Membrane Transporter/Ion Channel

Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins which allow the flow of ions across the membrane. The ion channels can be broadly grouped into six families including calcium channels, chloride channels, potassium channels, sodium channels, gap junction proteins and porins. Not all ion channels are gated, such as certain type of K+ and Cl– channels, transient receptor potential superfamily of cation channels, the ryanodine receptors and the IP3 receptors, but most Na+, K+, Ca2+ and some Cl– channels are all gated by voltage. Ligand-gated channels are regulated in response to ligand binding (e.g. neurotransmitters signaling). These ligand-gated neurotransmitter receptors are known as ionotropic receptors. Various neurotransmitters couple to ionotropic receptors such as glutamate, acetylcholine, glycine, GABA, and serotonin.
-
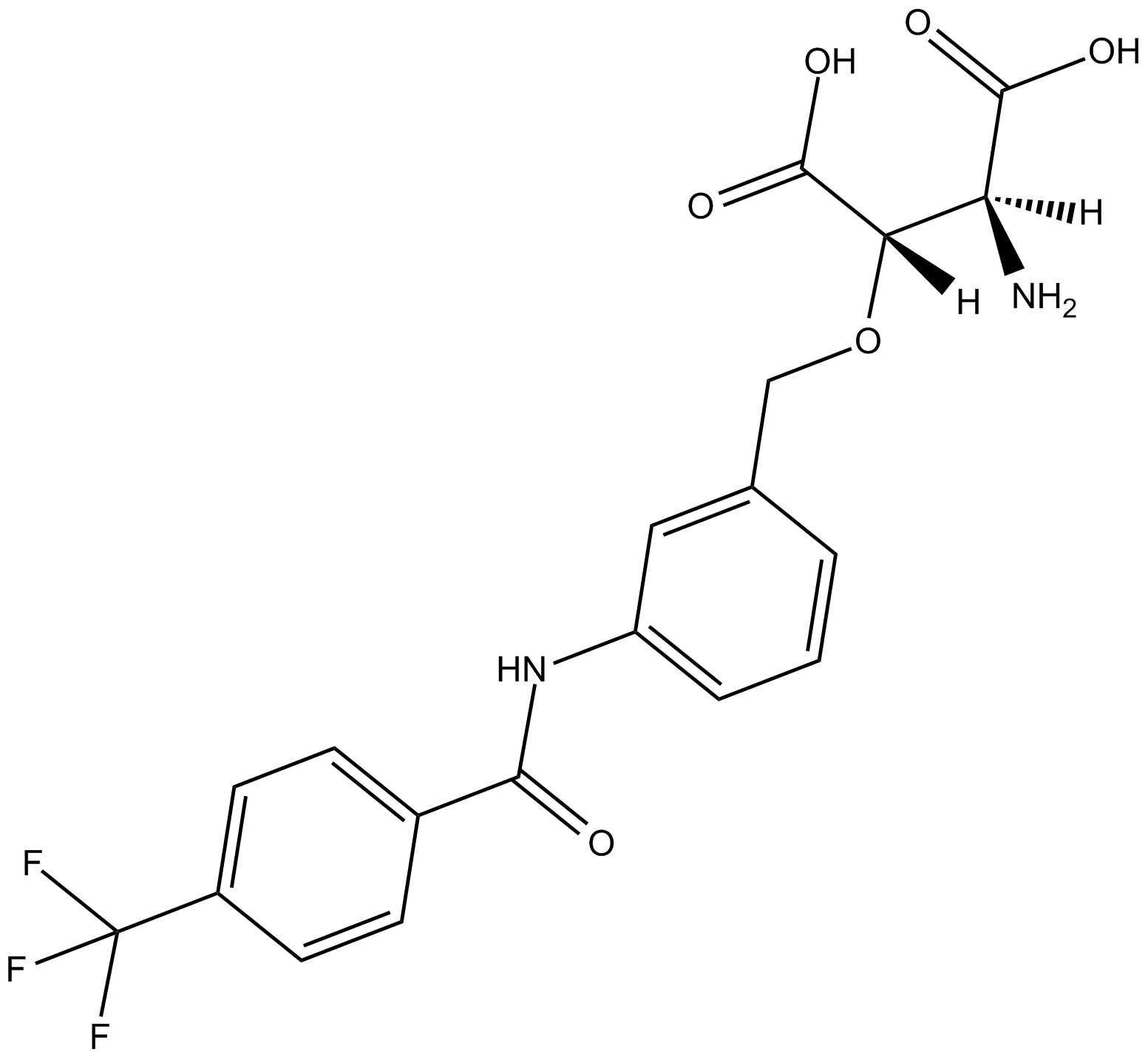 B5313 TFB-TBOASummary: glial glutamate transporter EAAT1 and EAAT2 inhibitor
B5313 TFB-TBOASummary: glial glutamate transporter EAAT1 and EAAT2 inhibitor -
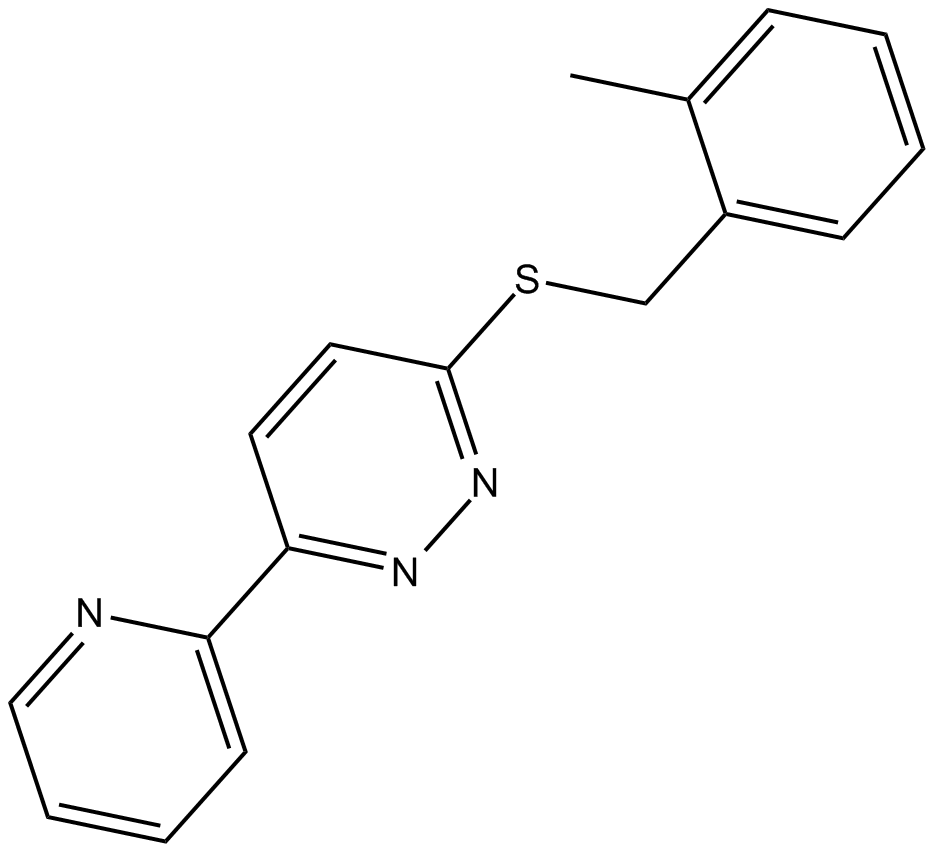 B5805 LDN 212320Summary: increases expression of glutamate transporter EAAT2
B5805 LDN 212320Summary: increases expression of glutamate transporter EAAT2 -
