Curcumin
Curcumin (CAS 458-37-7) is a polyphenolic natural compound, functioning as a specific inhibitor of acetyltransferases in both histone and non-histone proteins. Curcumin can suppress transcriptional activation and regulate gene expression through modulation of histone acetylation status, as well as affect the acetylation of other non-histone substrates. It is also reported to exert anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-proliferative, and anti-angiogenic activities. Curcumin stabilizes Nrf2 protein by inducing cysteine modification of Keap1, thereby modulating antioxidant defense mechanisms.
In Raji cell lines, curcumin demonstrates inhibitory effects with an IC50 of 24.1 ± 2.0 µM.
In pharmaceutical and biochemical research, curcumin is widely used for studies related to epigenetic regulation, inflammation, oxidative stress, cancer biology, and as a reference compound for exploring acetyltransferase inhibition.
- 1. Aimei Li, Xue Tian, et al. "Alkaline phosphatase-responsive peptide amphiphiles promote the apoptosis of HER2-positive breast cancer cells via increased drug accumulation." Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects. Volume 718, 5 August 2025, 136848.
- 2. Jiamin Qin, Guojuan Fan, et al. "Dynamic Covalent Bond-Based Nanoassembly of Curcumin to Enhance the Selective Photothermal Therapy for Tumor Treatment." Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Mar 30:20:3861-3875 PMID: 40181832
- 3. Maryam Khosravi. "Forward and Reverse Genetic Approaches to Studying Ciliopathy in Zebrafish." University College London.2019.
- 4. Byrd SK. "Apoptosis as the focus of an authentic research experience in a cell physiology laboratory. Adv Physiol Educ." 2016 Jun;40(2):257-64. PMID: 27231261
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 368.39 |
| Cas No. | 458-37-7 |
| Formula | C21H20O6 |
| Synonyms | Diferuloylmethane, Natural Yellow 3, Turmeric yellow |
| Solubility | ≥36.8 mg/mL in DMSO; insoluble in H2O; ≥3.5 mg/mL in EtOH with gentle warming and ultrasonic |
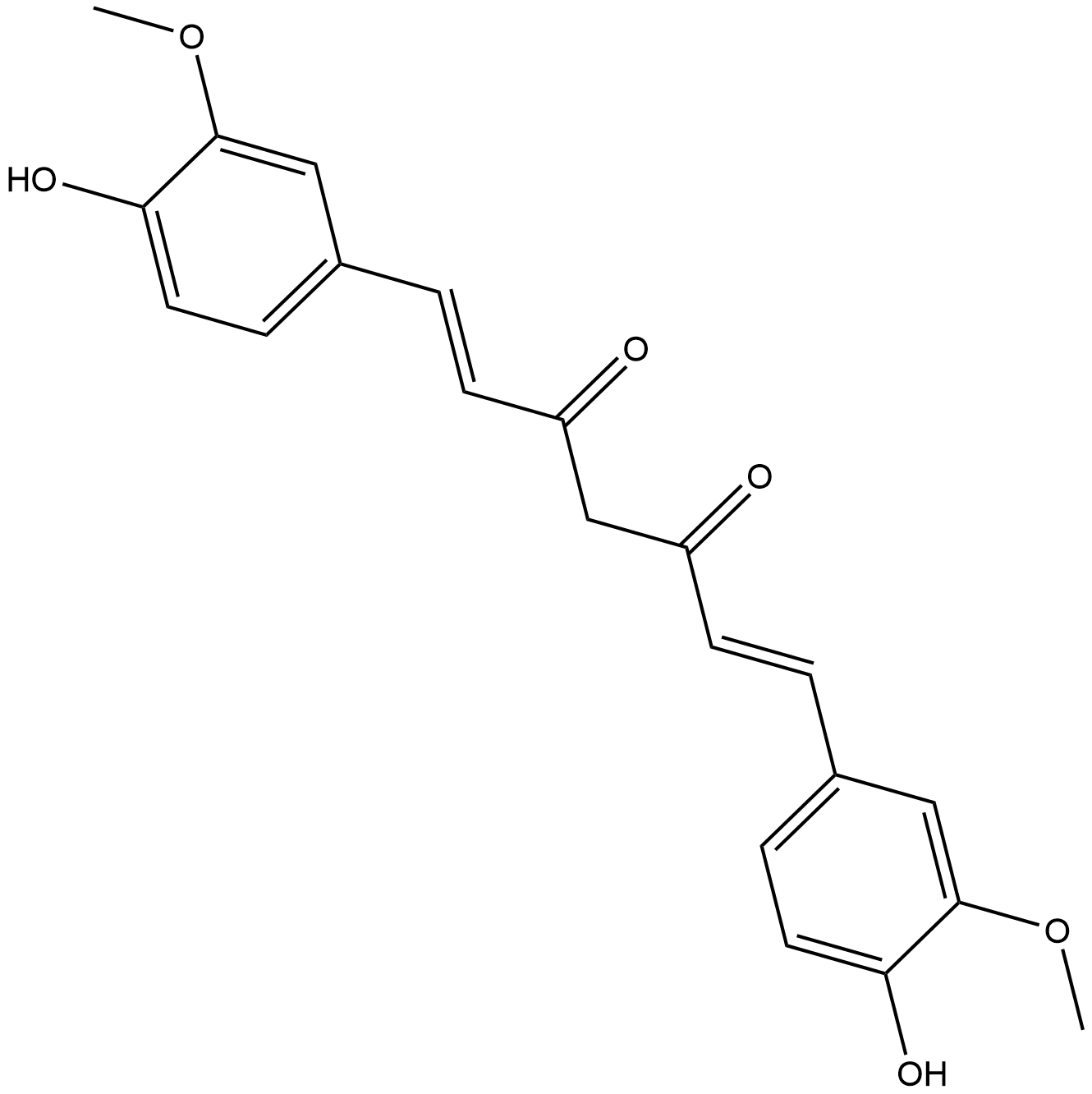
| Chemical Name | (1E,6E)-1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | COc(cc(/C=C/C(CC(/C=C/c(cc1)cc(OC)c1O)=O)=O)cc1)c1O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment:[1] | |
|
Cell lines |
B16-R melanoma cells resistant to doxorubicin |
|
Reaction Conditions |
1 ~ 200 μM curcumin for 24, 36 or 48 h incubation |
|
Applications |
Curcumin was found to be cytotoxic in vitro for B16-R melanoma cells resistant to doxorubicin either cultivated as monolayers (1 ~ 100 μM) or grown in three-dimensional cultures (1 ~ 200 μM). The cytotoxic effect observed in the 2 culture types was related to the induction of programmed cell death. |
| Animal experiment:[1] | |
|
Animal models |
Female B6D2F1 mice (6 ~ 8 weeks old) challenged subcutaneously with B16-R melanoma cells |
|
Dosage form |
25 mg/kg Once daily by intraperitoneal injection |
|
Applications |
The combination treatment consisting of curcumin and soluble B16-R proteins resulted in substantial inhibition of growth of B16-R melanoma, whereas each treatment by itself showed little effect. Moreover, animals receiving the combination therapy exhibited an enhancement of their humoral anti-soluble B16-R protein immune response and a significant increase in their median survival time. Therefore, curcumin may provide a valuable tool for the development of a therapeutic combination against the melanoma. |
|
Note |
The technical data provided above is for reference only. |
|
References: 1. Odot J, Albert P, Carlier A, et al. In vitro and in vivo anti-tumoral effect of curcumin against melanoma cells. International Journal of Cancer, 2004, 111(3): 381-387. |
|
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure