Angiogenesis
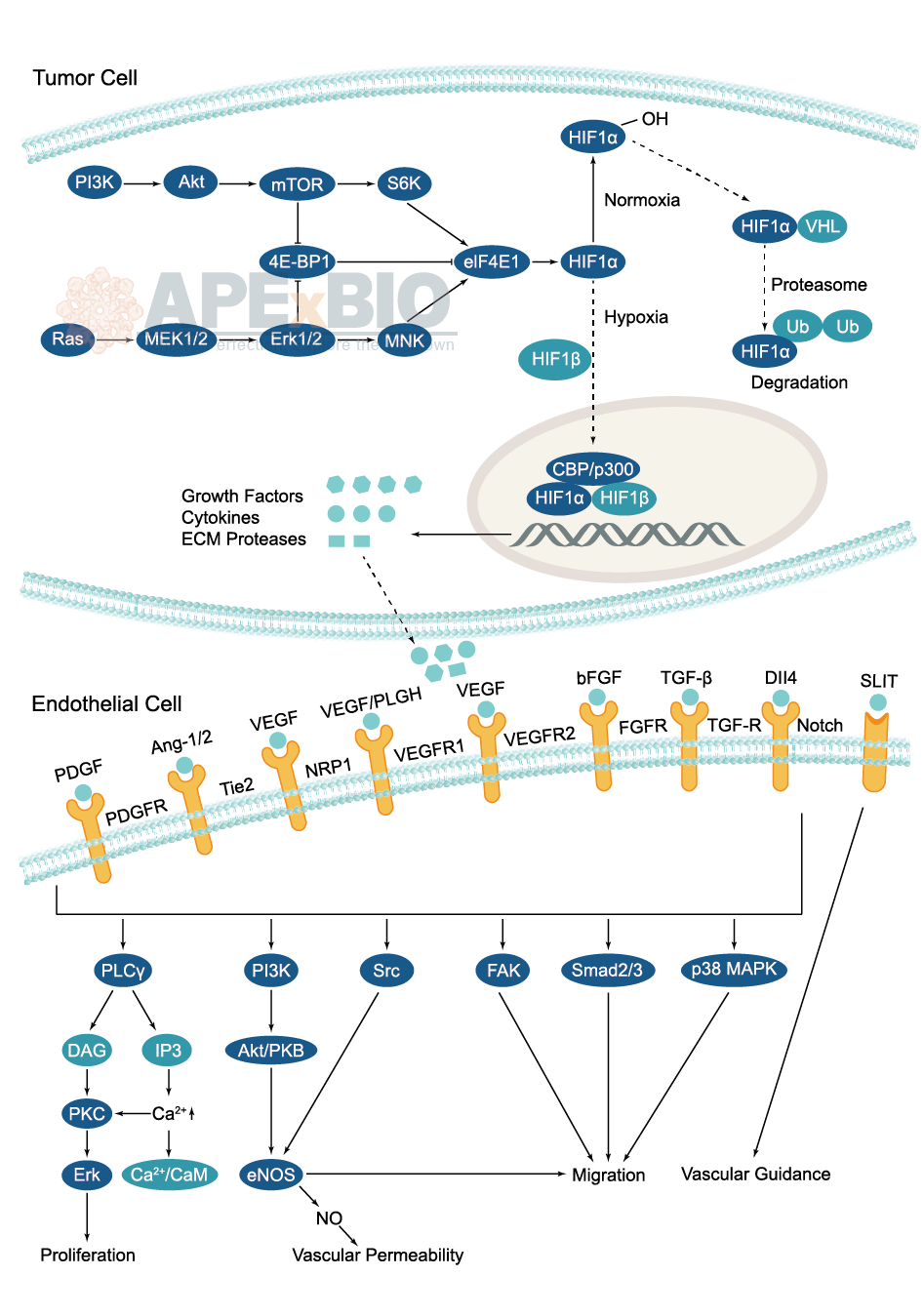

During tumor angiogenesis, cancer cells stimulate formation of new blood vessel for delivering oxygen and nutrients to a tumor. As the tumor grows, cells at the center of the mass become starved of oxygen, causing hypoxia. It stabilizes the expression of a transcription factor, HIF-1α (hypoxia inducible factor-1), which binds HIF-1β to upregulate the expression of several angiogenesis-promoting genes. Moreover, growth factor signaling also stimulates HIF-1 activity in order to maintain oxygen homeostasis for growing cells.
