Metabolism
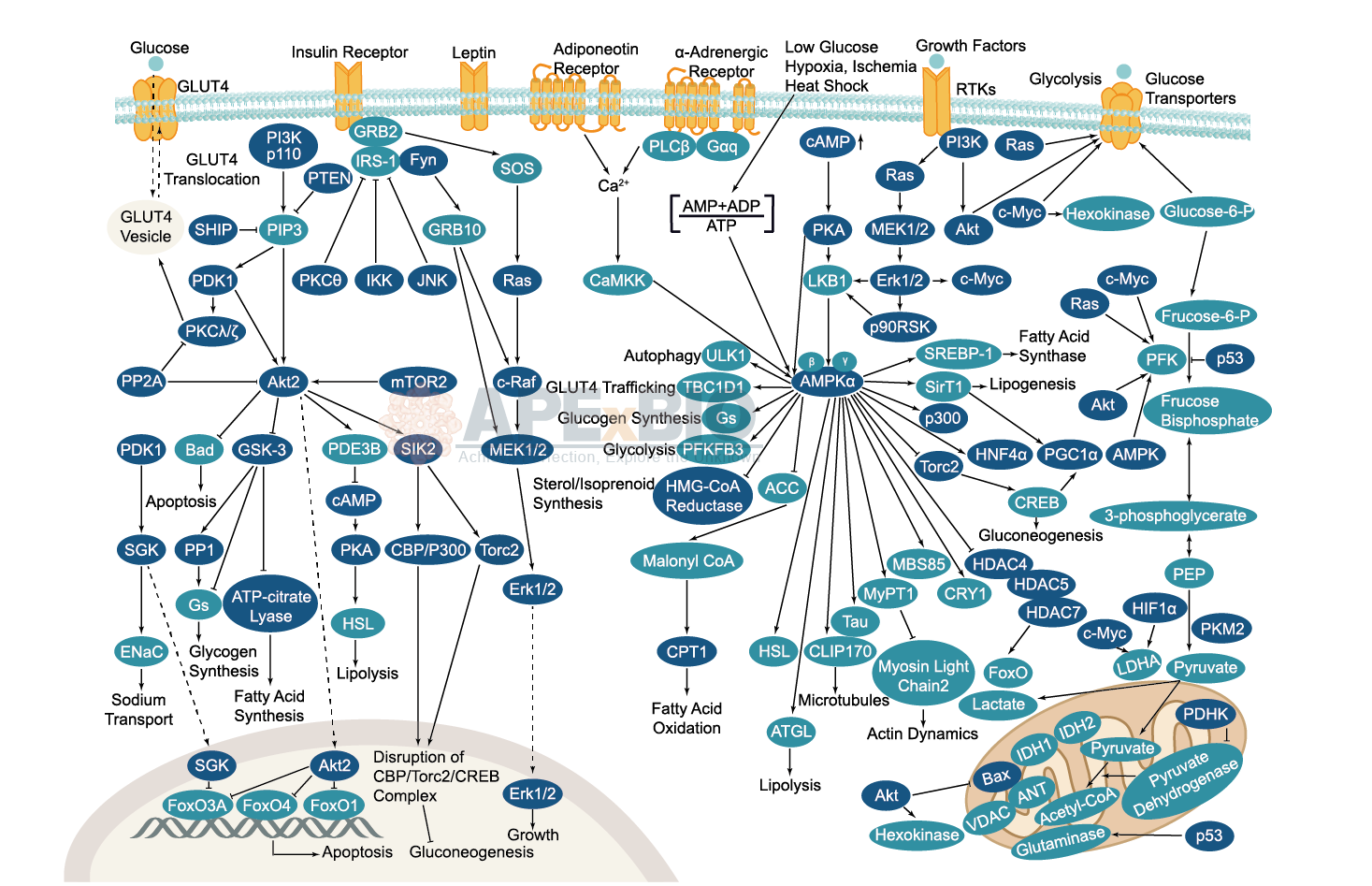

Serine/threonine kinase AMPK upregulates glucose uptake by promoting the expression and function of glucose transporters. AMPK is activated by increased AMP/ATP ratio, resulting from cellular and environmental stress, e.g. low glucose, heat shock, hypoxia and ischemia. AMPK activation positively modulates signaling transductions that refill ATP levels. Moreover, it also stimulates catabolic processes such as fatty acid oxidation and glycolysis through inhibition of ACC and activation of PFK2. AMPK negatively regulates various proteins which are important to ATP-consuming mechanisms, e.g. mTORC2, glycogen synthase, SREBP-1, and TSC2, causing the downregulation/inhibition of gluconeogenesis and glycogen, lipid and protein synthesis.
