Bromodomain
Bromodomains are a family of evolutionarily conserved protein modules of approximately 110 amino acids that have been found in chromatin-associated proteins as well as nuclear histone acetyltransferases (HATs). Besides its role in chromatin remodeling, recent studies have identified that bromodomains, as acetyl-lysine binding domains, are able to recognize and bind ε–N-acetylated lysine residues in histone and non-histone proteins. The nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopic analysis reveals that the chemical structure of bromodomains, consisting of four left-handed α-helices (including αZ, αA, αB and αC) connected by two loops (ZA and BC loops), forms a deep hydrophobic cavity serving as the acetyl-lysine recognition site.
-
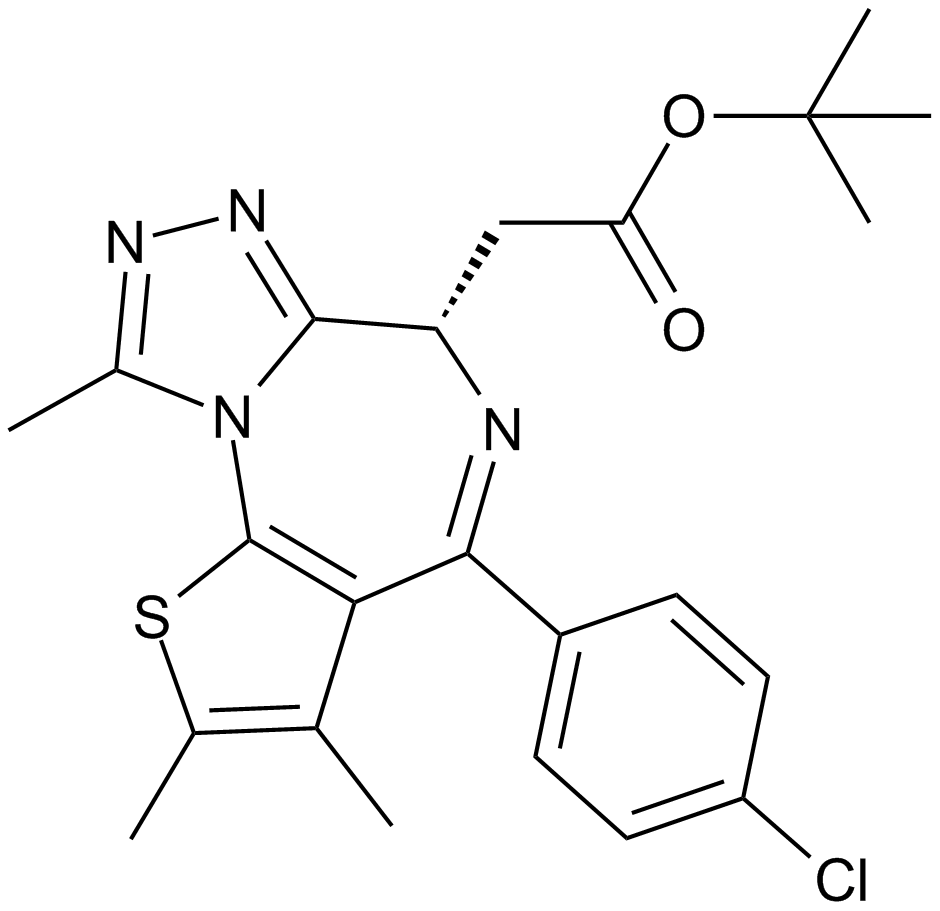 A1910 Bromodomain Inhibitor, (+)-JQ138 CitationTarget: BromodomainsSummary: BET bromodomain inhibitor
A1910 Bromodomain Inhibitor, (+)-JQ138 CitationTarget: BromodomainsSummary: BET bromodomain inhibitor -
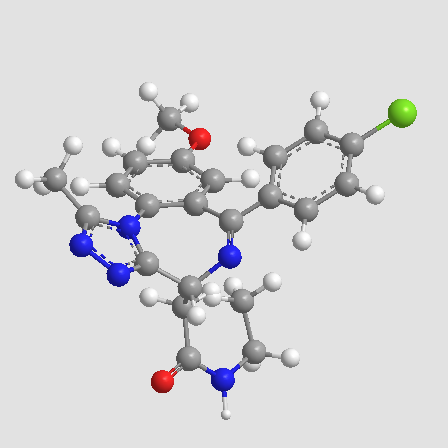 A3445 GSK 525768ASummary: inactive stereoisomer of I-BET-762
A3445 GSK 525768ASummary: inactive stereoisomer of I-BET-762 -
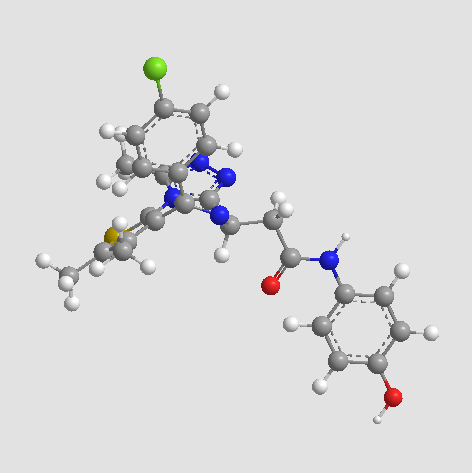 A3692 OTX-0153 CitationTarget: BromodomainsSummary: BRD inhibitor
A3692 OTX-0153 CitationTarget: BromodomainsSummary: BRD inhibitor -
 A3901 UNC12151 CitationTarget: L3MBTLSummary: Chemical probe for the methyllysine (Kme)
A3901 UNC12151 CitationTarget: L3MBTLSummary: Chemical probe for the methyllysine (Kme)