-
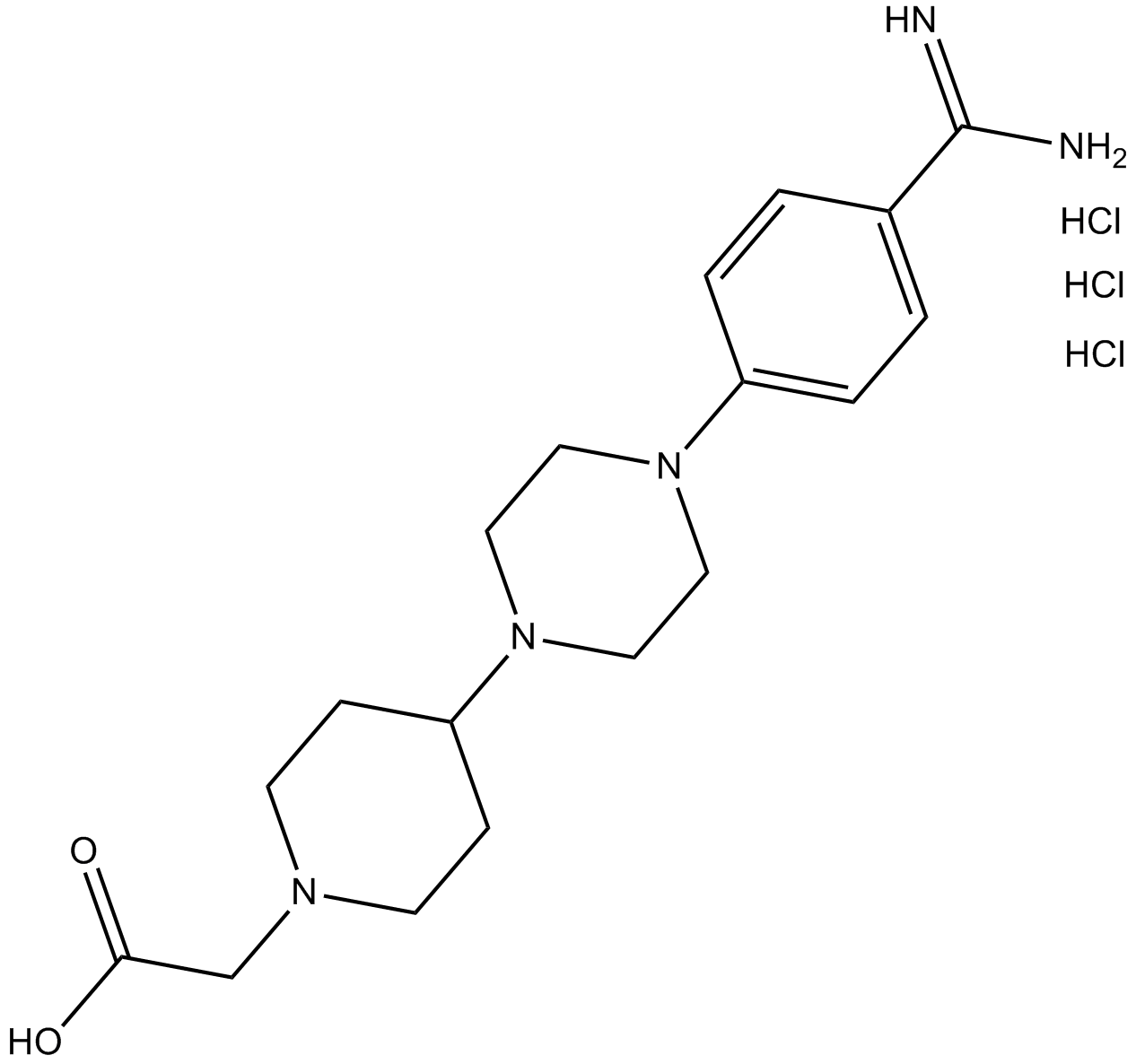 B6664 GR 144053 trihydrochlorideSummary: platelet fibrinogen receptor glycoprotein IIb/IIIa (GpIIb/IIIa) antagonist
B6664 GR 144053 trihydrochlorideSummary: platelet fibrinogen receptor glycoprotein IIb/IIIa (GpIIb/IIIa) antagonist -
