Rotenone
Rotenone (CAS 83-79-4)is an inhibitor of mitochondrial Complex I in the electron transport chain with an IC50 of 1.7–2.2 μM. By blocking electron transfer in Complex I, rotenone disrupts the mitochondrial proton gradient, impairing oxidative phosphorylation and leading to the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). In cellular research, rotenone is commonly utilized to investigate mitochondrial dysfunction, apoptosis, and autophagy pathways. Treatment of cultured cells, such as neuronal cell line SH-SY5Y, demonstrates rotenone-induced apoptosis mediated by caspase activation and activation of stress-responsive MAP kinase pathways, including p38 MAPK and JNK. Rotenone treatment also facilitates autophagic responses and ROS-mediated cell death in transformed and cancer cell lines, making it useful for mechanistic studies on mitochondria-driven cellular damage.
References:
[1]. Chen Y, McMillan-Ward E, Kong J, et al. Mitochondrial electron-transport-chain inhibitors of complexes I and II induce autophagic cell death mediated by reactive oxygen species. J Cell Sci, 2007, 120(Pt 23): 4155-4166.
[2]. Newhouse K, Hsuan SL, Chang SH, et al. Rotenone-induced apoptosis is mediated by p38 and JNK MAP kinases in human dopaminergic SH-SY5Y cells. Toxicol Sci, 2004, 79(1): 137-146.
[3]. Borland MK, Trimmer PA, Rubinstein JD, et al. Chronic, low-dose rotenone reproduces Lewy neurites found in early stages of Parkinson's disease, reduces mitochondrial movement and slowly kills differentiated SH-SY5Y neural cells. Mol Neurodegener, 2008, 3: 21.
- 1. Jie Gao, Liya Wang, et al. "ALDH2 Attenuates Blood-Brain Barrier Injury Induced by Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion via Alleviating ROS/NLRP3 Inflammasome Axis." Neurochem Res. 2025 Jul 3;50(4):224 PMID: 40608173
- 2. Wang Jiahui, Yu Xiang, et al. "The mitochondrial DNAJC co-chaperone TCAIM reduces α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase protein levels to regulate metabolism." Molecular Cell Volume 85, Issue 3P638-651.E9, February 06, 2025 PMID: 39889707
- 3. Jiawei Yan, Xin Zhang, et al. "Macrophage NRF1 promotes mitochondrial protein turnover via the ubiquitin proteasome system to limit mitochondrial stress and inflammation." Cell Rep. 2024 Sep 25;43(10):114780 PMID: 39325625
- 4. Jiahui Wang, Yuping Li, et al. "Effect of NLRP3 gene knockdown on pyroptosis and ferroptosis in diabetic cardiomyopathy injury." BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024 Jul 10;24(1):351 PMID: 38987672
- 5. Jun Xiao, Shuang Wang, et al. "25-Hydroxycholesterol regulates lysosome AMP kinase activation and metabolic reprogramming to educate immunosuppressive macrophages." Immunity. 2024 May 14;57(5):1087-1104.e7. PMID: 38640930
- 6. Chun-Feng Liu, et al. "Gut microbiota dysbiosis contributes to α-synuclein-related pathology associated with C/EBPβ/AEP signaling activation in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease." Neural Regen Res. 2024 Sep 1;19(9):2081-2088. PMID: 38227539
