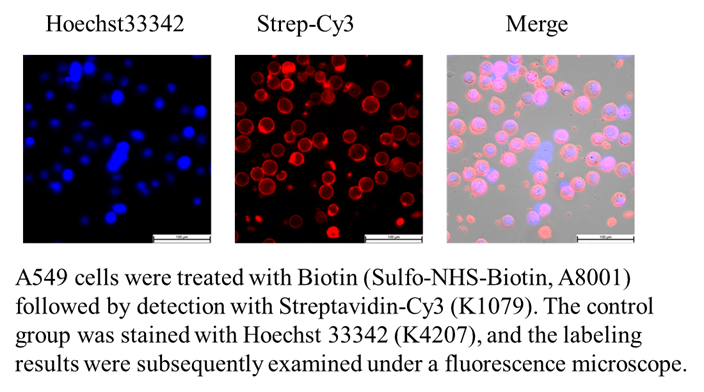
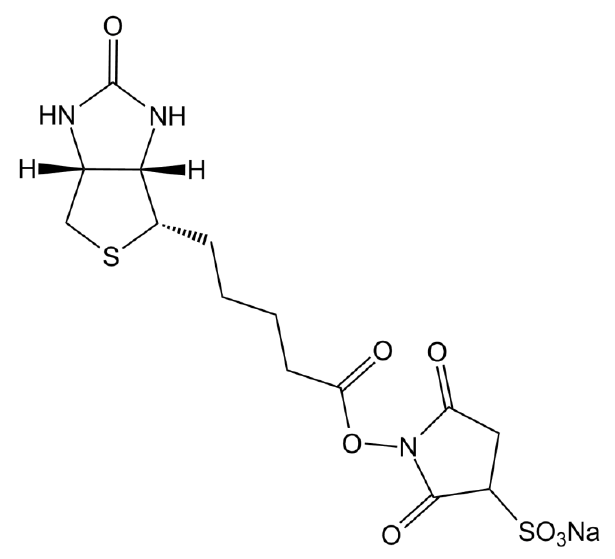
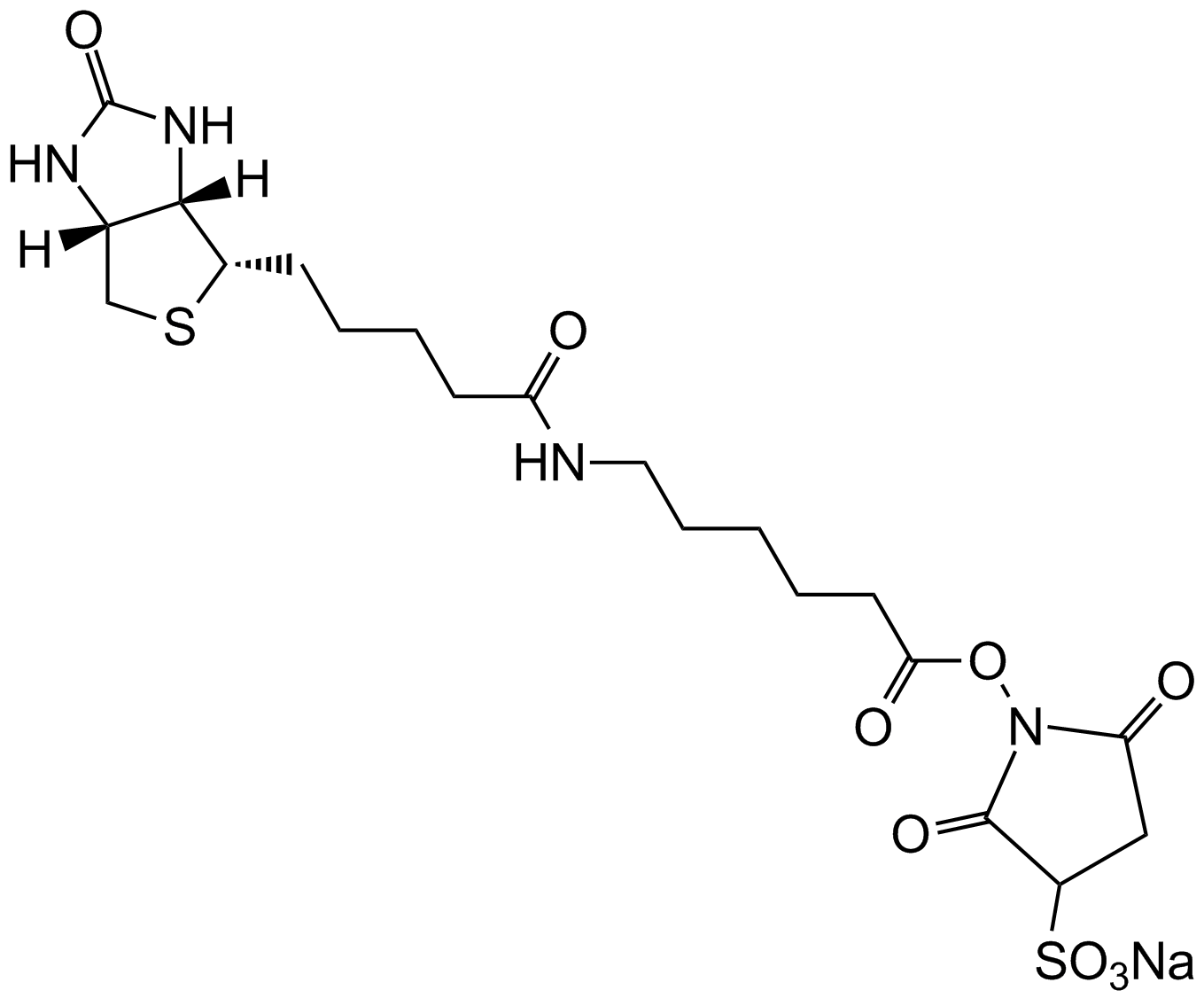
Sulfo-NHS-Biotin
Sulfo-NHS-Biotin is a water-soluble biotinylation reagent frequently utilized in biochemical research for labeling proteins and other biomolecules. Chemically, it contains an N-hydroxysulfosuccinimide (Sulfo-NHS) ester group, allowing for covalent linkage through amine-reactive chemistry. Upon interaction with primary amines on lysine residues or peptide N-termini, the Sulfo-NHS ester undergoes nucleophilic attack, forming stable amide bond conjugates and releasing an NHS derivative. Its solubility in aqueous solutions facilitates direct addition to biological samples without prior dissolution in organic solvents. Common research applications include protein purification, affinity chromatography, immunoprecipitation assays, and detection in protein interaction studies.
Reference
Bioconjugate Techniques , 2nd ed. By Greg T.Hermanson (Pierce Biotechnology, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Rockford, IL). Academic Press (an imprint of Elsevier): London, Amsterdam, Burlington, San Diego . 2008. ISBN 978-0-12-370501-3.
- 1. Sandra Peña-Díaz, Joseph D. Chao, et al. "Glycogen synthase kinase 3 inhibition controls Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection." VOLUME 27, ISSUE 8, 110555, AUGUST 16, 2024
- 2. Chao Wei, Wei Jiang, et al. "Brain endothelial GSDMD activation mediates inflammatory BBB breakdown." Nature. 2024 May;629(8013):893-900. PMID: 38632402
- 3. Patrick Needham, Richard C Page, et al. "Phage-layer interferometry: a companion diagnostic for phage therapy and a bacterial testing platform." Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 12;14(1):6026. PMID: 38472239
- 4. Zhijun Lin, Mengyao Liu, et al. "A near-infrared fluorescence-enhancing plasmonic biosensing microarray identifies soluble PD-L1 and ICAM-1 as predictive checkpoint biomarkers for cancer immunotherapy" Biosensors and Bioelectronics. 15 November 2023, 115633.
- 5. Jonathan Perr, Andreas Langen, et al. "RNA binding proteins and glycoRNAs form domains on the cell surface for cell penetrating peptide entry" bioRvix. September 05, 2023.
- 6. Nathaniel M. Myers, Noelle K. Comolli, et al. "Optimization and modeling of PEGylated, hydrocortisone-17-butryate-loaded poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) microspheres" Wiley Online Library. 20 March 2023.
- 7. Udani S, Langerman J, et al. "Secretion encoded single-cell sequencing (SEC-seq) uncovers gene expression signatures associated with high VEGF-A secretion in mesenchymal stromal cells." bioRxiv 2023 Jan 08 PMID: 36711480
- 8. Le Wang, Song Huang, et al. "Bio-inspirited Three-Dimensional Hierarchical Micro/Nano-Structured Microdevice for Enhanced Capture and Effective Release of Circulating Tumor Cells." Chemical Engineering Journal. Volume 435, Part 1, 1 May 2022, 134762.
- 9. Jun Lin, Xiaoxiao Jiang, et al. "Hepatokine Pregnancy Zone Protein Governs the Diet‐Induced Thermogenesis Through Activating Brown Adipose Tissue." Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021 Nov;8(21):e2101991. PMID: 34514733
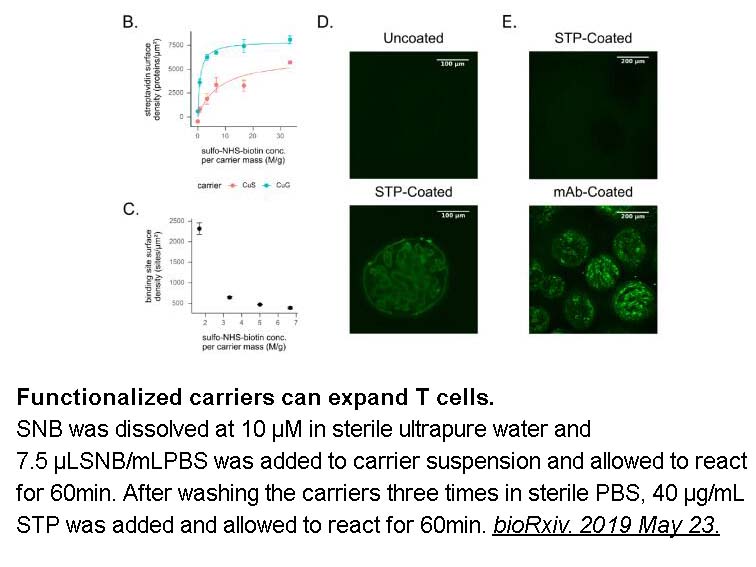
- 10. Nathan J. Dwarshuis, Hannah W. Song, et al. "Functionalized microcarriers improve T cell manufacturing by facilitating migratory memory T cell production and increasing CD4/CD8 ratio." bioRxiv. 2019 May 23.
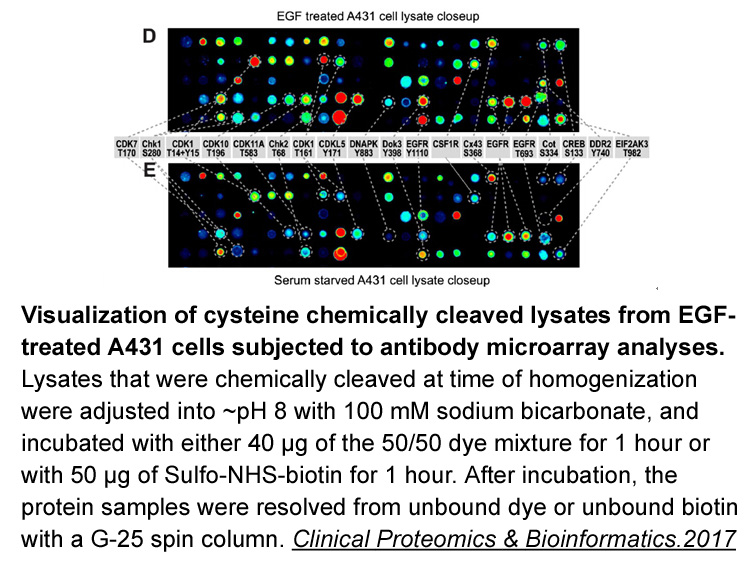
- 11. Lambert Yue, Christine Sam, et al. "Antibody microarray and immunoblotting analyses of the EGF signaling phosphorylation network in human A431 epidermoid carcinoma cells." Clinical Proteomics & Bioinformatics. 2017.
