Immunology/Inflammation


The adaptive immune system consists of B and T lymphocytes which mediate humoral immunity (e.g. antibody response) and cell-mediated immunity, respectively. B cell receptor and T cell receptor signaling is responsible for activation of Src family tyrosine kinases, such as Blk, Fyn, and Lyn in B cells and Fyn and Lck in T cells, resulting phosphorylation of the receptor-associated ITAM motifs. Phosphorylated ITAMs serve as the docking sites for Syk family tyrosine kinases, e.g. Syk in B cells and Zap-70 in T cells. Activated Syk kinases then propagate the signals via phosphorylation of downstream proteins. Furthermore, lymphocyte receptor signaling facilitates B and T cell development, differentiation, proliferation and survival.
-
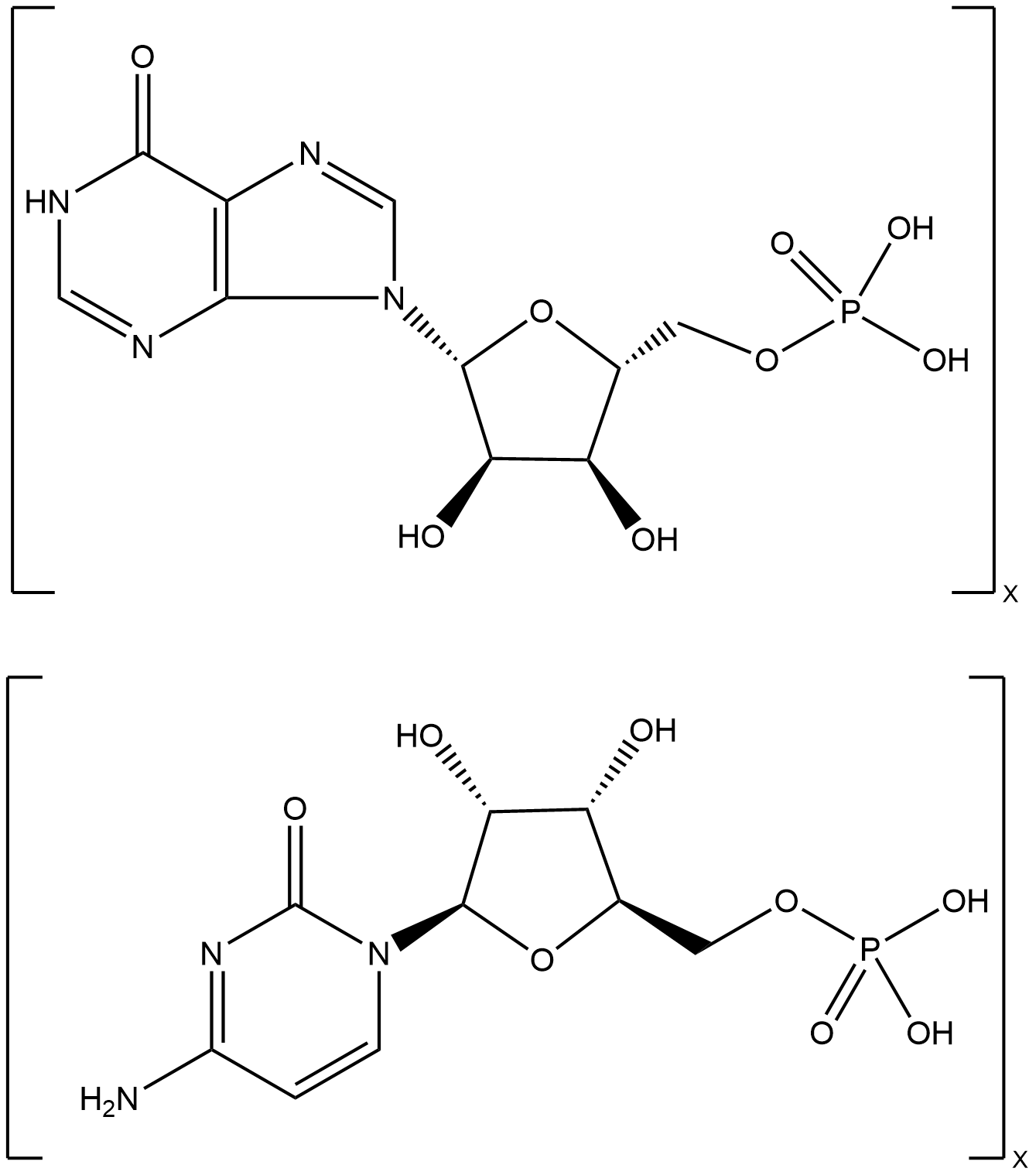 B5551 Poly(I:C)20 CitationTarget: Toll-like