- 7. Ji-Man Park, Da-Hye Lee, et al. "Redefining the role of AMPK in autophagy and the energy stress response." Nat Commun. 2023 May 24;14(1):2994. PMID: 37225695
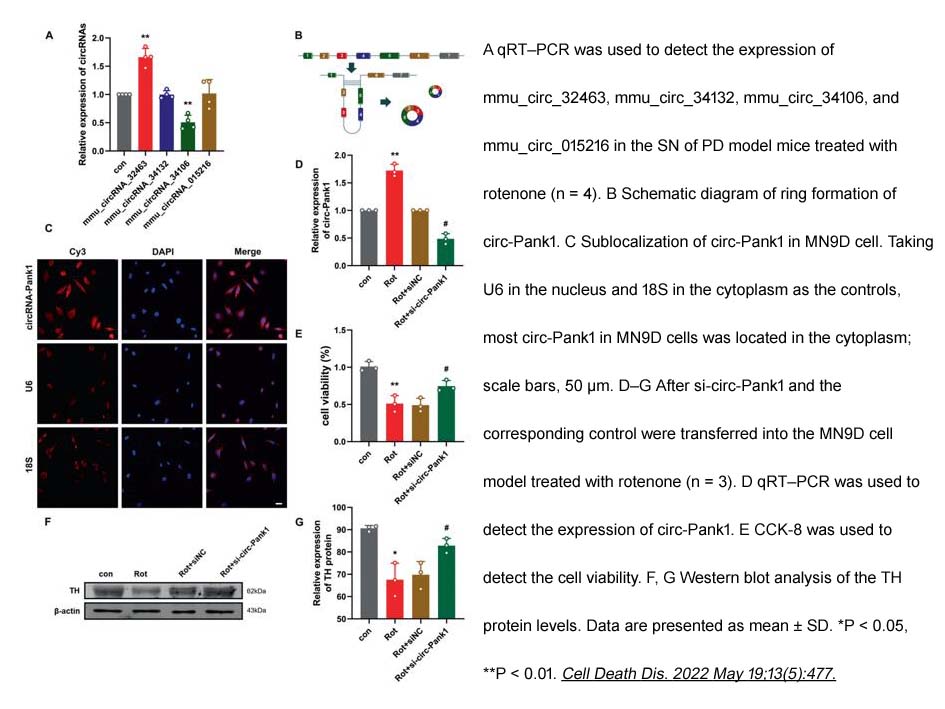
- 8. Qing Liu, Qiyao Li, et al. "circ-Pank1 promotes dopaminergic neuron neurodegeneration through modulating miR-7a-5p/α-syn pathway in Parkinson's disease." Cell Death Dis. 2022 May 19;13(5):477. PMID: 35589691
- 9. Fangfang Wang, Zhang Dan, et al. "ALCAM regulates multiple myeloma chemoresistant side population." Cell Death Dis. 2022 Feb 10;13(2):136. PMID: 35145058
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at RT |
| M.Wt | 394.42 |
| Cas No. | 83-79-4 |
| Formula | C23H22O6 |
| Solubility | insoluble in EtOH; insoluble in H2O; ≥77.6 mg/mL in DMSO |
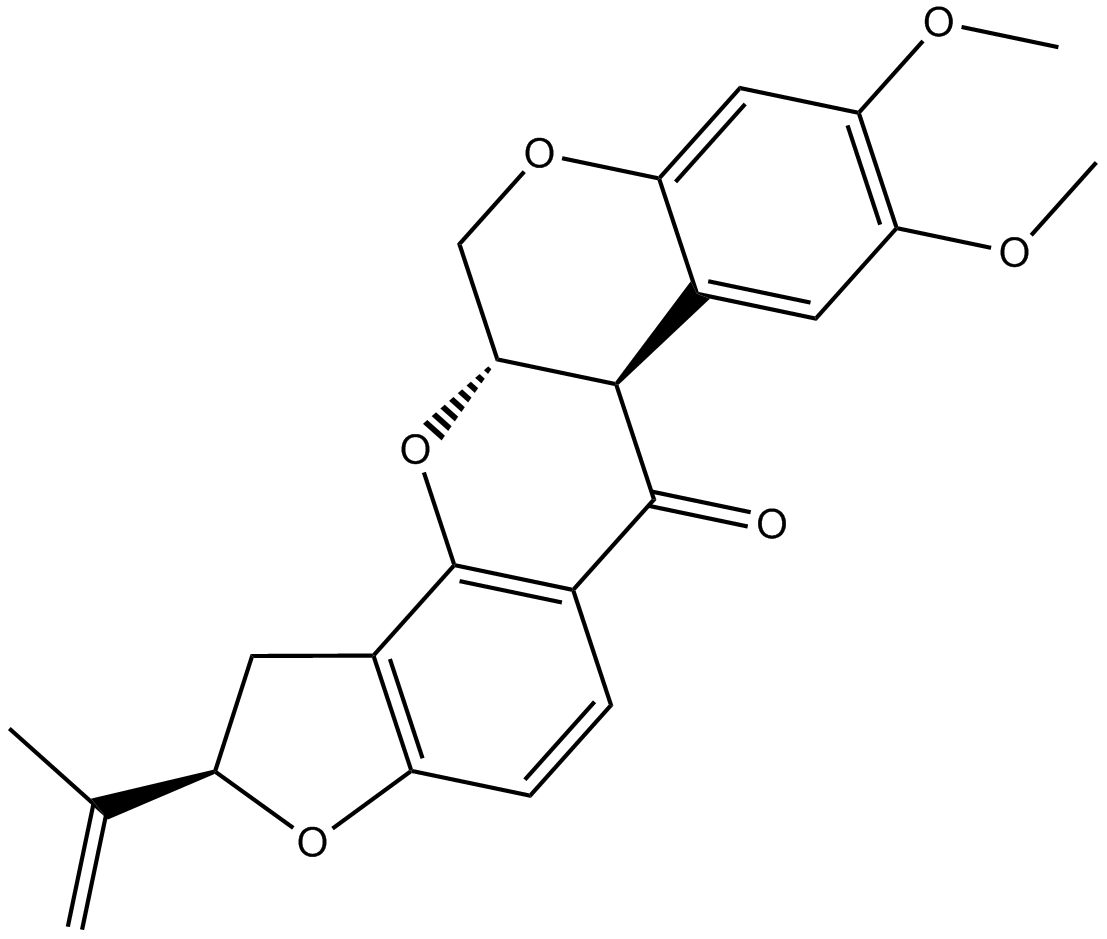
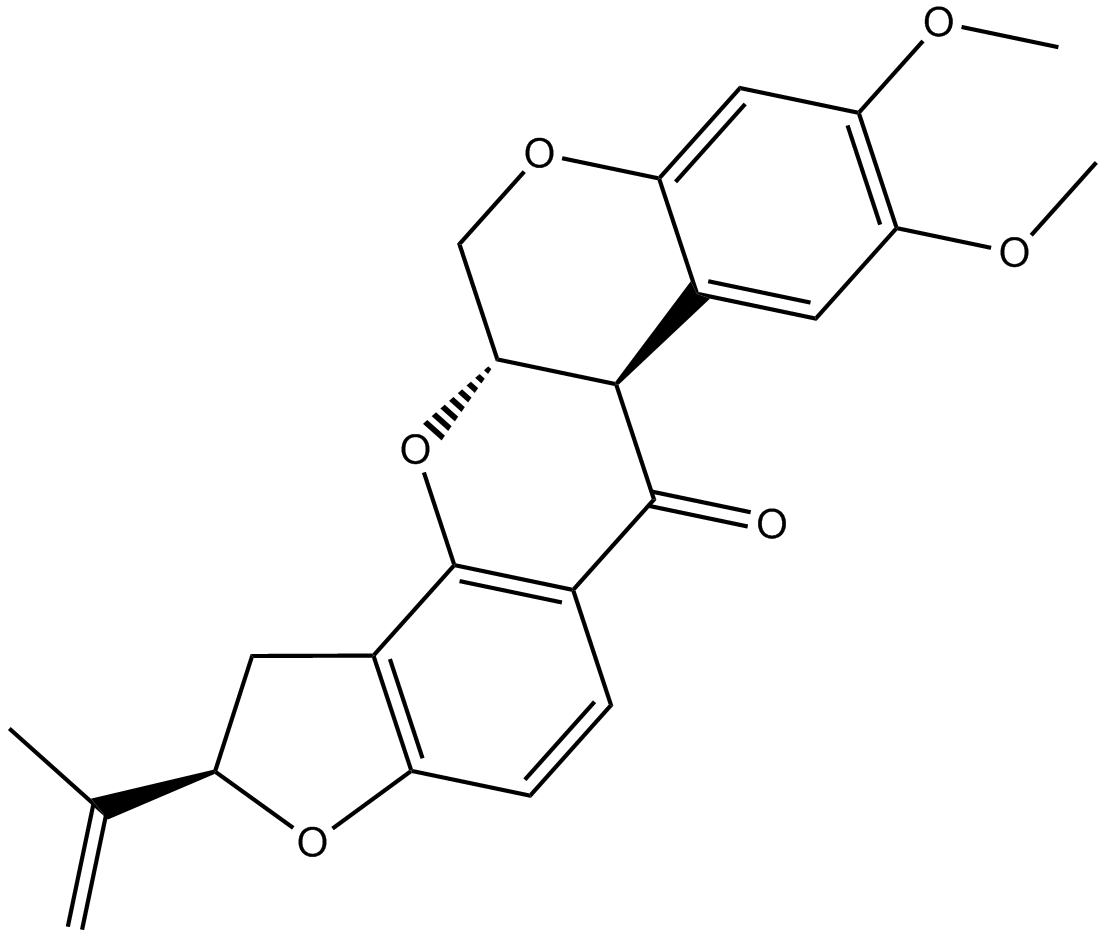
| Chemical Name | (2R,6aS,12aS)-8,9-dimethoxy-2-(prop-1-en-2-yl)-1,2,12,12a-tetrahydrochromeno[3,4-b]furo[2,3-h]chromen-6(6aH)-one |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | O=C1C=2C(=C3C(O[C@@H](C(C)=C)C3)=CC2)O[C@]4([C@@]1(C=5C(OC4)=CC(OC)=C(OC)C5)[H])[H] |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment [1]: | |
|
Cell lines |
differentiated SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells |
|
Preparation method |
The solubility of this compound in DMSO is ≥77.6 mg/mL. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37℃ for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while. Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. |