-
 C5183 IbudilastSummary: inhibitor of PDE4
C5183 IbudilastSummary: inhibitor of PDE4 -
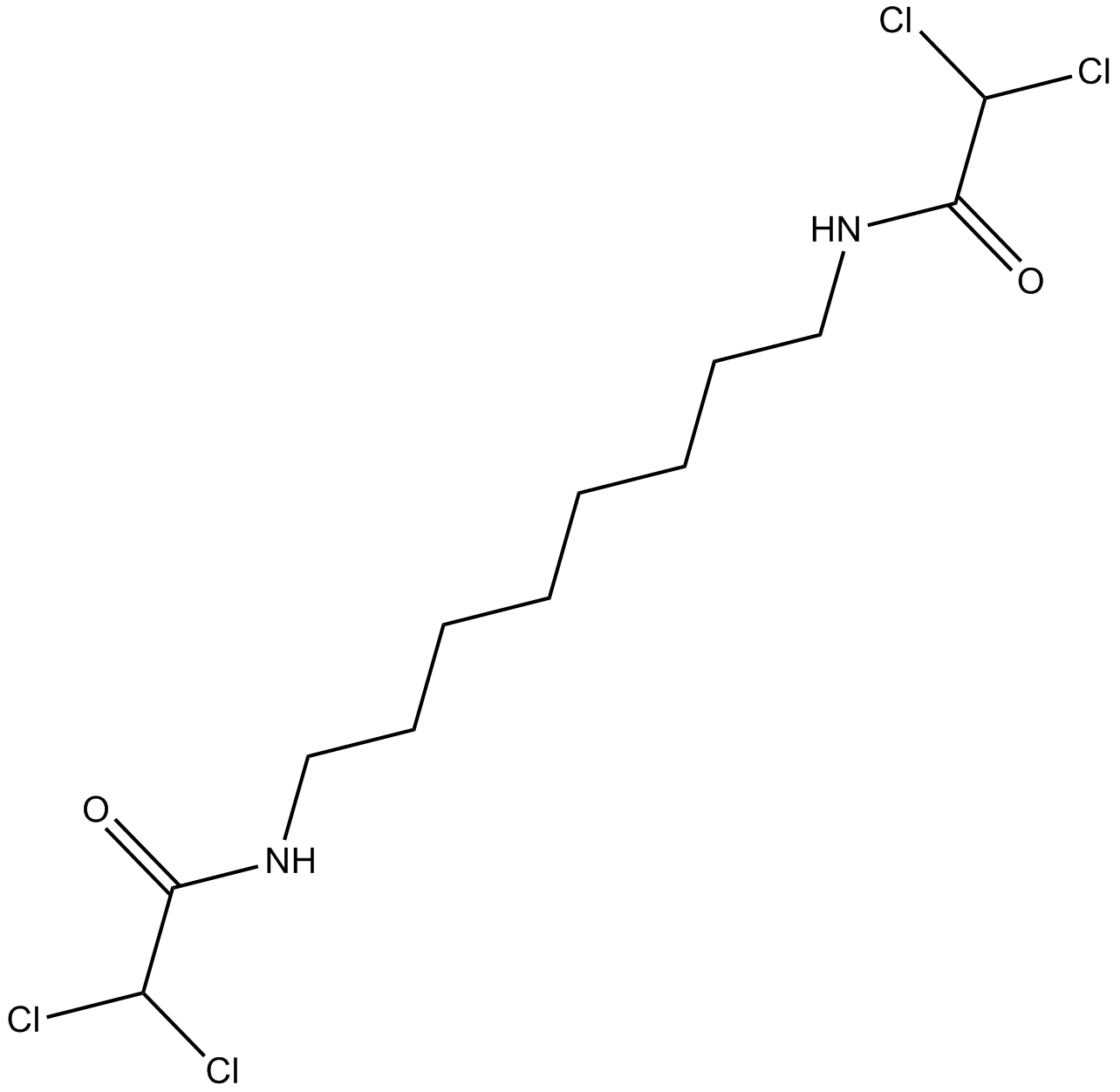 B5697 WIN 18446Summary: inhibitor of aldehyde dehydrogenase 1a2 (ALDH1a2)
B5697 WIN 18446Summary: inhibitor of aldehyde dehydrogenase 1a2 (ALDH1a2) -
