Immunology/Inflammation


The adaptive immune system consists of B and T lymphocytes which mediate humoral immunity (e.g. antibody response) and cell-mediated immunity, respectively. B cell receptor and T cell receptor signaling is responsible for activation of Src family tyrosine kinases, such as Blk, Fyn, and Lyn in B cells and Fyn and Lck in T cells, resulting phosphorylation of the receptor-associated ITAM motifs. Phosphorylated ITAMs serve as the docking sites for Syk family tyrosine kinases, e.g. Syk in B cells and Zap-70 in T cells. Activated Syk kinases then propagate the signals via phosphorylation of downstream proteins. Furthermore, lymphocyte receptor signaling facilitates B and T cell development, differentiation, proliferation and survival.
-
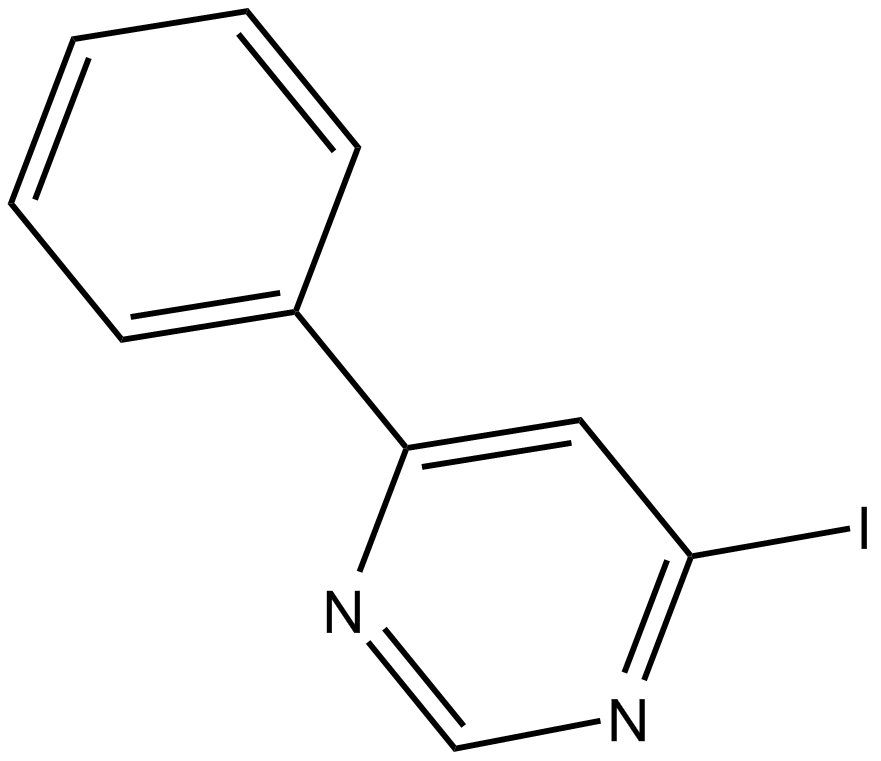 B5429 4-IPPSummary: Inhibitor of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF)
B5429 4-IPPSummary: Inhibitor of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) -
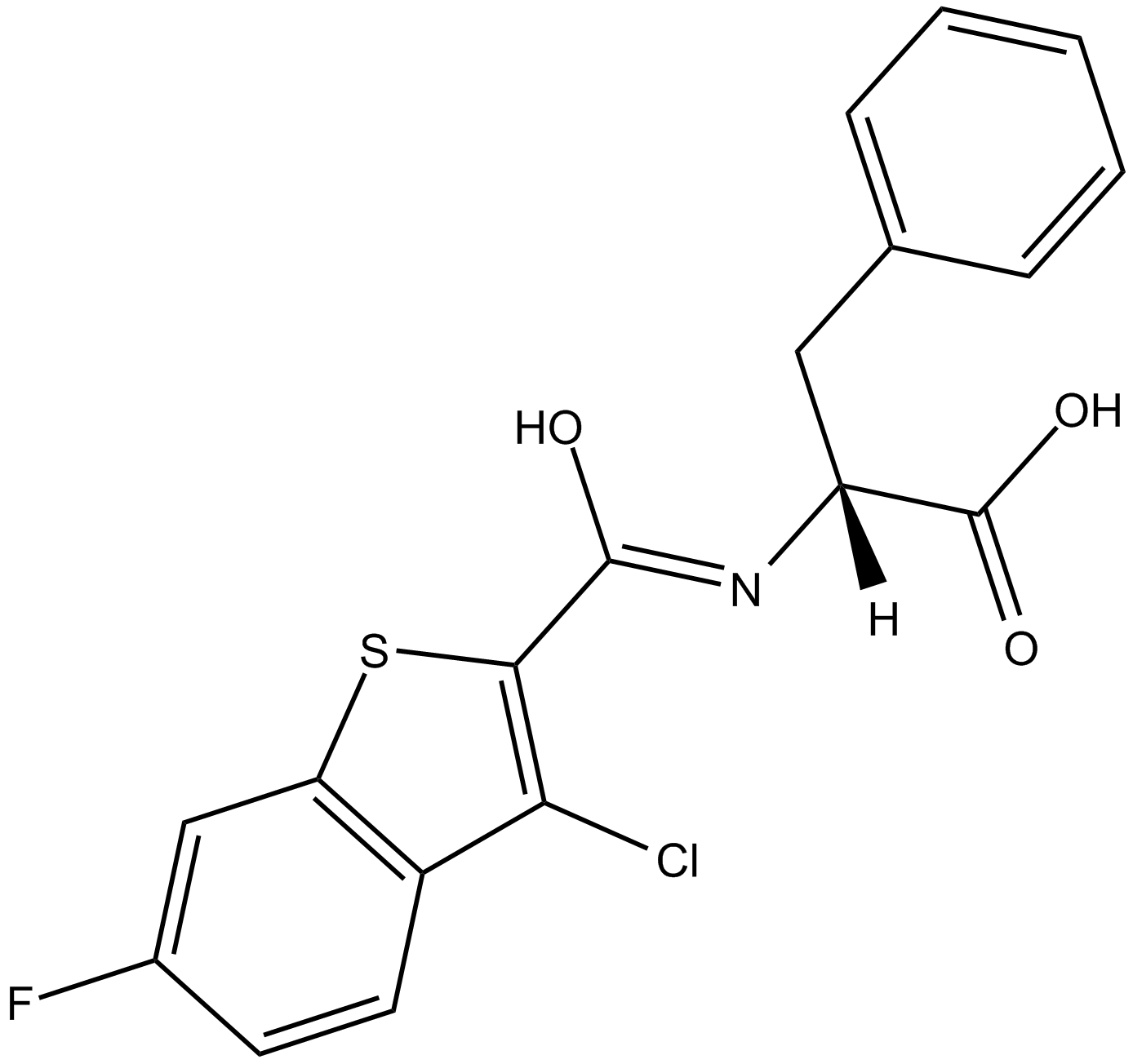 B5752 CU CPT 4a2 CitationSummary: TLR3 inhibitor
