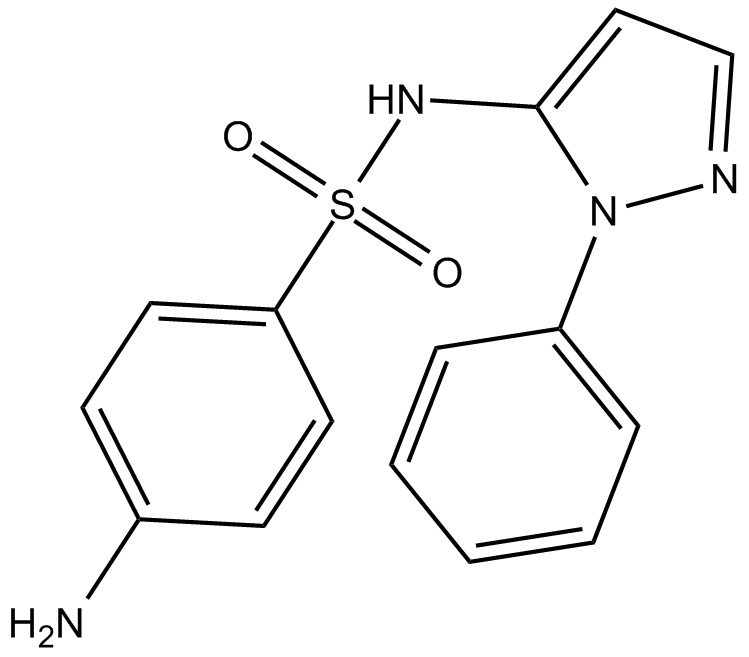
Sulfaphenazole
Sulfaphenazole (CAS No. 526-08-9) is a sulfonamide compound whose core targets include bacterial dihydropteroate synthase (DHPS, exerting antibacterial effects by competitively inhibiting folic acid synthesis) and cytochrome P450 2C6/2C9 (CYP2C6/2C9, reducing oxidative stress by inhibiting enzyme activity). It has clear concentration data related to biological activity: the IC₅₀ for CYP2C9 inhibition is 0.63 μM, the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) against Mycobacterium tuberculosis H₃₇Rv is 5.51 μg/mL, the MIC against extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis (XDR-TB) is 12.59 μg/mL, and the cytotoxic IC₅₀ on Vero cells is >64 μg/mL. Commonly used concentrations in laboratory settings: 0.5~11.5 μM for CYP enzyme inhibition assays, 5~30 μg/mL for in vitro anti-tuberculosis experiments, and 1~10 μM for cell function research. Effective therapeutic concentrations in clinical and animal experiments: in animal studies, 5.13 mg/kg intraperitoneal injection daily (for improving vascular function in diabetic mice and treating pressure/thermal injuries); it was previously used clinically for leprosy treatment (specific oral dosage not specified, falling within the conventional administration range of sulfonamide antibiotics). Its biological activities cover multiple aspects: antibacterial activity (against Mycobacterium tuberculosis, etc., and can be combined with trimethoprim to enhance efficacy), inhibiting CYP2C-mediated oxidative stress to restore endothelium-dependent vasodilation, reducing ischemia-reperfusion injury (improving tissue perfusion and reducing hypoxia), and promoting the healing of pressure and thermal injury wounds (reducing inflammation and fibrosis, enhancing macrophage bactericidal activity). It has good safety profile, low cytotoxicity, and no obvious adverse reactions.
References:
[1] Elmi S, Sallam NA, Rahman MM, Teng X, Hunter AL, Moien-Afshari F, Khazaei M, Granville DJ, Laher I. Sulfaphenazole treatment restores endothelium-dependent vasodilation in diabetic mice. Vascul Pharmacol. 2008 Jan;48(1):1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2007.09.001. Epub 2007 Sep 15. PMID: 17974492.
[2] Chen H, Wang B, Li P, Yan H, Li G, Huang H, Lu Y. The optimization and characterization of functionalized sulfonamides derived from sulfaphenazole against Mycobacterium tuberculosis with reduced CYP 2C9 inhibition. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2021 May 15;40:127924. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2021.127924. Epub 2021 Mar 9. PMID: 33705901.
[3] Turner CT, Pawluk M, Bolsoni J, Zeglinski MR, Shen Y, Zhao H, Ponomarev T, Richardson KC, West CR, Papp A, Granville DJ. Sulfaphenazole reduces thermal and pressure injury severity through rapid restoration of tissue perfusion. Sci Rep. 2022 Jul 23;12(1):12622. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-16512-9. PMID: 35871073; PMCID: PMC9308818.
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 314.4 |
| Cas No. | 526-08-9 |
| Formula | C15H14N4O2S |
| Synonyms | SPZ; SPA |
| Solubility | insoluble in H2O; ≥13.15 mg/mL in DMSO; ≥9.92 mg/mL in EtOH with ultrasonic |
| Chemical Name | 4-amino-N-(1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)-benzenesulfonamide |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | Nc(cc1)ccc1S(Nc1ccn[n]1-c1ccccc1)(=O)=O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
-
Purity = 98.00%
- COA (Certificate Of Analysis)
- MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheet)
- Datasheet
Chemical structure