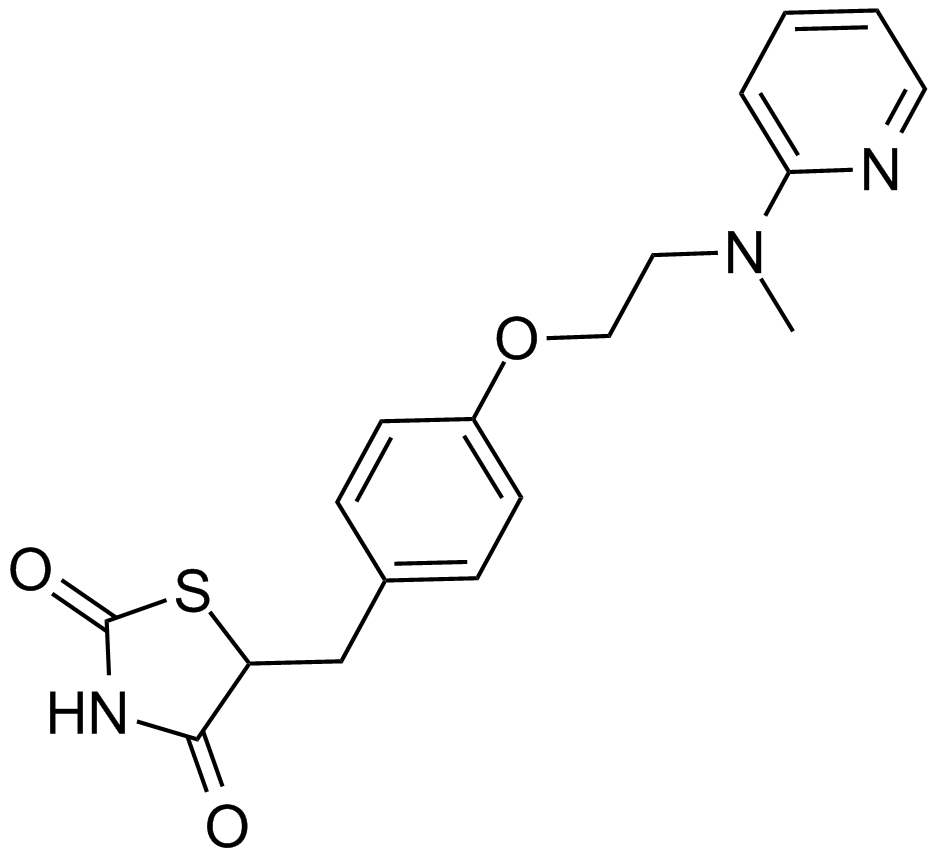 A4304 Rosiglitazone5 CitationSummary: Potent PPARγ agonist
A4304 Rosiglitazone5 CitationSummary: Potent PPARγ agonist -
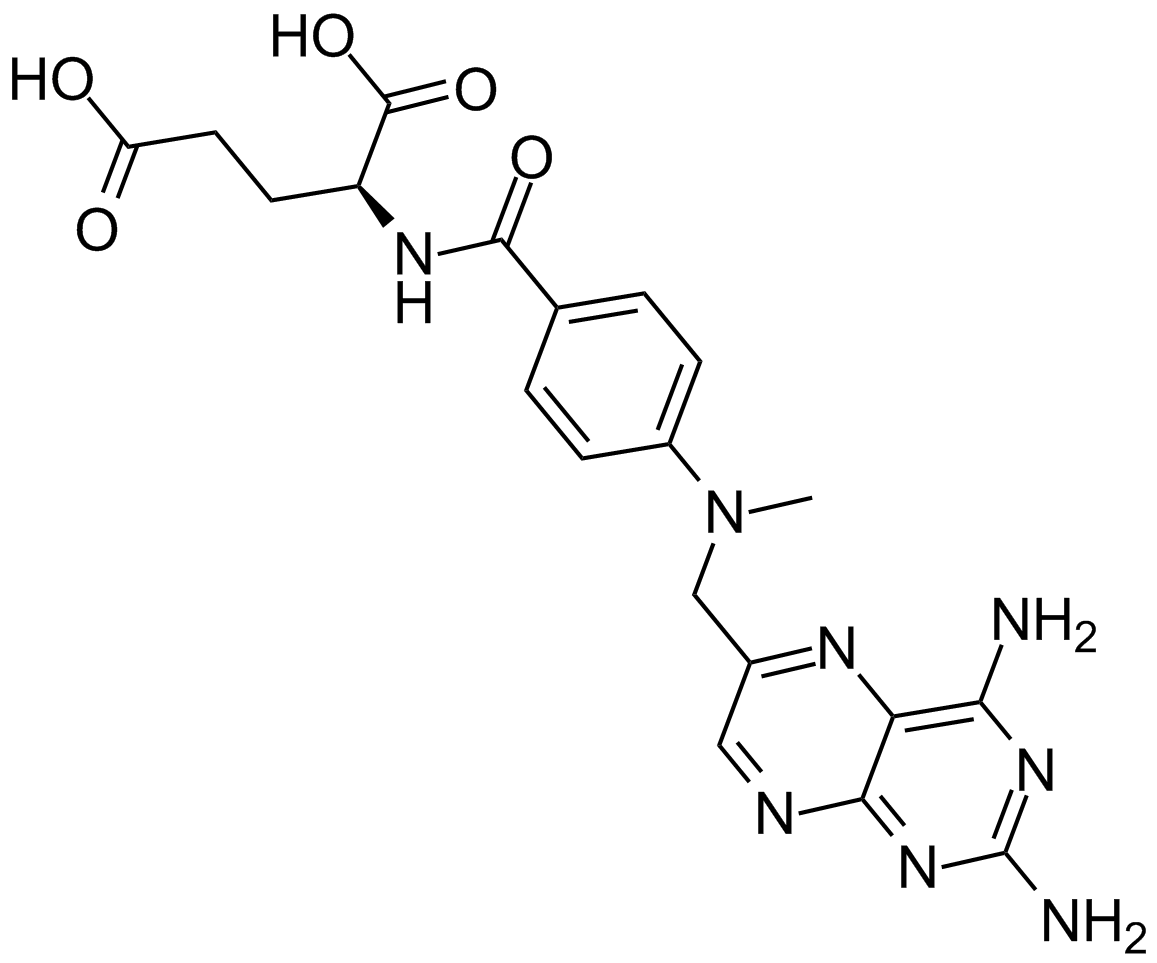 A4347 Methotrexate5 CitationTarget: Folate AnalogueSummary: Folate antagonist,inhibits DFHR
