Angiogenesis
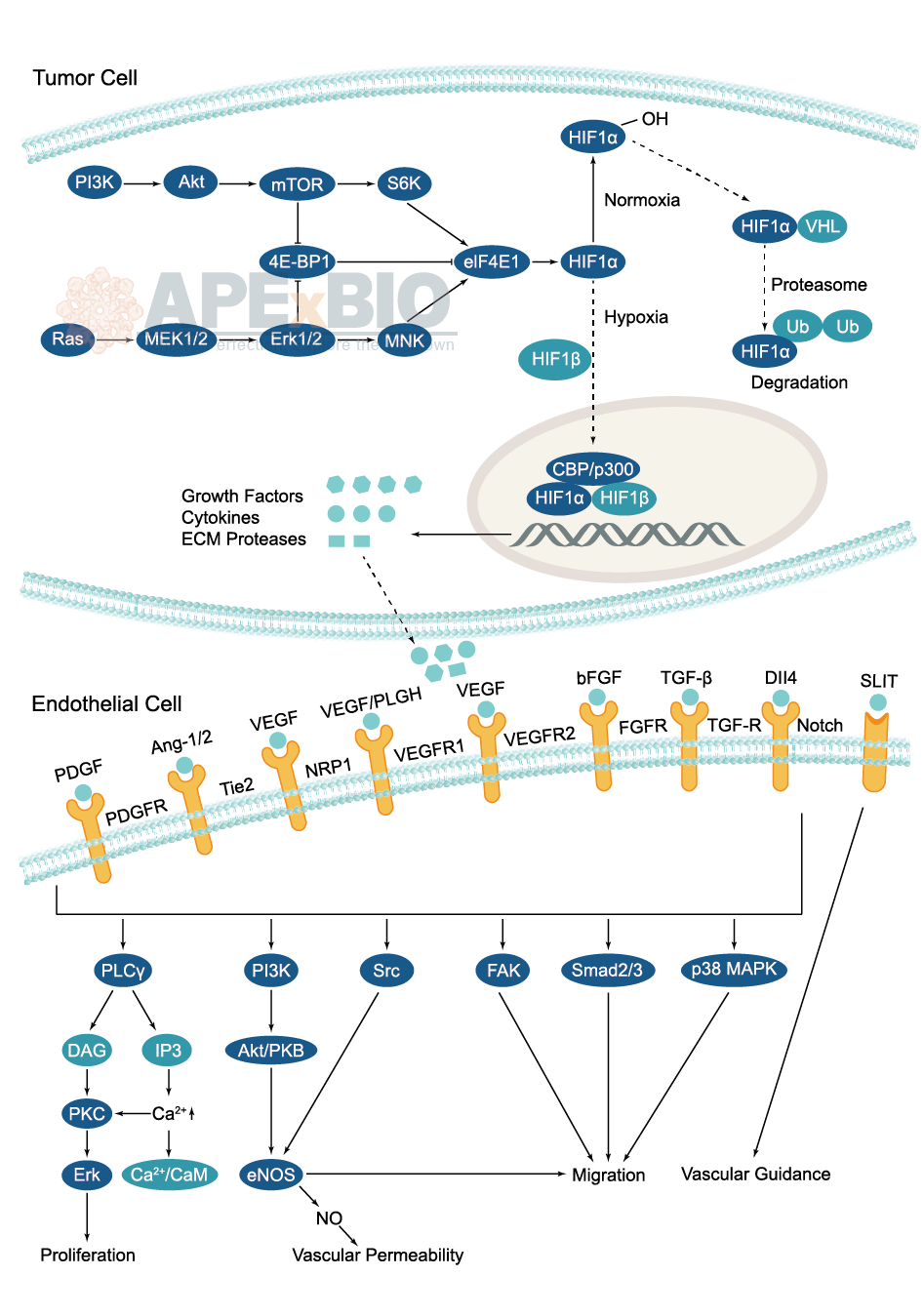

During tumor angiogenesis, cancer cells stimulate formation of new blood vessel for delivering oxygen and nutrients to a tumor. As the tumor grows, cells at the center of the mass become starved of oxygen, causing hypoxia. It stabilizes the expression of a transcription factor, HIF-1α (hypoxia inducible factor-1), which binds HIF-1β to upregulate the expression of several angiogenesis-promoting genes. Moreover, growth factor signaling also stimulates HIF-1 activity in order to maintain oxygen homeostasis for growing cells.