B5752 CU CPT 4a2 CitationSummary: TLR3 inhibitor -
 B5753 CU CPT 22Summary: toll-like receptor 1/2 (TLR1/2) inhibitor
B5753 CU CPT 22Summary: toll-like receptor 1/2 (TLR1/2) inhibitor -
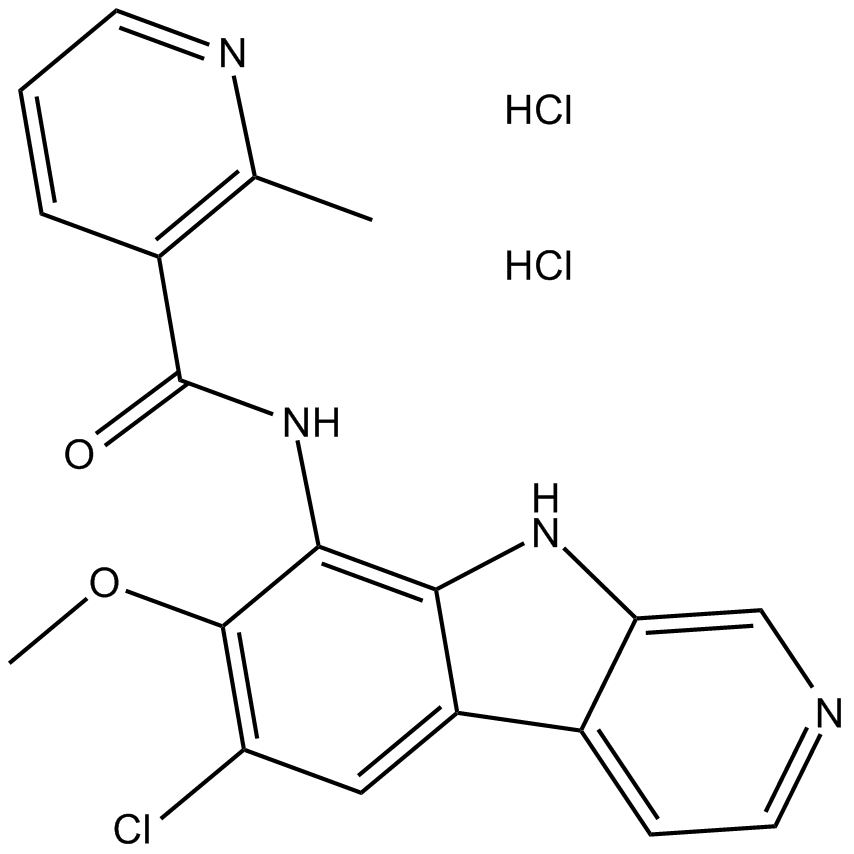 B5756 ML 120B dihydrochlorideSummary: IKK2-selective inhibitor
B5756 ML 120B dihydrochlorideSummary: IKK2-selective inhibitor -
