eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3
Molecular : C47H84N14O14S
Eukaryotic initiation factors (eIF) are proteins involved in the initiation phase of eukaryotic translation. eIF3 binds to the ribosome subunit-mRNA complex. It has been implicated in preventing the large ribosomal subunit from binding the small subunit before it is ready to commence elongation. In mammals, eIF3 is the largest scaffolding initiation factor, made up of 13 subunits (a-m). It is roughly ~750 kDa and it controls the assembly of40S ribosomal subunit on mRNA that have a 5' cap or an IRES (Internal Ribosomal Entry Site). eIF3 uses the eIF4F complex or IRES from viruses to position the mRNA strand near the exit site of the 40S ribosome subunit, thus promoting the assembly of the pre-initiation complex.[1]
PTK2 and EIF3S3 genes may be amplification targets at 8q23-q24 and are associated with large hepatocellular carcinomas. [2]. Amplification of EIF3S3 gene is common in late-stage prostate cancersuggesting that it may be functionally involved in the progression of the disease [3]. Recent study shows that eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 subunit 3 does not seem to be overrepresentedindependent of c-myc in prostate cancer [4].
Ref:
1. Umadas Maitra, Jayanta Chaudhuri; Jayanta Chaudhuri, Kausik Si (21). "Function of Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Factor 1A (eIF1A) (Formerly Called eIF-4C) in Initiation of Protein Synthesis". The Journal of BIological Chemistry 272 (12): 7883–7891. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.12.7883. Retrieved 19 February 2012.
2. PTK2 and EIF3S3 genes may be amplification targets at 8q23-q24 and are associated with large hepatocellular carcinomas. Okamoto, H., Yasui, K., Zhao, C., Arii, S., Inazawa, J. Hepatology (2003) [Pubmed]
3. Amplification of EIF3S3 gene is associated with advanced stage in prostate cancer. Saramäki, O., Willi, N., Bratt, O., Gasser, T.C., Koivisto, P., Nupponen, N.N., Bubendorf, L., Visakorpi, T. Am. J. Pathol. (2001) [Pubmed]
4. Mapping and gene expression profile of the minimally overrepresented 8q24 region in prostate cancer. Tsuchiya, N., Kondo, Y., Takahashi, A., Pawar, H., Qian, J., Sato, K., Lieber, M.M., Jenkins, R.B. Am. J. Pathol. (2002) [Pubmed]
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 1101.32 |
| Formula | C47H84N14O14S |
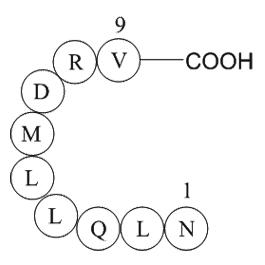
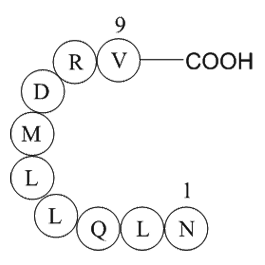
| Synonyms | H2N-Asn-Leu-Gln-Leu-Leu-Met-Asp-Arg-Val-OH |
| Solubility | ≥110.1 mg/mL in DMSO; insoluble in H2O; insoluble in EtOH |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | NC(CC(N)=O)C(NC(CC(C)C)C(NC(CCC(N)=O)C(NC(CC(C)C)C(NC(CC(C)C)C(NC(CCSC)C(NC(CC(O)=O)C(NC(CCCNC(N)=N)C(NC(C(C)C)C(O)=O)=O)=O)=O)=O)=O)=O)=O)=O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure