TGF-β / Smad Signaling
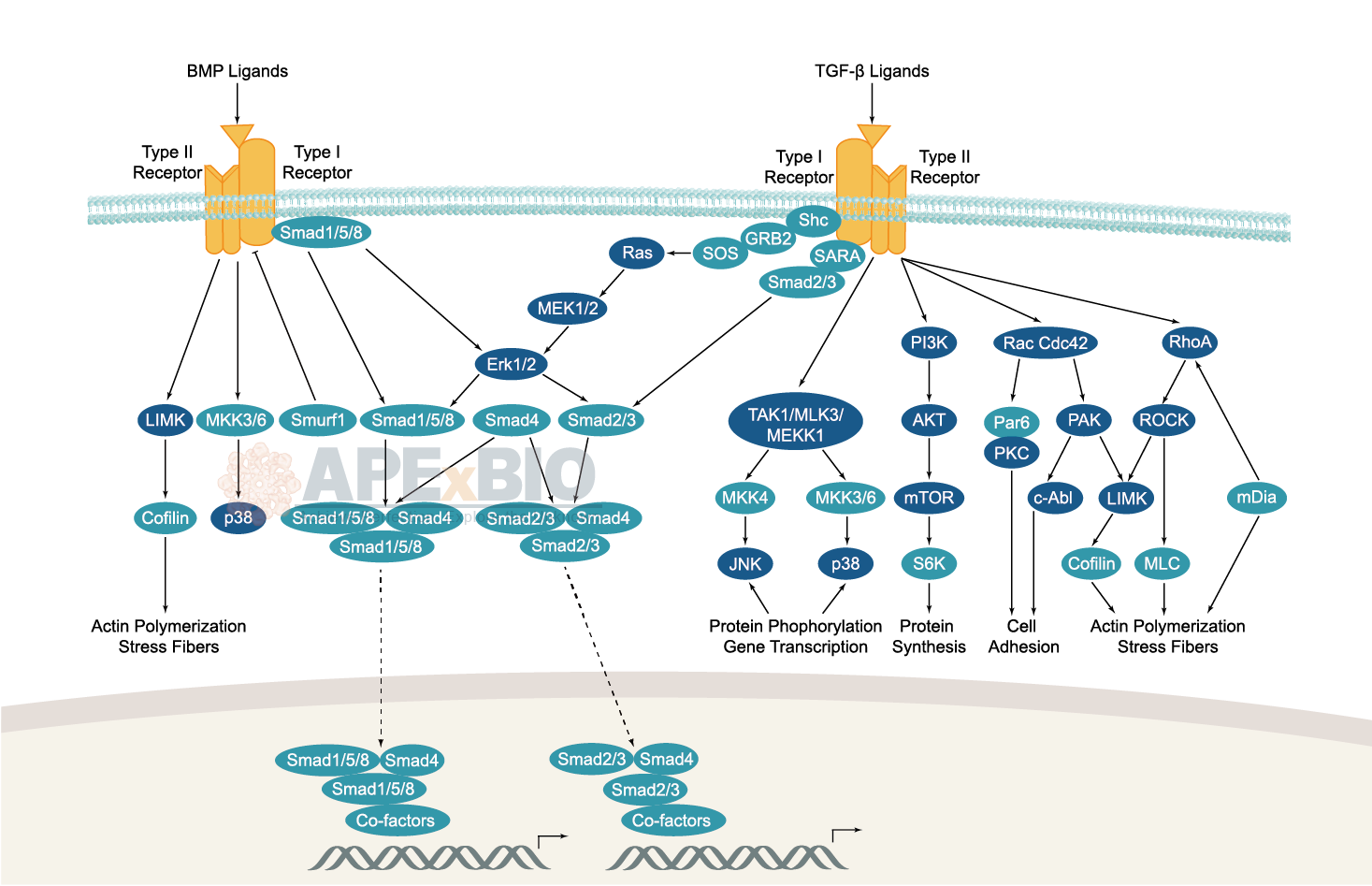
The TGF-β family is generally classified into two sub-families, TGF-β ligands, and bone morphogenic protein (BMP) ligands. In canonical signaling, receptor activation lead to phosphorylation of a group of transcription factors called Smads. TGF-β ligands bind to type II receptors (TGF-β II) which recruit and phosphorylate type I receptor (TGF-β I) on serine/threonine residues. The TGF-β I then recruits and phosphorylates a receptor regulated Smad (R-Smad). The R-Smad binds to the common Smad (Co-Smad) and forms a heterodimeric complex. This complex then translocates into the cell nucleus where it binds with nuclear co-factors to regulate the transcription of various target genes. Dysregulation of TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway is associated with a number of pathological conditions including fibrosis, cancer, immunodeficiency, diabetes and cardiovascular diseases etc.
