TGF-β / Smad Signaling
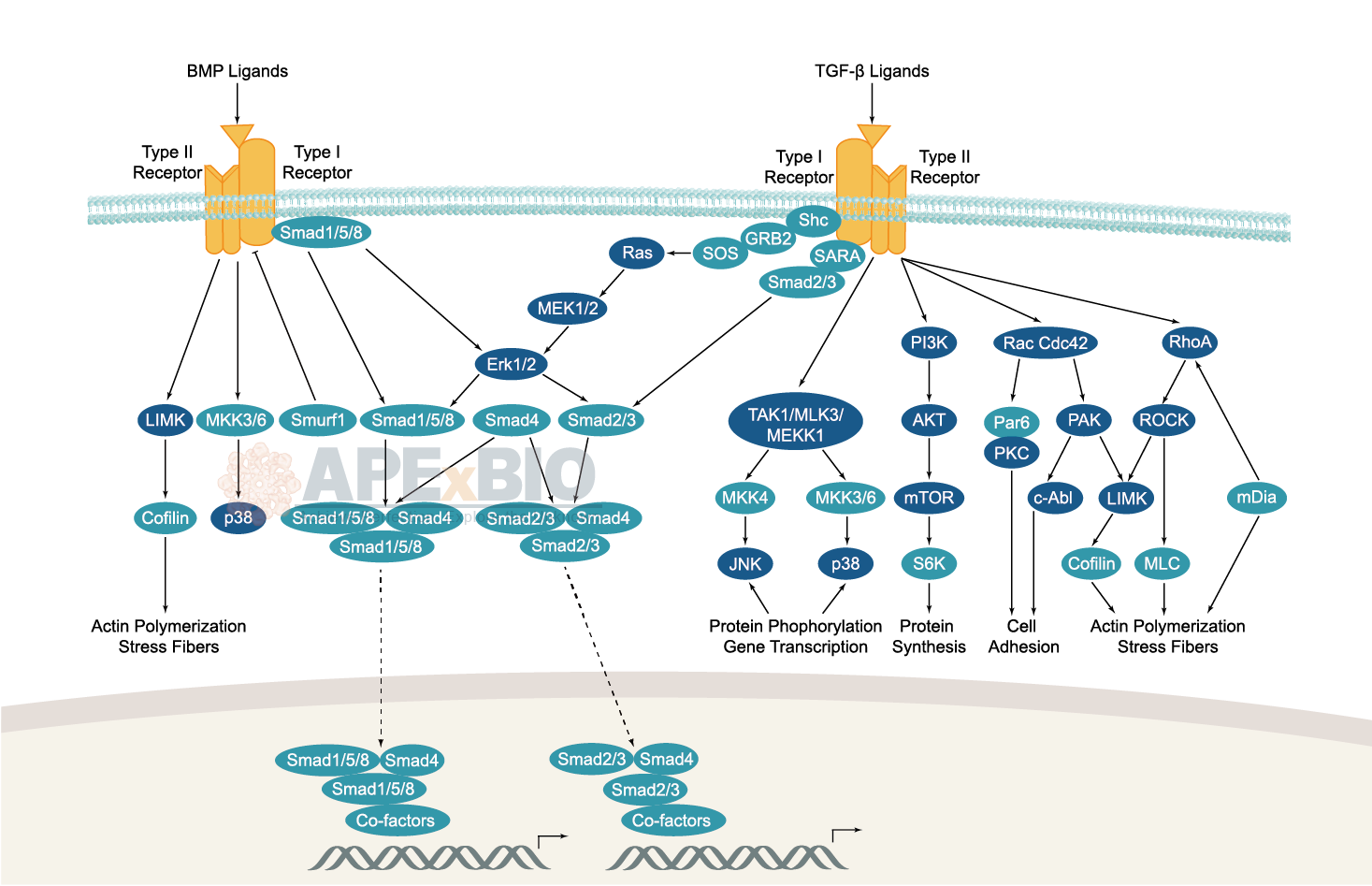
The TGF-β family is generally classified into two sub-families, TGF-β ligands, and bone morphogenic protein (BMP) ligands. In canonical signaling, receptor activation lead to phosphorylation of a group of transcription factors called Smads. TGF-β ligands bind to type II receptors (TGF-β II) which recruit and phosphorylate type I receptor (TGF-β I) on serine/threonine residues. The TGF-β I then recruits and phosphorylates a receptor regulated Smad (R-Smad). The R-Smad binds to the common Smad (Co-Smad) and forms a heterodimeric complex. This complex then translocates into the cell nucleus where it binds with nuclear co-factors to regulate the transcription of various target genes. Dysregulation of TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway is associated with a number of pathological conditions including fibrosis, cancer, immunodeficiency, diabetes and cardiovascular diseases etc.
