Angiogenesis
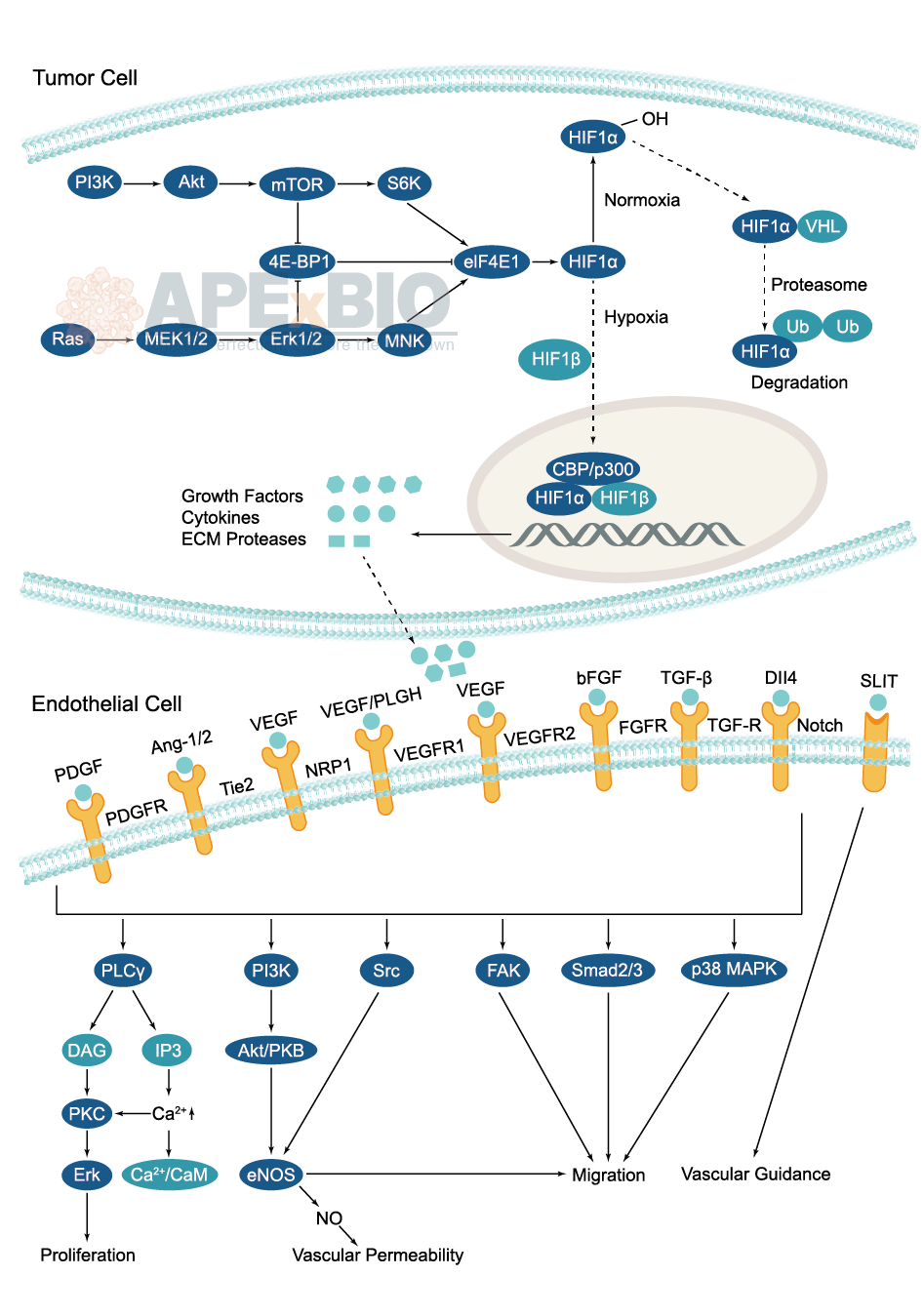

During tumor angiogenesis, cancer cells stimulate formation of new blood vessel for delivering oxygen and nutrients to a tumor. As the tumor grows, cells at the center of the mass become starved of oxygen, causing hypoxia. It stabilizes the expression of a transcription factor, HIF-1α (hypoxia inducible factor-1), which binds HIF-1β to upregulate the expression of several angiogenesis-promoting genes. Moreover, growth factor signaling also stimulates HIF-1 activity in order to maintain oxygen homeostasis for growing cells.