-
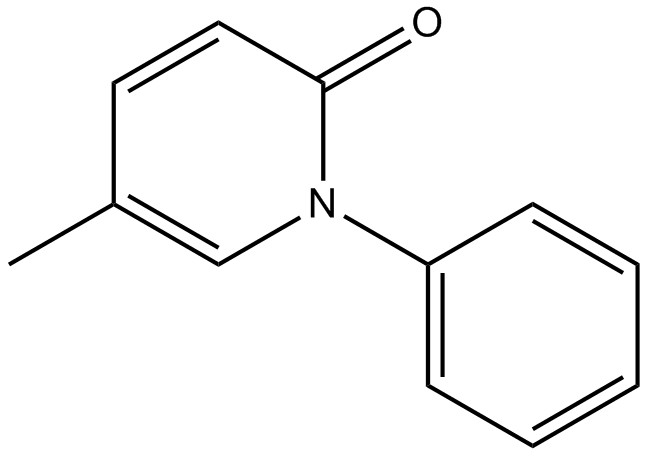 B2288 PirfenidoneSummary: TGF-β production inhibitor
B2288 PirfenidoneSummary: TGF-β production inhibitor -
 A8192 Staurosporine6 CitationSummary: serine/threonine protein kinases inhibitor
A8192 Staurosporine6 CitationSummary: serine/threonine protein kinases inhibitor -
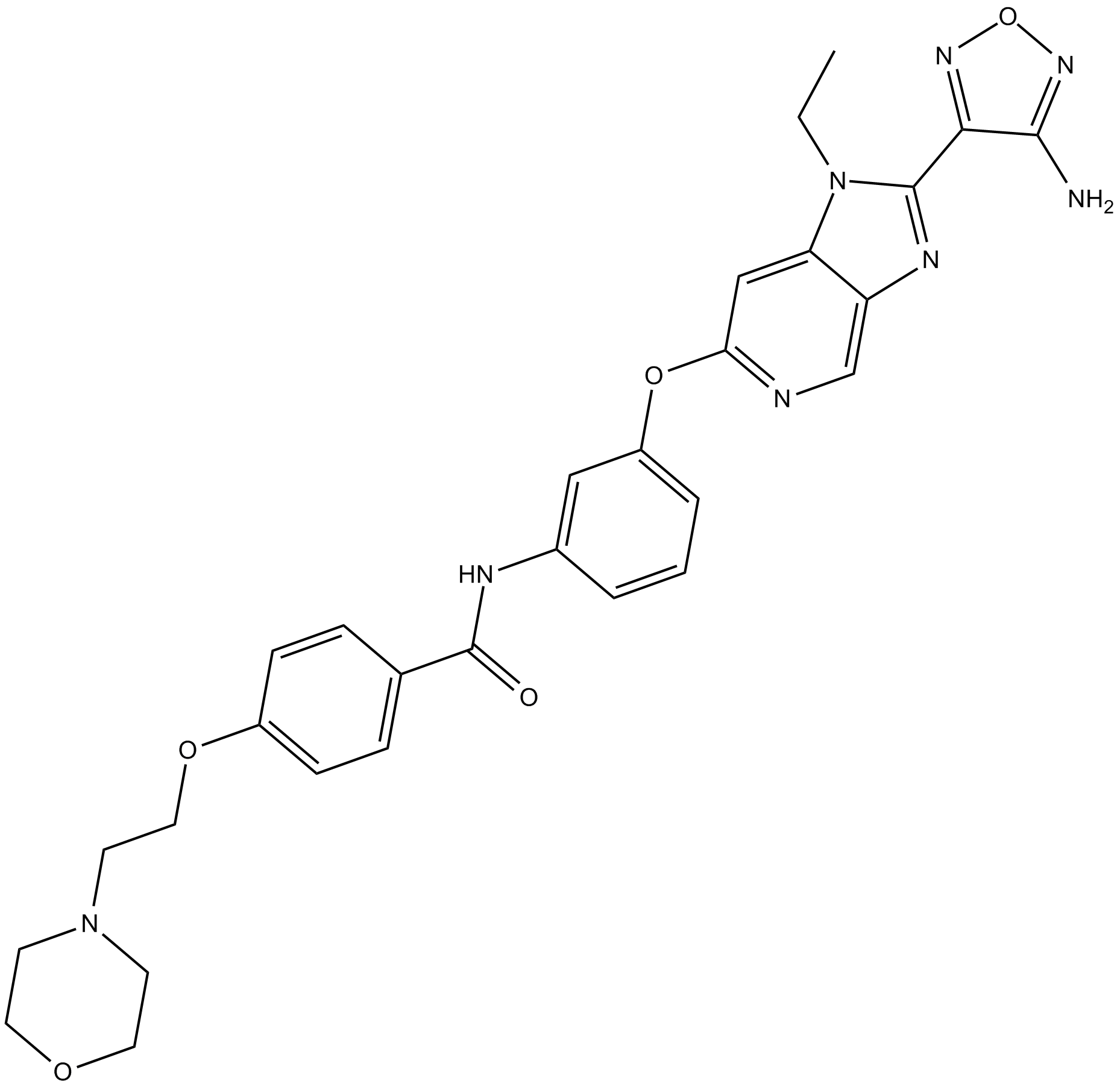 B3392 GSK269962ATarget: ROCK|RSK|MSKSummary: ROCK inhibitor
B3392 GSK269962ATarget: ROCK|RSK|MSKSummary: ROCK inhibitor -
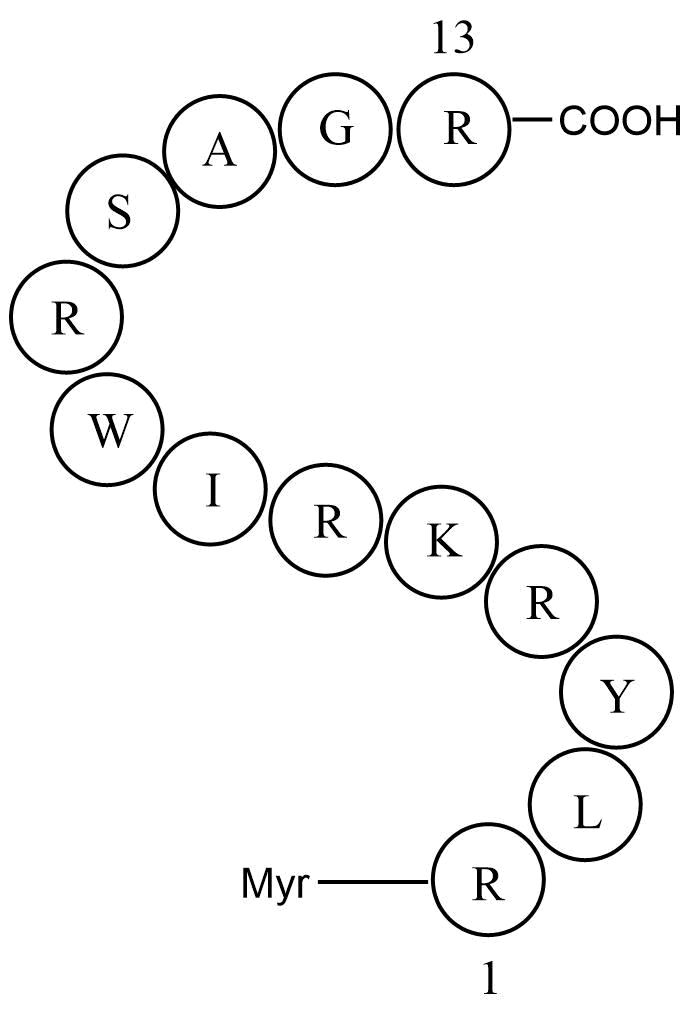 A8830 ZIP (SCRAMBLED)Summary: PKMζ inhibitor