 A1024 LEP (116-130) (mouse)Summary: An antiobesity hormone
A1024 LEP (116-130) (mouse)Summary: An antiobesity hormone -
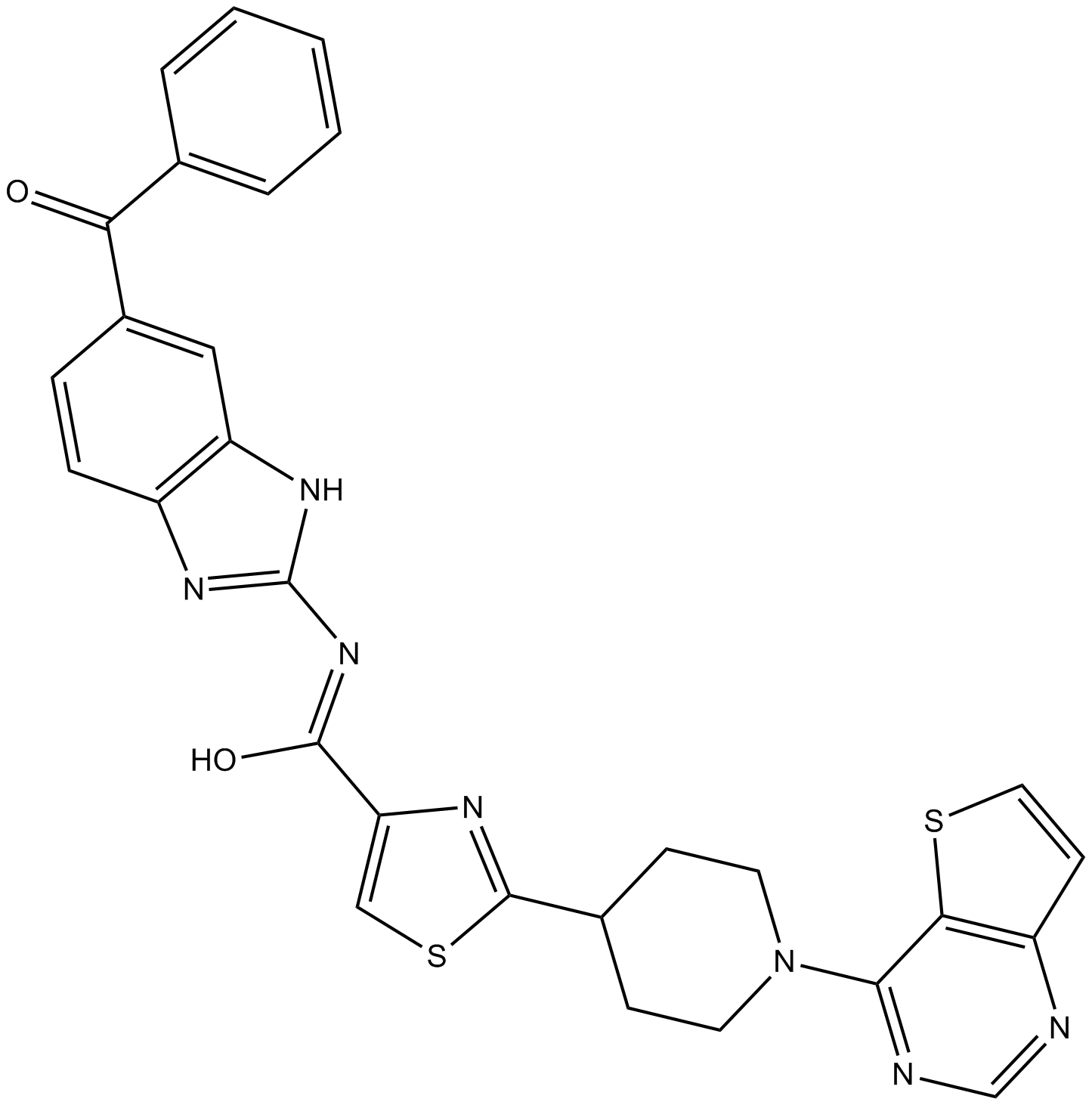 B4749 SC75741Summary: NF-κB inhibitor, potent
B4749 SC75741Summary: NF-κB inhibitor, potent -
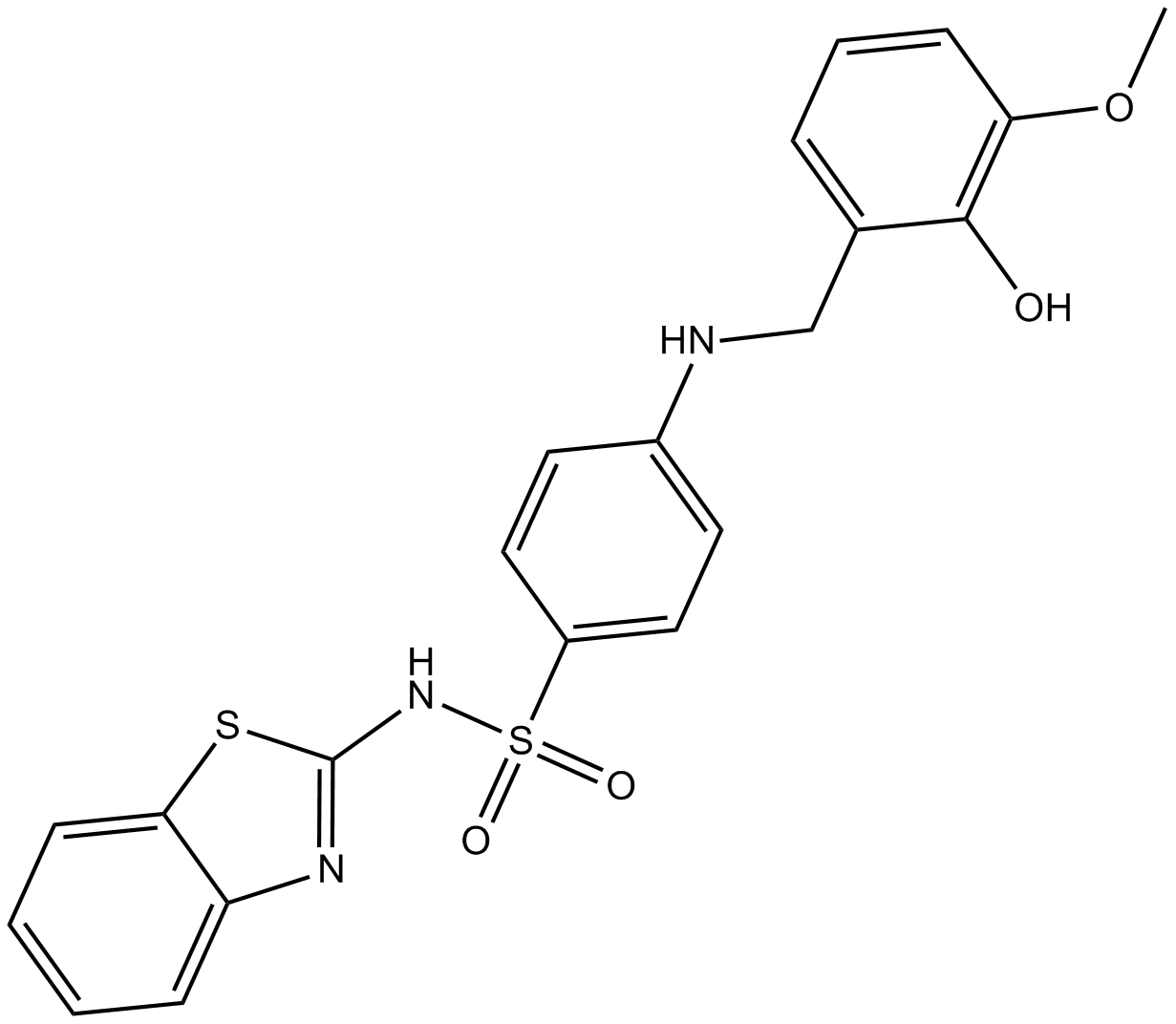 B8014 ML355Summary: 12-LOX inhibitor