-
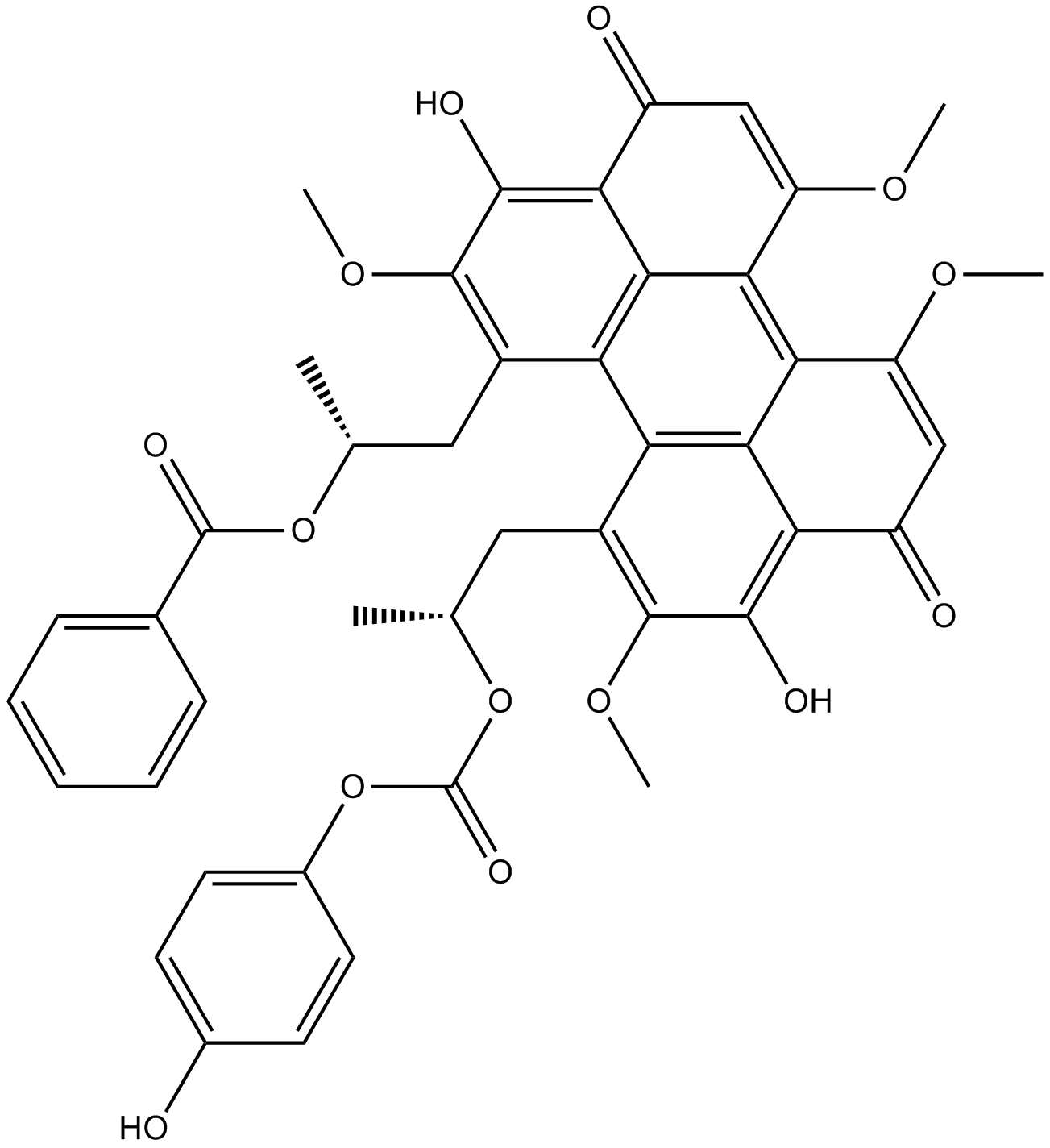 B6807 Calphostin CSummary: protein kinase C inhibitor
B6807 Calphostin CSummary: protein kinase C inhibitor -
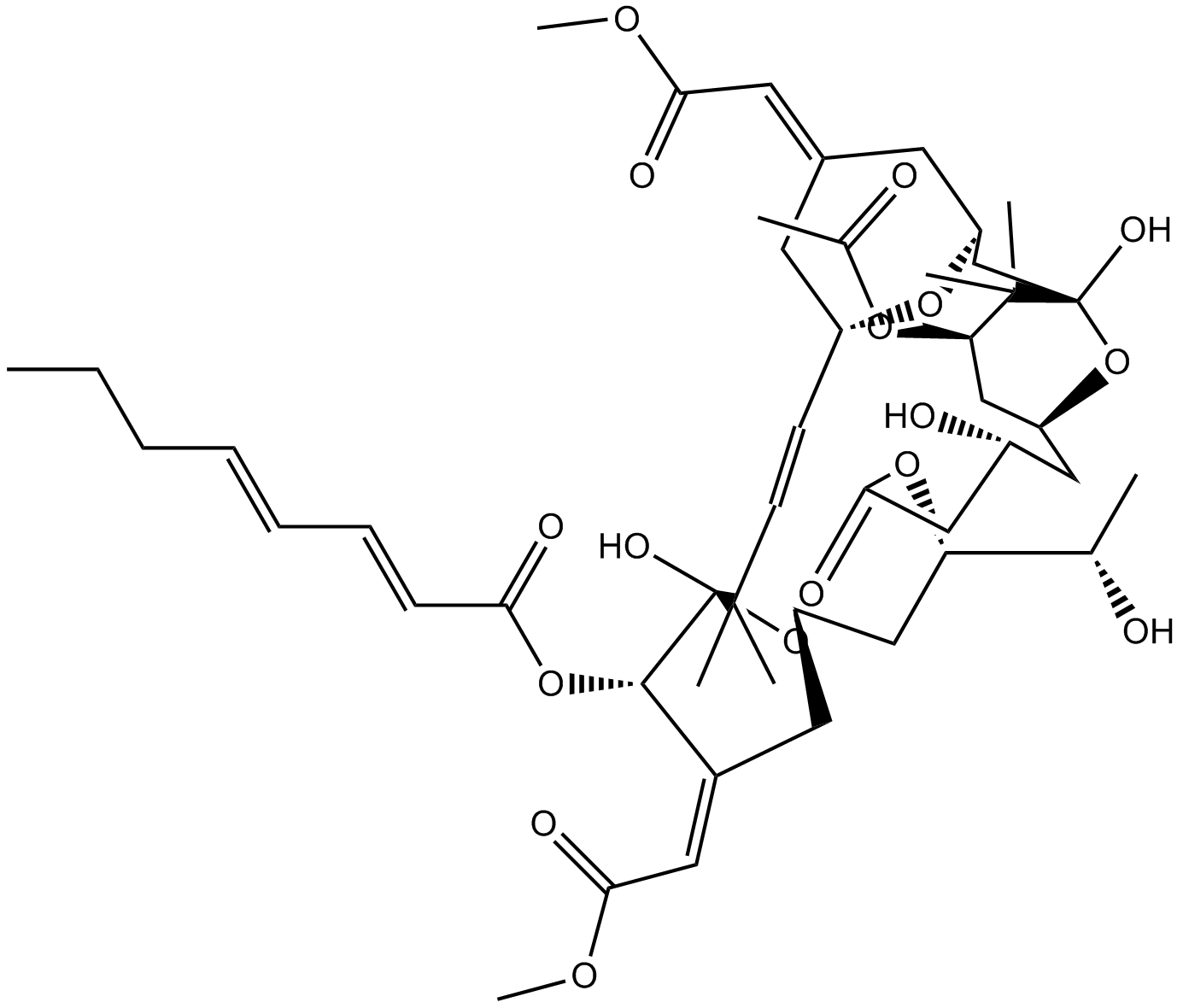 B7033 Bryostatin 11 CitationSummary: PKC activator
B7033 Bryostatin 11 CitationSummary: PKC activator -