A8830 ZIP (SCRAMBLED)Summary: PKMζ inhibitor -
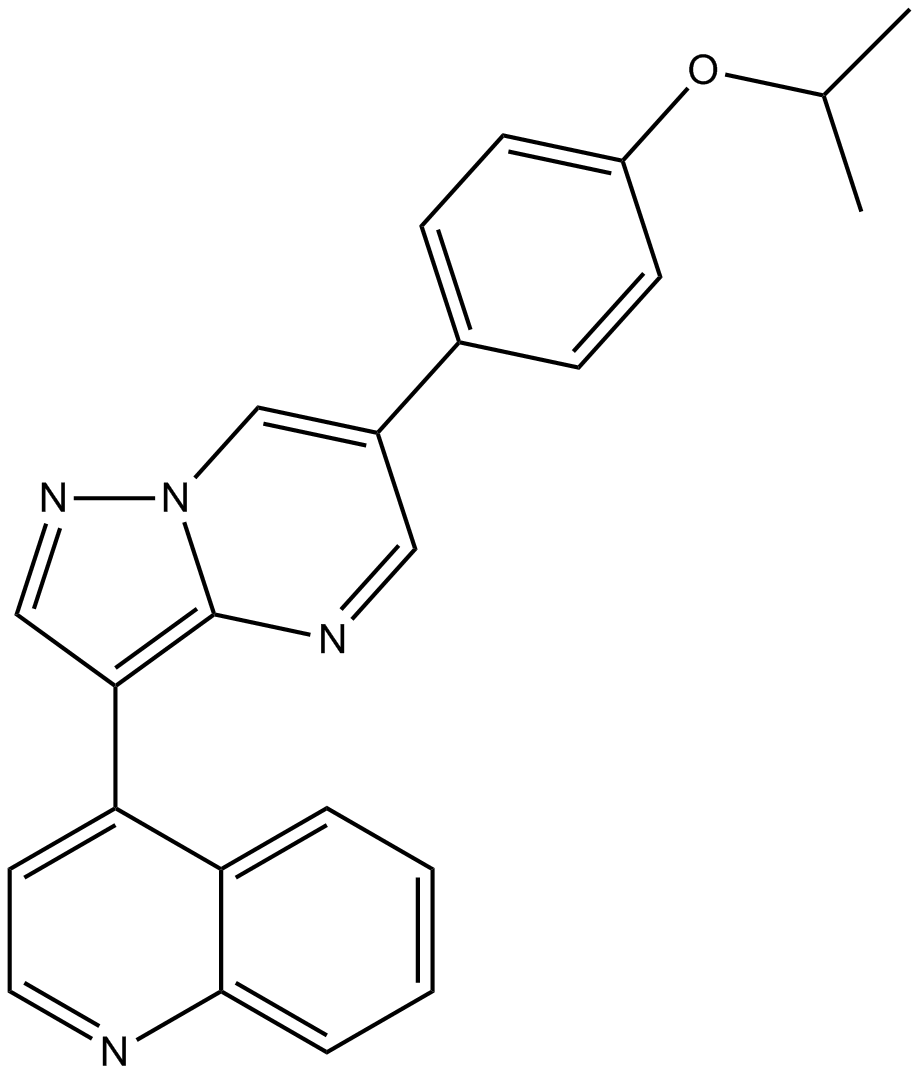 B3686 DMH-1Target: BMP and Other Activin ReceptorsSummary: Selective BMP ALK2 receptor
B3686 DMH-1Target: BMP and Other Activin ReceptorsSummary: Selective BMP ALK2 receptor -