-
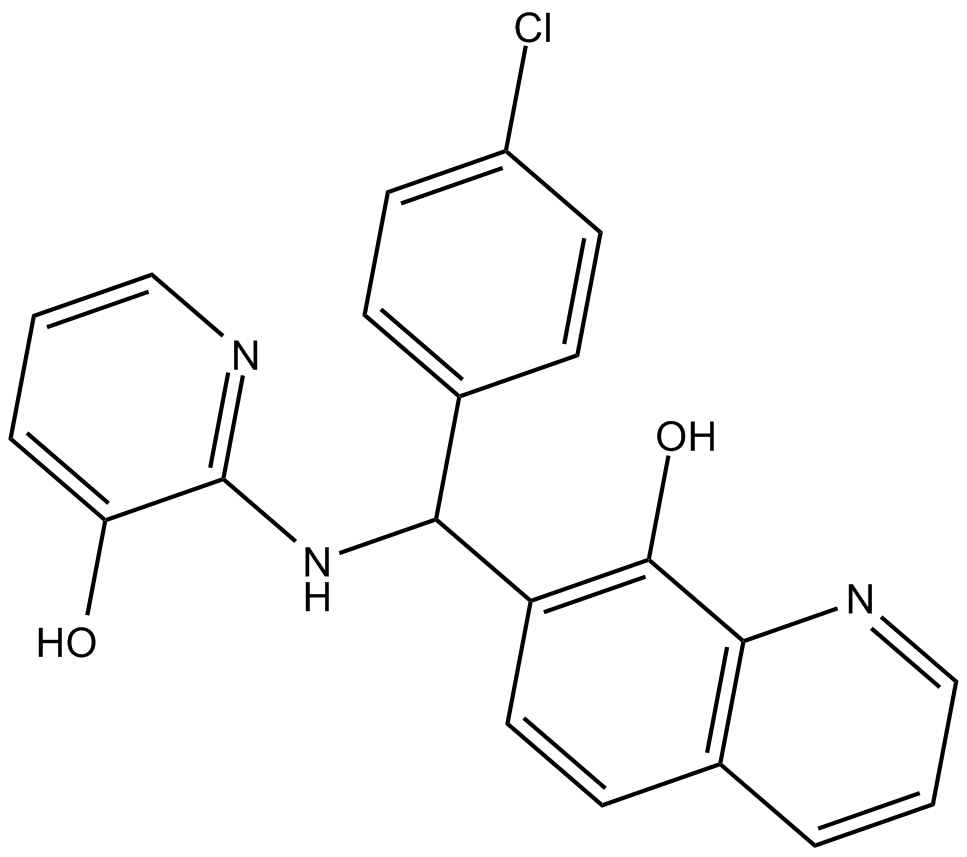 C4377 Adaptaquin1 CitationSummary: HIF-prolyl hydroxylase-2 (PHD2) inhibitor
C4377 Adaptaquin1 CitationSummary: HIF-prolyl hydroxylase-2 (PHD2) inhibitor -
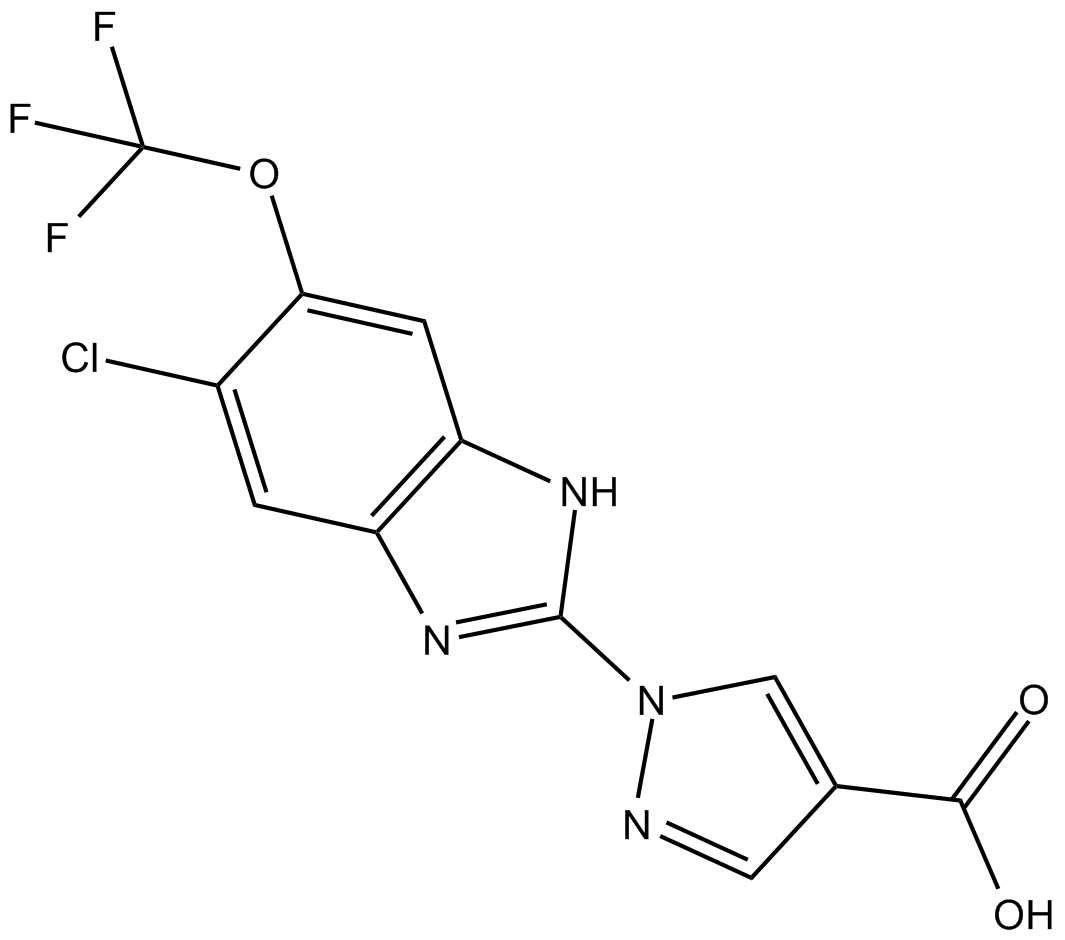 C4752 JNJ-42041935Summary: Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) prolyl