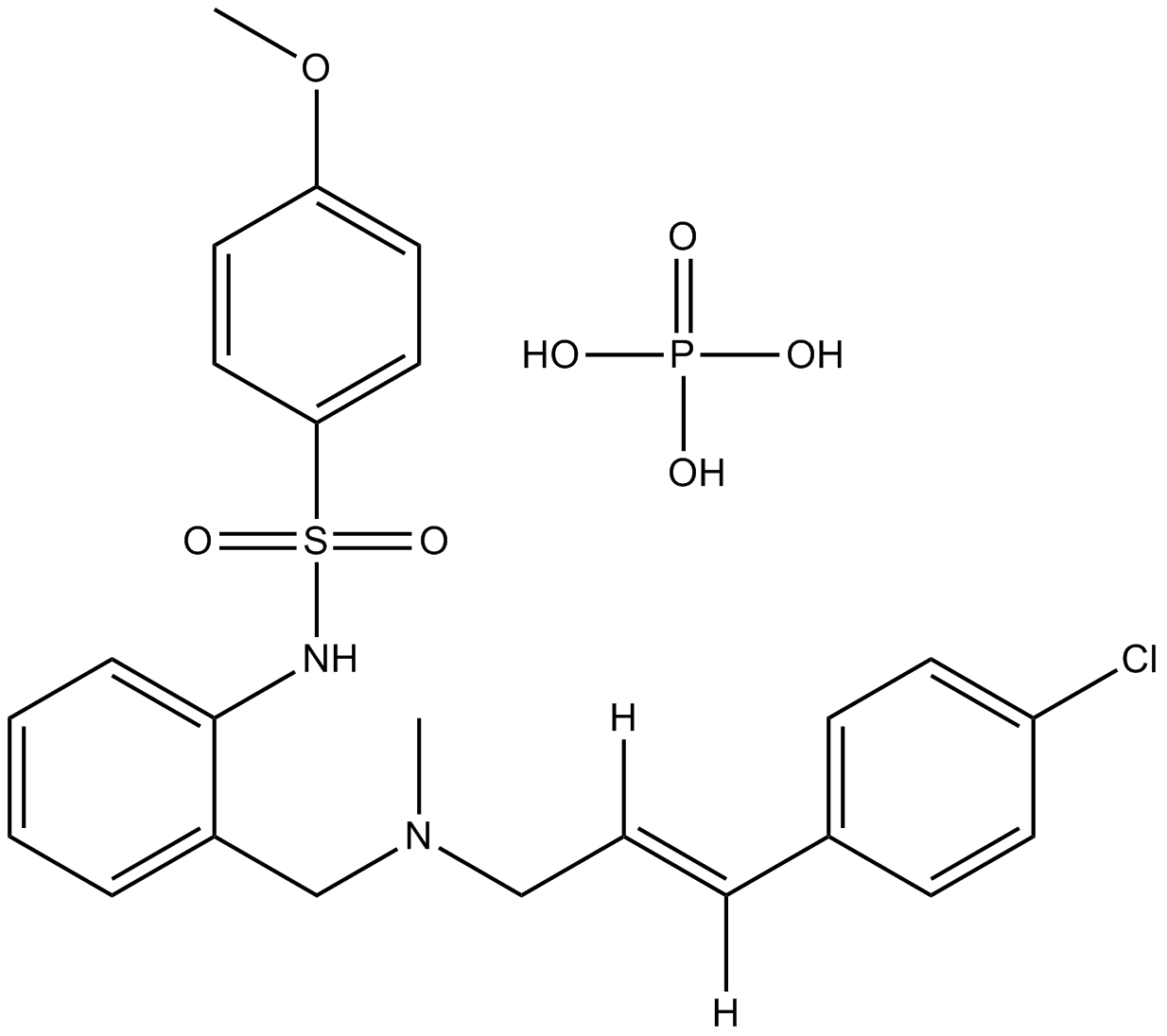
KN-92 phosphate
KN-92 is the inactive analog of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase II (CaMKII) inhibitor KN-93. KN-92 has been often used as negative control for KN-93.KN-92 significantly reduced the sustained current amplitudes at the end of the 5-s depolarizing pulses of a wide range of Kv channels such as Kv1.5 and Kv1.2 [1].
Reference:
[1]. Rezazadeh S, Claydon TW, Fedida D.KN-93(2-[N-(2-hydroxyethyl)]-N-(4-methoxybenzenesulfonyl)]amino-N-(4-chlorocinnamyl)-N-methylbenzylamine), a calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II inhibitor, is a direct extracellular blocker of voltage-gated potassium channels.J PharmacolExpTher. 2006 Apr;317(1):292-9.
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 554.98 |
| Cas No. | 1135280-28-2 |
| Formula | C24H28ClN2O7PS |
| Synonyms | KN 92 phosphate;KN92 phosphate |
| Solubility | ≥25 mg/mL in DMSO; insoluble in H2O; ≥43.1 mg/mL in EtOH with gentle warming |
| Chemical Name | (E)-N-(2-(((3-(4-chlorophenyl)allyl)(methyl)amino)methyl)phenyl)-4-methoxybenzenesulfonamide phosphate |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | CN(CC1=CC=CC=C1NS(C2=CC=C(OC)C=C2)(=O)=O)C/C([H])=C([H])/C3=CC=C(Cl)C=C3.OP(O)(O)=O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment [1]: | |
|
Cell lines |
rabbit hypertrophic cardiac myocytes |
|
Preparation method |
The solubility of this compound in DMSO is >25mg/mL. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37℃ for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while. Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. |
|
Reacting condition |
0.5 μmol/L and 1 μmol/L |
|
Applications |
KN-92 is the inactive analog of KN-93. Under the conditions of low potassium, low magnesium Tyrode’s solution perfusion, and slow frequency electrical stimulation, the incidence of early after-depolarizations (EADs) was 0/12, 11/12, 10/12, and 5/12 in sham group, left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) group, KN-92 group (0.5 μmol/L), and KN-93 group (0.5 μmol/L), respectively. When the drug concentration was increased to 1 μmol/L in KN-92 group and KN-93 group, the incidence of EADs was 10/12 and 2/12, respectively. When the drug concentration was 0.5 μmol/L in KN-92 and KN-93 groups, the peak ICa, L at 0 mV was decreased by (9.4±2.8)% and (10.5±3.0)%, respectively. When the drug concentration was increased to 1 μmol/L, the peak ICa, L values were lowered by (13.4±3.7)% and (40±4.9)%, respectively. |
| Animal experiment [2]: | |
|
Animal models |
Spontaneously hypertensive rats |
|
Dosage form |
1 μmol/L |
|
Application |
In spontaneously hypertensive rats, action potential duration alternans (APD-ALT) was evoked at significantly lower pacing rate, KN-93 (1 μmol/L), but not its inactive analog, KN-92 (1 μmol/L), completely reversed these changes in APD-ALT. The magnitude of APD-ALT was also significantly greater in SHR than WKY and was completely normalized by KN-93. KN-93 also abolished ventricular fibrillation (VF) induced by rapid pacing in SHR. |
|
Other notes |
Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
|
References: [1]. Ke J1, Chen F, Zhang C, et al. Effects of calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II inhibitor, KN-93, on electrophysiological features of rabbit hypertrophic cardiac myocytes. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2012 Aug;32(4):485-9. [2]. Mitsuyama H1, Yokoshiki H2, Watanabe M1, et al. Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II increases the susceptibility to the arrhythmogenic action potential alternans in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2014 Jul 15;307(2):H199-206. |
|
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure