Search results for: 'signaling pathways chromatin epigenetics bromodomain'
-
 A8315 NU7441 (KU-57788)4 CitationTarget: PI3K|DNA-PKSummary: DNA-PK inhibitor
A8315 NU7441 (KU-57788)4 CitationTarget: PI3K|DNA-PKSummary: DNA-PK inhibitor -
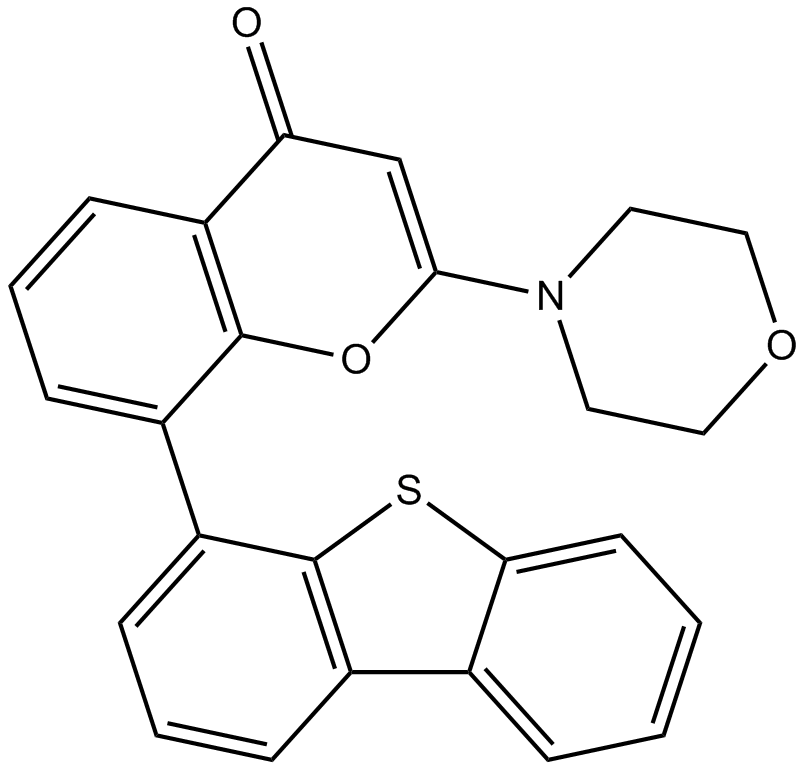
 A1910 Bromodomain Inhibitor, (+)-JQ166 CitationTarget: BromodomainsSummary: BET bromodomain inhibitor
A1910 Bromodomain Inhibitor, (+)-JQ166 CitationTarget: BromodomainsSummary: BET bromodomain inhibitor -
 L1029 DiscoveryProbe™ Epigenetics Compound LibrarySummary: A unique collection of 328 epigenetics-related small molecules for epigenetics reasearch.
L1029 DiscoveryProbe™ Epigenetics Compound LibrarySummary: A unique collection of 328 epigenetics-related small molecules for epigenetics reasearch. -
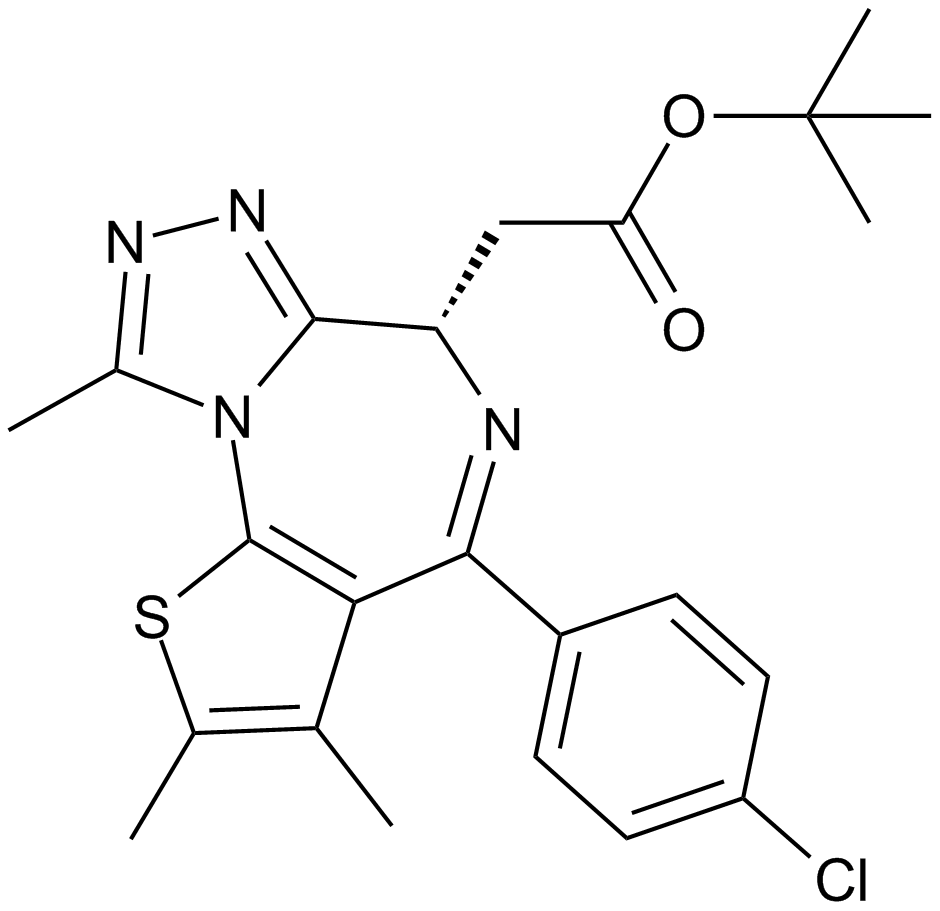
 A8221 EPZ-64385 CitationSummary: EZH2 inhibitor
A8221 EPZ-64385 CitationSummary: EZH2 inhibitor -
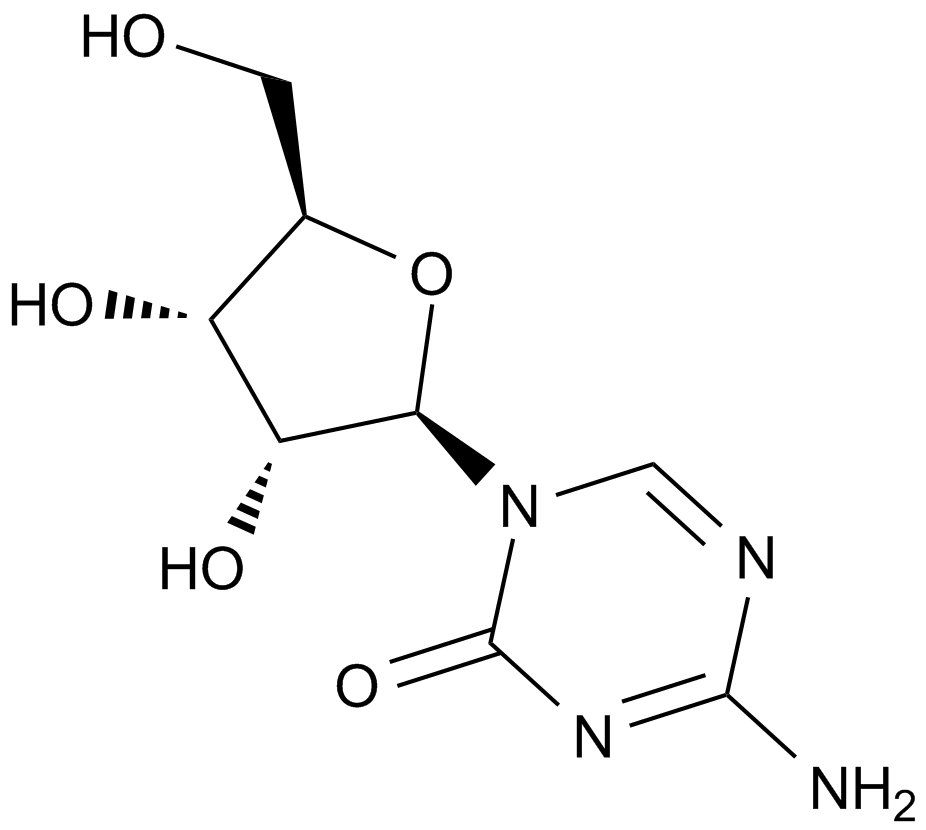 A1907 5-Azacytidine6 CitationTarget: DNA MethyltransferasesSummary: DNA methyltransferase inhibitor.