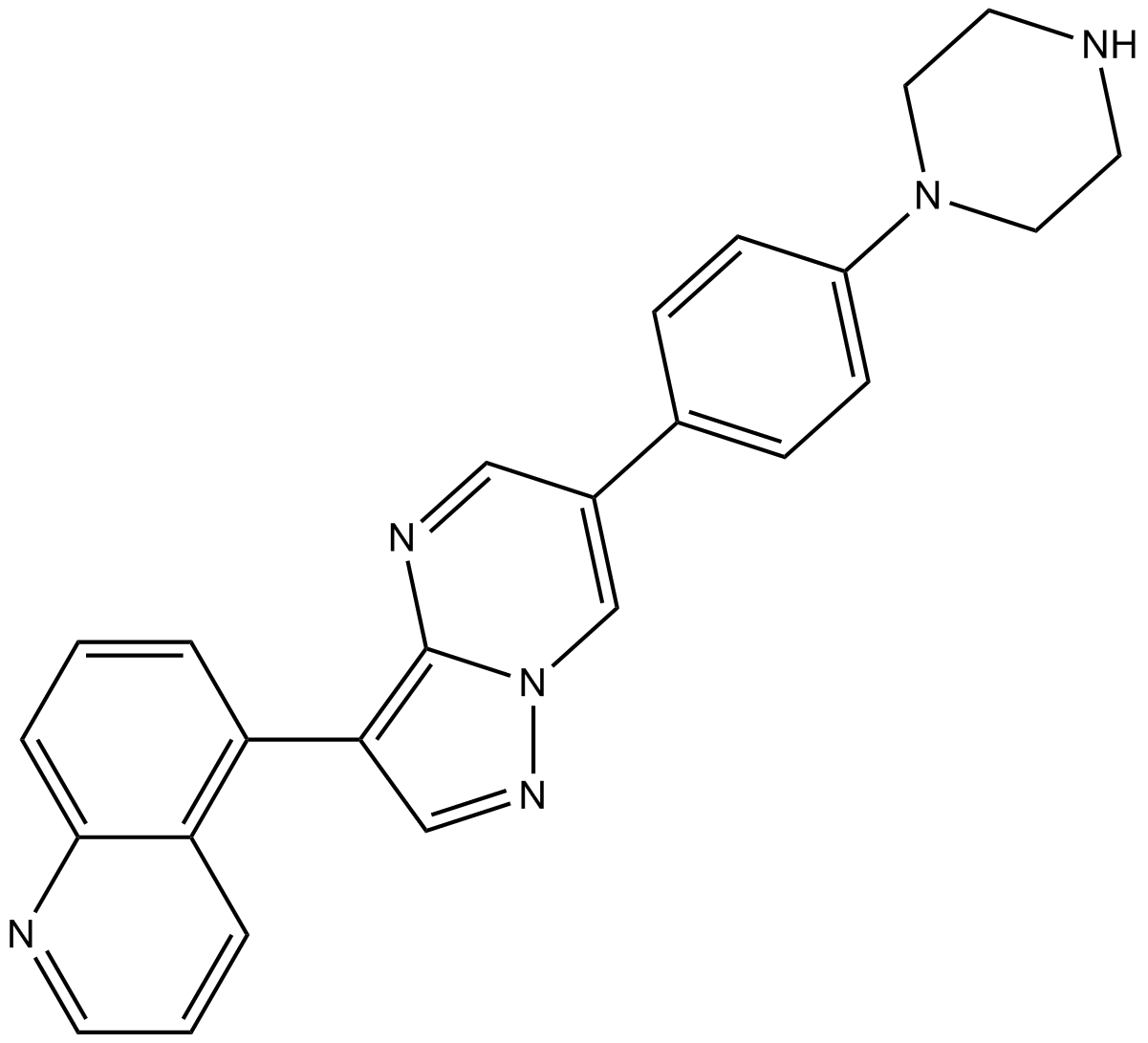 B3687 LDN-212854Summary: BMP receptor inhibitor,potent and selective
B3687 LDN-212854Summary: BMP receptor inhibitor,potent and selective -
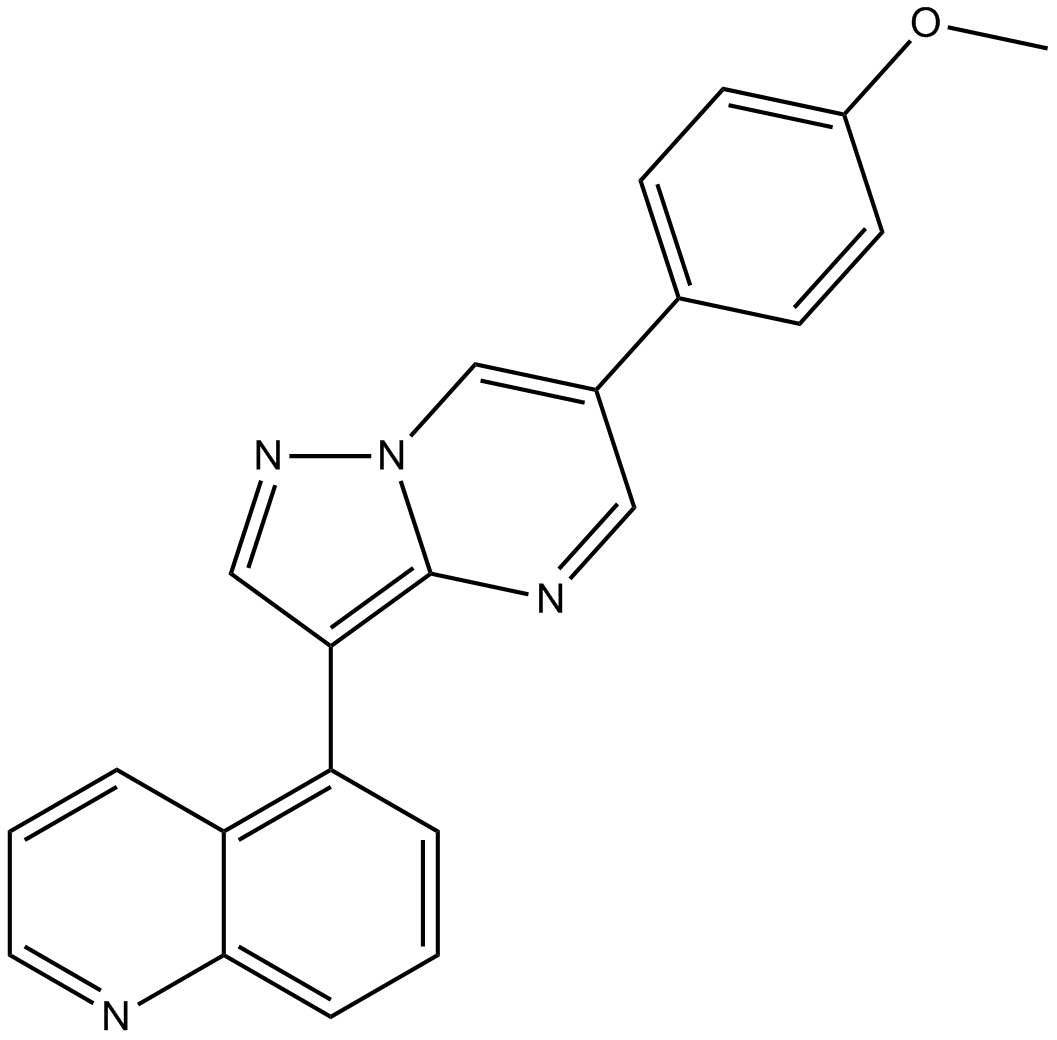 B3688 ML347Target: BMP and Other Activin ReceptorsSummary: BMP receptor inhibitor,potent and selective
B3688 ML347Target: BMP and Other Activin ReceptorsSummary: BMP receptor inhibitor,potent and selective -
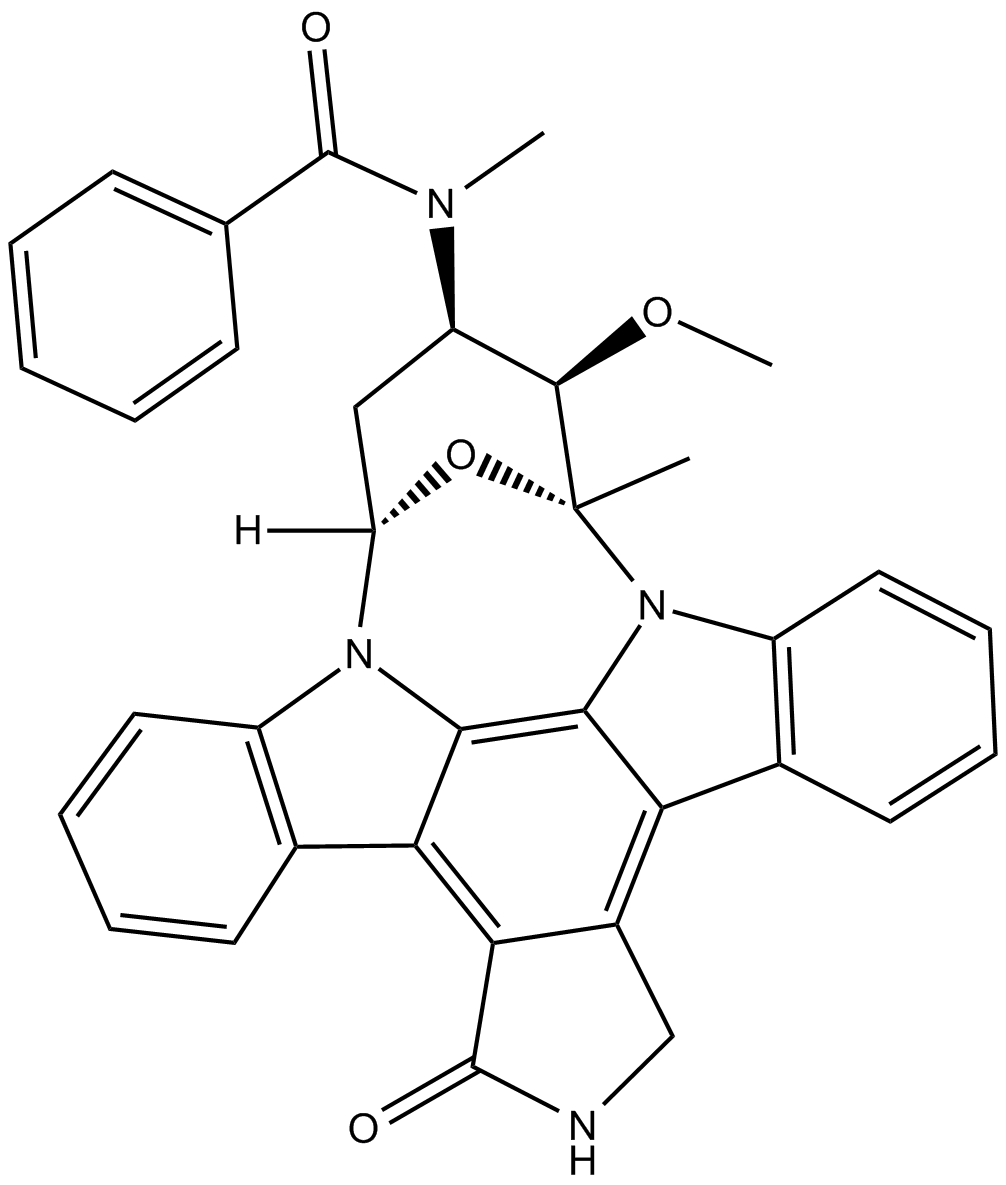 B3709 Midostaurin (PKC412)Target: PKC|PKA|KDR|Flk1|PPK|c-Syk|CDK1/CyclinBSummary: PKC inhibitor