receptors (TLRs)Summary: Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) agonist
B5551 Poly(I:C)20 CitationTarget: Toll-like receptors (TLRs)Summary: Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) agonist -
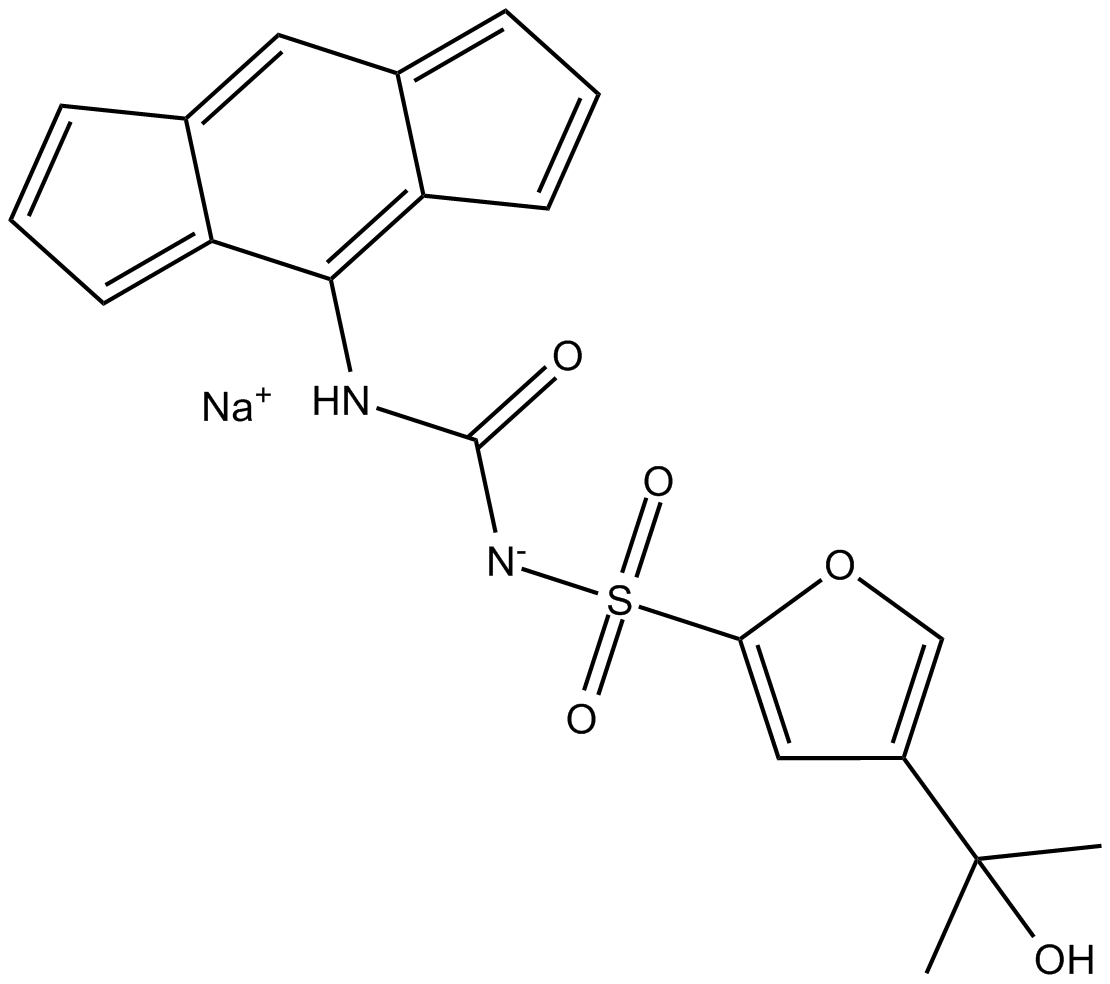 B7946 MCC950 sodium7 CitationSummary: Potent NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitor
B7946 MCC950 sodium7 CitationSummary: Potent NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitor -
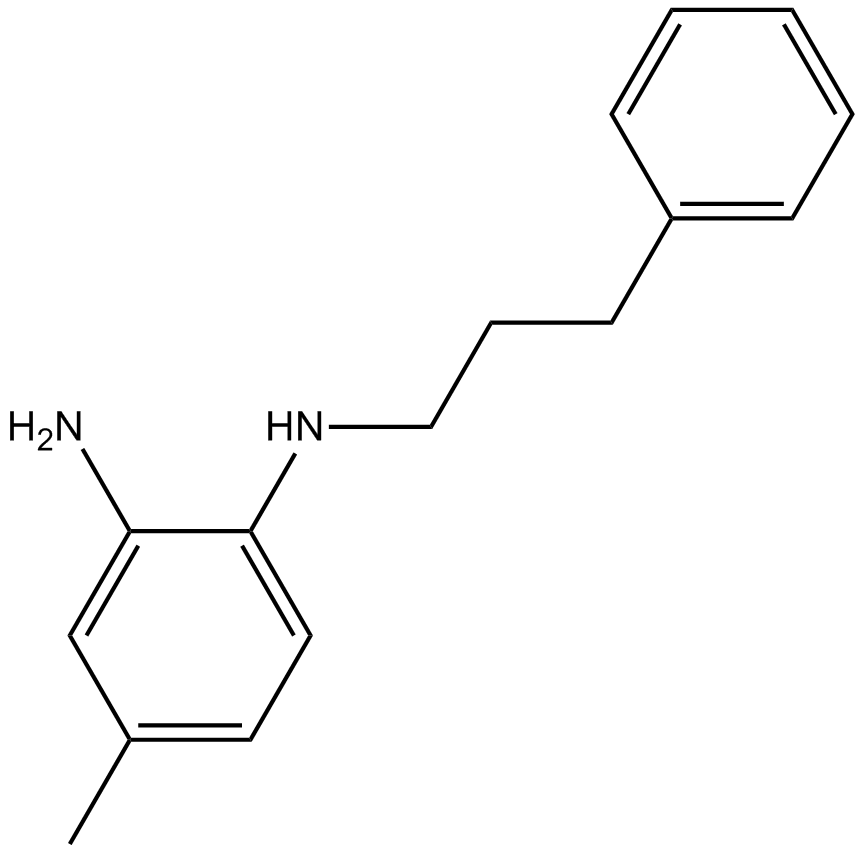 B1645 JSH-235 CitationSummary: NF-κB inhibitor
B1645 JSH-235 CitationSummary: NF-κB inhibitor -
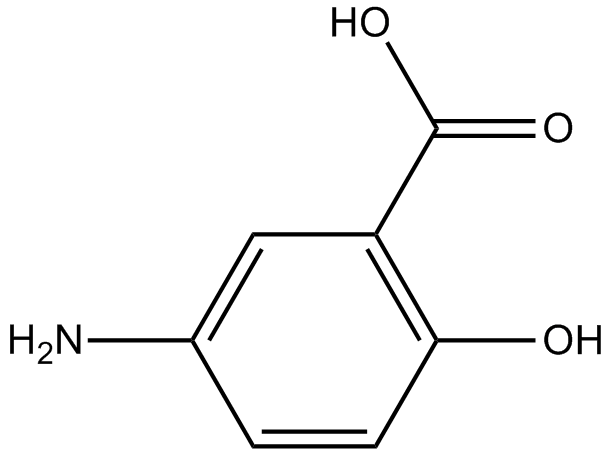 B1969 Mesalamine1 CitationSummary: IKK inhibitor
B1969 Mesalamine1 CitationSummary: IKK inhibitor -
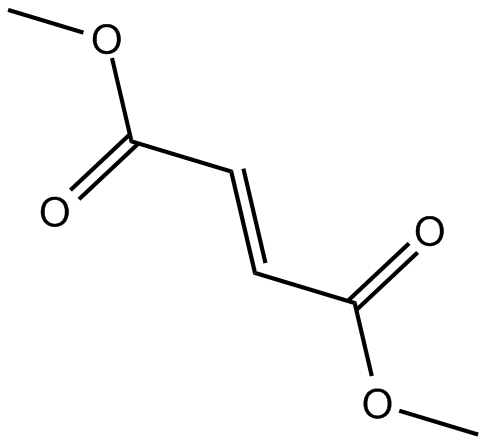 B1931 Dimethyl FumarateSummary: nuclear factor (erythroid-derived)-like 2 (Nrf2) pathway activator
