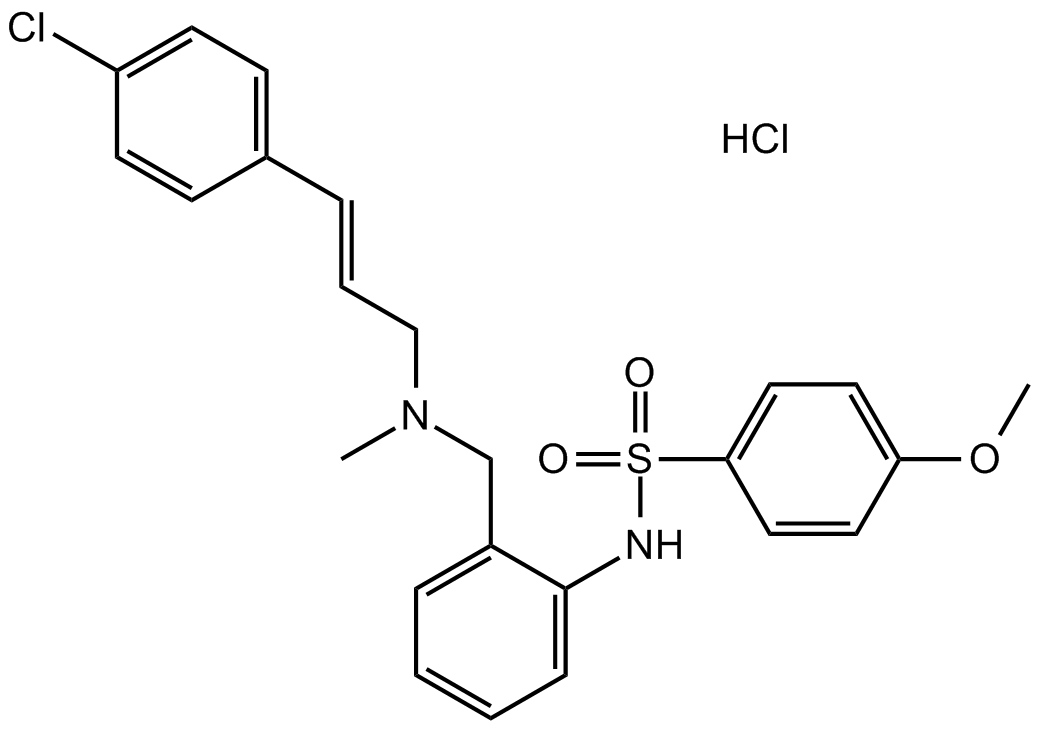
KN-92 hydrochloride
KN-92 is an inactive analog of KN-93. KN-93 is the CaM kinase II inhibitor. [1]
Hearts were treated with the CaM kinase inhibitor KN-93 or the inactive analog KN-92 (0.5 μM) for 10 min before clofilium exposure. Early afterdepolarizations (EADs) were largely inhibited by KN-93 contrasted to KN-92. There were little differences in parameters favoring EADs such as monophasic action potential duration or heart rate in KN-92- or KN-93- treated hearts. CaM kinase activity in situ increased 37% in hearts with EADs compared to hearts without EADs. This increase in CaM kinase activity was prevented by pretreatment with KN-93. [1]
In vitro, KN-93 potently suppressed rabbit myocardial CaM kinase activity (calculated Ki ≤ 2.58 μM), but the inactive analog KN-92 did not (Ki > 100 μM). The actions of KN-93 and KN-92 on ICa and other repolarizing K+currents did not illustrate preferential EAD suppression by KN-93. [1]
Reference:
1. KN-93, an inhibitor of multifunctional Ca++/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase, decreases early afterdepolarizations in rabbit heart. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1998 Dec;287(3):996-1006.
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 493.45 |
| Cas No. | 1431698-47-3 |
| Formula | C24H26Cl2N2O3S |
| Synonyms | KN 92 hydrochloride;KN92 hydrochloride |
| Solubility | ≥24.65 mg/mL in DMSO; insoluble in H2O; ≥11.73 mg/mL in EtOH with gentle warming and ultrasonic |
| Chemical Name | (E)-N-(2-(((3-(4-chlorophenyl)allyl)(methyl)amino)methyl)phenyl)-4-methoxybenzenesulfonamide hydrochloride |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | ClC1=CC=C(/C=C/CN(C)CC2=CC=CC=C2NS(C3=CC=C(OC)C=C3)(=O)=O)C=C1.Cl |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment[1]: | |
|
Cell lines |
NIH 3T3 fibroblasts |
|
Preparation method |
The solubility of this compound in DMSO is > 10 mM. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37 ℃ for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while. Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. |
|
Reacting condition |
72 h, 4-24 μM |
|
Applications |
KN-92 is an inactive derivative of KN-93. KN-92 is usually used as a control in studies to elucidate the effect of KN-93. KN-93 inhibits fibroblast CaMK-II activity and cell growth, whereas KN-92 had no effect on CaMK-II activity or cell growth. |
| Animal experiment [2]: | |
|
Animal models |
AC3-I and AC3-C transgenic mice |
|
Dosage form |
20 μmol/kg, intraperitoneal |
|
Application |
Treatment with KN-93 in WT mice resulted in a dose-dependent improvement in left ventricular function compared to WT mice treated with KN-92. Surviving myocytes from infarcted wild-type mice without treatment or treated with control drug KN-92 exhibited severely disordered Ca2+ homeostasis. In contrast, Ca2+ homeostasis was preserved after myocardial infarction in wild-type mice treated with KN-93. |
|
Other notes |
Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
|
References: [1]. Tombes R M, Grant S, Westin E H, et al. G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis are induced in NIH 3T3 cells by KN-93, an inhibitor of CaMK-II (the multifunctional Ca2+/CaM kinase)[J]. Cell growth & differentiation: the molecular biology journal of the American Association for Cancer Research, 1995, 6(9): 1063. [2]. Zhang R, Khoo M S C, Wu Y, et al. Calmodulin kinase II inhibition protects against structural heart disease[J]. Nature medicine, 2005, 11(4): 409-417. |
|
| Description | KN-92 hydrochloride is a negative control for KN-93. | |||||
| Targets | ||||||
| IC50 | ||||||
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure