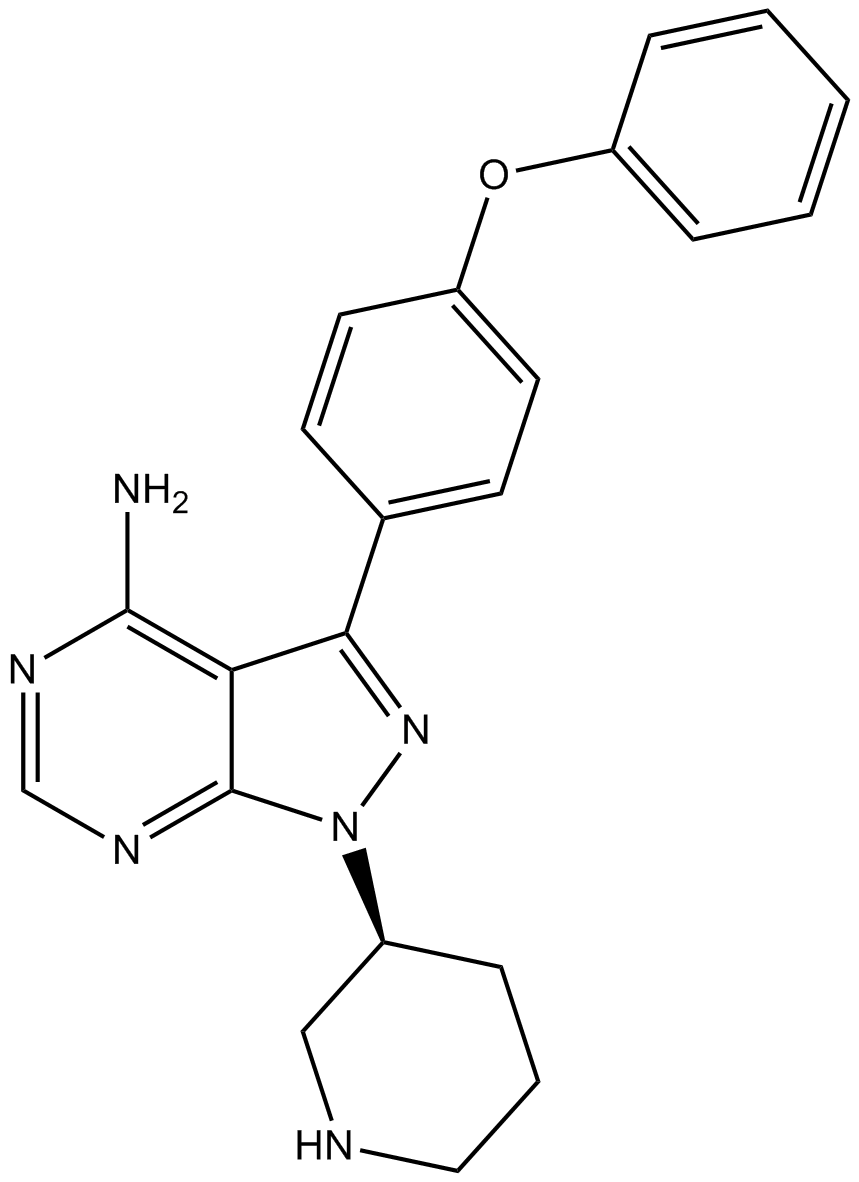 B3243 Btk inhibitor 1 R enantiomerSummary: Btk kinase inhibitor
B3243 Btk inhibitor 1 R enantiomerSummary: Btk kinase inhibitor -
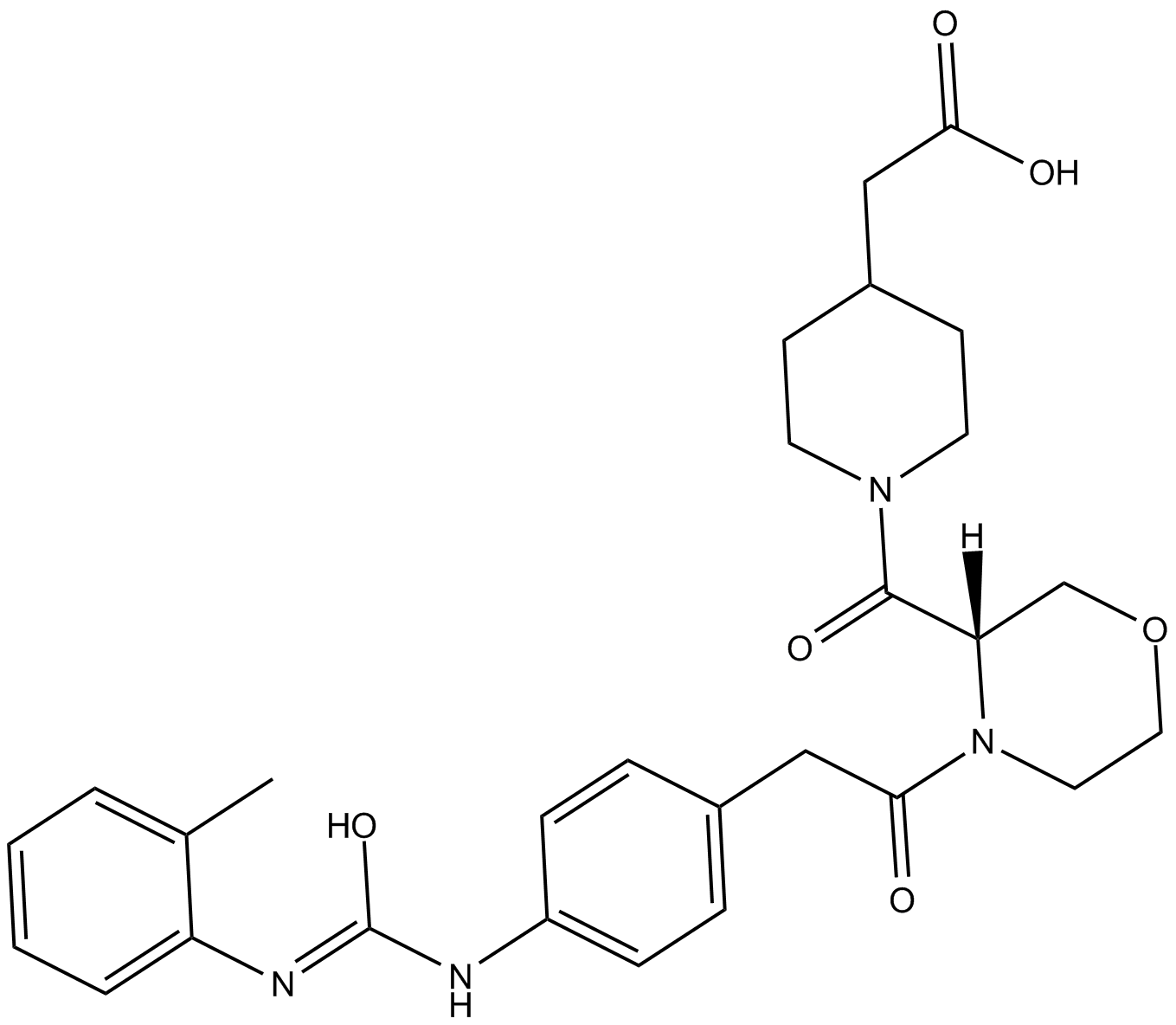 B5492 TCS 2314Summary: integrin very late antigen-4 (VLA-4; α4β1) antagonist
B5492 TCS 2314Summary: integrin