B1931 Dimethyl FumarateSummary: nuclear factor (erythroid-derived)-like 2 (Nrf2) pathway activator -
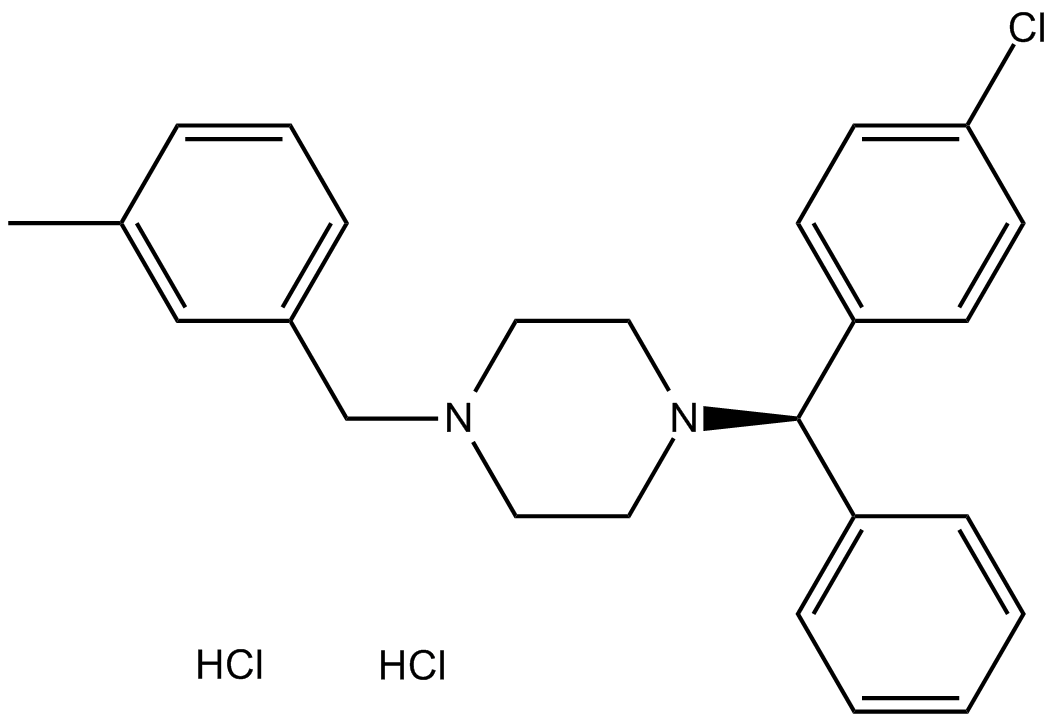 B1786 Meclizine 2HCl3 CitationSummary: Histamine H1 receptor antagonist
B1786 Meclizine 2HCl3 CitationSummary: Histamine H1 receptor antagonist -
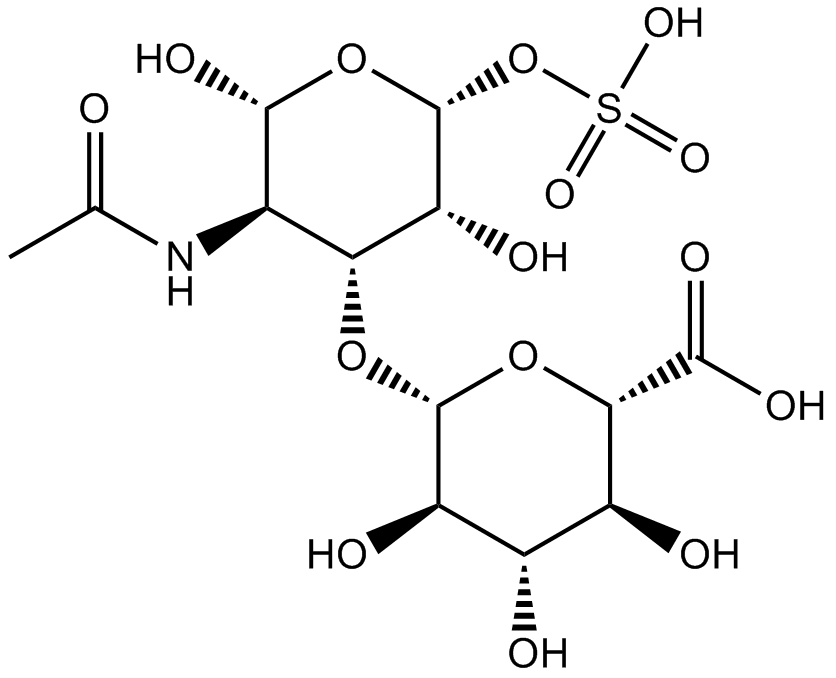 N2730 Chondroitin sulfate
N2730 Chondroitin sulfate -