A4347 Methotrexate5 CitationTarget: Folate AnalogueSummary: Folate antagonist,inhibits DFHR -
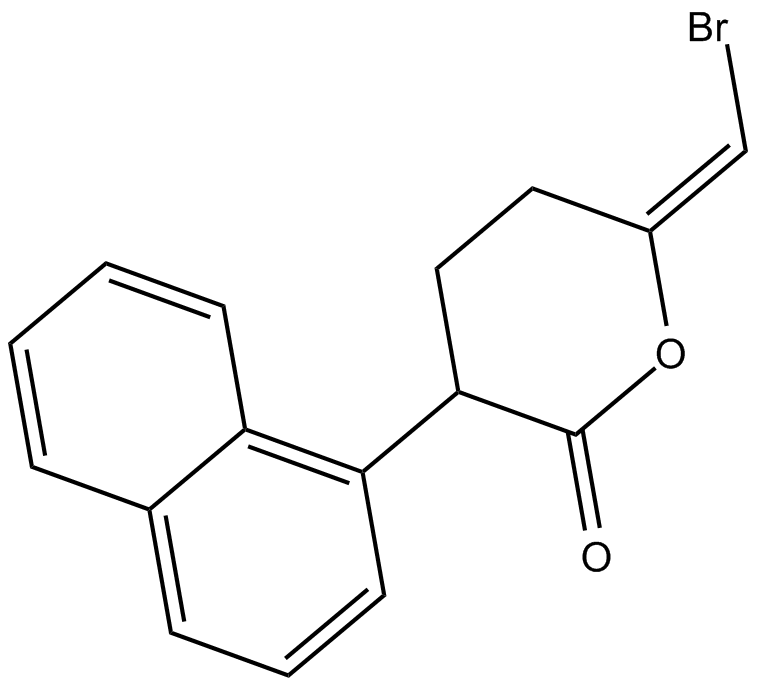 C5081 Bromoenol lactoneSummary: Inhibitor of myocardial cytosolic calcium-independent phospholipase A2 (iPLA2)
C5081 Bromoenol lactoneSummary: Inhibitor of myocardial cytosolic calcium-independent phospholipase A2 (iPLA2) -
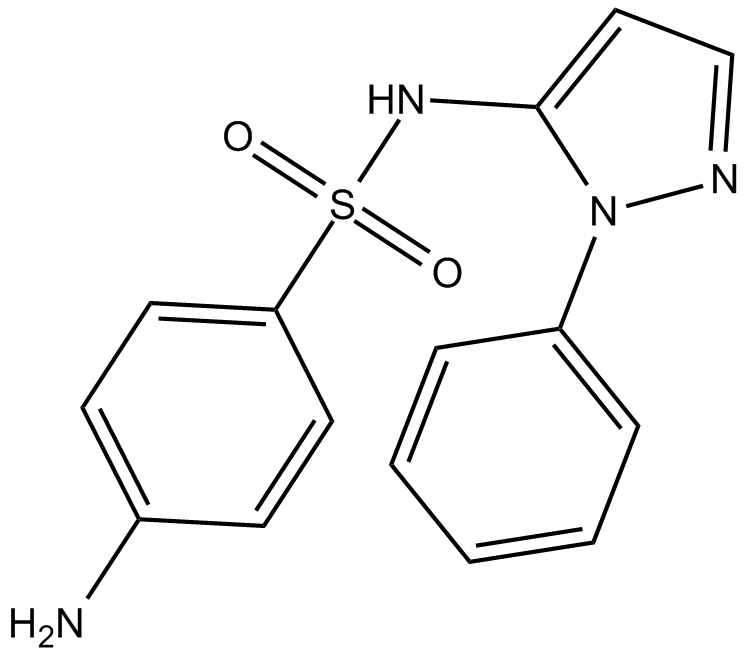 C4131 SulfaphenazoleSummary: A CYP2C6/2C9 inhibitor
C4131 SulfaphenazoleSummary: A CYP2C6/2C9 inhibitor -
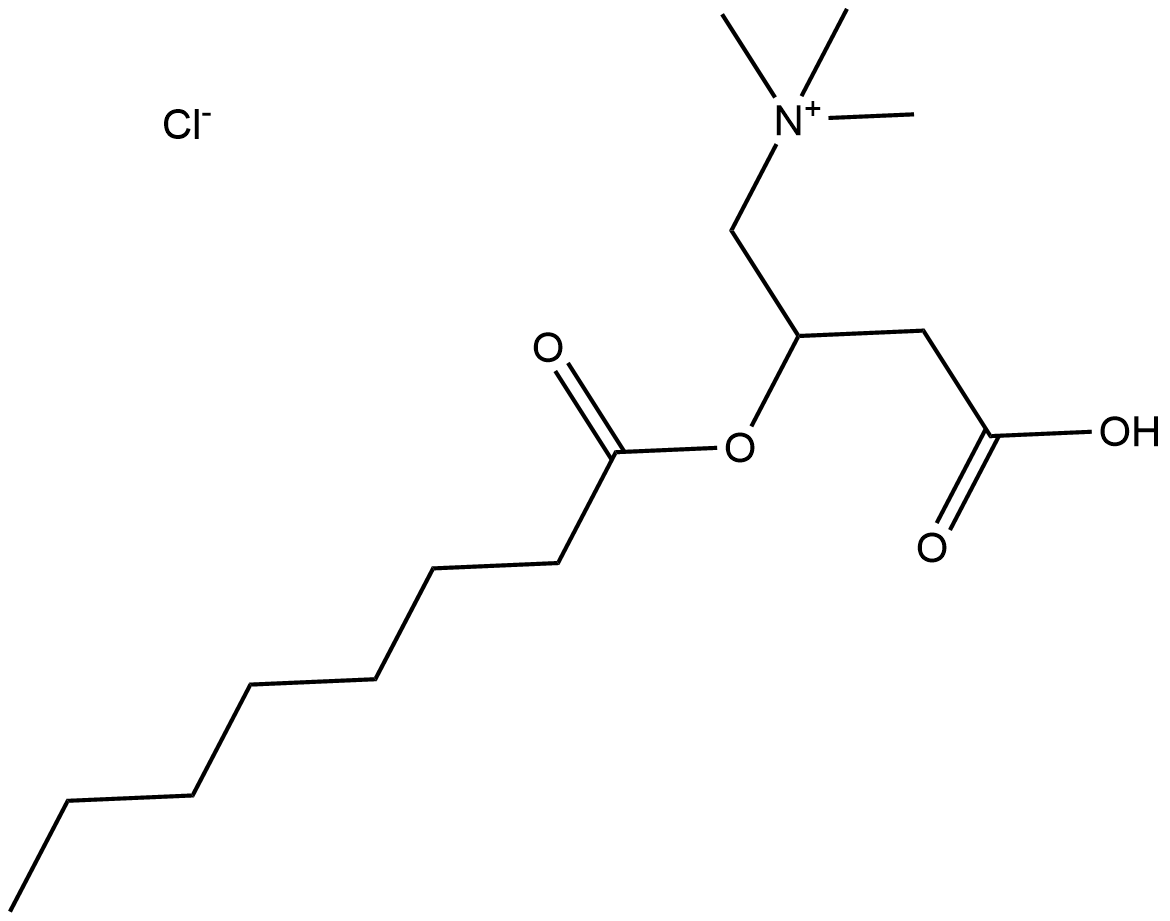 B6371 (±)-Octanoylcarnitine chloride5 CitationSummary: an intermediate in fatty acid metabolism
B6371 (±)-Octanoylcarnitine chloride5 CitationSummary: an intermediate in fatty acid metabolism -
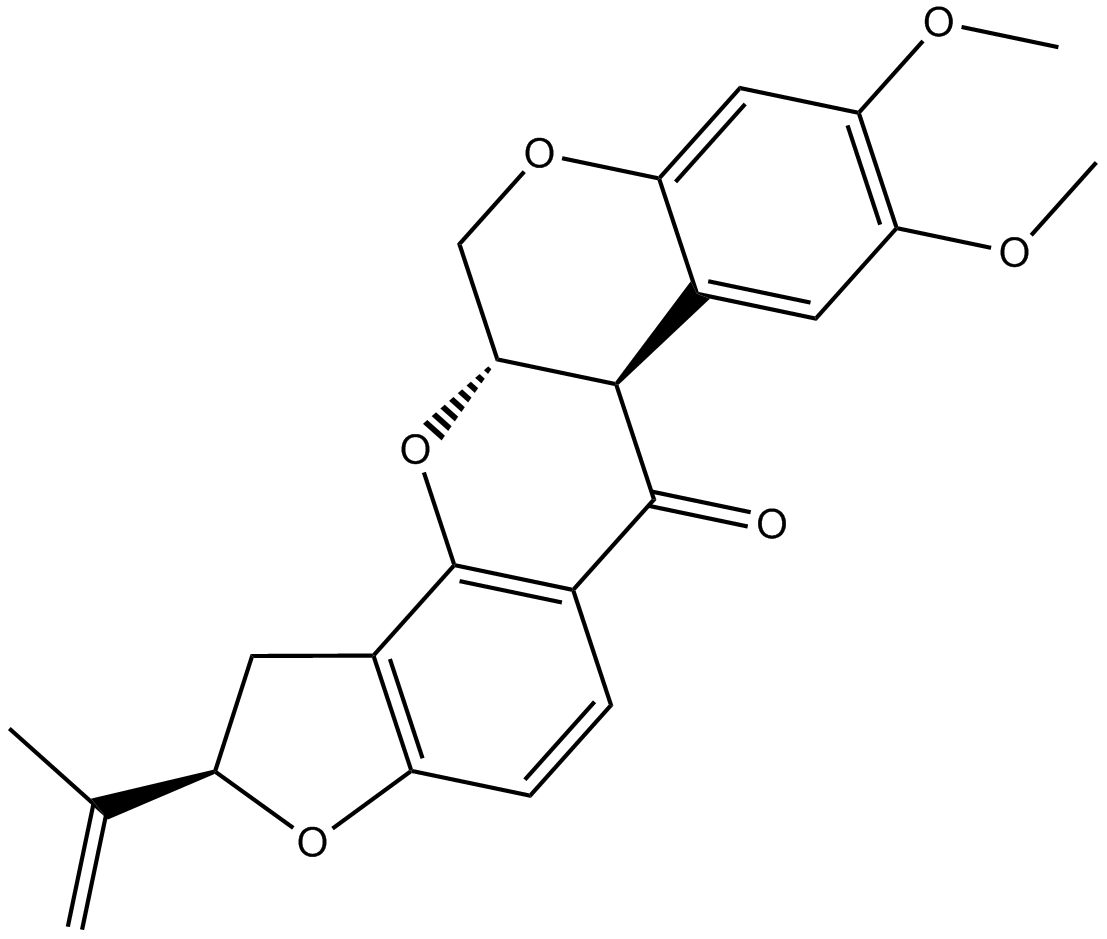 B5462 Rotenone9 CitationTarget: complex I of the mitochondrial