B8014 ML355Summary: 12-LOX inhibitor -
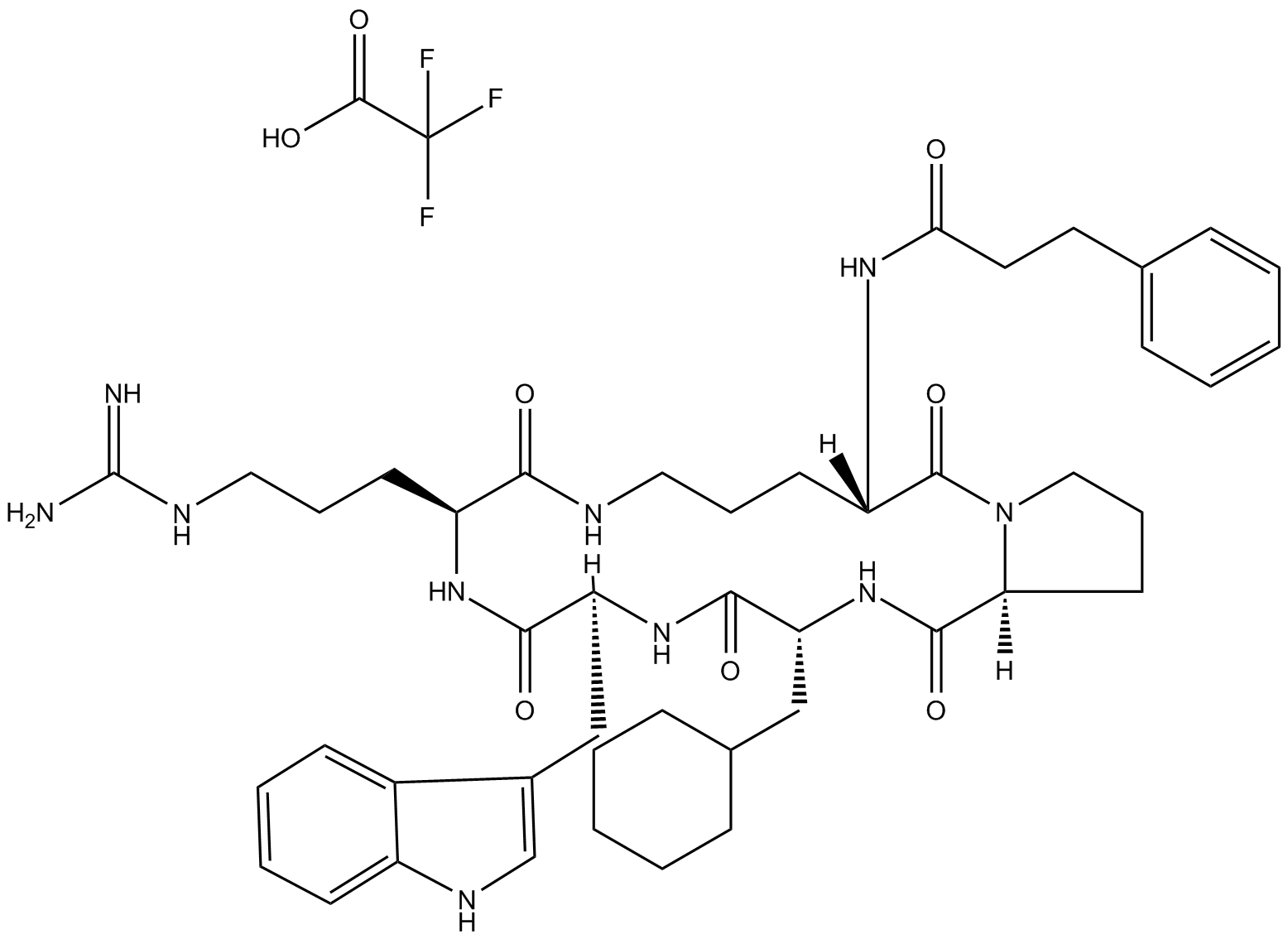 B7787 PMX 205 TrifluoroacetateTarget: C5a receptorsSummary: C5a receptor peptide antagonist
B7787 PMX 205 TrifluoroacetateTarget: C5a receptorsSummary: C5a receptor peptide antagonist -
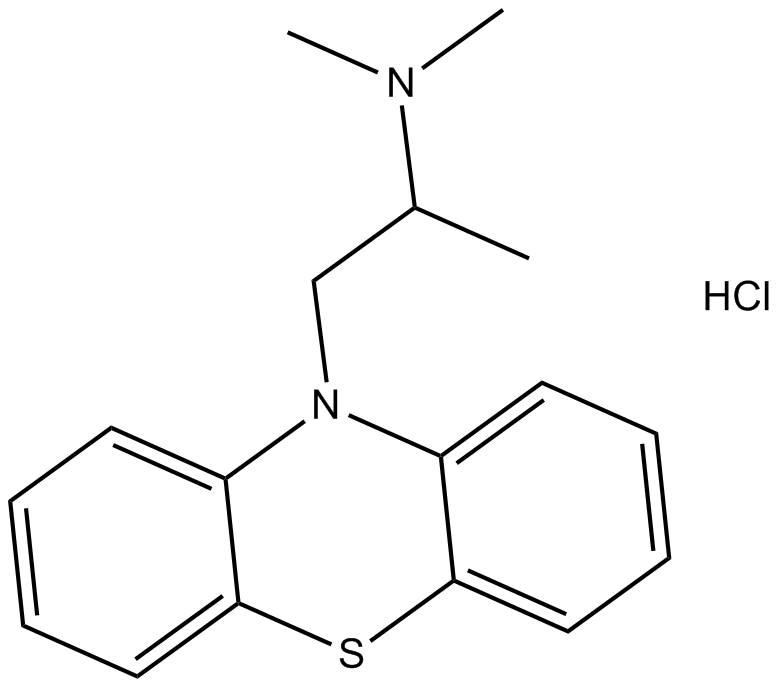 B4784 Promethazine HClSummary: histamine H1 receptor antagonist
