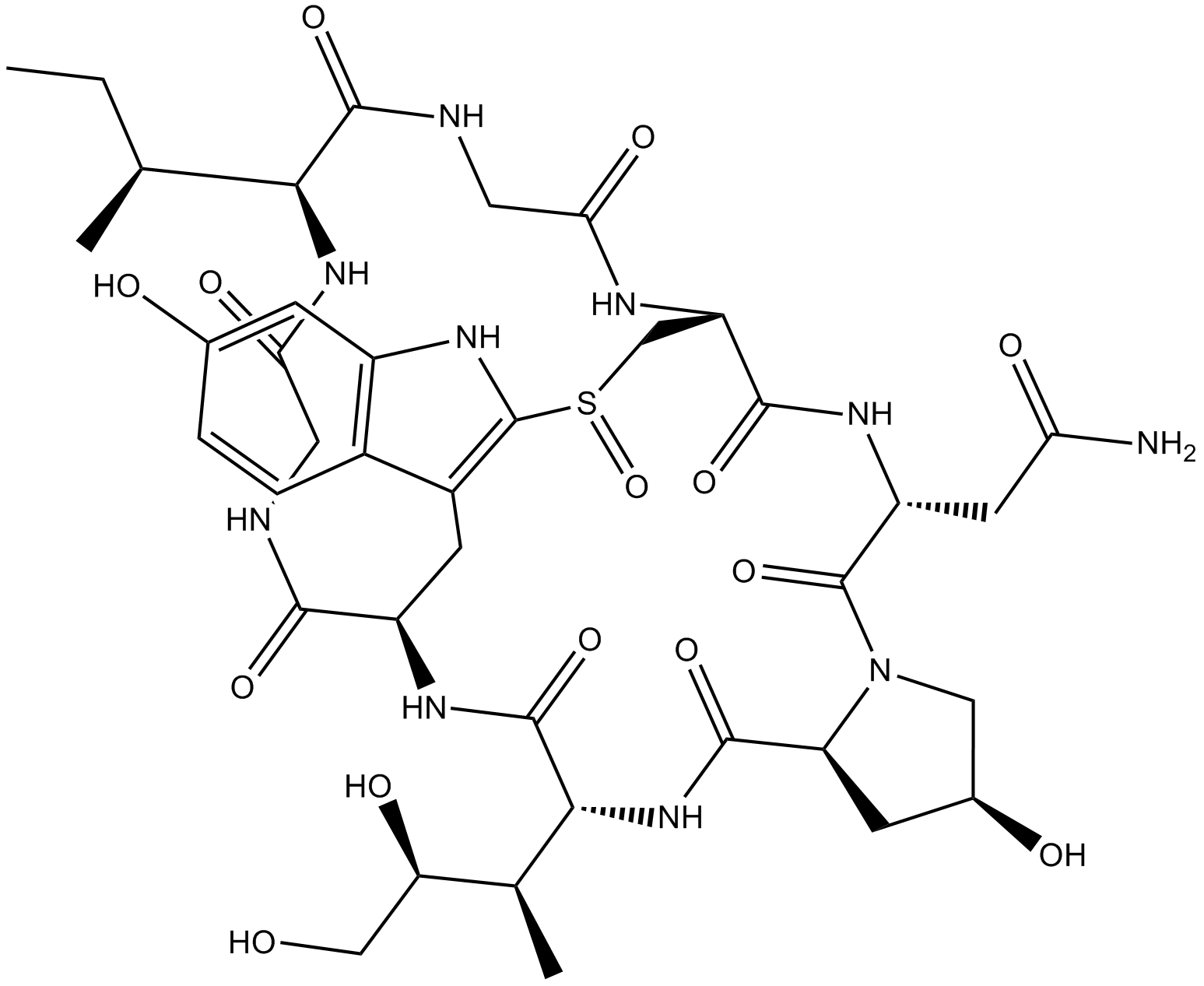
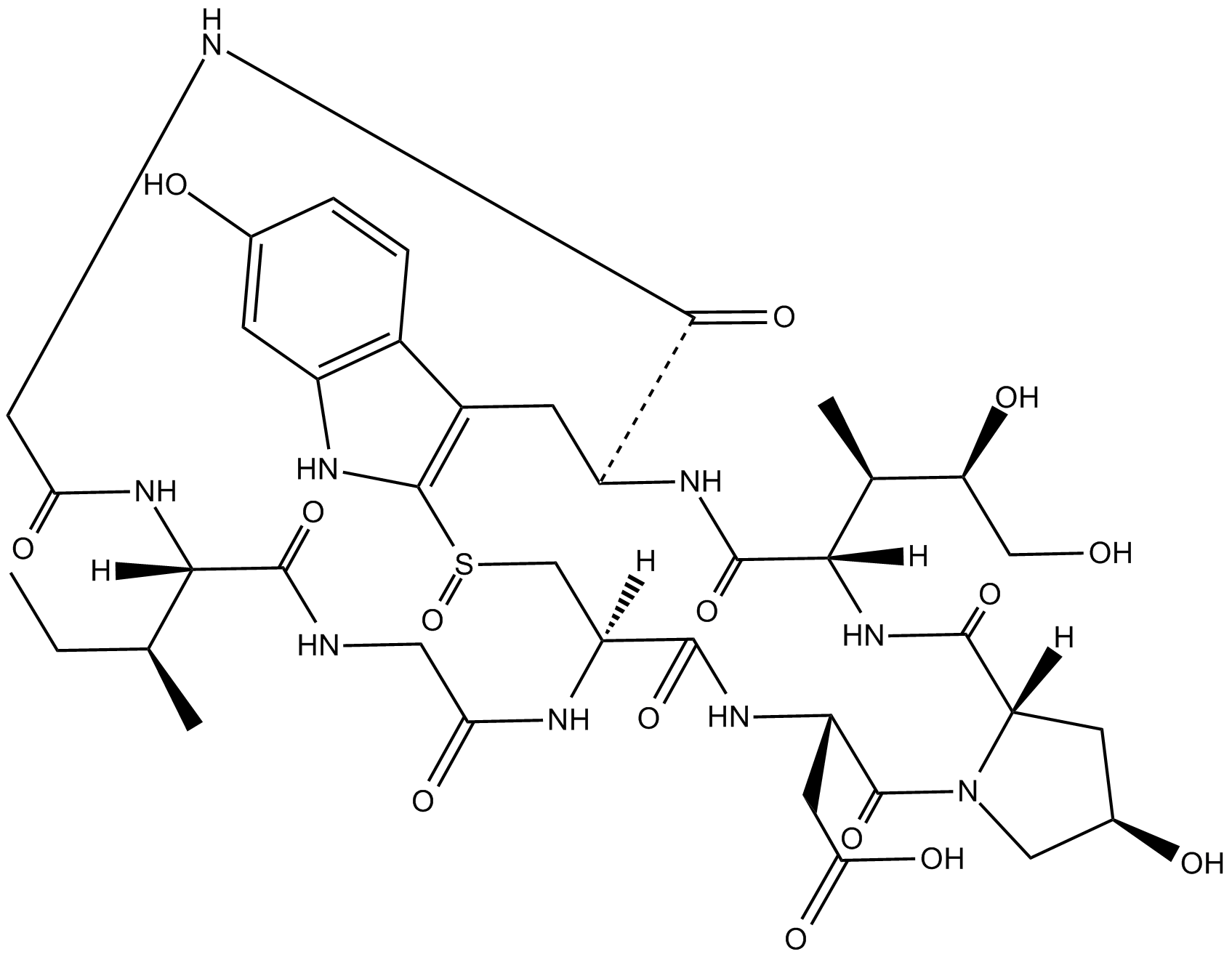
α-Amanitin
α-Amanitin (CAS 23109-05-9) is a cyclic peptide toxin isolated from Amanita mushrooms, known primarily for its inhibition of eukaryotic RNA polymerase II. Mechanistically, α-Amanitin binds specifically and with high affinity to RNA polymerase II, preventing nucleic acid transcription elongation and consequently blocking mRNA synthesis. Due to this precise molecular inhibitory function, α-Amanitin serves as a widely-employed biochemical tool in vitro and in cell-based assays, facilitating the study of transcriptional regulation, RNA polymerase function, and gene expression pathways. Additionally, its selective inhibition properties are utilized experimentally to dissect complex biological processes dependent upon RNA polymerase II-mediated transcription in cellular research models.
- 1. Liangzhen Dong, Jiayu Wang,et al. "Chemically modified tRNA enhances the translation capacity of mRNA rich in cognate codons." Nat Commun 16, 7825 (2025)
- 2. Chunhui Zhu, Gang Liu, et al. "tRF16 affects NFKBIA stability and promotes osteoarthritis progression by regulating ALKBH5 expression in m6A-dependent manner." Commun Biol. 2025 Jun 5;8(1):868. PMID: 40473927
- 3. Jinfang Xue, Xiran Lou, et al. "Ezetimibe Protects Against Alpha - Amanitin - Induced Hepatotoxicity by Targeting the NTCP Receptor: Mechanistic Insights from In Vitro and In Vivo Models." Toxicon. 2025 Sep:264:108423 PMID: 40449755
- 4. Hui Xu, Jian Sun, et al. "PP2A attenuates α - amanitin - induced liver injury by promoting autophagy and inhibiting apoptosis in mouse models." Chem Biol Interact. 2025 Aug 25:417:111558 PMID: 40379039
- 5. Jing WangWang LiJing Guo, et al. "Reconstitution of chromatin reorganization during mammalian oocyte development." Jul 27, 2024
- 6. Bei Wang, Yu Xu, et al. "Integrating genome-wide CRISPR screens and in silico drug profiling for targeted antidote development." Nat Protoc. 2024 May 30. PMID: 38816517
- 7. Duo Wu, Huang Huang, et al. "The BRCA1/BARD1 complex recognizes pre-ribosomal RNA to facilitate homologous recombination." Cell Discov. 2023 Oct 3;9(1):99. PMID: 37789001
- 8. Bei Wang, Arabella H Wan, et al. "Identification of indocyanine green as a STT3B inhibitor against mushroom α-amanitin cytotoxicity." Nat Commun. 2023 May 16;14(1):2241. PMID: 37193694
- 9. Jiangli Lang, Chen Yang, et al. "High Glucose Activates ERK1/2 to Stabilize AP1 and Increase MMP9 Expression in Diabetic Foot Ulcers." Exp Cell Res. 2021 Mar 3;112550. PMID: 33675806
- 10. Huo X, Ji L, et al. "The Nuclear Matrix Protein SAFB Cooperates with Major Satellite RNAs to Stabilize Heterochromatin Architecture Partially through Phase Separation." Mol Cell. 2019 Oct 28. pii: S1097-2765(19)30761-0. PMID: 31677973
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C, protect from light |
| M.Wt | 918.97 |
| Cas No. | 23109-05-9 |
| Formula | C39H54N10O14S |
| Solubility | ≥1 mg/mL in H2O; Soluble in Ethanol |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | CCC(C)C1C(=O)NCC(=O)NC2CS(=O)C3=C(CC(C(=O)NCC(=O)N1)NC(=O)C(NC(=O)C4CC(CN4C(=O)C(NC2=O)CC(=O)N)O)C(C)C(CO)O)C5=C(N3)C=C(C=C5)O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment:[1] | |
|
Cell lines |
Mouse blastocysts |
|
Reaction Conditions |
1.1 μg/ml α-amanitin |
|
Applications |
α-Amanitin inhibited the incorporation of 3H-UMP into embryos. α-Amanitin at the concentration of 1.1 μg/ml was found to inhibit RNA polymerase activity by 32%. |
| Animal experiment:[1] | |
|
Animal models |
Preimplantation mouse embryos at the two-cell stage of development collected from CF1 female mice |
|
Dosage form |
0 ~ 1 μg/ml α-amanitin 48 h |
|
Applications |
Less than 1% of the embryos which had been treated with 1 μg/ml of α-amanitin developed to the morula or blastocyst stages. α-Amanitin can be used to determine which forms of RNA polymerase are active and the relative amounts of each form which are present in preimplantation mouse embryos. |
|
Note |
The technical data provided above is for reference only. |
|
References: 1. Warner CM, Versteegh LR. In vivo and in vitro effect of alpha-amanitin on preimplantation mouse embryo RNA polymerase. Nature, 1974, 248(5450): 678-680. |
|
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure

Related Biological Data

Related Biological Data

Related Biological Data