Immunology/Inflammation

The adaptive immune system consists of B and T lymphocytes which mediate humoral immunity (e.g. antibody response) and cell-mediated immunity, respectively. B cell receptor and T cell receptor signaling is responsible for activation of Src family tyrosine kinases, such as Blk, Fyn, and Lyn in B cells and Fyn and Lck in T cells, resulting phosphorylation of the receptor-associated ITAM motifs. Phosphorylated ITAMs serve as the docking sites for Syk family tyrosine kinases, e.g. Syk in B cells and Zap-70 in T cells. Activated Syk kinases then propagate the signals via phosphorylation of downstream proteins. Furthermore, lymphocyte receptor signaling facilitates B and T cell development, differentiation, proliferation and survival.
-
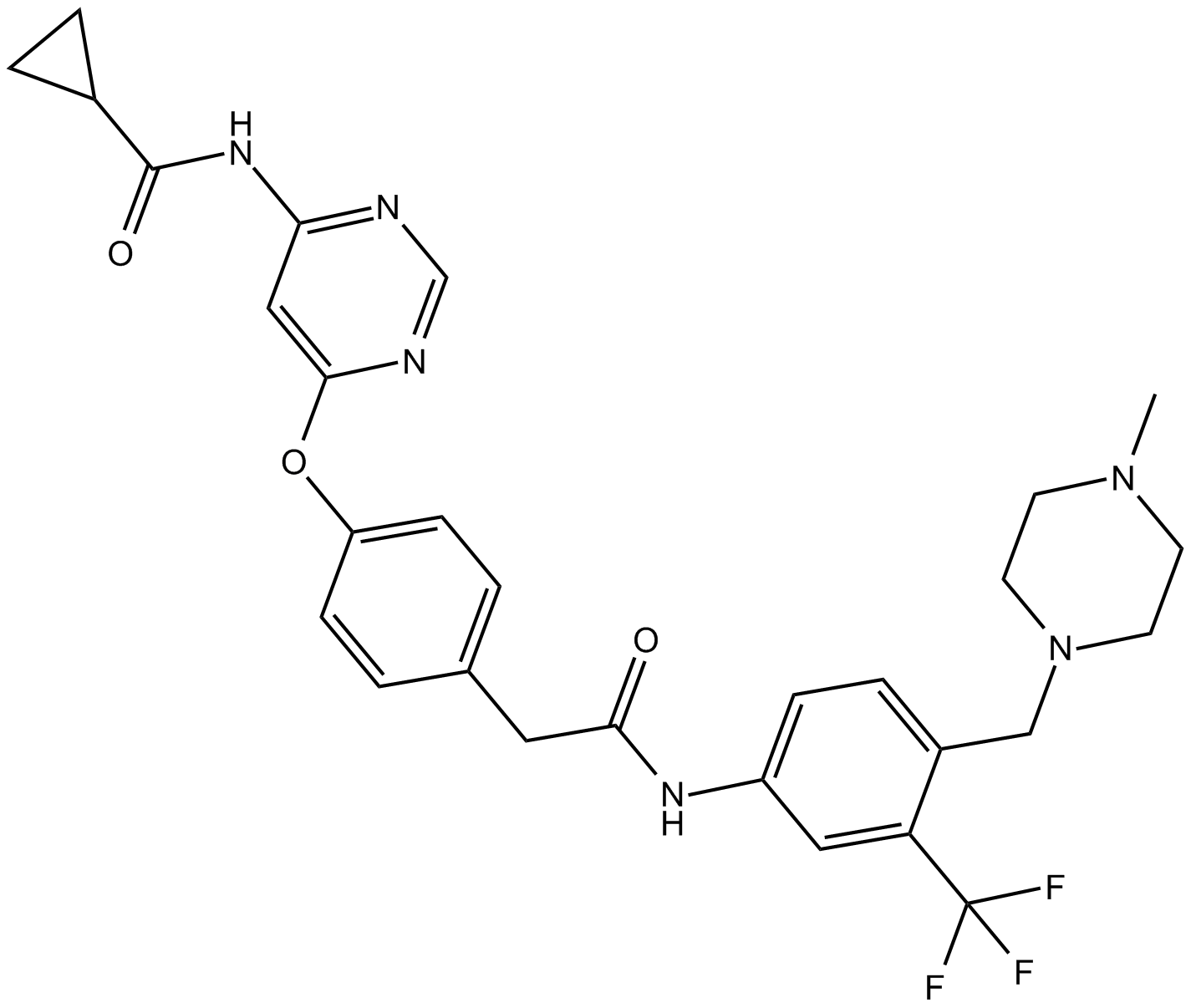 B4880 WS6Summary: inducer of β cell proliferation
B4880 WS6Summary: inducer of β cell proliferation -
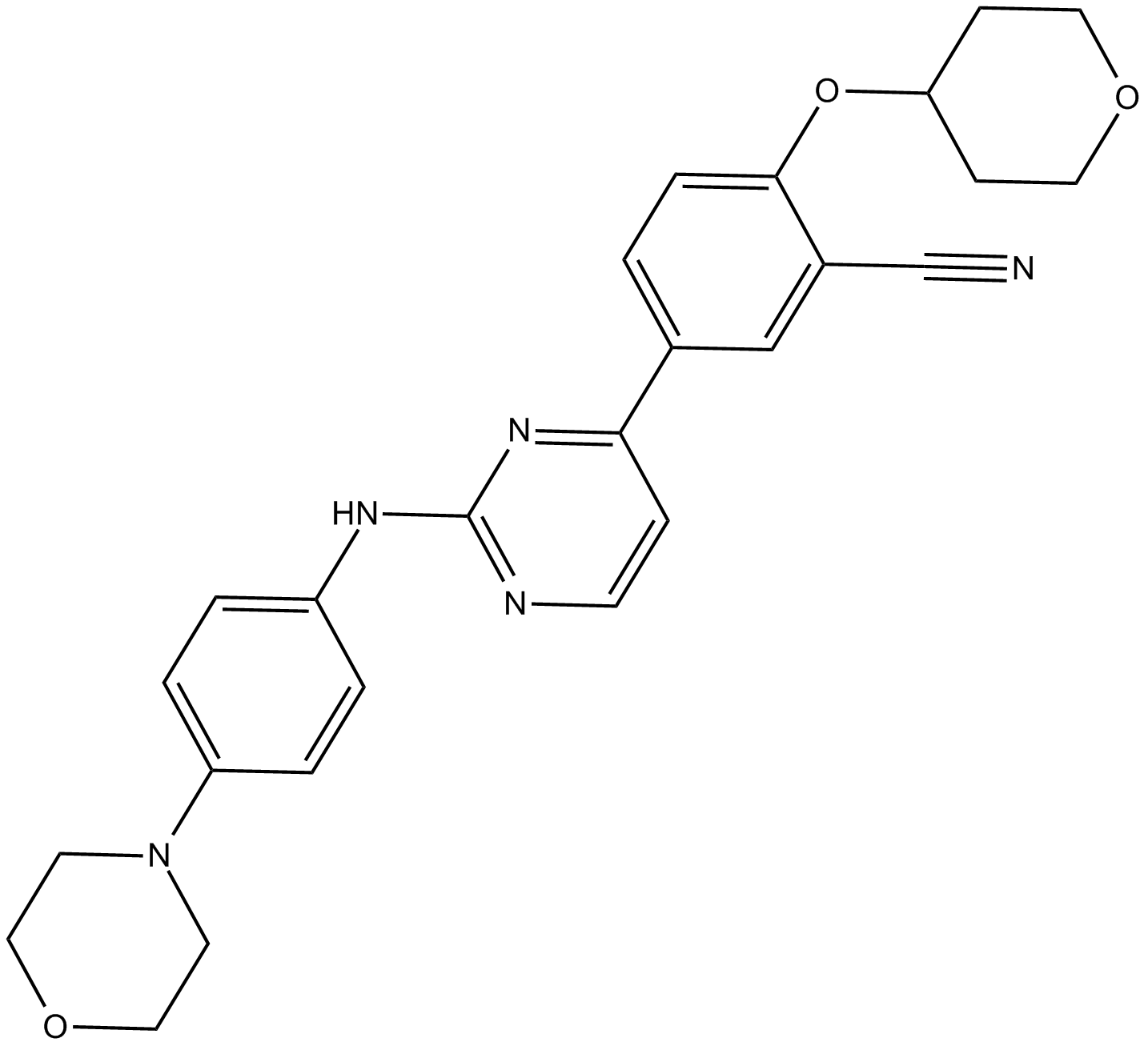 B4825 IKKε-IN-1Summary: potent IKKε inhibitor
B4825 IKKε-IN-1Summary: potent IKKε inhibitor -
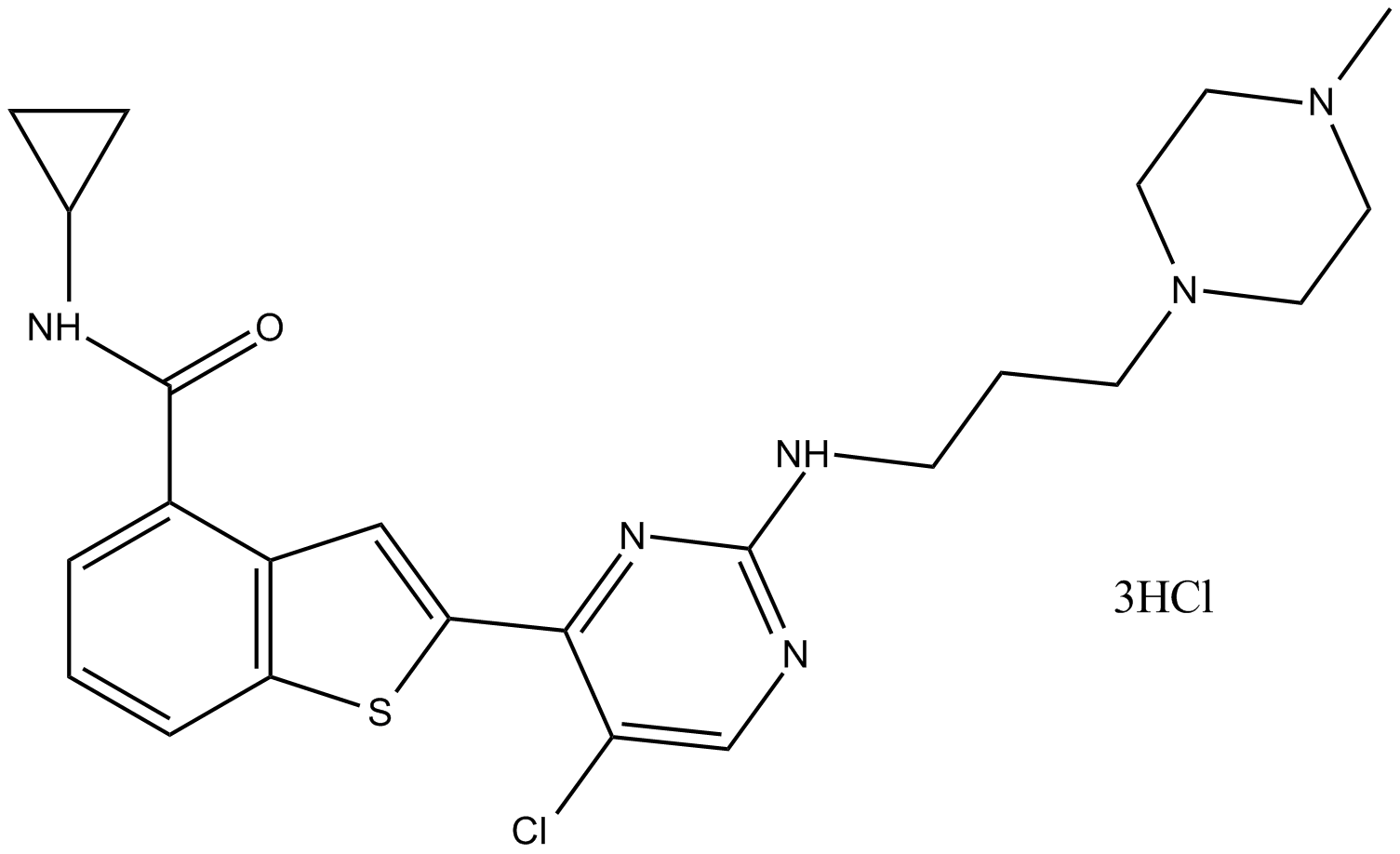 B4986 LY2409881Summary: potent and selective IKK2 inhibitor
B4986 LY2409881Summary: potent and selective IKK2 inhibitor -
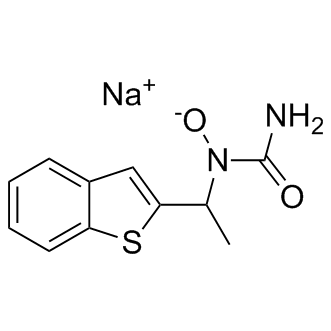 B1207 Zileuton sodiumSummary: 5-lipoxygenase and leukotrienes inhibitor
B1207 Zileuton sodiumSummary: 5-lipoxygenase and leukotrienes inhibitor -
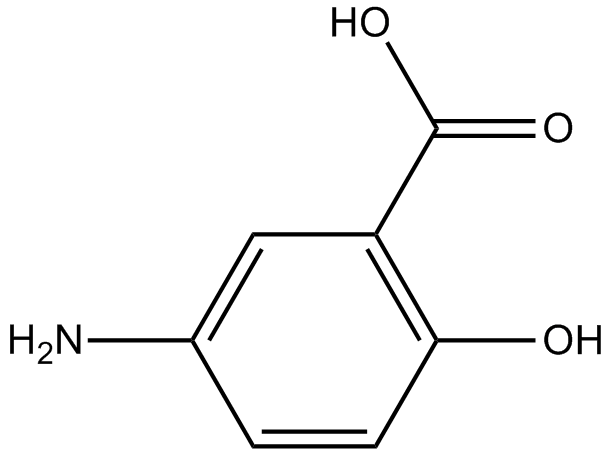 B1969 MesalamineSummary: IKK inhibitor
B1969 MesalamineSummary: IKK inhibitor -
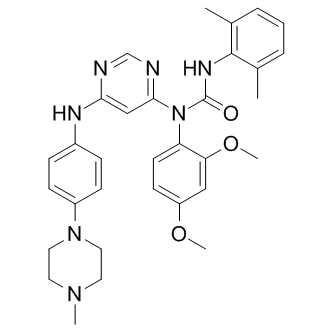 B1052 HG-9-91-012 CitationSummary: Pan-SIK (salt-inducible kinases) inhibitor
B1052 HG-9-91-012 CitationSummary: Pan-SIK (salt-inducible kinases) inhibitor -
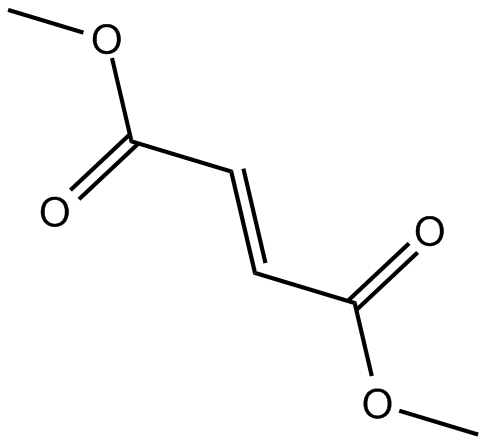 B1931 Dimethyl FumarateSummary: nuclear factor (erythroid-derived)-like 2 (Nrf2) pathway activator