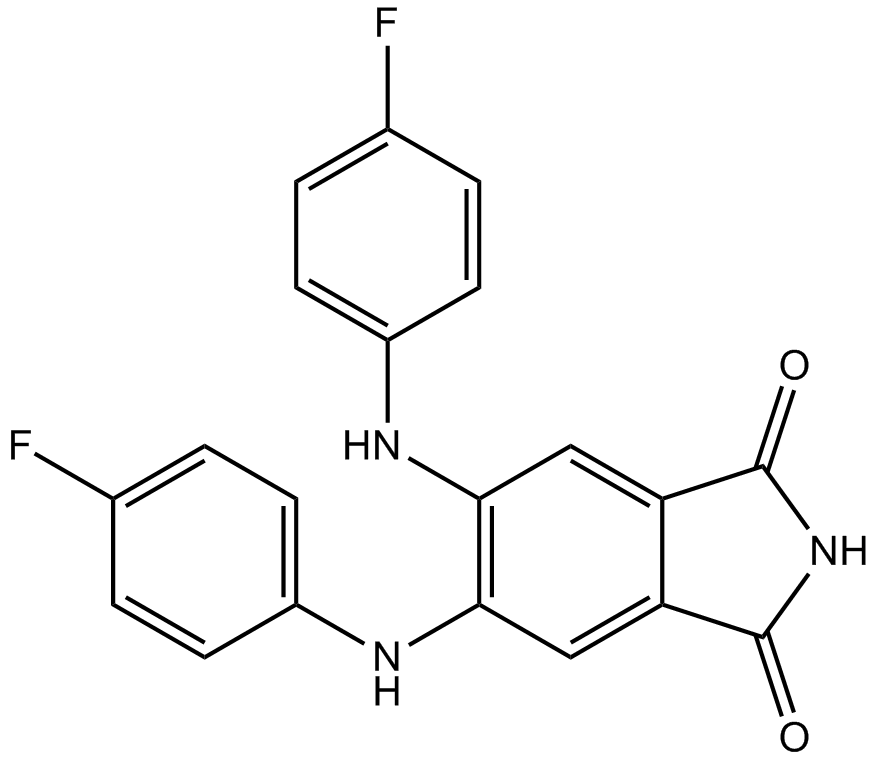 B7056 CGP 53353Summary: PKCβII inhibitor
B7056 CGP 53353Summary: PKCβII inhibitor -
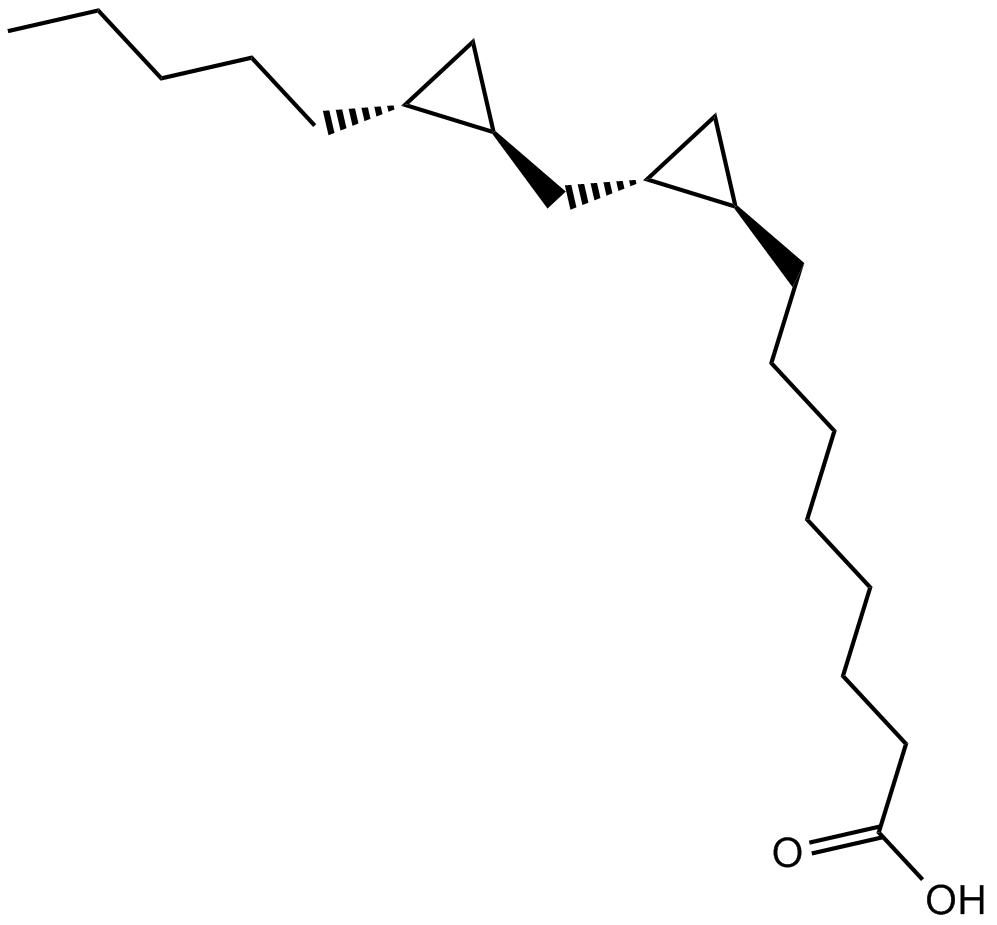 B7272 FR 2369241 CitationSummary: PKC-ε activator, selective
B7272 FR 2369241 CitationSummary: PKC-ε activator, selective -
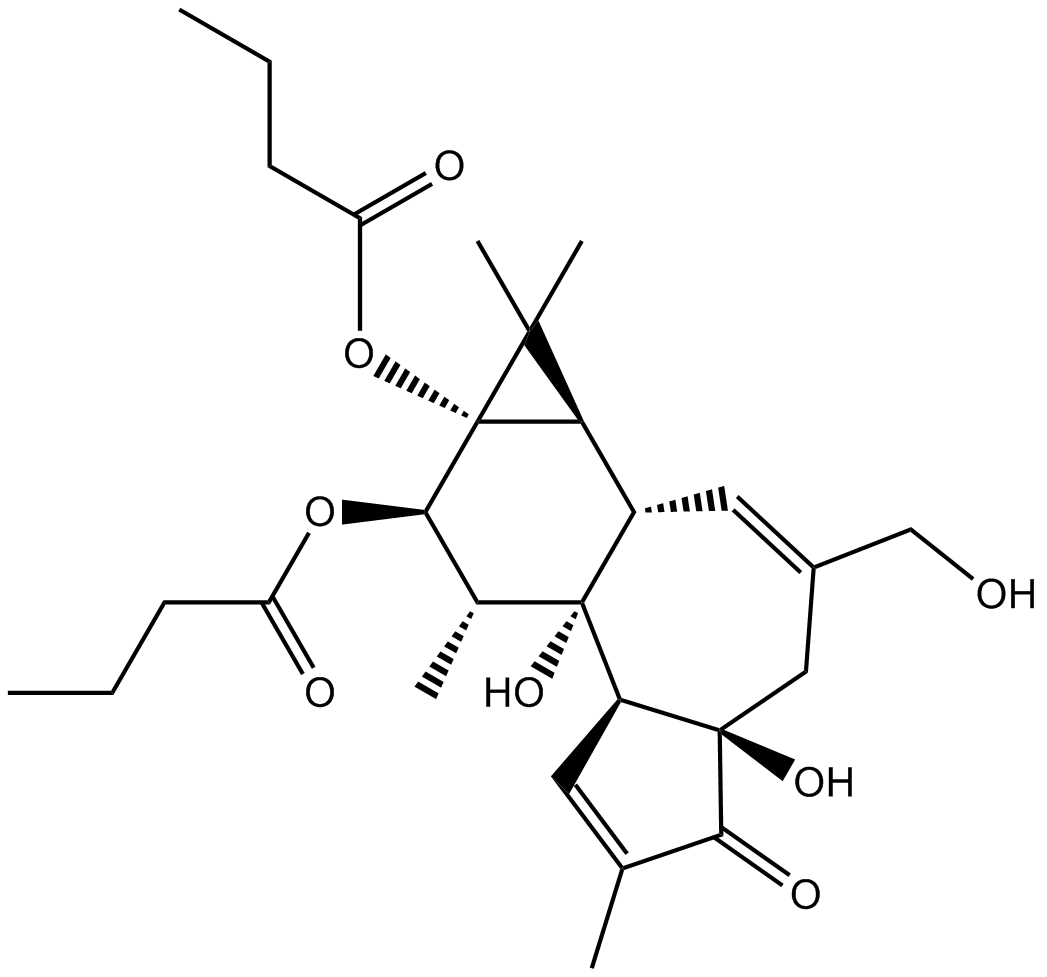 B7598 Phorbol 12,13-dibutyrateSummary: A protein kinase C (PKC) activator
B7598 Phorbol 12,13-dibutyrateSummary: A protein kinase C (PKC) activator -
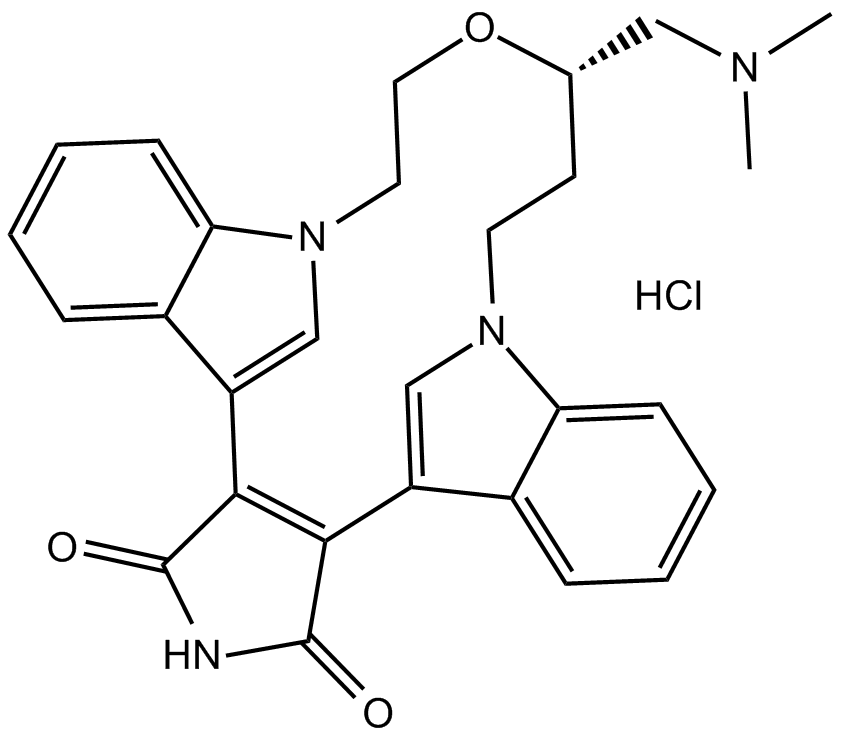 B7704 LY 333531 hydrochlorideSummary: PKCβ inhibitor