A1907 5-Azacytidine6 CitationTarget: DNA MethyltransferasesSummary: DNA methyltransferase inhibitor. -
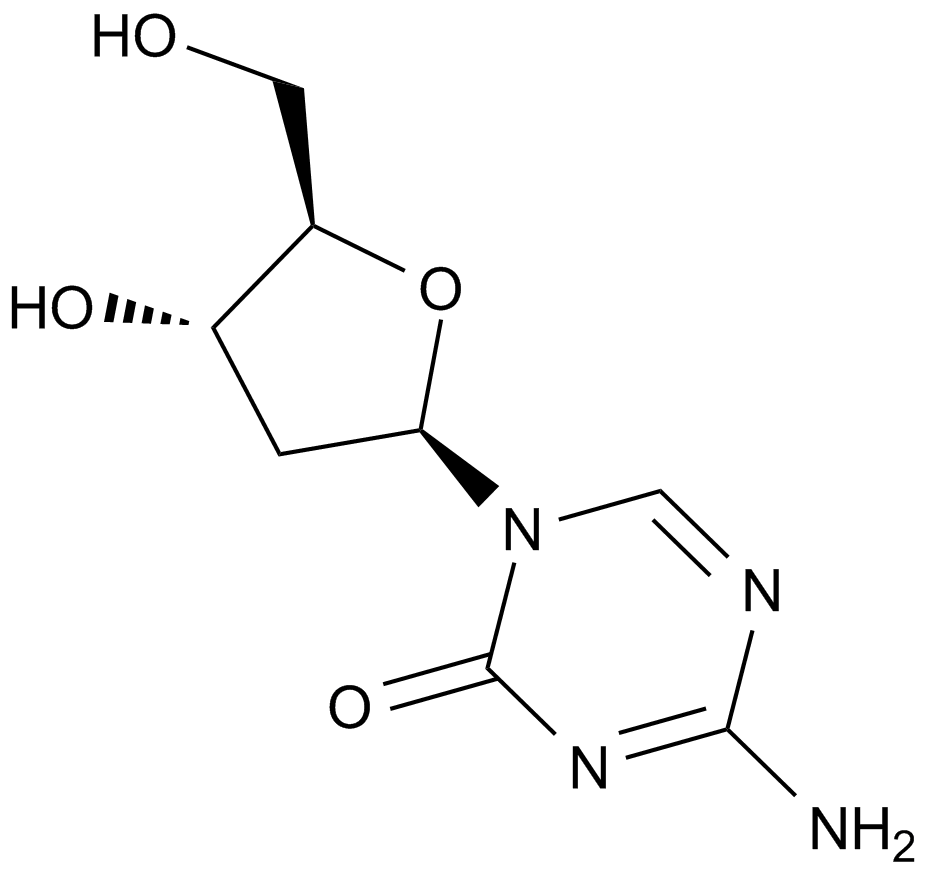 A1906 Decitabine (NSC127716, 5AZA-CdR)Summary: Deoxycytidine analog and cellular diifferentiation inducer
A1906 Decitabine (NSC127716, 5AZA-CdR)Summary: Deoxycytidine analog and cellular diifferentiation inducer -
 L1044 DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling LibrarySummary: A unique collection of 73 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research.