electron transport chainSummary: mitochondrial Complex I inhibitor
B5462 Rotenone9 CitationTarget: complex I of the mitochondrial electron transport chainSummary: mitochondrial Complex I inhibitor -
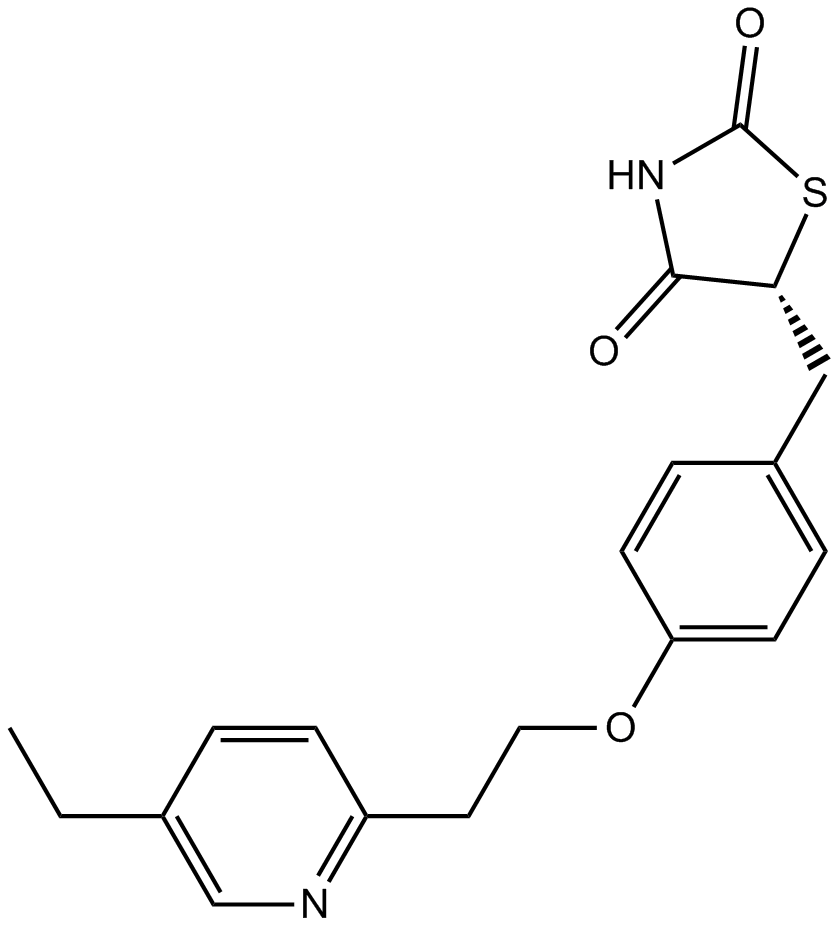 B2117 Pioglitazone1 CitationSummary: PPAR agonist