B7704 LY 333531 hydrochlorideSummary: PKCβ inhibitor -
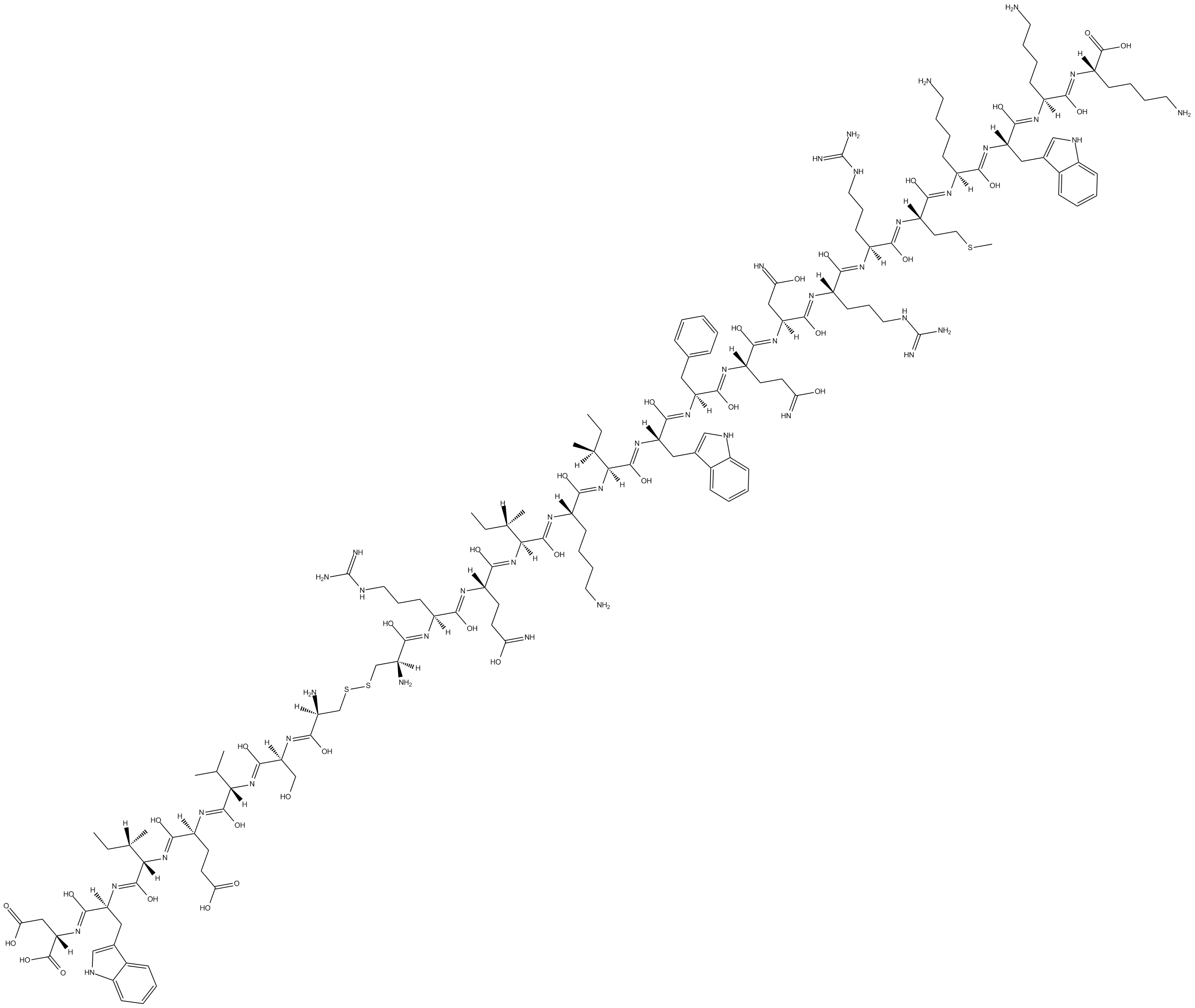 B5172 Pseudo RACK1Summary: Activator of protein kinase C
B5172 Pseudo RACK1Summary: Activator of protein kinase C -
 B5174 PKC β pseudosubstrateSummary: Selective cell-permeable peptide inhibitor of protein kinase C
B5174 PKC β pseudosubstrateSummary: Selective cell-permeable peptide inhibitor of protein kinase C -
![[Ala107]-MBP (104-118)](/pub/media/prod_images/b/5/b5218.png) B5218 [Ala107]-MBP (104-118)Summary: Non-competitive inhibitor of PKC
B5218 [Ala107]-MBP (104-118)Summary: Non-competitive inhibitor of PKC -
![[Ala113]-MBP (104-118)](/pub/media/prod_images/b/5/b5219.png) B5219 [Ala113]-MBP (104-118)Summary: Non-competitive inhibitor of PKC
B5219 [Ala113]-MBP (104-118)Summary: Non-competitive inhibitor of PKC