B3709 Midostaurin (PKC412)Target: PKC|PKA|KDR|Flk1|PPK|c-Syk|CDK1/CyclinBSummary: PKC inhibitor -
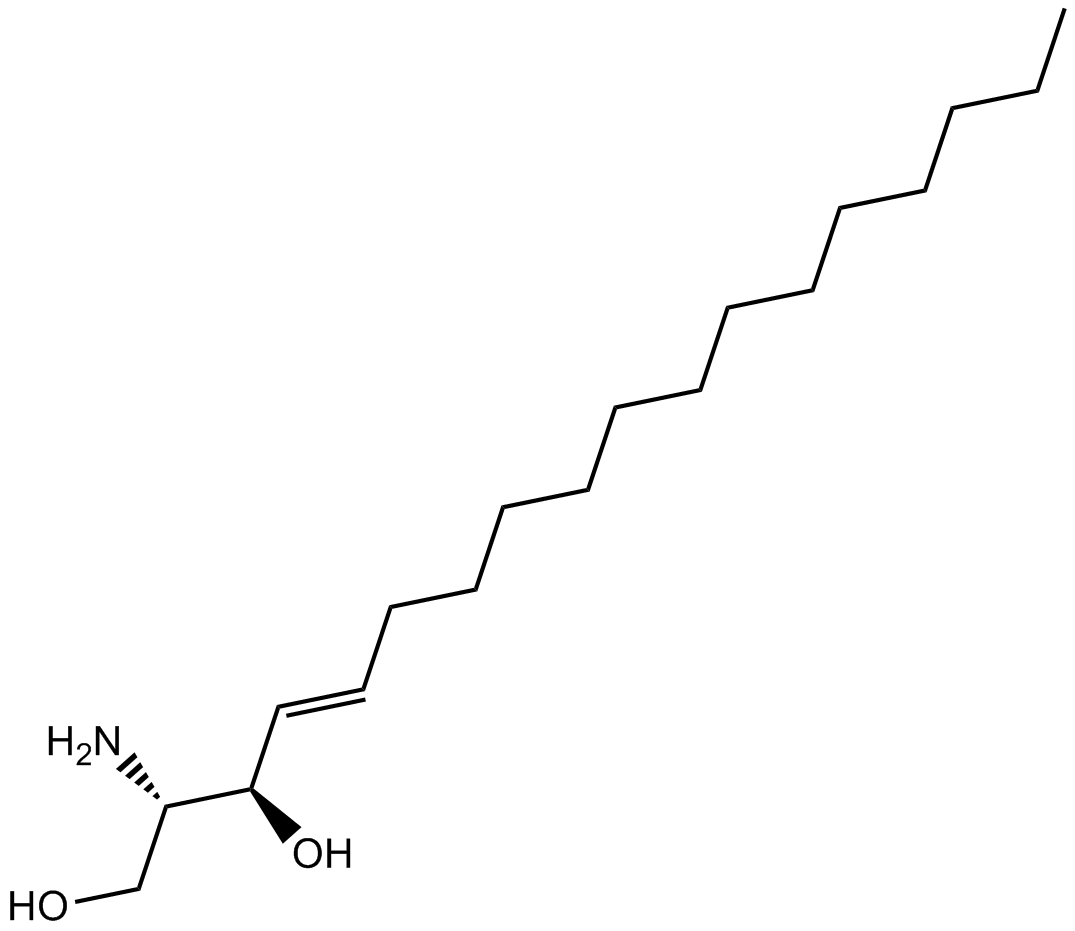 B6385 D-erythro-Sphingosine (synthetic)Summary: protein kinase C and calmodulin-dependent enzymes inhibitor