very late antigen-4 (VLA-4; α4β1) antagonist -
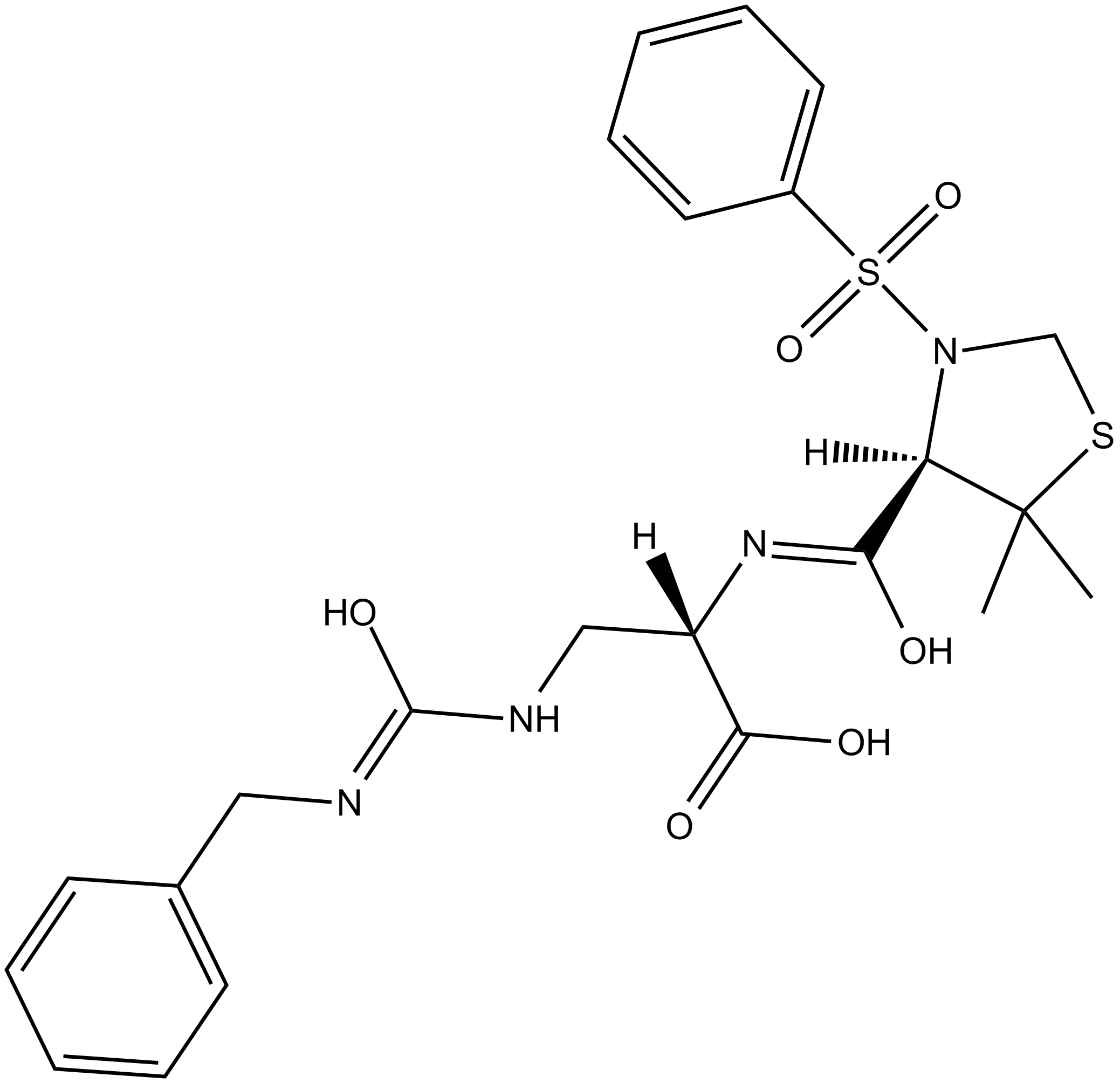 B5631 TC-I 15Summary: α2β1 integrin inhibitor
B5631 TC-I 15Summary: α2β1 integrin inhibitor -