-
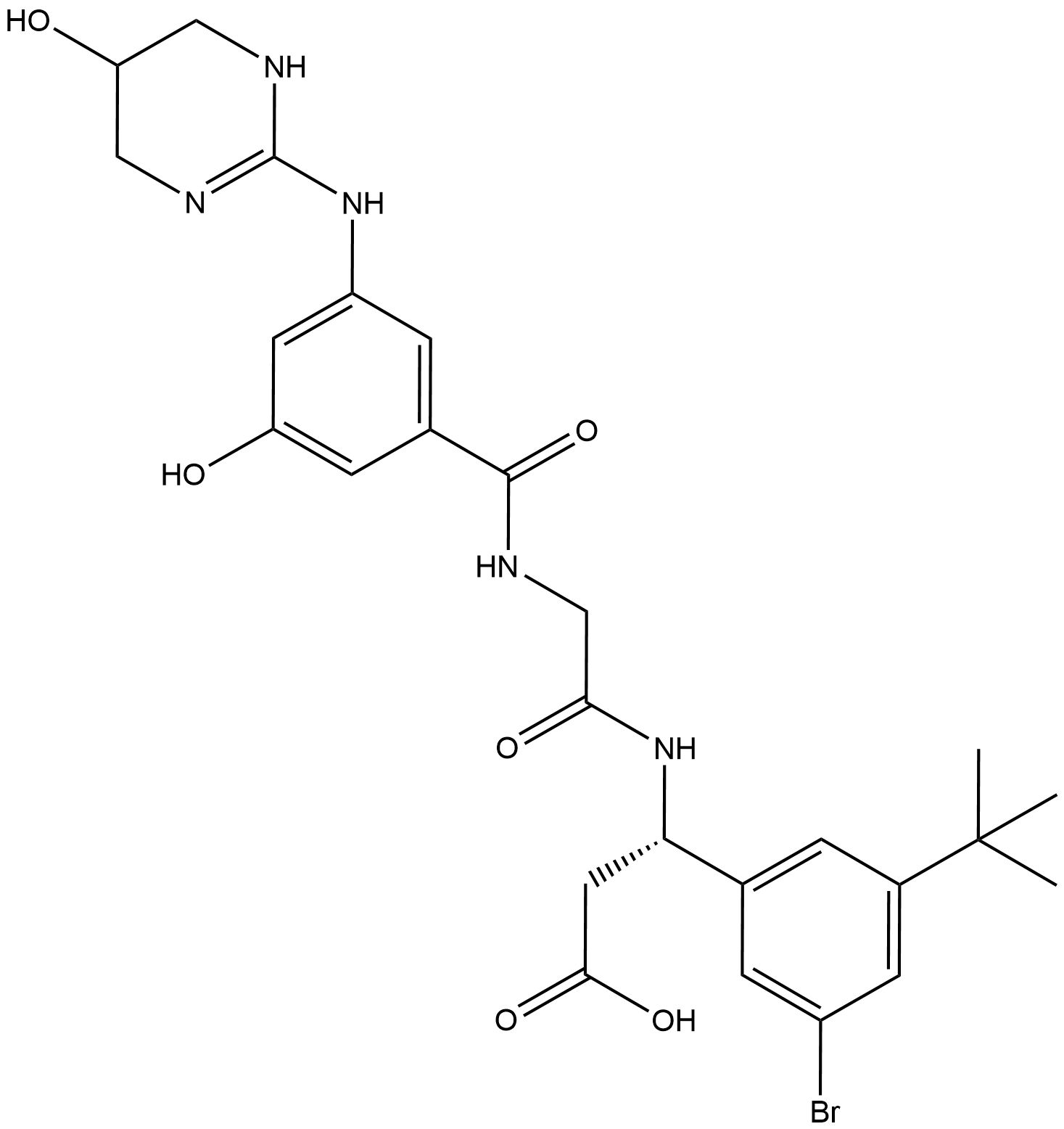 B4862 CWHM-12Summary: inhibitor of αV integrins
B4862 CWHM-12Summary: inhibitor of αV integrins -
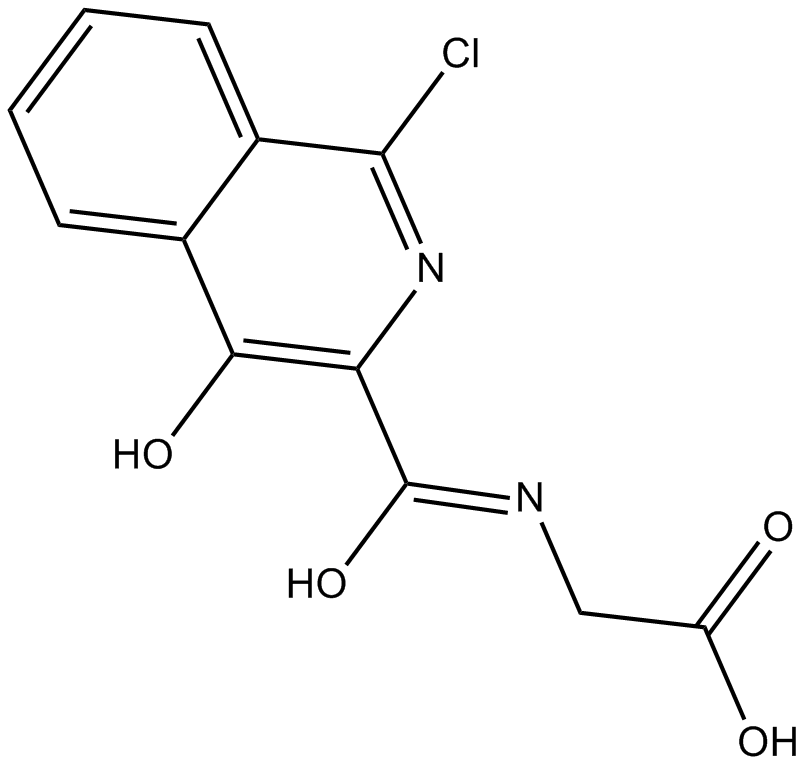 B5851 FG2216Target: Pyruvate dehydrogenases (PDH)Summary: HIF-prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor
B5851 FG2216Target: Pyruvate dehydrogenases (PDH)Summary: HIF-prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor -
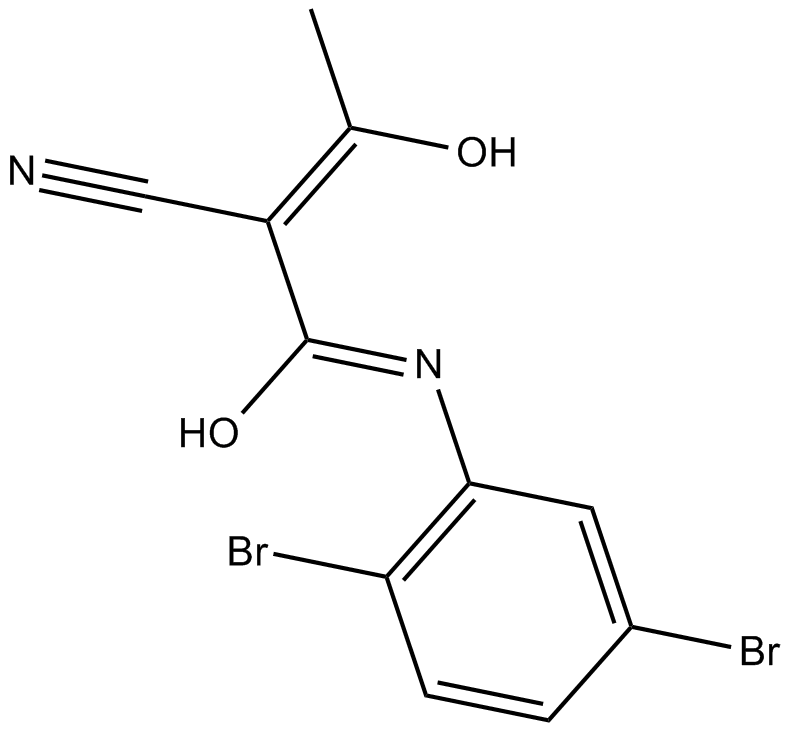 B5952 LFM-A13Summary: BTK-specific tyrosine kinase inhibitor
B5952 LFM-A13Summary: BTK-specific tyrosine kinase inhibitor -
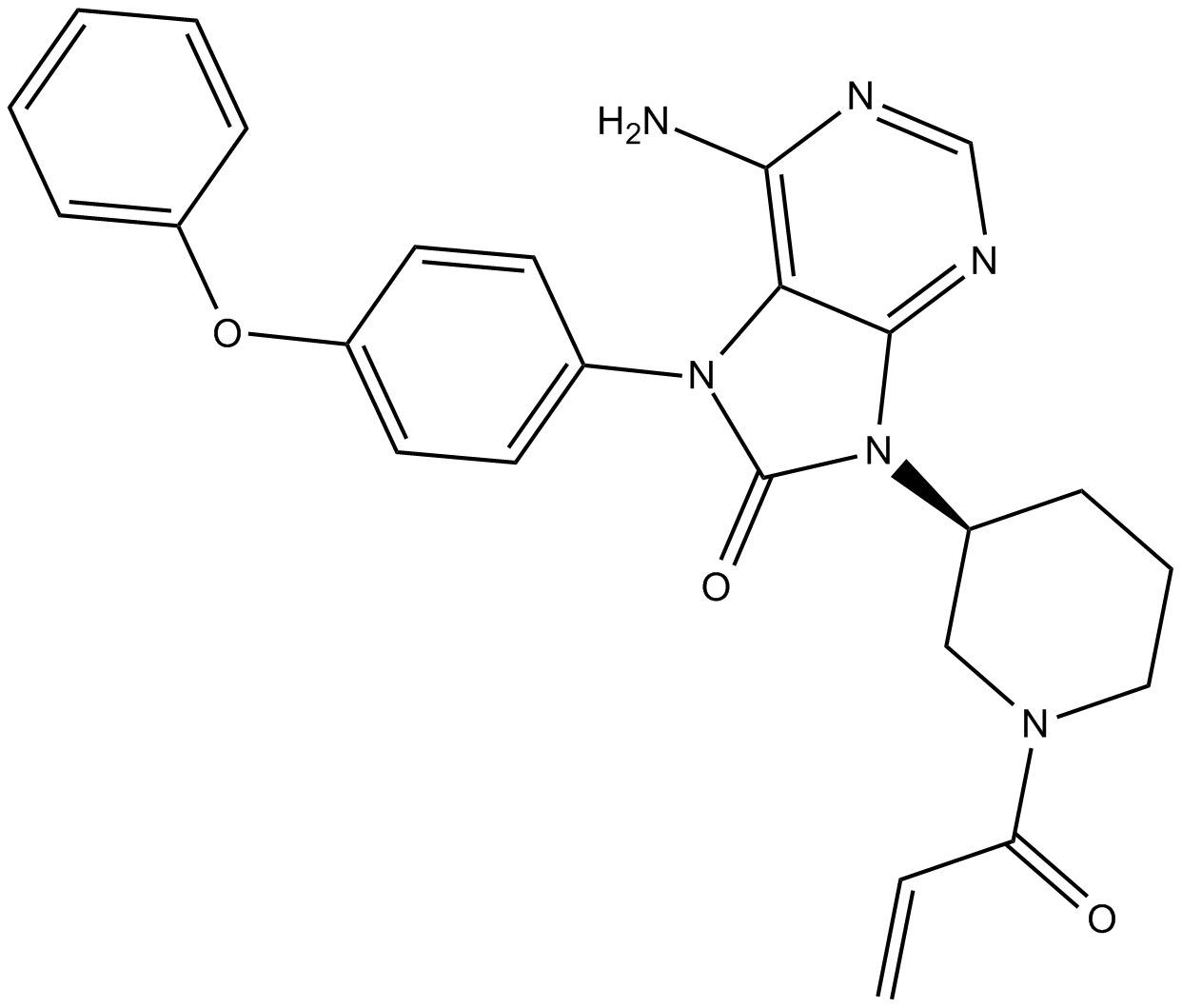 B5941 ONO-4059Summary: Highly potent and selective oral Btk inhibitor