B6385 D-erythro-Sphingosine (synthetic)Summary: protein kinase C and calmodulin-dependent enzymes inhibitor -
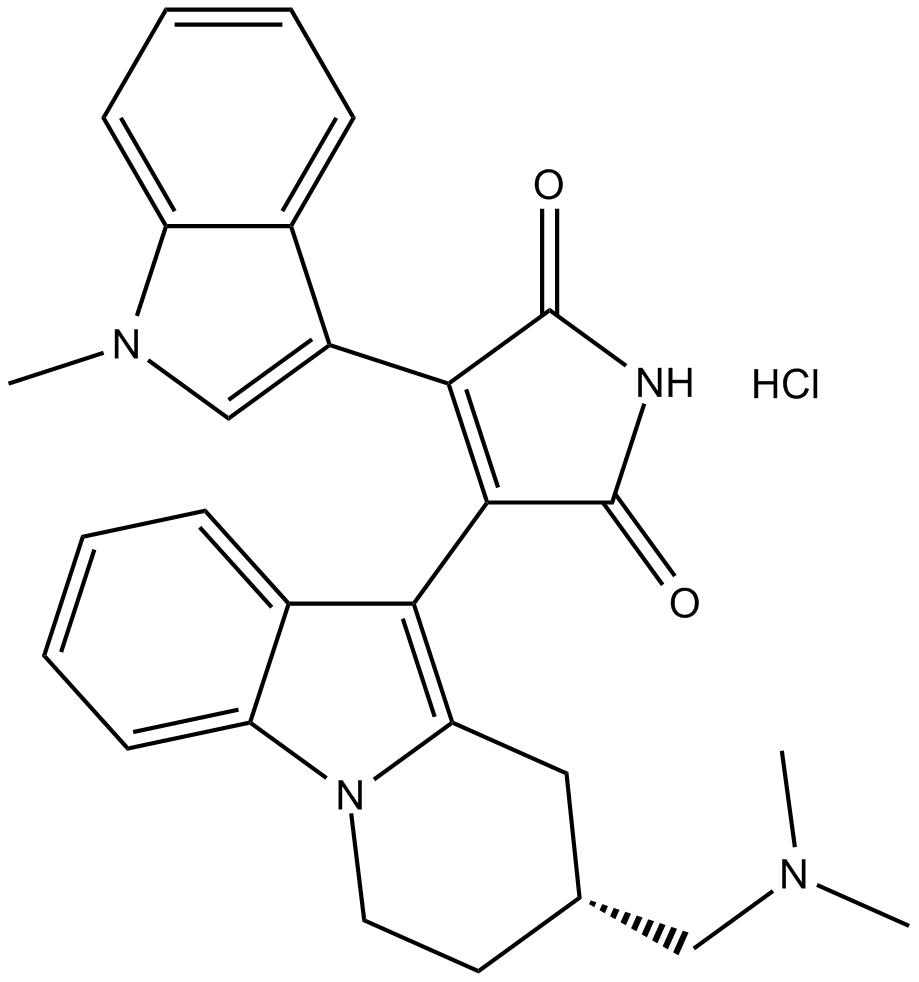 B6798 Ro 32-0432 hydrochlorideSummary: protein kinase C inhibitor
B6798 Ro 32-0432 hydrochlorideSummary: protein kinase C inhibitor