B1931 Dimethyl FumarateSummary: nuclear factor (erythroid-derived)-like 2 (Nrf2) pathway activator -
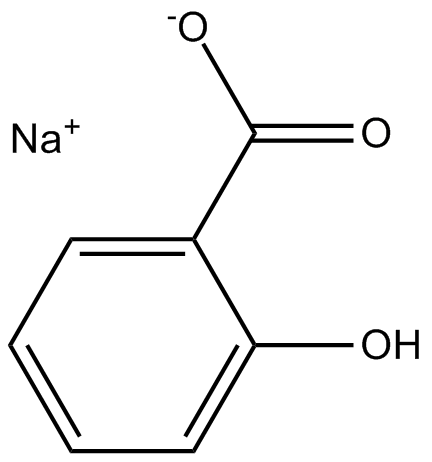 B2028 Sodium salicylateSummary: NF-κB inhibitor
B2028 Sodium salicylateSummary: NF-κB inhibitor -
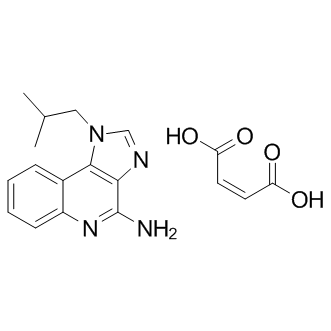 B1187 Imiquimod maleateSummary: Immune response modifier
B1187 Imiquimod maleateSummary: Immune response modifier -
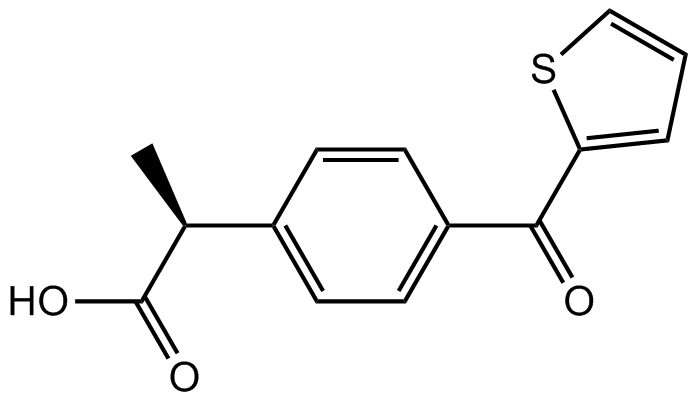 B2133 SuprofenTarget: COXSummary: dual COX-1/COX-2 inhibitor
B2133 SuprofenTarget: COXSummary: dual COX-1/COX-2 inhibitor