hydroxylase (PHD) inhibitor
C4752 JNJ-42041935Summary: Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) prolyl hydroxylase (PHD) inhibitor -
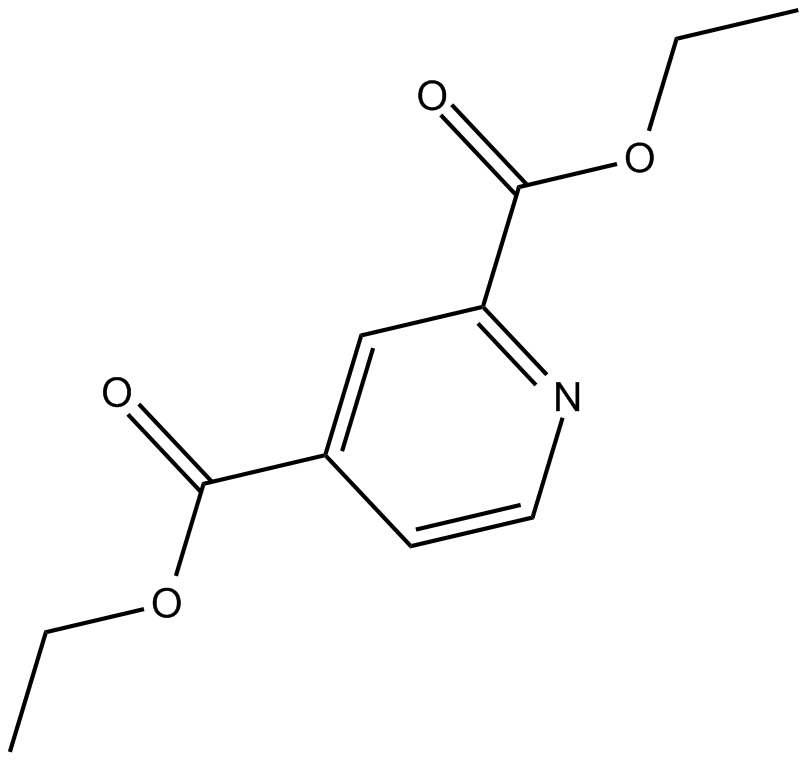 C4887 2,4-DPDSummary: cell permeable, competitive inhibitor of HIF-PH
C4887 2,4-DPDSummary: cell permeable, competitive inhibitor of HIF-PH -
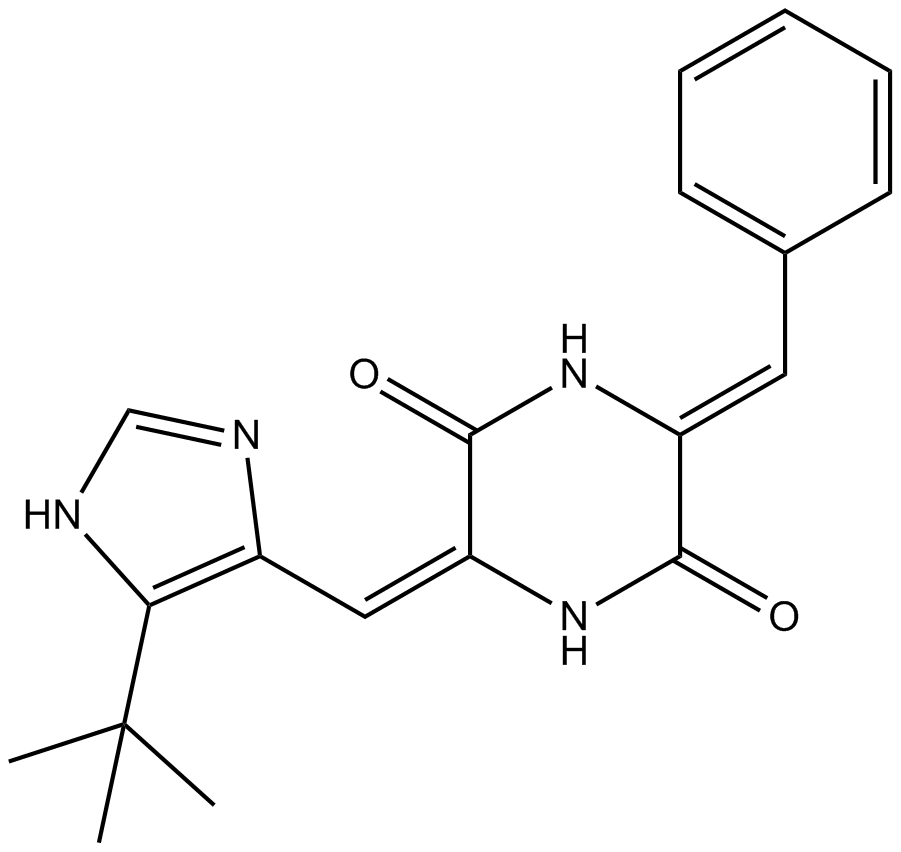 B2298 Plinabulin (NPI-2358)Target: Vascular Disrupting Agents (VDA)Summary: vascular disrupting agent
B2298 Plinabulin (NPI-2358)Target: Vascular Disrupting Agents (VDA)Summary: vascular disrupting agent -