L1044 DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling LibrarySummary: A unique collection of 73 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research. -
 L1026 DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Library1 CitationSummary: A unique collection of 556 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch.
L1026 DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Library1 CitationSummary: A unique collection of 556 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch. -
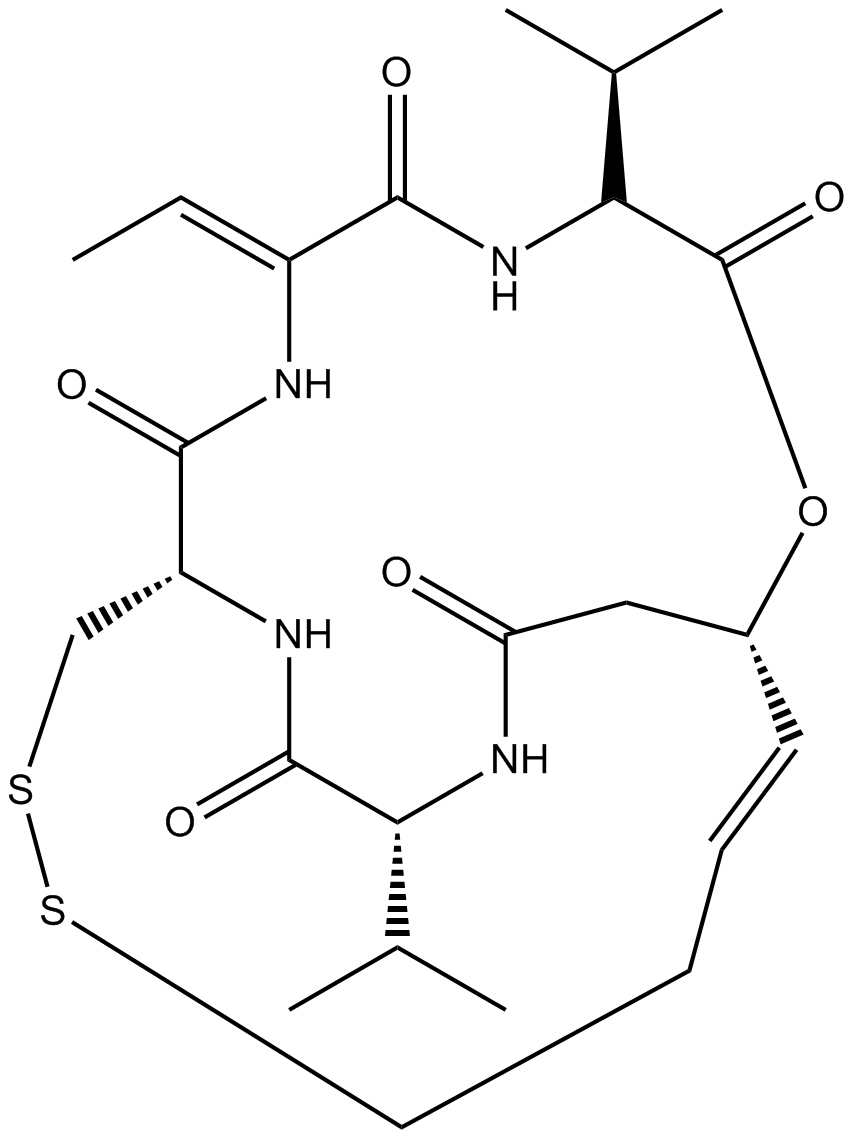 A8173 Romidepsin (FK228, depsipeptide)7 CitationTarget: Histone Deacetylases (HDACs)Summary: HDAC1/HDAC2 inhibitor, potent and selective
A8173 Romidepsin (FK228, depsipeptide)7 CitationTarget: Histone Deacetylases (HDACs)Summary: HDAC1/HDAC2 inhibitor, potent and selective -
 L1044P DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling Compound Library PlusSummary: A unique collection of 178 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research.
L1044P DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling Compound Library PlusSummary: A unique collection of 178 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research.


