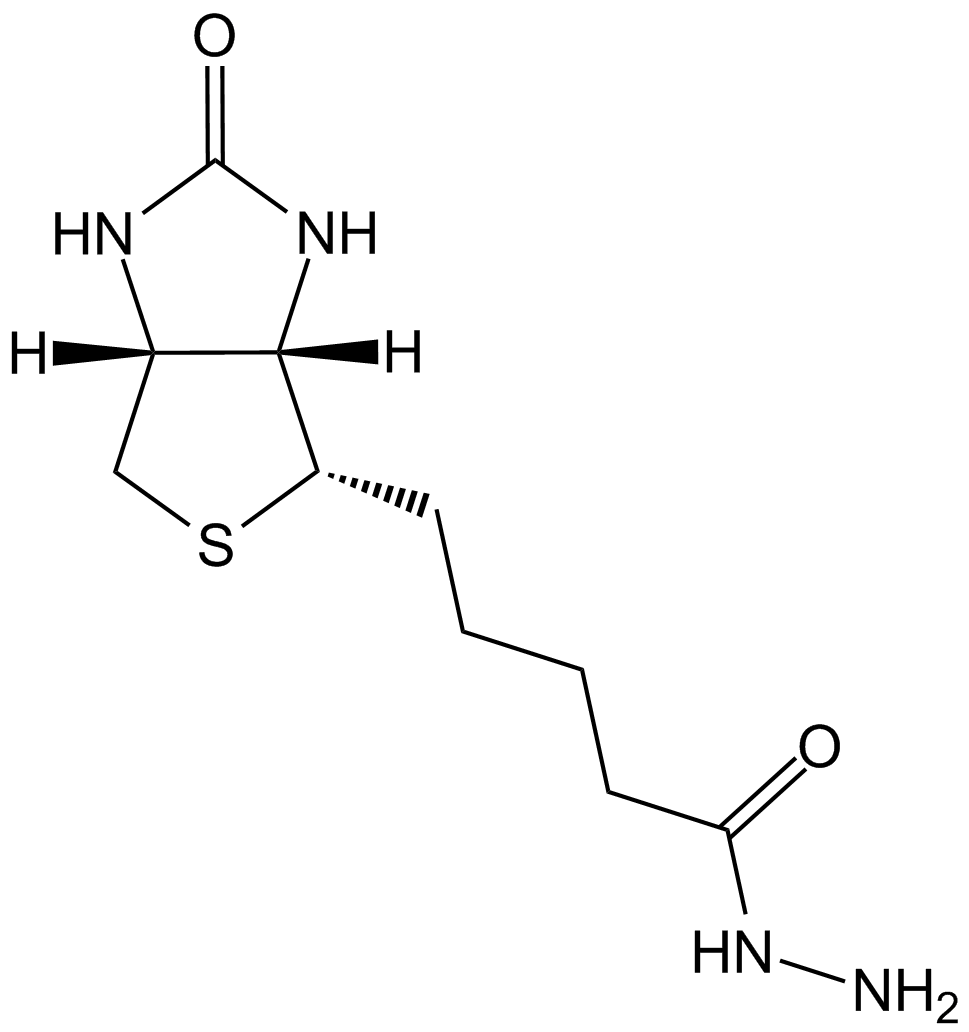
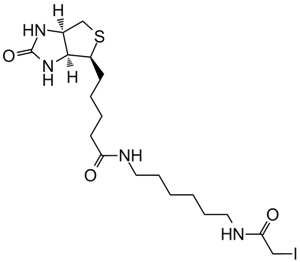
Biotin
Biotin, also known as vitamin B7 or vitamin H, is a water-soluble B-vitamin that is essential for human health. It plays several critical roles in the body, including serving as a coenzyme for five carboxylases involved in the synthesis of fatty acids, isoleucine, and valine, as well as gluconeogenesis. Additionally, biotin is indispensable for cell growth, fatty acid production, and the metabolism of fats and amino acids. Due to its significance in biochemical processes, biotin is also commonly used in biotin labeling techniques, a method that utilizes the ability of biotin to bind with specific molecules for the detection and localization of biomolecules. In summary, biotin not only plays a central role in human metabolism but also serves as a valuable tool in scientific research and medical diagnostics.
- 1. Alina Batiuk, Markus Höpfler, et al. "Soluble αβ-tubulins reversibly sequester TTC5 to regulate tubulin mRNA decay." Nat Commun. 2024 Nov 17;15(1):9963 PMID: 39551769
- 2. Qiang Zhang, et al. "Molecular Mechanisms of Intracellular Delivery of Nanoparticles Monitored by an Enzyme-Induced Proximity Labeling." Nanomicro Lett. 2024 Feb 1;16(1):103. PMID: 38300384
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 244.31 |
| Cas No. | 58-85-5 |
| Formula | C10H16N2O3S |
| Synonyms | Vitamin B7, D-Biotin, Vitamin H, or D-Biotin (Vitamin H) |
| Solubility | ≥24.4 mg/mL in DMSO; insoluble in H2O; insoluble in EtOH |
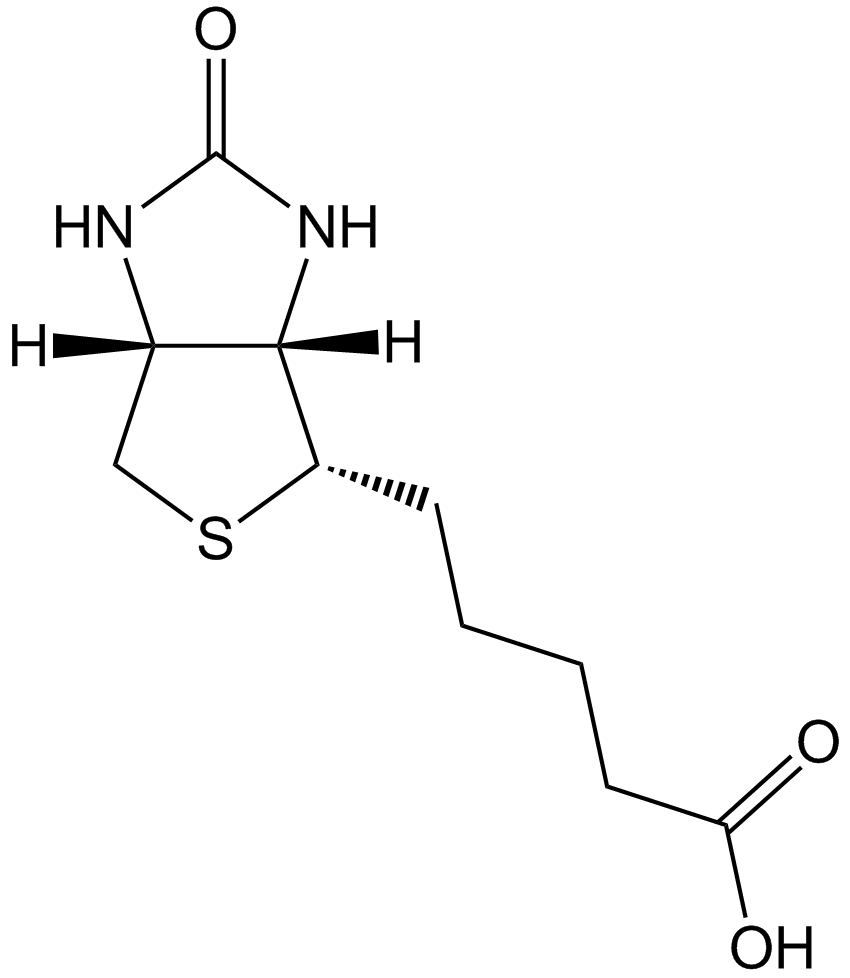
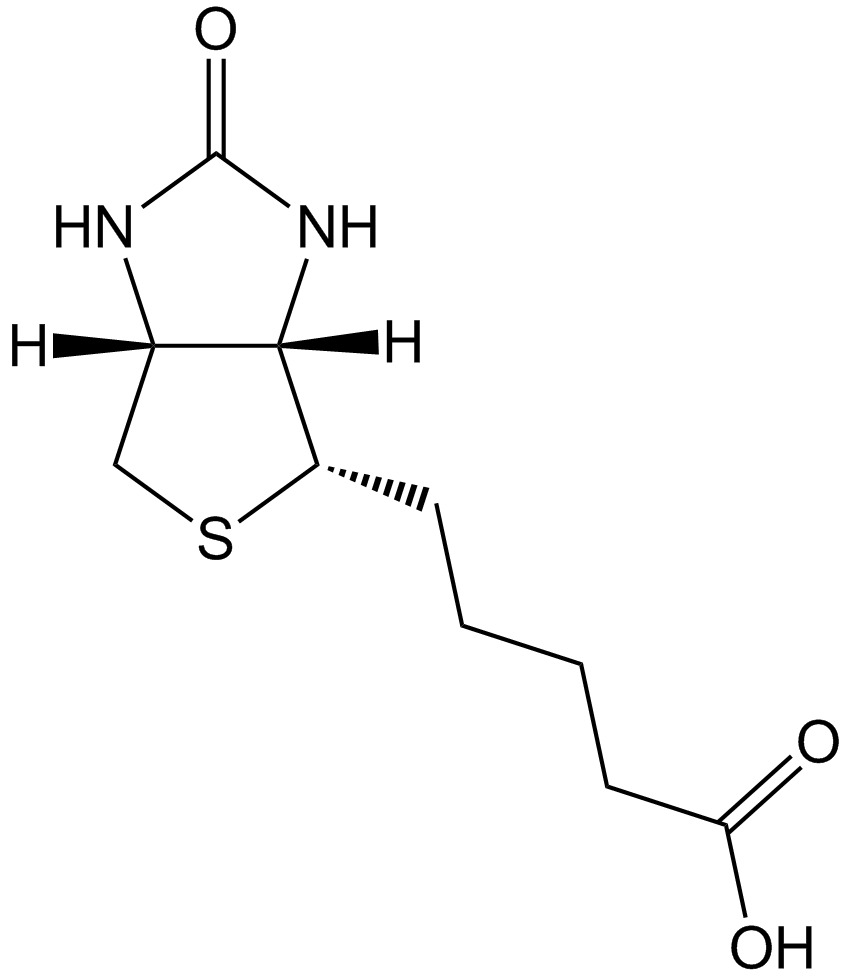
| Chemical Name | 5-[(3aS,4S,6aR)-2-oxo-1,3,3a,4,6,6a-hexahydrothieno[3,4-d]imidazol-4-yl]pentanoic acid |
| SDF | Download SDF |
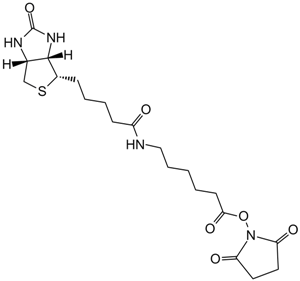
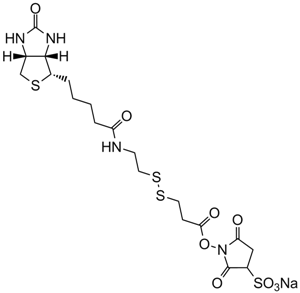
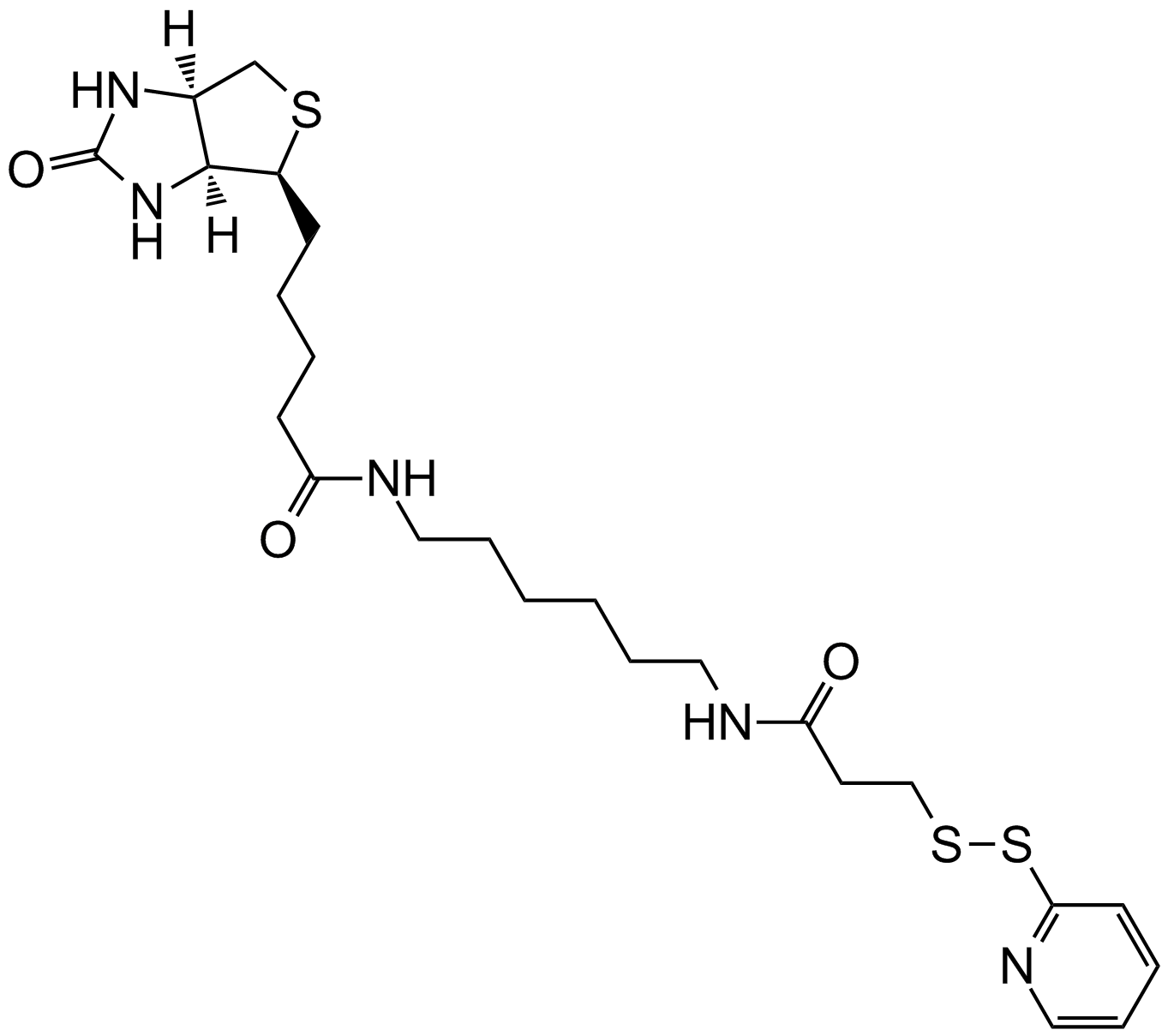
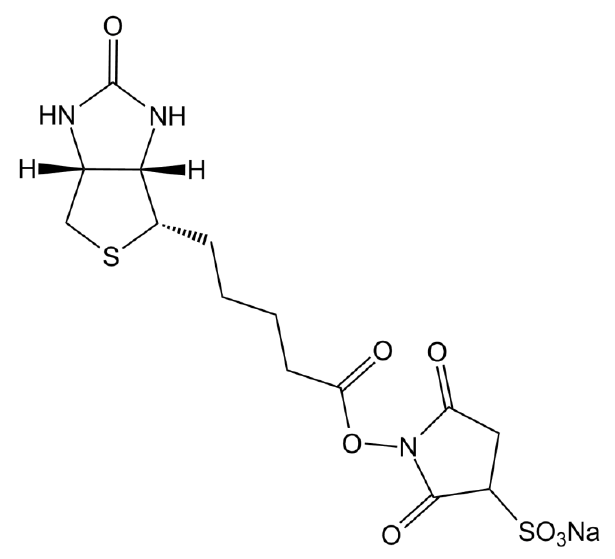
| Canonical SMILES | C1C2C(C(S1)CCCCC(=O)O)NC(=O)N2 |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Biotinylation method [1]: | |
|
Sample |
Proteins |
|
Preparation method |
Soluble in DMSO > 10 mM. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37 ℃ for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while. Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. |
|
Reaction Conditions |
room temperature for 1 h |
|
Applications |
Biotin-labeling of proteins: Biotinyl-N-hydroxysuccinimide (BNHS) was used for introducing biotin moieties into proteins. In order to obtain the desired molar ratio of BNHS to free amino groups of the protein, a solution of 0.1 M NaHCO: containing 10 mg/ml of protein was mixed with various volumes of 0.1 M solution of BNHS. The reaction mixture was incubated at room temperature for 1 h and then dialyzed for 24 h at 4℃ against several changes of PBS. After dialysis, an equal volume of glycerol was added and the preparation was kept at -20℃ until used. A fresh solution of BNHS was prepared each time immediately before use. The 2, 4, 6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid procedure was used to determine the free amino groups in native and biotin-substituted proteins. Total biotin covalently bound to IgG was determined by an avidin-binding assay. |
|
References: [1]. JEAN-LUC GUESDON, THERESE TERNYNCK AND STRATIS AVRAMEAS. The Use of Avidin-Biotin Interaction in Immunoenzymatic Techniques. THE JOURNAL OF HISTOCHEMISTRY AND CYTOCHEMISTRY. 1979. |
|
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure
Related Biological Data