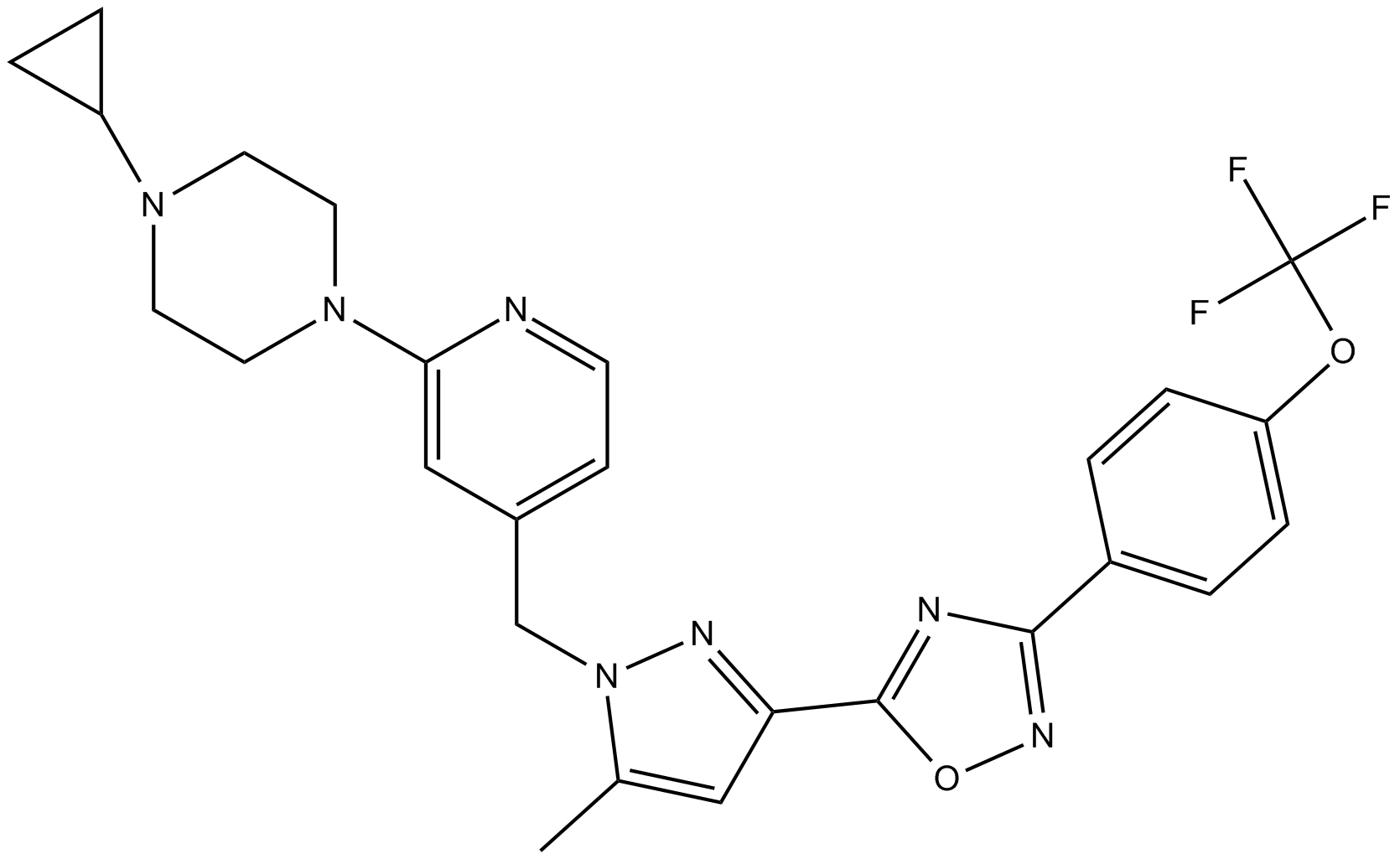 B1115 BAY 87-2243Target: Hypoxia Inducible Factors (HIFs)Summary: HIF-1 inhibitor,potent and selective
B1115 BAY 87-2243Target: Hypoxia Inducible Factors (HIFs)Summary: HIF-1 inhibitor,potent and selective -