• Protein labeling—biotinylate antibodies to facilitate immobilization, purification or detection using streptavidin resins or probes
• Cell surface labeling—do not penetrate the plasma membrane, biotinylates only surface proteins of whole cells
• Amine-reactive—reacts with primary amines (-NH2), such as lysine side-chains or the N-terminal-amine
• Solubility—charged sulfo-NHS group increases reagent water solubility compared to ordinary NHS-ester compounds
• Irreversible—forms permanent amide bonds; spacer arm cannot be cleaved
• Very short—spacer arm is 13.5 angstroms; it consists of the native biotin valeric acid group only
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Desiccate at -20°CThe product is not stable in solution, please dissolve it immediately before use. |
| M.Wt | 443.4 |
| Cas No. | 119616-38-5 |
| Formula | C14H18N3NaO8S2 |
| Synonyms | Sulfo-NHS Biotin |
| Solubility | ≥22.17 mg/mL in DMSO; insoluble in EtOH; ≥16.8 mg/mL in H2O with ultrasonic |
| Chemical Name | sodium;1-[5-[(3aS,6aR)-2-oxo-1,3,3a,4,6,6a-hexahydrothieno[3,4-d]imidazol-4-yl]pentanoyloxy]-2,5-dioxopyrrolidine-3-sulfonate |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | [O-]S(C(CC(N1OC(CCCCC([C@H]2N3)SC[C@@H]2NC3=O)=O)=O)C1=O)(=O)=O.[Na+] |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Biotinylation method [1]: | |
|
Sample |
THUMPa protein |
|
Preparation method |
Soluble in water, DMSO or DMF. |
|
Reaction Conditions |
2 mM, room temperature for 30 min |
|
Applications |
Sulfo-NHS-biotin reagents were dissolved at 2 mM in a 50-mM K2HPO4/KH2PO4 buffer (pH 7.5) containing 50 mM of NaCl. They were immediately used in separated assays to modify 1.66 nmol of THUMPa protein. The labeling reactions were incubated 30 min at room temperature. The samples were then dialyzed for 15 min against a 50-mM K2HPO4/KH2PO4 buffer (pH 7.5) containing 50 mM of NaCl. TTotal biotin covalently bound to proteins was determined by an avidin-binding assay. |
|
References: [1]. Guillaume Gabant, Julie Augier and Jean Armengaud. Assessment of solvent residues accessibility using three Sulfo-NHS-biotin reagents in parallel: application to footprint changes of a methyltransferase upon binding its substrate. J. Mass Spectrom. 2008; 43: 360–370. |
|
| Description | Water-soluble biotinyltation reagent to attach biotin to primary amines | |||||
| Targets | ||||||
| IC50 | ||||||
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
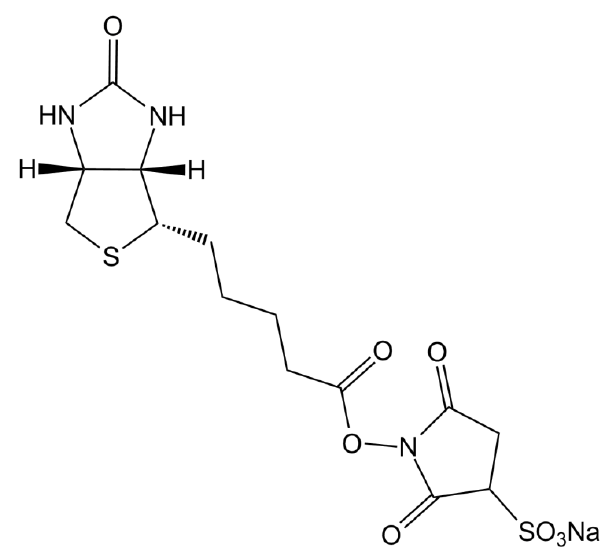
Chemical structure
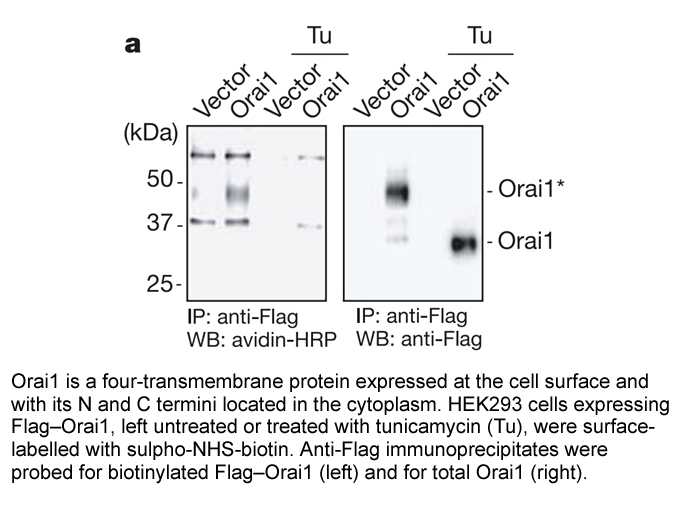
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data