B2117 Pioglitazone1 CitationSummary: PPAR agonist -
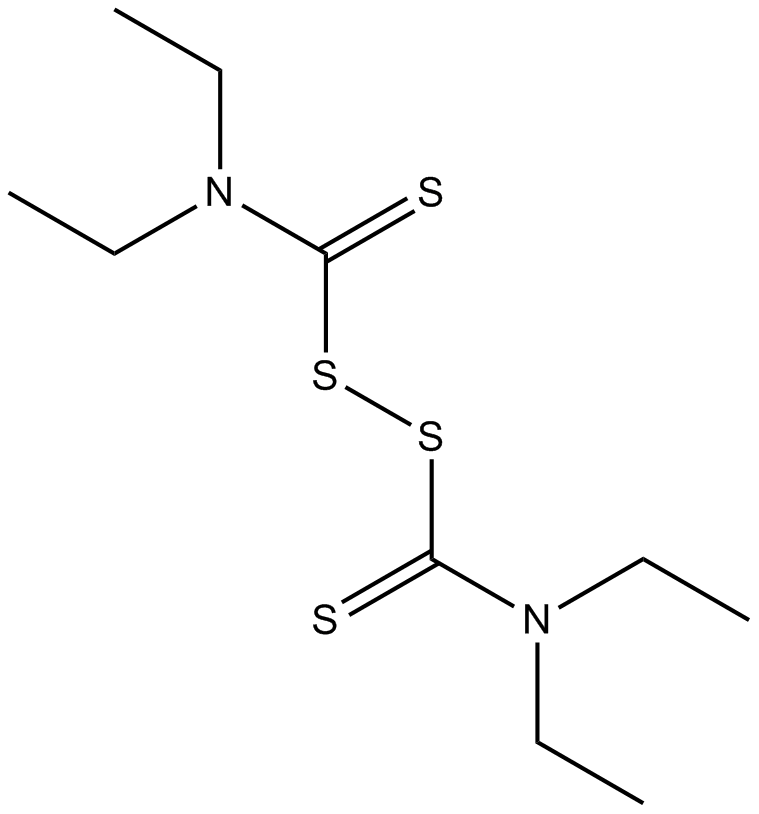 A4015 DisulfiramTarget: Aldehyde DehydrogenasesSummary: Dopamine β-hydroxylase inhibitor
A4015 DisulfiramTarget: Aldehyde DehydrogenasesSummary: Dopamine β-hydroxylase inhibitor