 B7199 Withaferin A2 CitationSummary: Prevents NF-κB activation by inhibiting activation of IKKβ
B7199 Withaferin A2 CitationSummary: Prevents NF-κB activation by inhibiting activation of IKKβ -
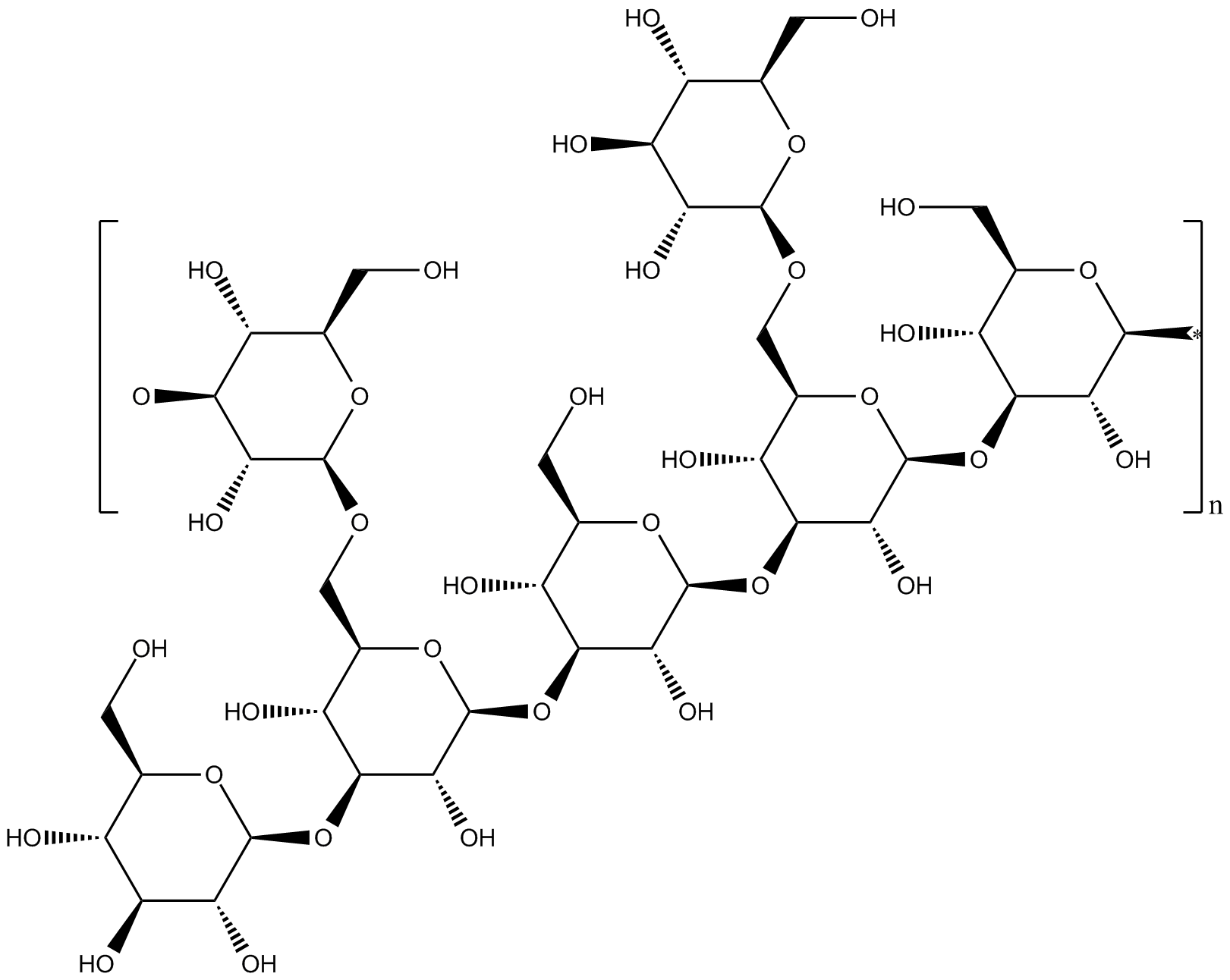 C6501 Lentinan
C6501 Lentinan -
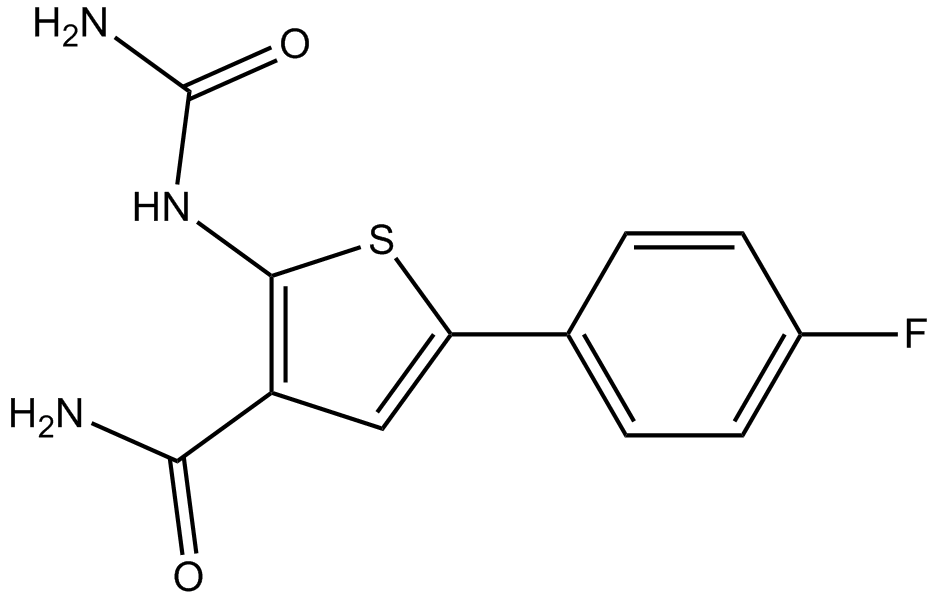 A4602 TPCA-12 CitationSummary: IKK-2 inhibitor,potent and selective
A4602 TPCA-12 CitationSummary: IKK-2 inhibitor,potent and selective


