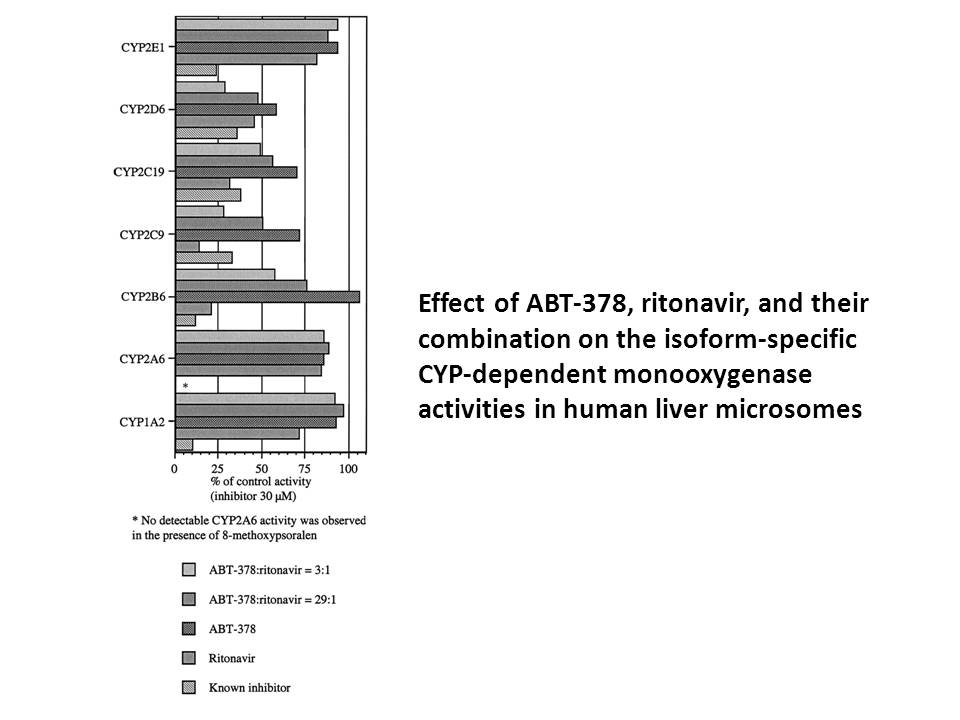
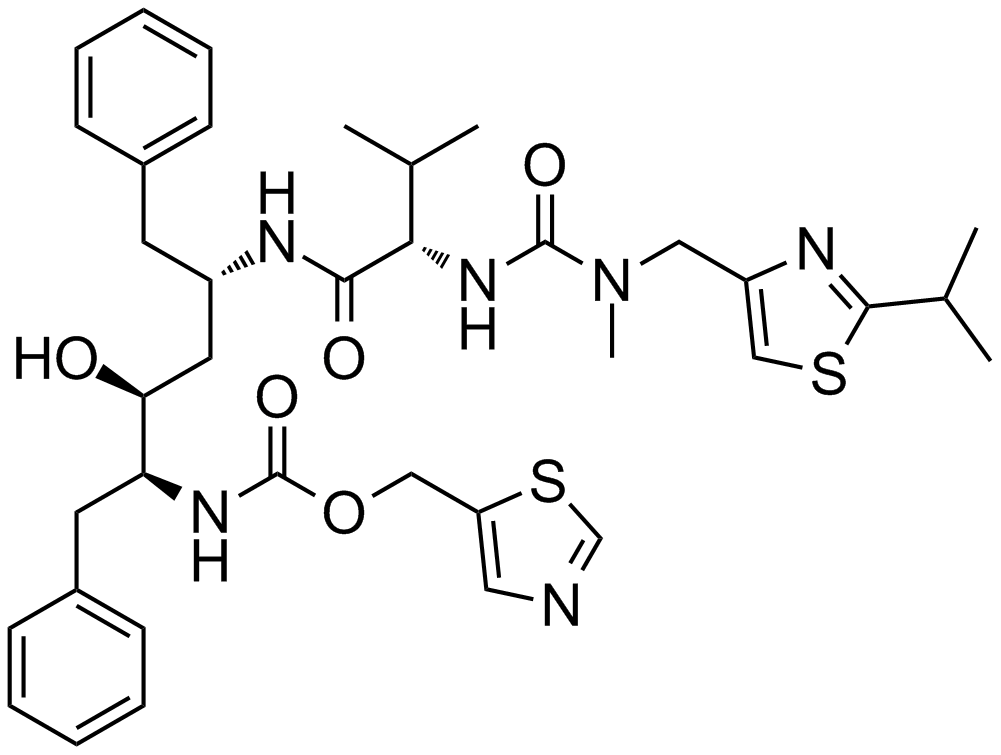
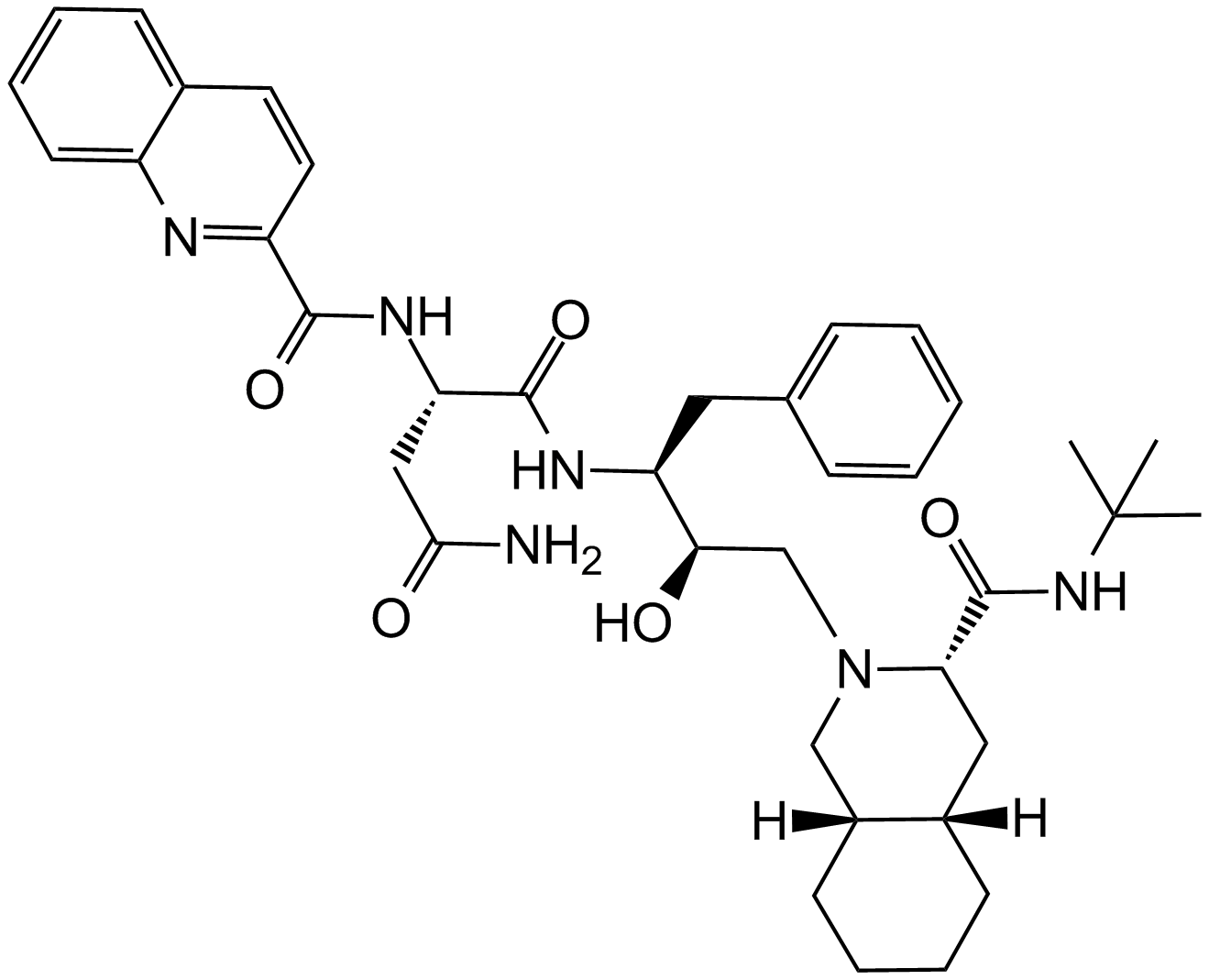
Ritonavir
Ritonavir, previously known as ABT-538, is a potent inhibitor of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) protease that exhibits potent in vitro inhibition against HIV-1 strain as well as HIV-2 strain with 50% effective concentration EC50 values of 0.022 μM and 0.16 μM respectively. Ritonavir binds to the HIV-1 protease inactivating its function to cleave the Gag and Gag-Pol polyproteins into the core proteins and viral enzymes, which results in the formation of noninfectious viral particles. X-ray crystallographic analysis reveals a hydrophobic cluster between the isopropyl substituent on the P3 thiazolyl group of ritonavir and the side chains of Pro-81 and Val-82 of HIV-1 protease within the complex of ritonavir/HIV-1 protease.
Reference
Kempf DJ, Marsh KC, Denissen JF, McDonald E, Vasavanonda S, Flentge CA, Green BE, Fino L, Park CH, Kong XP, et al. ABT-538 is a potent inhibitor of human immunodeficiency virus protease and has high oral bioavailability in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Mar 28;92(7):2484-8.
Markowitz M, Saag M, Powderly WG, Hurley AM, Hsu A, Valdes JM, Henry D, Sattler F, La Marca A, Leonard JM, et al. A preliminary study of ritonavir, an inhibitor of HIV-1 protease, to treat HIV-1 infection. N Engl J Med. 1995 Dec 7;333(23):1534-9.
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 720.9 |
| Cas No. | 155213-67-5 |
| Formula | C37H48N6O5S2 |
| Synonyms | Abbott 84538, ABT-538,Ritonavir |
| Solubility | ≥26 mg/mL in DMSO with gentle warming; insoluble in H2O; ≥9.02 mg/mL in EtOH |
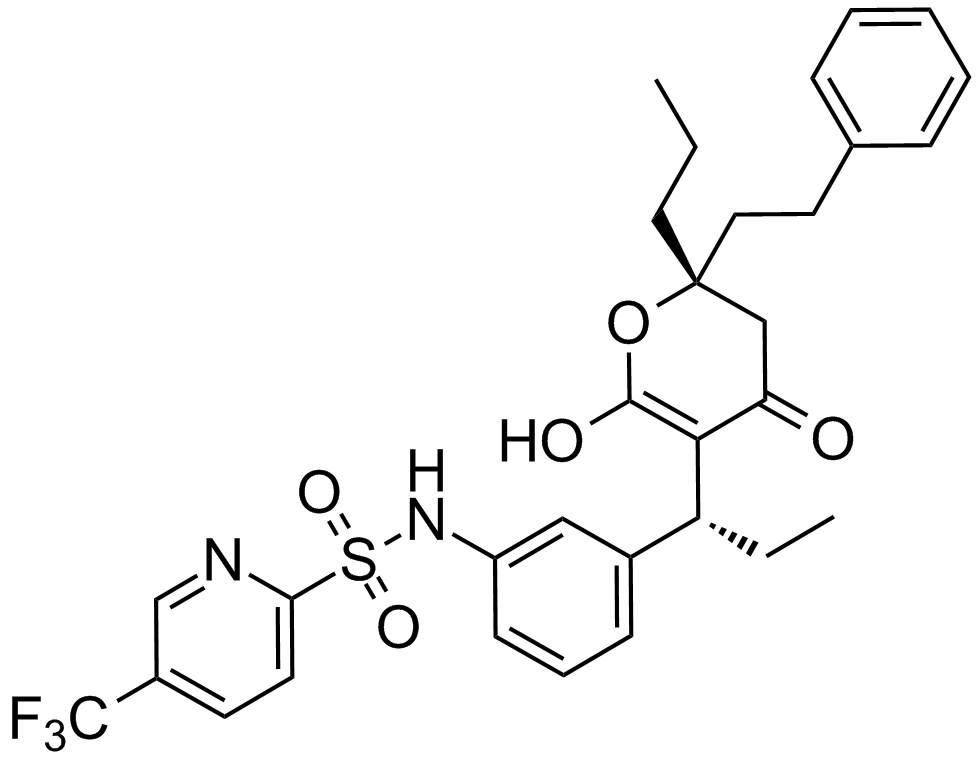
| Chemical Name | thiazol-5-ylmethyl ((2S,3S,5S)-3-hydroxy-5-((S)-2-(3-((2-isopropylthiazol-4-yl)methyl)-3-methylureido)-3-methylbutanamido)-1,6-diphenylhexan-2-yl)carbamate |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | CC(C1=NC(CN(C(N[C@H](C(N[C@H](C[C@H](O)[C@@H](NC(OCC2=CN=CS2)=O)CC3=CC=CC=C3)CC4=CC=CC=C4)=O)C(C)C)=O)C)=CS1)C |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Anti-virus experiment [1]: | |
|
Viruses |
HIV |
|
Preparation method |
The solubility of this compound in DMSO is > 10 mM. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37 °C for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while. Stock solution can be stored below - 20 °C for several months. |
|
Reacting condition |
0 ~ 0.16 μM |
|
Applications |
Ritonavir potently inhibited the activity of laboratory and clinical strains of HIV-1 with the EC50 values ranging from 0.022 to 0.13 μM. Moreover, Ritonavir also efficiently inhibited the activity of HIV-2, with the EC50 value of 0.16 μM. |
| Animal experiment [1]: | |
|
Animal models |
Male SD rats |
|
Dosage form |
10 mg/kg; p.o. |
|
Applications |
In rats, oral administration of 10 mg/kg Ritonavir resulted in prolonged absorption (tmax = 2.0 hrs). The peak of plasma Ritonavir concentration was > 100 folds of the EC50 value. The calculated oral bioavailability reached 78%. |
|
Other notes |
Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
|
References: [1]. Kempf DJ, Marsh KC, Denissen JF, McDonald E, Vasavanonda S, Flentge CA, Green BE, Fino L, Park CH, Kong XP, et al. ABT-538 is a potent inhibitor of human immunodeficiency virus protease and has high oral bioavailability in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Mar 28;92(7):2484-8. |
|
| Description | Ritonavir is an antiretroviral (HIV) drug and inhibitor of particular liver enzyme that normally metabolizes protease inhibitors, cytochrome P450-3A4 (CYP3A4). | |||||
| Targets | HIV Protease | |||||
| IC50 | ||||||
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure
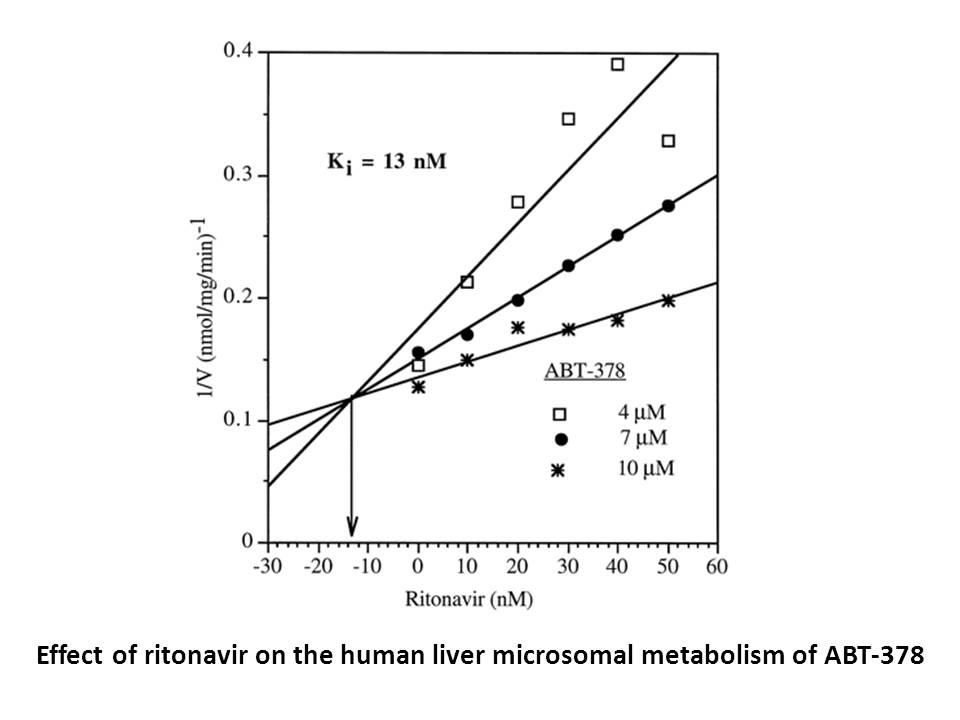
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data