B5941 ONO-4059Summary: Highly potent and selective oral Btk inhibitor -
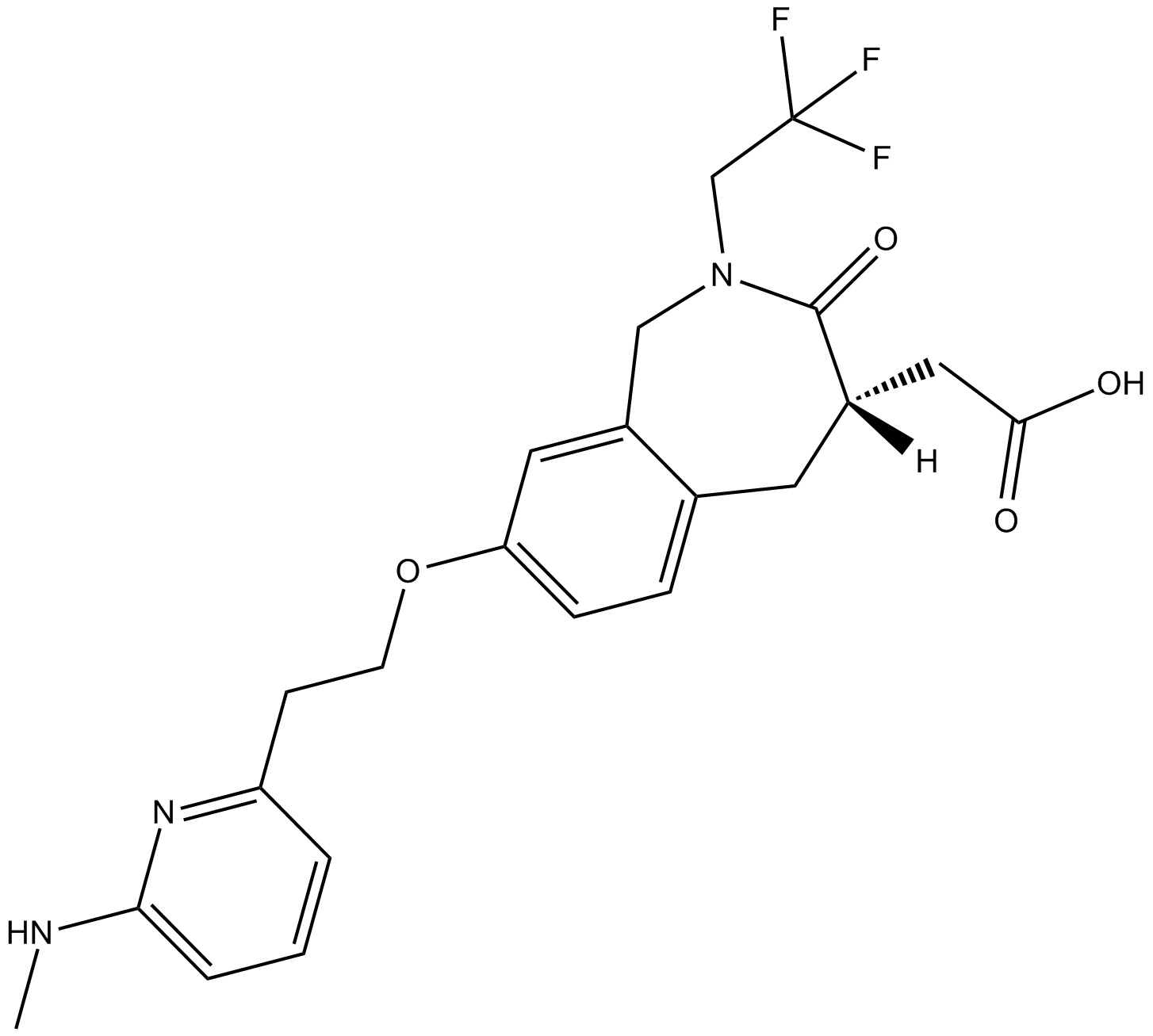 B6003 SB273005Summary: αvβ3 antagonist
B6003 SB273005Summary: αvβ3 antagonist -
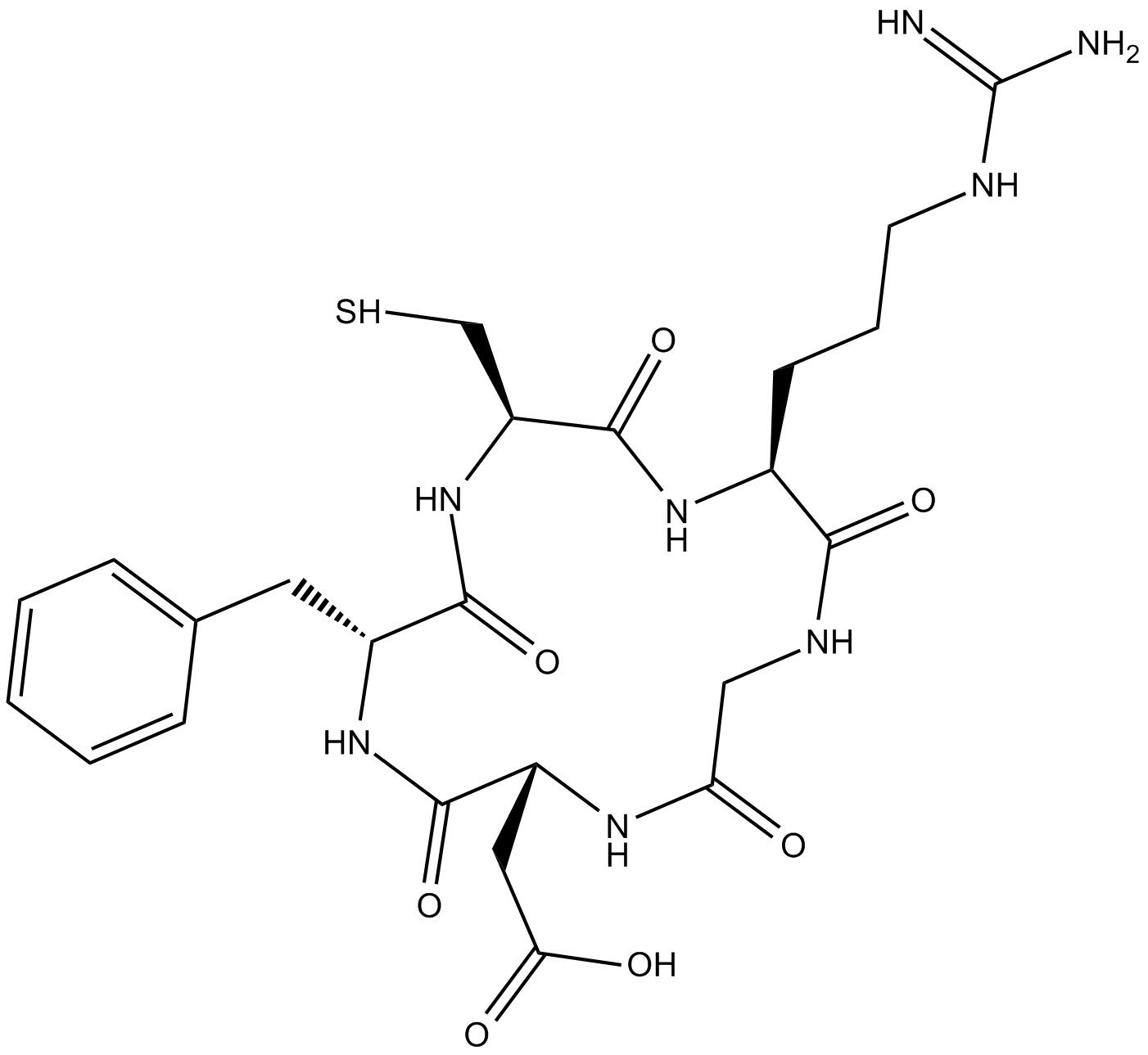 A8790 Cyclo (-RGDfC)1 Citation
A8790 Cyclo (-RGDfC)1 Citation -
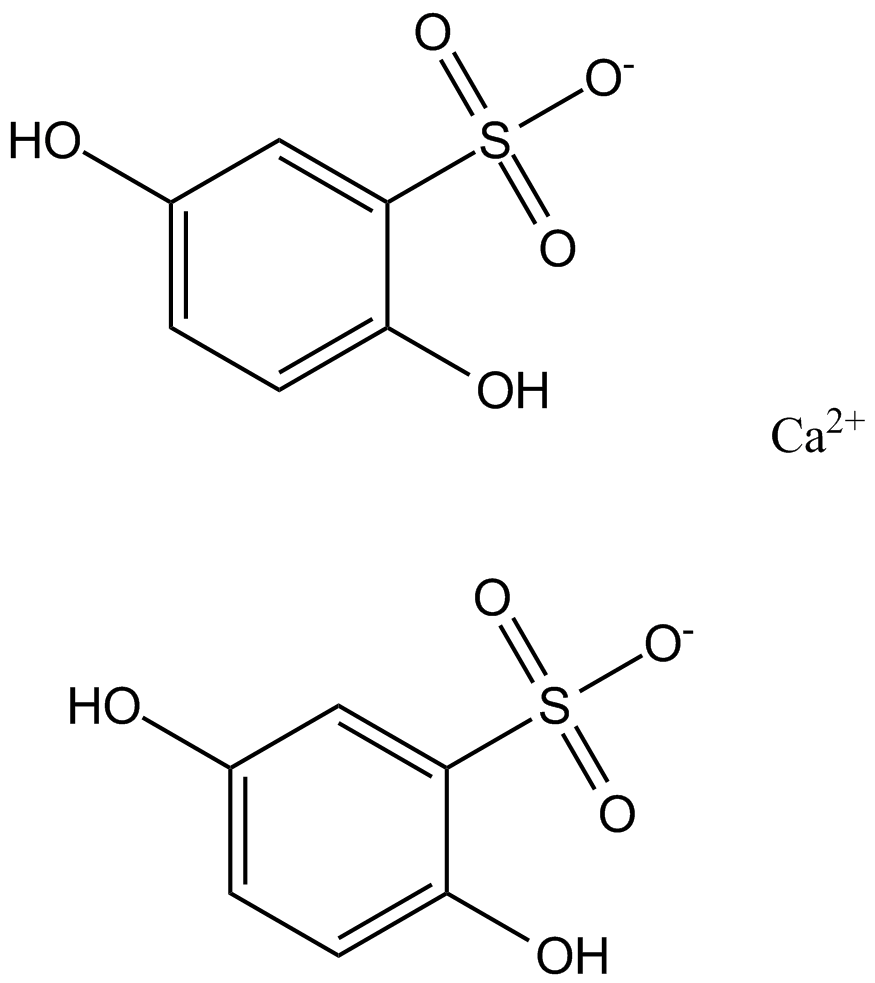 C6371 Calcium dobesilate
C6371 Calcium dobesilate -
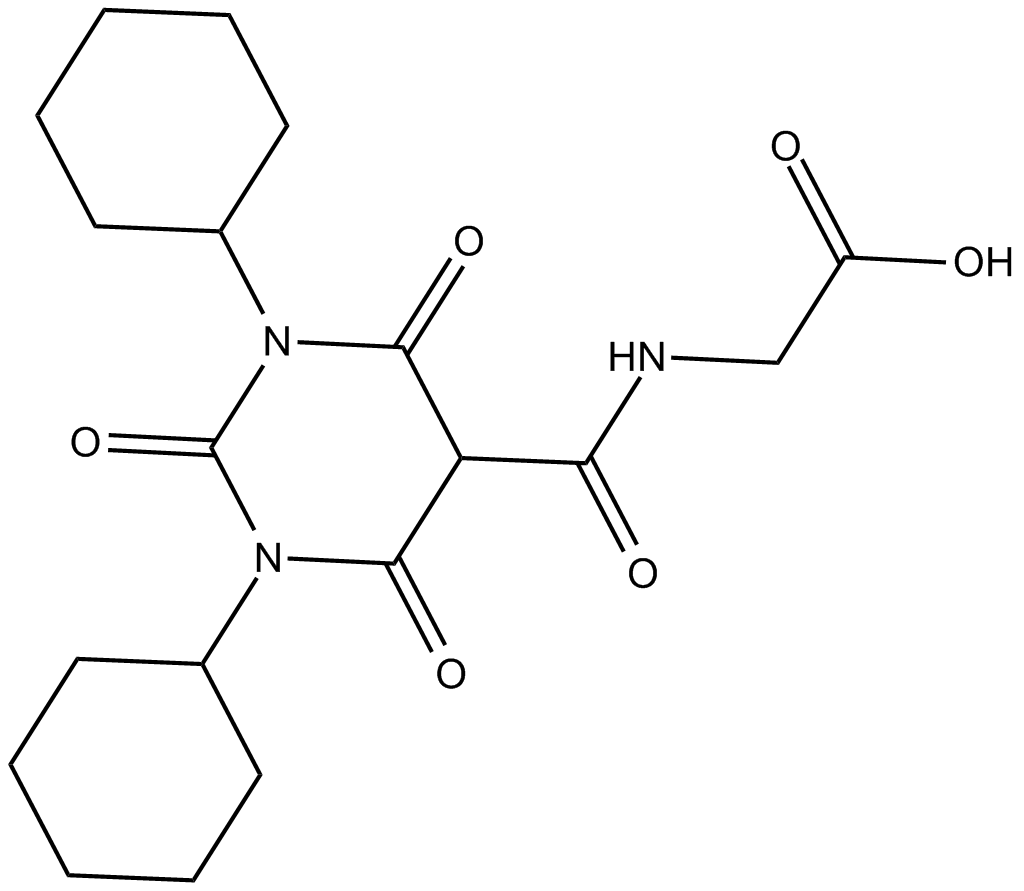 B6106 Daprodustat(GSK1278863)Summary: HIF-prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor
B6106 Daprodustat(GSK1278863)Summary: HIF-prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor -
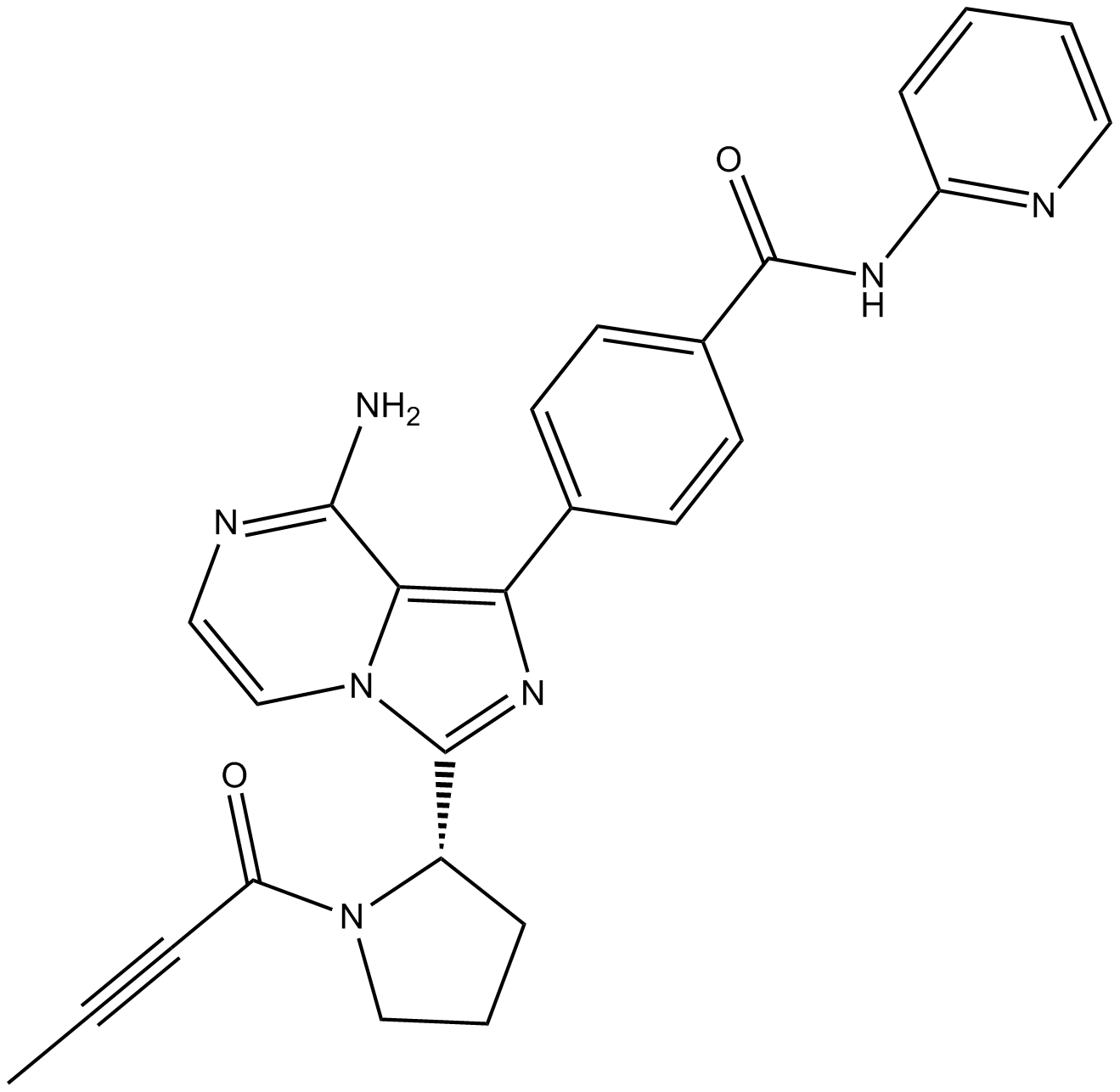 B6185 ACP-196Target: BTKSummary: irreversible BTK inhibitor