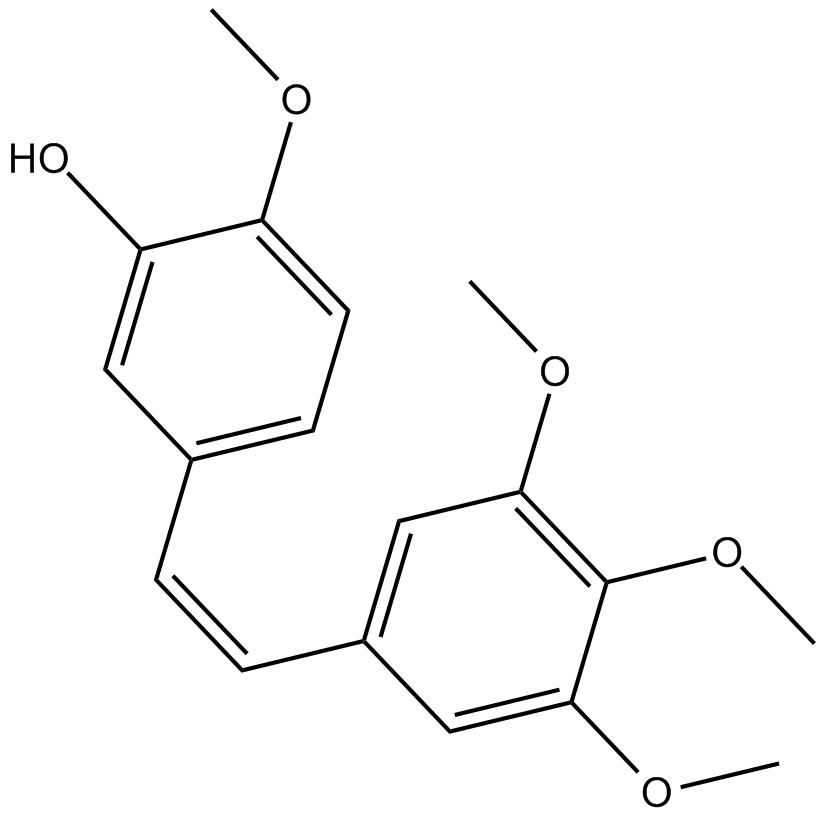 B6764 Combretastatin A4Summary: tubulin polymerization inhibitor
B6764 Combretastatin A4Summary: tubulin polymerization inhibitor -
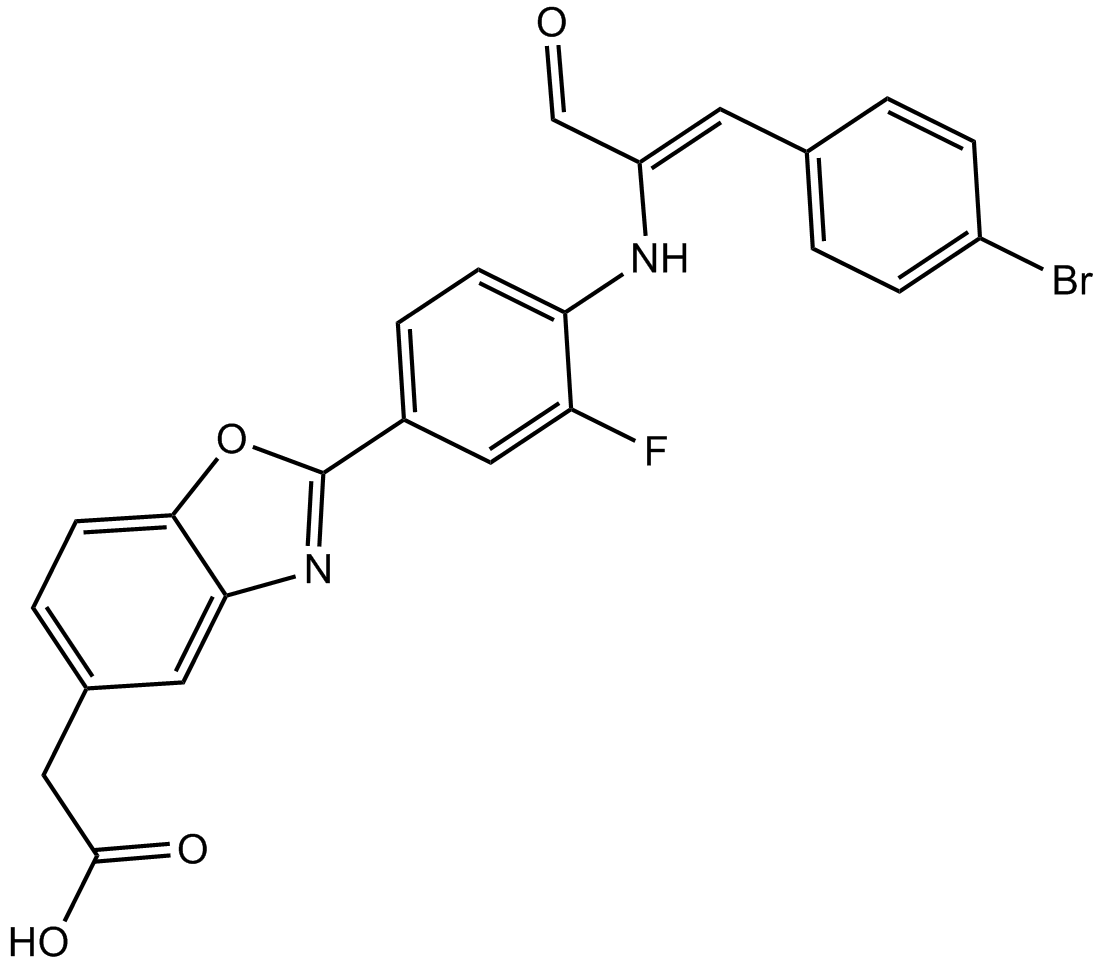 B7157 OGT 2115Target: HeparanasesSummary: Heparanase inhibitor
B7157 OGT 2115Target: HeparanasesSummary: Heparanase inhibitor -
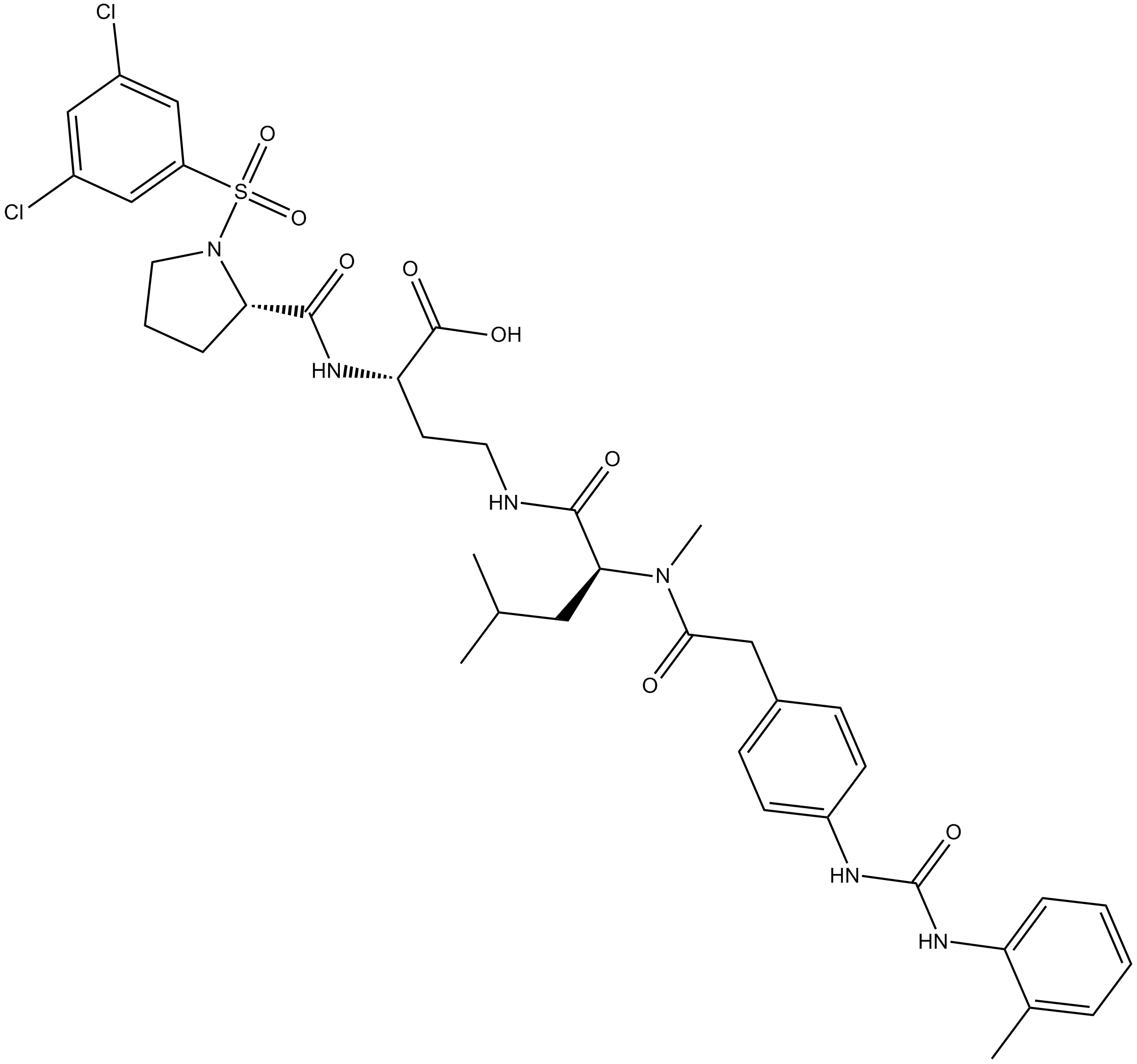 B7741 BIO 51921 CitationSummary: α4β1 inhibitor
B7741 BIO 51921 CitationSummary: α4β1 inhibitor -
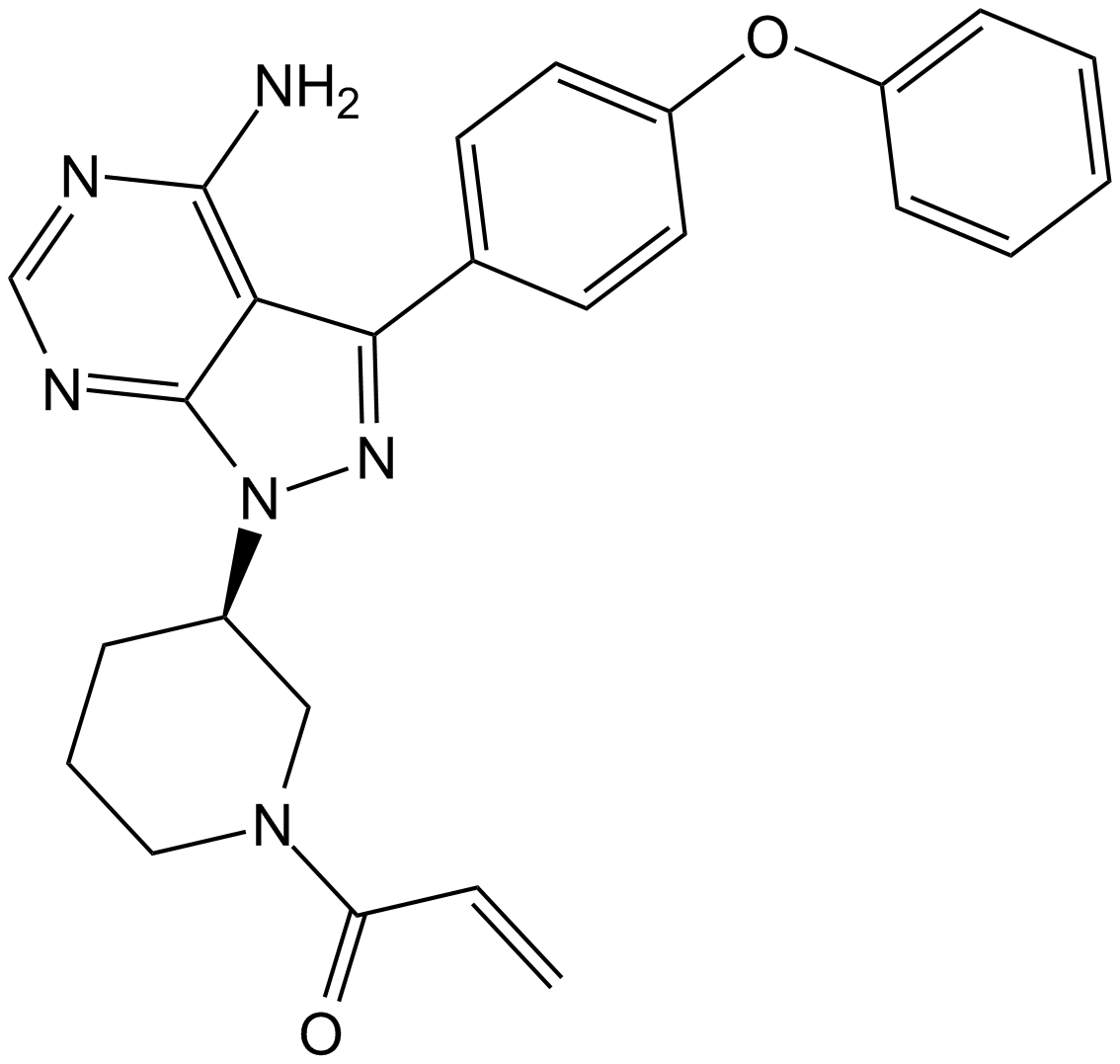 A3001 Ibrutinib7 CitationSummary: Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor
A3001 Ibrutinib7 CitationSummary: Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor -
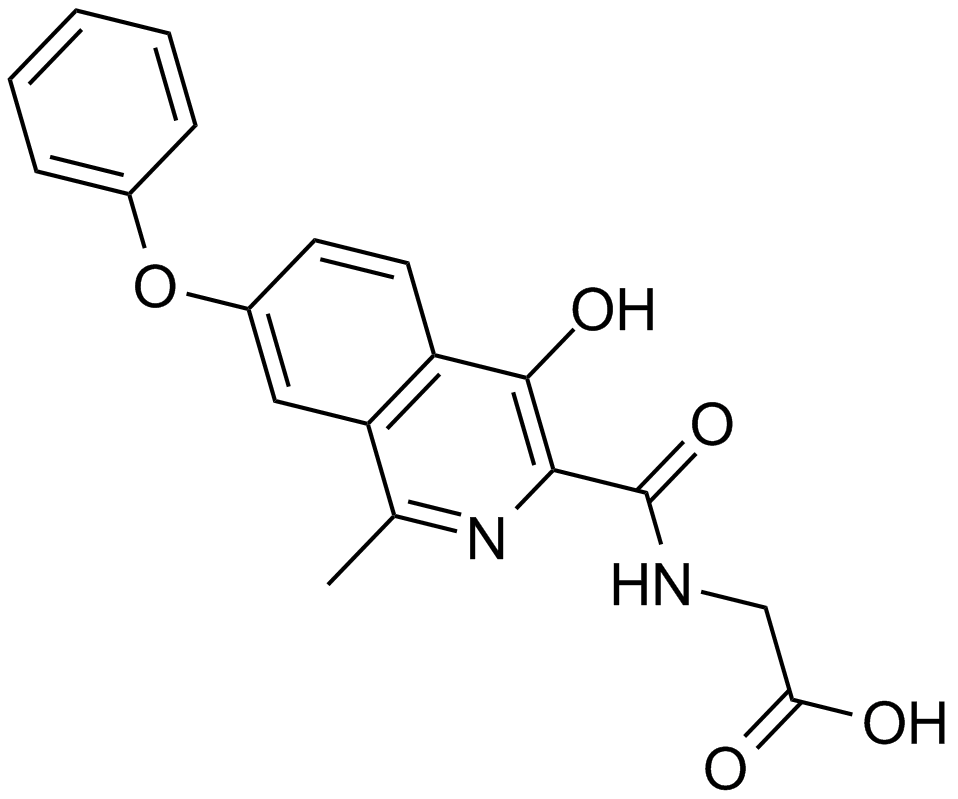 A4187 FG-4592 (ASP1517)5 CitationSummary: HIF prolyl-hydroxylase inhibitor