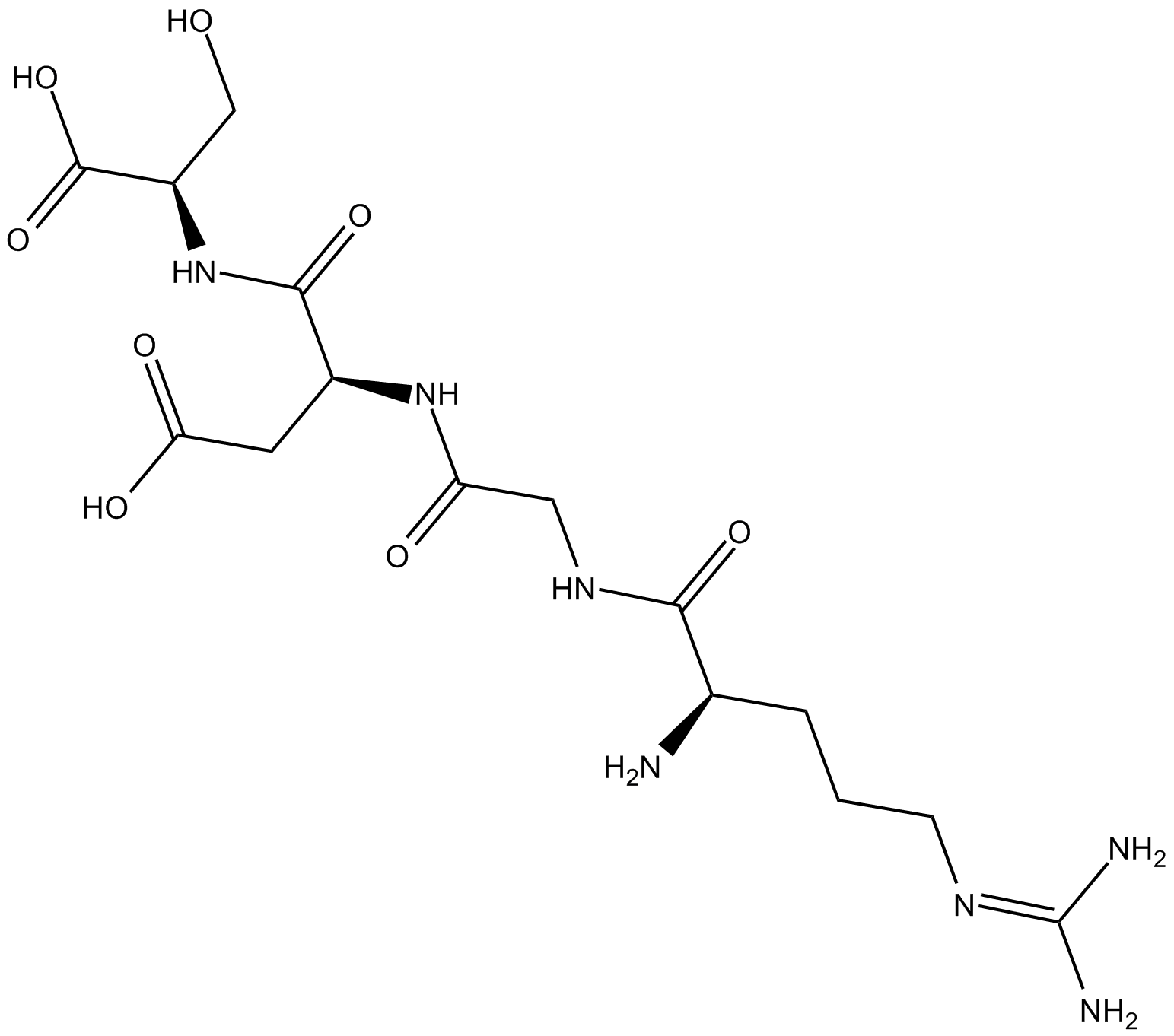 B7412 RGDS peptideSummary: Integrin binding sequence that inhibits integrin receptor function
B7412 RGDS peptideSummary: Integrin binding sequence that inhibits integrin receptor function -
 B5391 Echistatin, α1 isoformSummary: Potent irreversible αVβ3 integrin antagonist
B5391 Echistatin, α1 isoformSummary: Potent irreversible αVβ3 integrin antagonist -
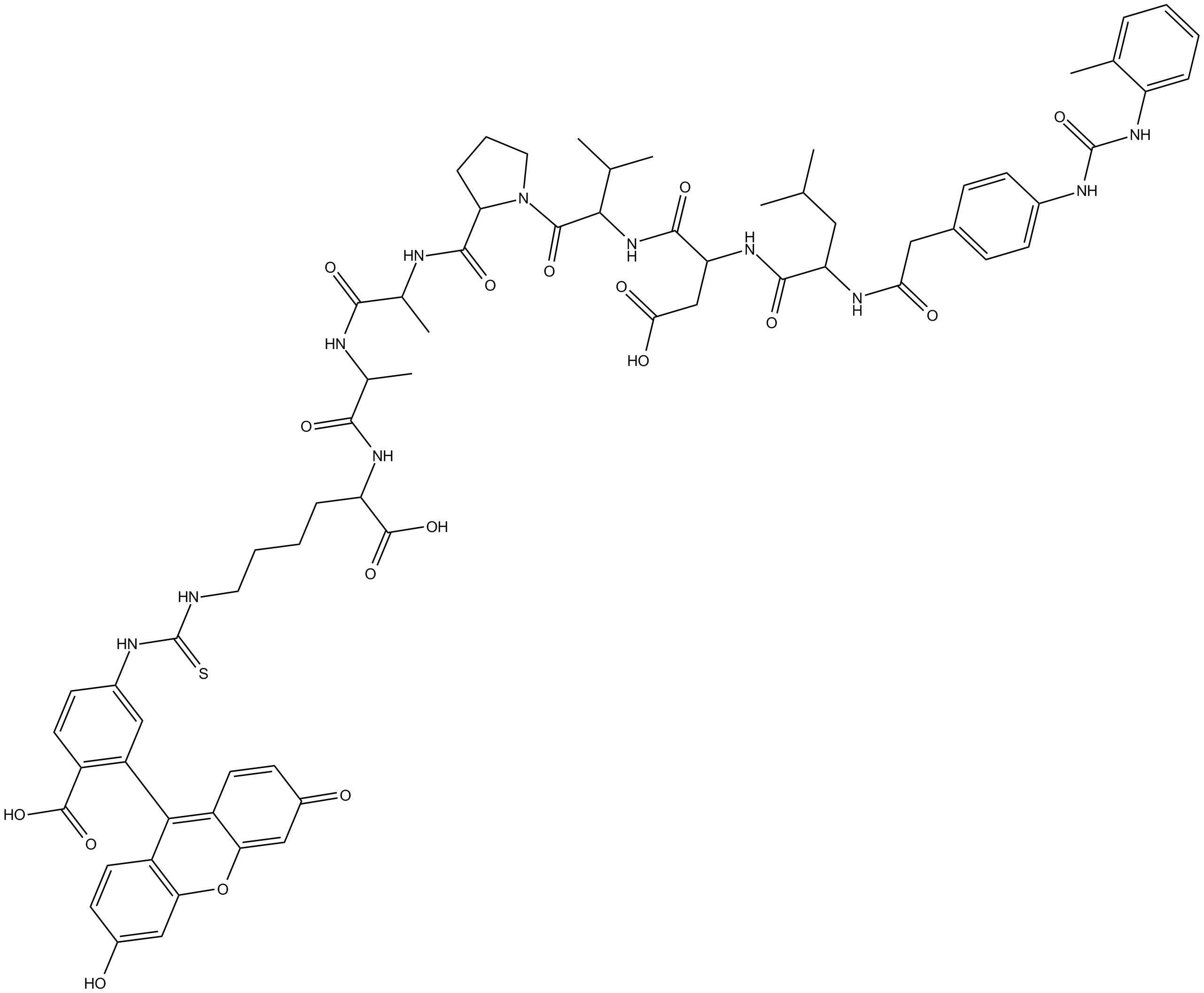 B5644 LDV FITCSummary: fluorescent ligand that binds to the α4β1 integrin (VLA-4)
B5644 LDV FITCSummary: fluorescent ligand that binds to the α4β1 integrin (VLA-4) -
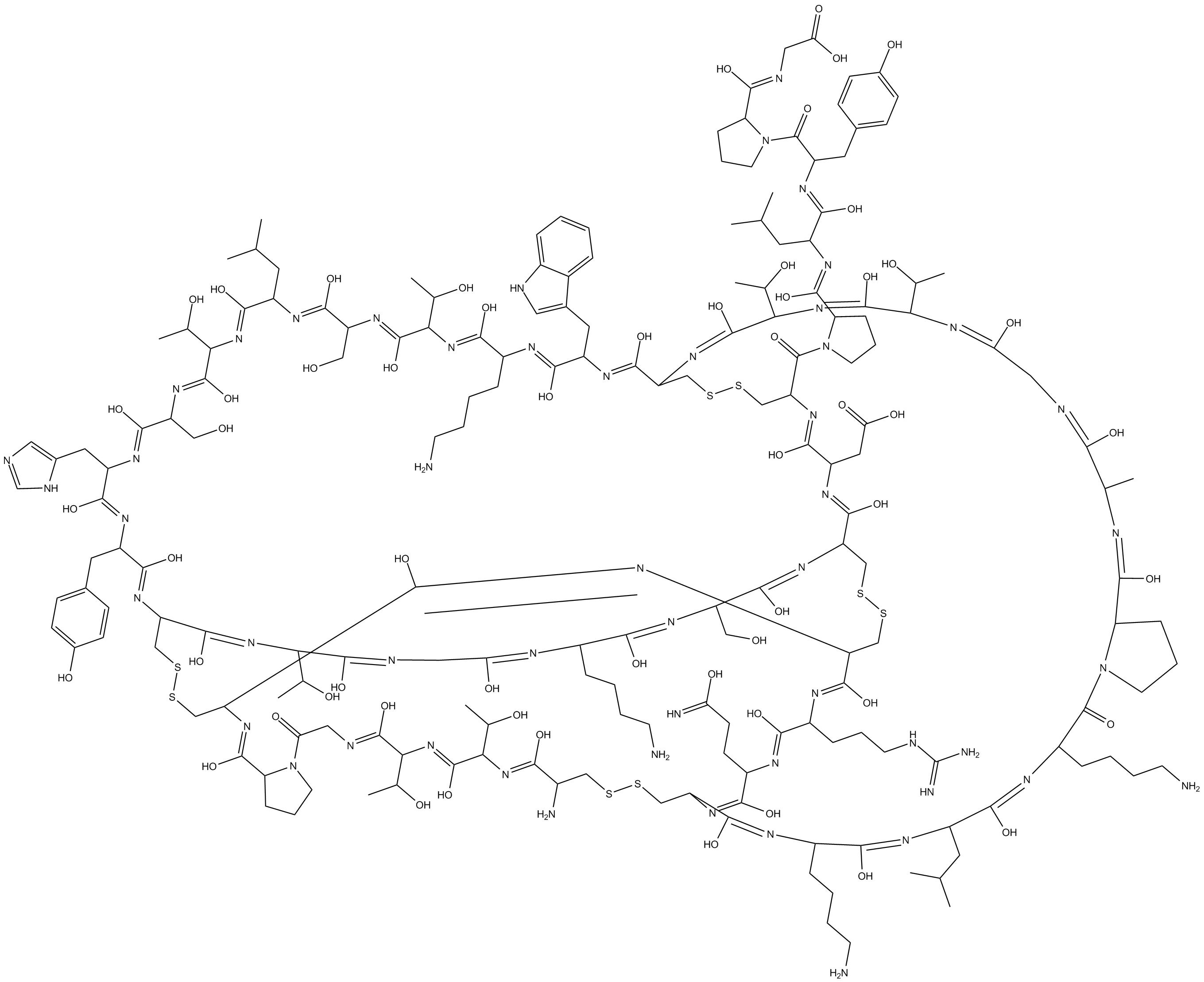 B5675 ObtustatinSummary: integrin α1β1 inhibitor
B5675 ObtustatinSummary: integrin α1β1 inhibitor -
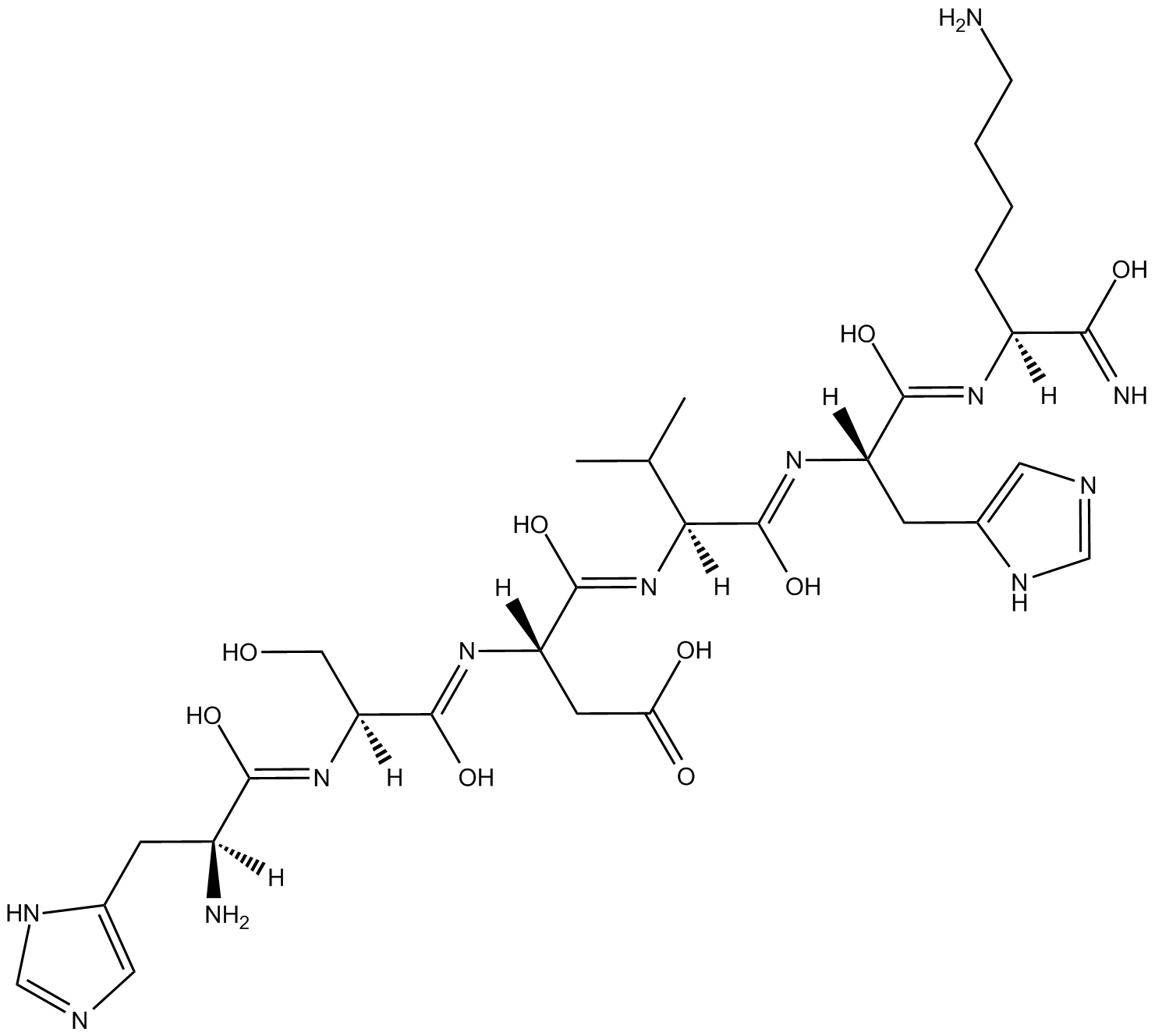 B5699 P11Summary: antagonist of the integrin αvβ3-vitronectin interaction
B5699 P11Summary: antagonist of the integrin αvβ3-vitronectin interaction