B6185 ACP-196Target: BTKSummary: irreversible BTK inhibitor -
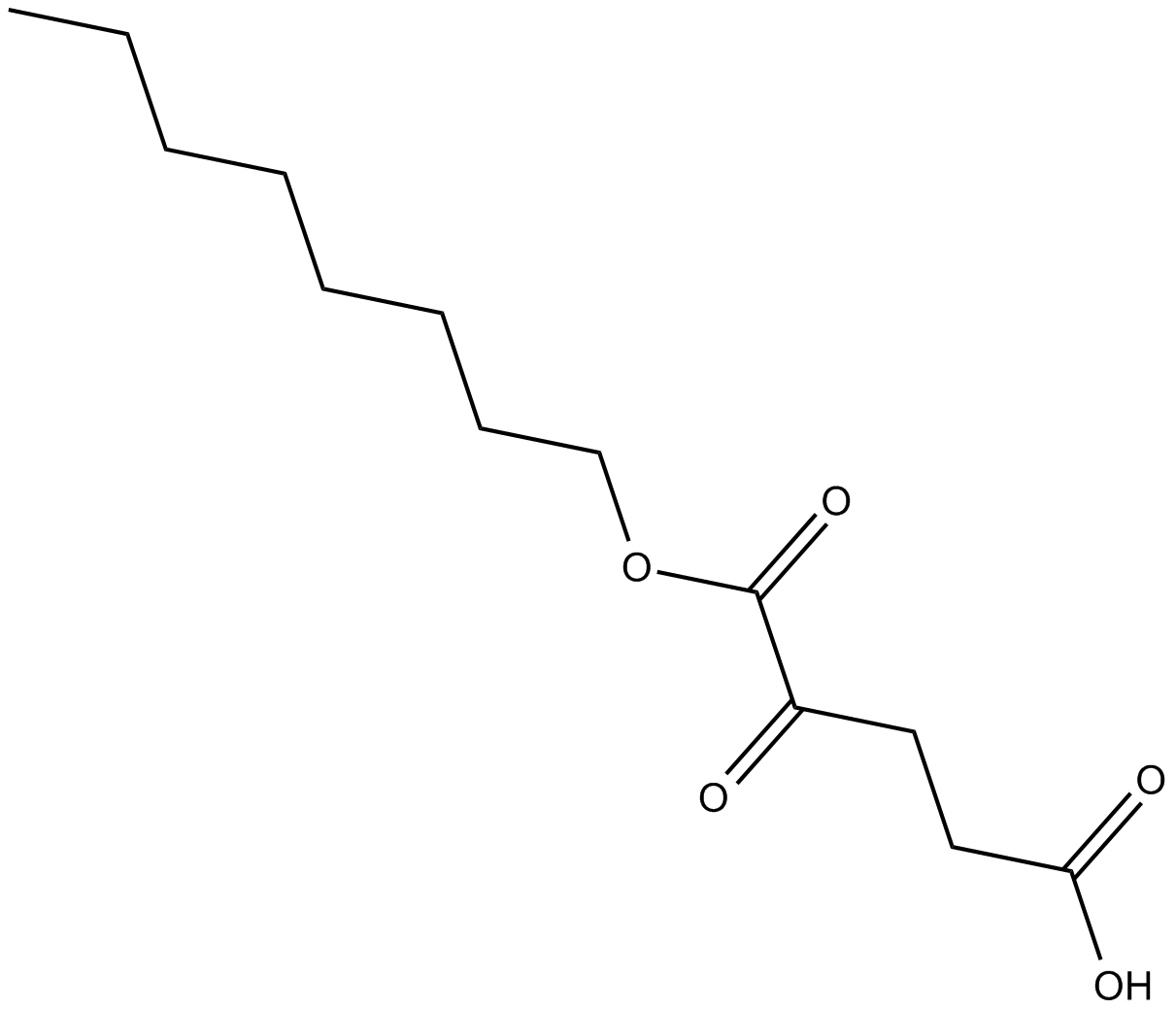 C4321 Octyl-α-ketoglutarateSummary: prolyl hydroxylases (PHD) activator
C4321 Octyl-α-ketoglutarateSummary: prolyl hydroxylases (PHD) activator