A4187 FG-4592 (ASP1517)5 CitationSummary: HIF prolyl-hydroxylase inhibitor -
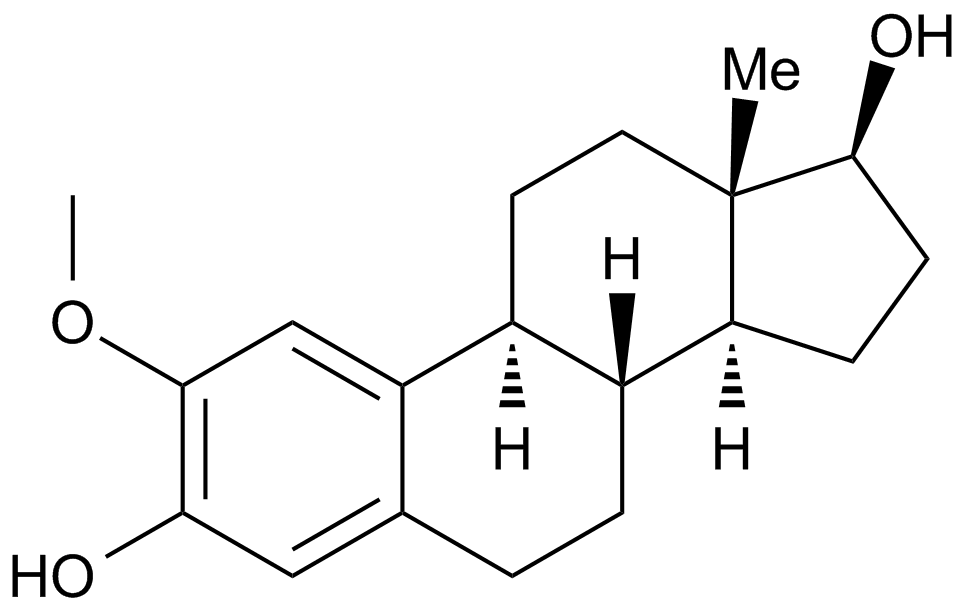 A4188 2-Methoxyestradiol (2-MeOE2)2 CitationSummary: Apoptotic, antiproliferative and antiangiogenic agent
A4188 2-Methoxyestradiol (2-MeOE2)2 CitationSummary: Apoptotic, antiproliferative and antiangiogenic agent -
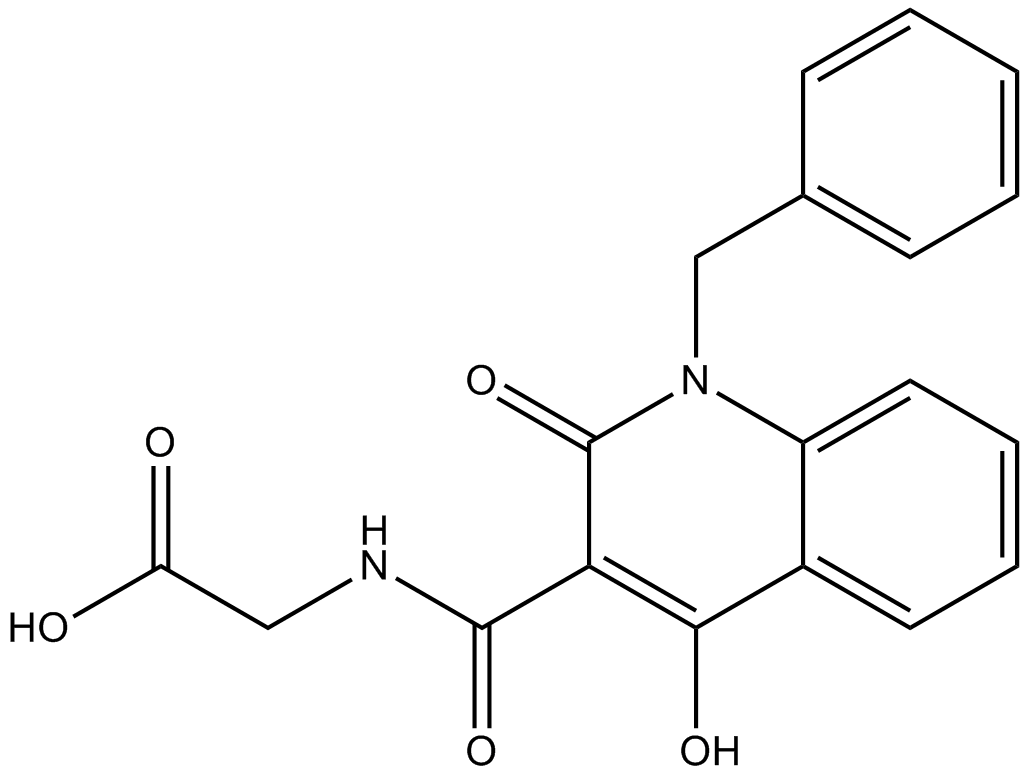 A4189 IOX2(Glycine)1 CitationSummary: HIF-1α prolyl hydroxylase-2 (PHD2) inhibitor
A4189 IOX2(Glycine)1 CitationSummary: HIF-1α prolyl hydroxylase-2 (PHD2) inhibitor -