|
Reacting condition |
50 nM; 21 days |
|
Applications |
In differentiated SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells, Rotenone (50 nM) produced a biphasic survival curve with ~40% loss by 6 days and a second decline to ~60% loss between 18 and 21 days. Mitochondrial movement velocities were reduced at 8 days. |
| Animal experiment [2]: | |
|
Animal models |
20-25 weekold female BALB/c mice |
|
Dosage form |
(rotenone: 0.35 mg/kg; DMSO: 9.86 mg/kg) or vehicle (DMSO: 9.86 mg/kg); injected into the right-side nasal cavity of mice; once a day for 2 weeks |
|
Application |
In mice, rotenone attenuated the olfactory function and retarded the inhibitory input into the mitral cells, which are output neurons in the olfactory bulb (OB). Rotenone also caused neurite degeneration of DA neurons in the substantia nigra. |
|
Other notes |
Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
|
References: [1]. Borland MK, Trimmer PA, Rubinstein JD, et al. Chronic, low-dose rotenone reproduces Lewy neurites found in early stages of Parkinson's disease, reduces mitochondrial movement and slowly kills differentiated SH-SY5Y neural cells. Mol Neurodegener, 2008, 3: 21. [2]. Sasajima H1, Miyazono S, Noguchi T, et al. Intranasal Administration of Rotenone to Mice Induces Dopaminergic Neurite Degeneration of Dopaminergic Neurons in the Substantia Nigra. Biol Pharm Bull. 2017;40(1):108-112. |
|
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure
Related Biological Data

Related Biological Data