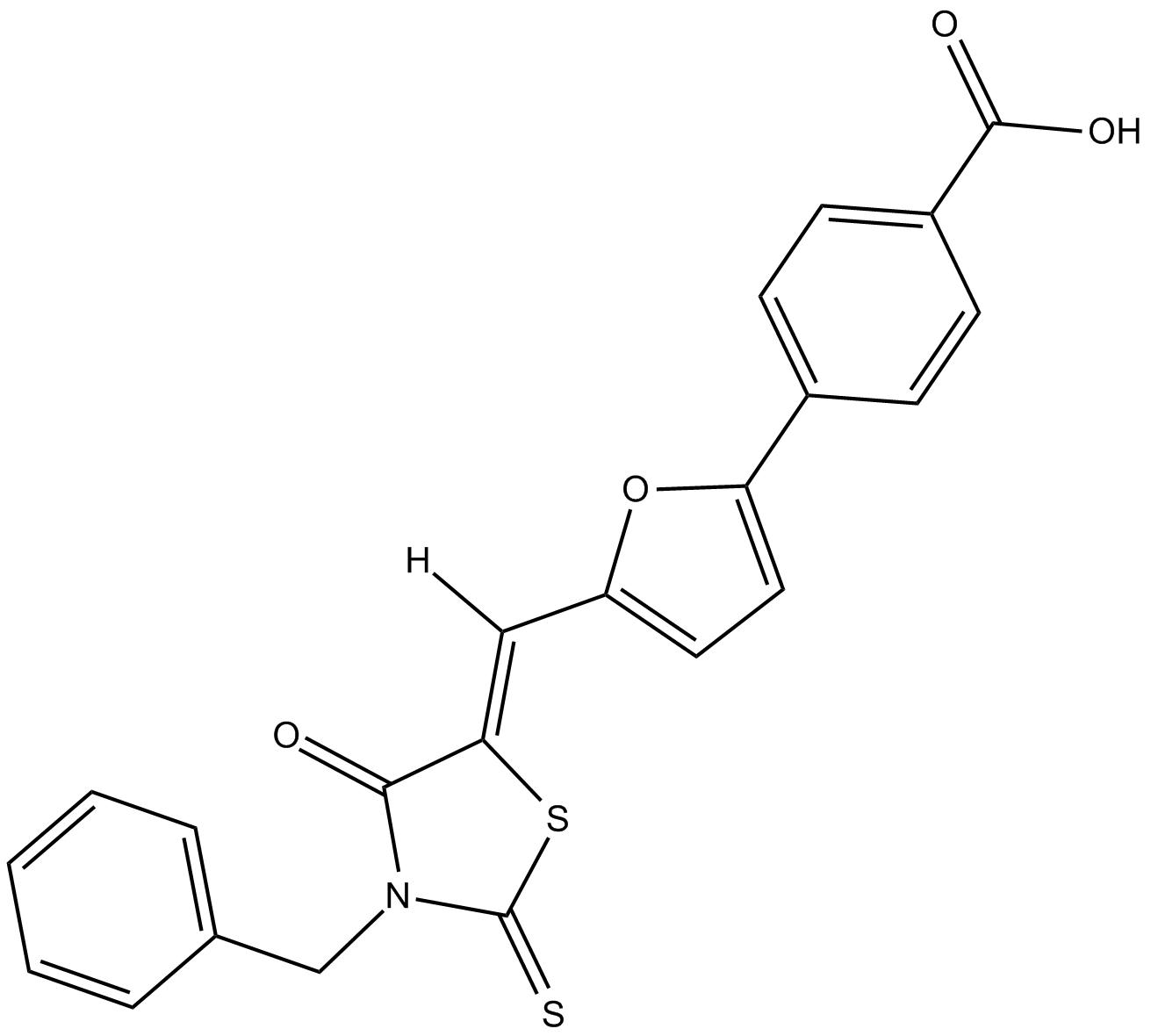 B5770 Leukadherin 1Summary: CD11b/CD18 activator
B5770 Leukadherin 1Summary: CD11b/CD18 activator