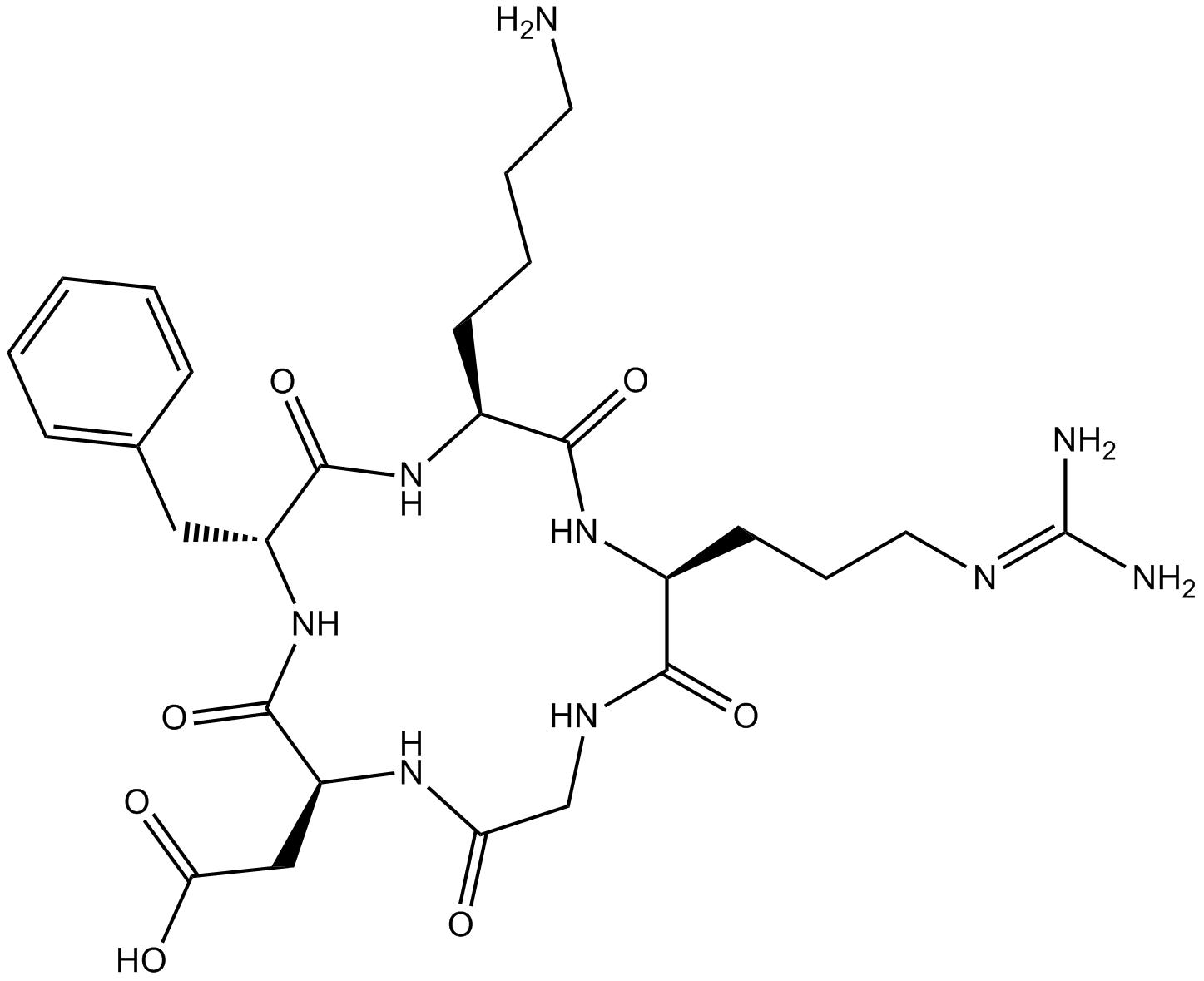 A8164 Cyclo (-RGDfK)6 CitationSummary: Inhibitor of αvβ3 integrin
A8164 Cyclo (-RGDfK)6 CitationSummary: Inhibitor of αvβ3 integrin -
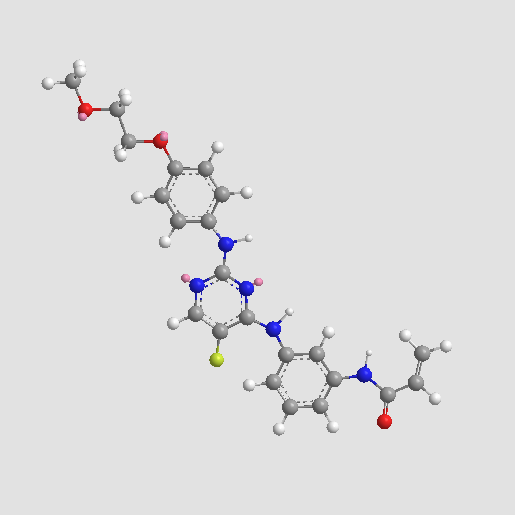 A3206 AVL-292Summary: Btk inhibitor
A3206 AVL-292Summary: Btk inhibitor