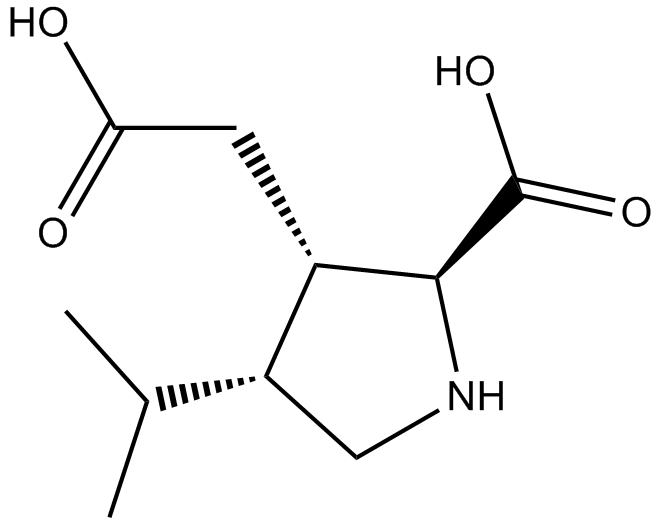 B6208 Dihydrokainic acidSummary: EAAT2(GLT1)-selective non-transportable inhibitor of L-glutamate and L-aspartate uptake
B6208 Dihydrokainic acidSummary: EAAT2(GLT1)-selective non-transportable inhibitor of L-glutamate and L-aspartate uptake -
 B6218 L-(-)-threo-3-Hydroxyaspartic acidSummary: EAAT1-4 inhibitor/non-transportable EAAT5 inhibitor
B6218 L-(-)-threo-3-Hydroxyaspartic acidSummary: EAAT1-4 inhibitor/non-transportable EAAT5 inhibitor -
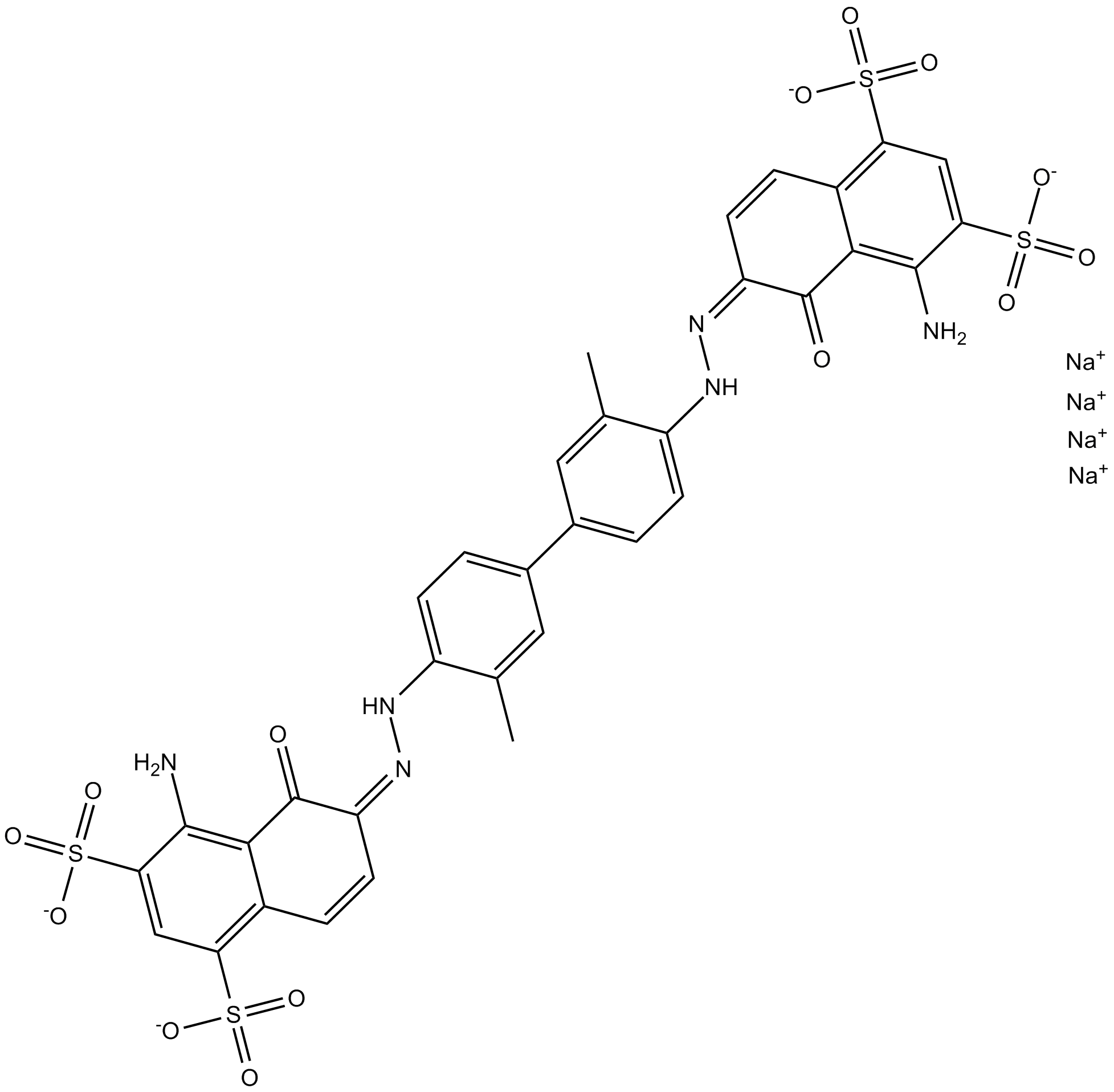 B6472 Evans Blue tetrasodium saltSummary: L-glutamate uptake inhibitor,dye used to detect cell viability and plasma membrane integrity