B4784 Promethazine HClSummary: histamine H1 receptor antagonist -
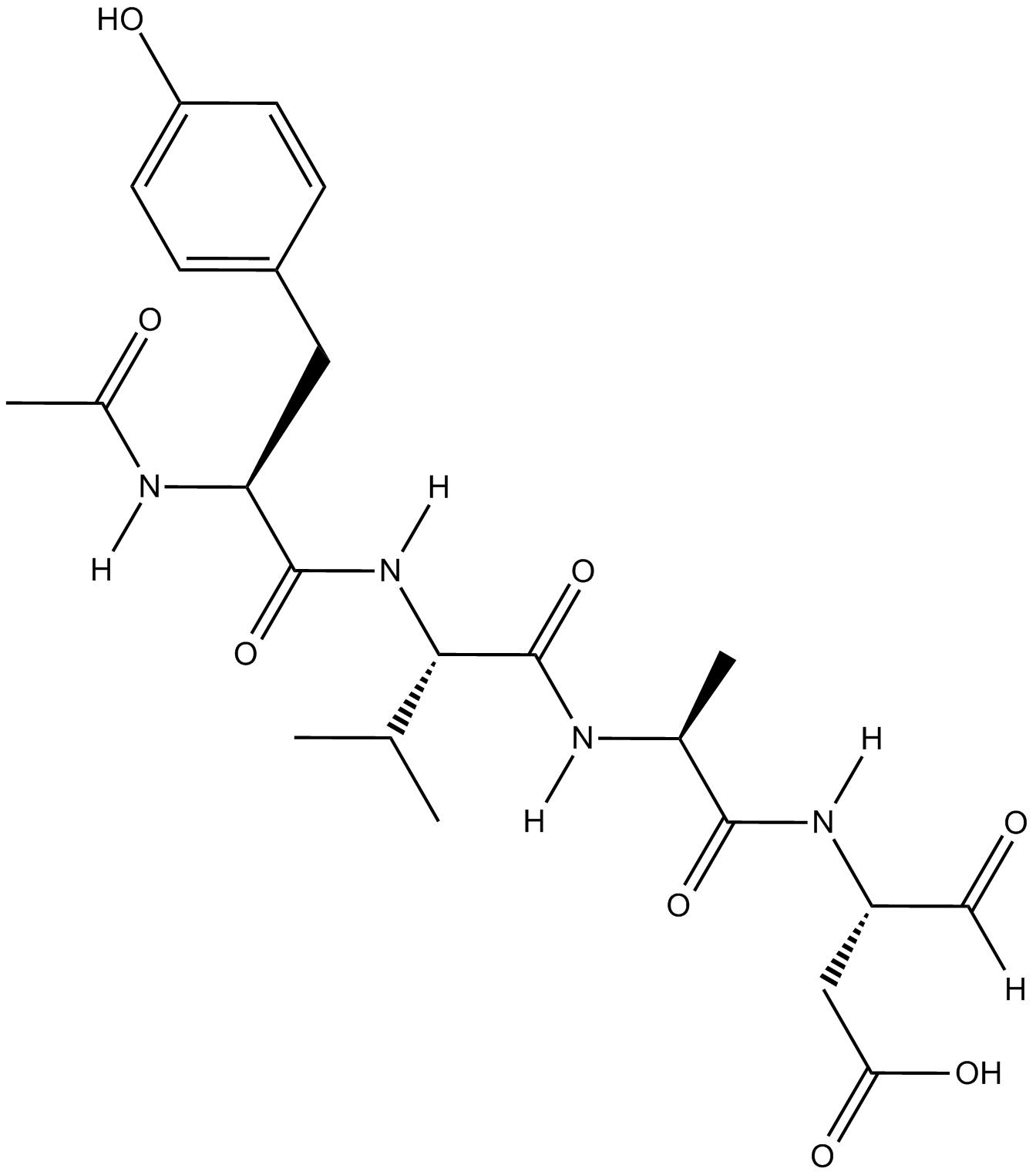 A8954 Ac-YVAD-CHO1 CitationTarget: CaspasesSummary: Selective inhibitor of interleukin-1β converting enzyme (ICE; Caspase-1)
A8954 Ac-YVAD-CHO1 CitationTarget: CaspasesSummary: Selective inhibitor of interleukin-1β converting enzyme (ICE; Caspase-1)


