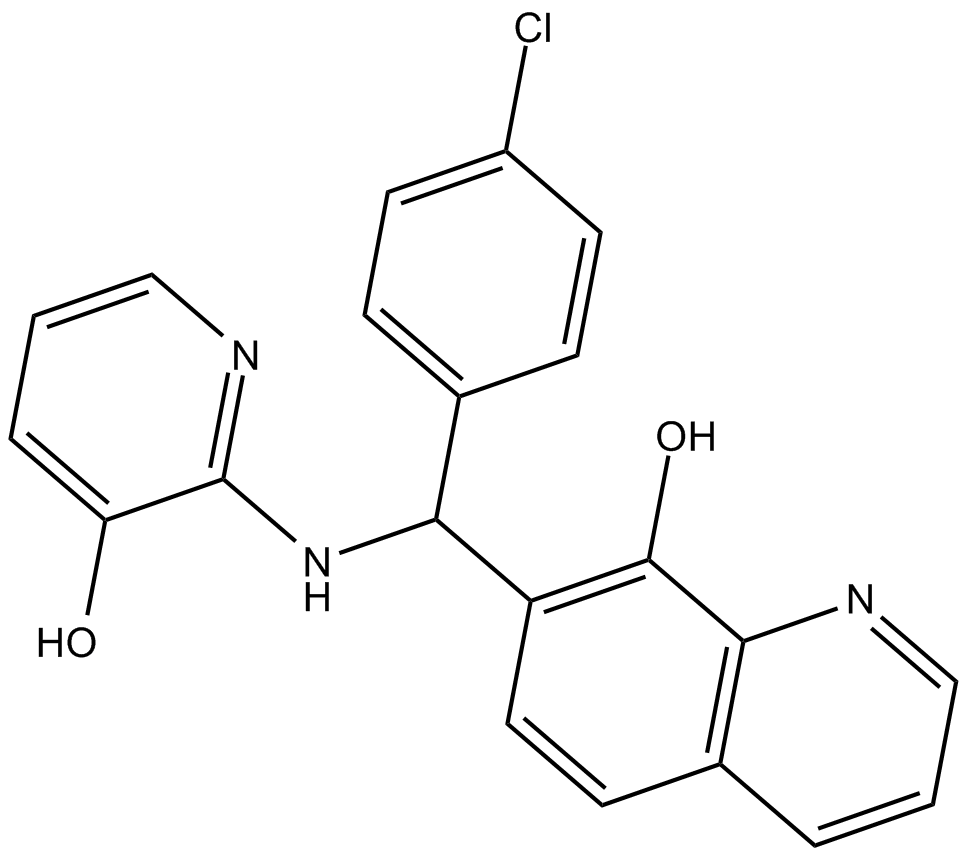
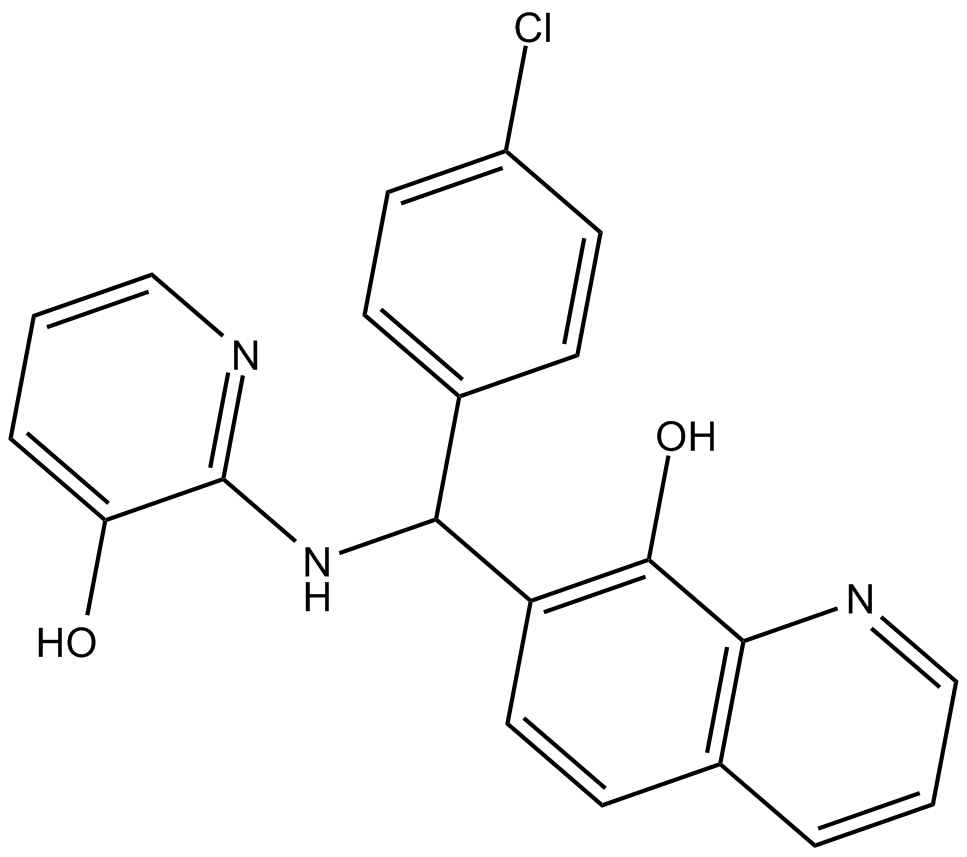
Adaptaquin
Adaptaquin is a selective hydroxyquinoline HIF prolyl hydroxylase (HIF-PHD) inhibitor [1][2].
The hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase domain enzymes (HIF-PHDs) are a family of oxygen sensors that has been implicated in neuronal survival. Catalysis by the HIF-PHDs destabilizes the transcriptional activator HIF-1a under normoxia. HIF-PHDs are promising target candidates for mitochondrial protection in paradigms of oxidative stress. The inhibition of HIF-PHDs prevented neuronal cell death induced by mitochondrial toxins [1][2].
Adaptaquin is a hydroxyquinoline HIF-PHD inhibitor. Adaptaquin inhibited purified and recombinant PHD2. Adaptaquin (30 mg/kg) penetrated the blood-brain barrier, resulting in inhibition of the oxygen-sensing HIF-PHDs and activation of HIF-dependent gene expression [1]. In HT-22 cells, Adaptaquin protected against glutamate-induced cell death. Adaptaquin could also restore the mitochondrial ATP production [2].
In intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) mice model, Adaptaquin decreased edema and significantly improved tape removal task, which were associated with a reduction in the number of degenerating neurons in perihematomal and hematomal areas of the mouse striatum [1].
References:
[1]. Karuppagounder SS, Alim I, Khim SJ, et al. Therapeutic targeting of oxygen-sensing prolyl hydroxylases abrogates ATF4-dependent neuronal death and improves outcomes after brain hemorrhage in several rodent models. Sci Transl Med. 2016 Mar 2;8(328):328ra29.
[2]. Neitemeier S, Dolga AM, Honrath B, et al. Inhibition of HIF-prolyl-4-hydroxylases prevents mitochondrial impairment and cell death in a model of neuronal oxytosis. Cell Death Dis. 2016 May 5;7:e2214.
| Physical Appearance | A crystalline solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 377.8 |
| Cas No. | 385786-48-1 |
| Formula | C21H16ClN3O2 |
| Synonyms | HIF prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor |
| Solubility | ≤30mg/ml in DMSO;30mg/ml in dimethyl formamide |
| Chemical Name | 7-[(4-chlorophenyl)[(3-hydroxy-2-pyridinyl)amino]methyl]-8-quinolinol |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | Oc1cccnc1NC(c(cc1)ccc1Cl)c(ccc1c2nccc1)c2O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
-
Purity ≥ 95.00%
- COA (Certificate Of Analysis)
- MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheet)
Chemical structure