B6472 Evans Blue tetrasodium saltSummary: L-glutamate uptake inhibitor,dye used to detect cell viability and plasma membrane integrity -
 B6531 MPDCSummary: inhibitor of the Na+-dependent high-affinity synaptosomal glutamate transporter
B6531 MPDCSummary: inhibitor of the Na+-dependent high-affinity synaptosomal glutamate transporter -
 B6982 (±)-HIP-ASummary: excitatory amino acid transporter (EAAT) blocker
B6982 (±)-HIP-ASummary: excitatory amino acid transporter (EAAT) blocker -
 B6983 (±)-HIP-BSummary: excitatory amino acid transporter (EAAT) blocker
B6983 (±)-HIP-BSummary: excitatory amino acid transporter (EAAT) blocker -
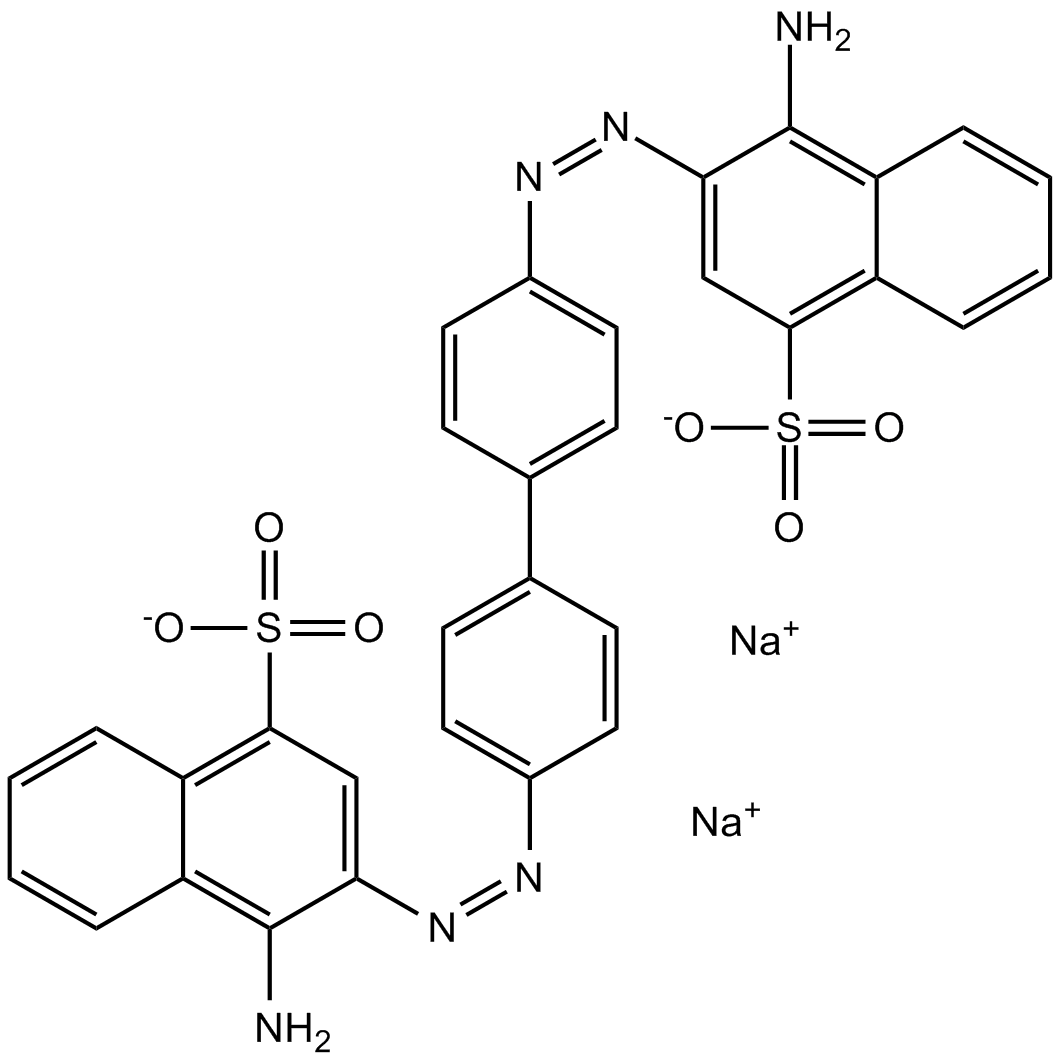 B7766 Congo RedSummary: VGlut inhibitor/dye for amyloidosis,amyloid in the cell walls of plants and fungi,outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria
B7766 Congo RedSummary: VGlut inhibitor/dye for amyloidosis,amyloid in the cell walls of plants and fungi,outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria -
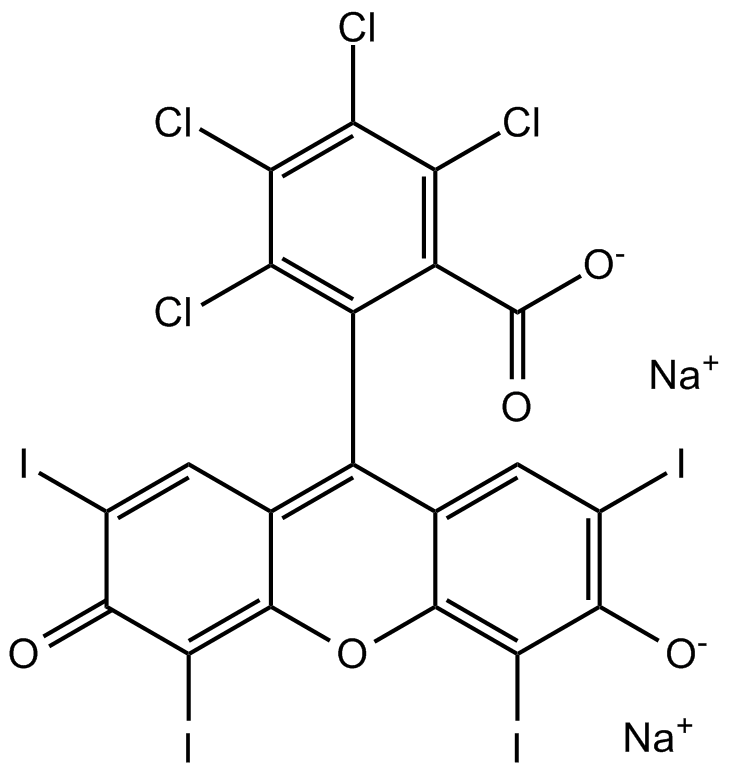 B7767 Rose BengalSummary: VGlut and vesicular monoamine transporter (VMAT) inhibitor
B7767 Rose BengalSummary: VGlut and vesicular monoamine transporter (VMAT) inhibitor

