Immunology/Inflammation

The adaptive immune system consists of B and T lymphocytes which mediate humoral immunity (e.g. antibody response) and cell-mediated immunity, respectively. B cell receptor and T cell receptor signaling is responsible for activation of Src family tyrosine kinases, such as Blk, Fyn, and Lyn in B cells and Fyn and Lck in T cells, resulting phosphorylation of the receptor-associated ITAM motifs. Phosphorylated ITAMs serve as the docking sites for Syk family tyrosine kinases, e.g. Syk in B cells and Zap-70 in T cells. Activated Syk kinases then propagate the signals via phosphorylation of downstream proteins. Furthermore, lymphocyte receptor signaling facilitates B and T cell development, differentiation, proliferation and survival.
-
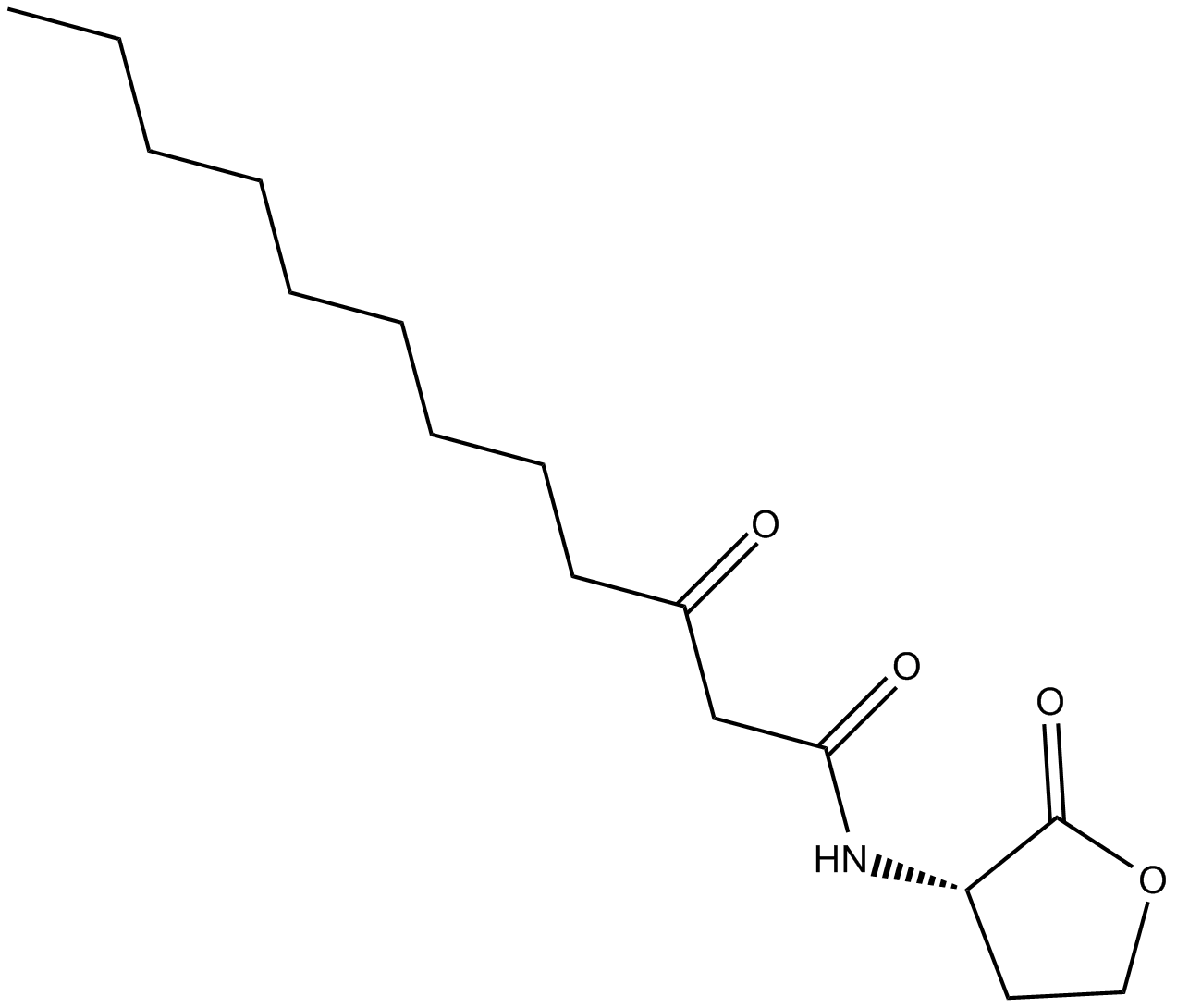 C4107 N-3-oxo-dodecanoyl-L-Homoserine lactoneSummary: NF-κB and AP-2 activator
C4107 N-3-oxo-dodecanoyl-L-Homoserine lactoneSummary: NF-κB and AP-2 activator -
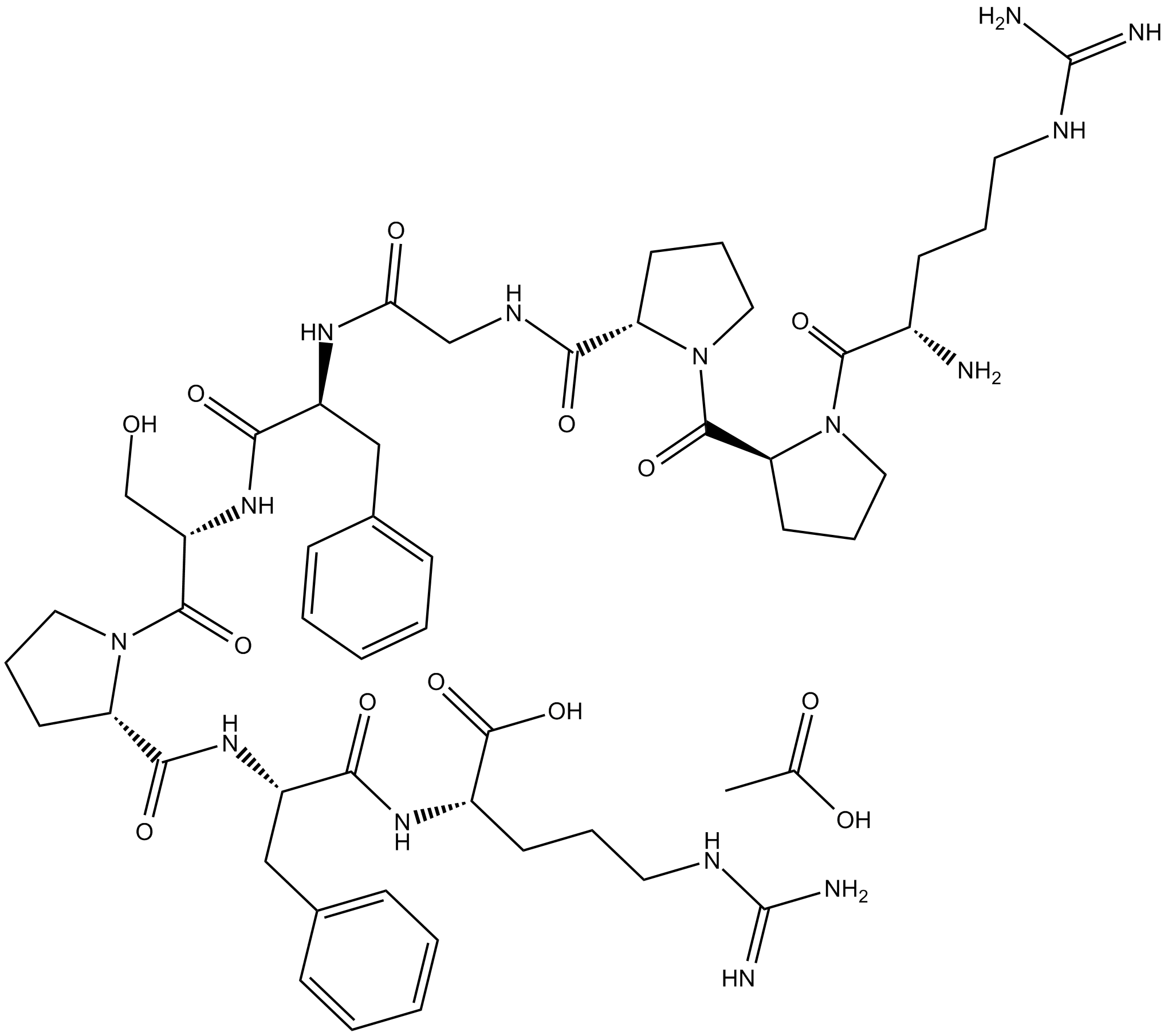 C4126 Bradykinin (acetate)Summary: inflammatory mediator
C4126 Bradykinin (acetate)Summary: inflammatory mediator -
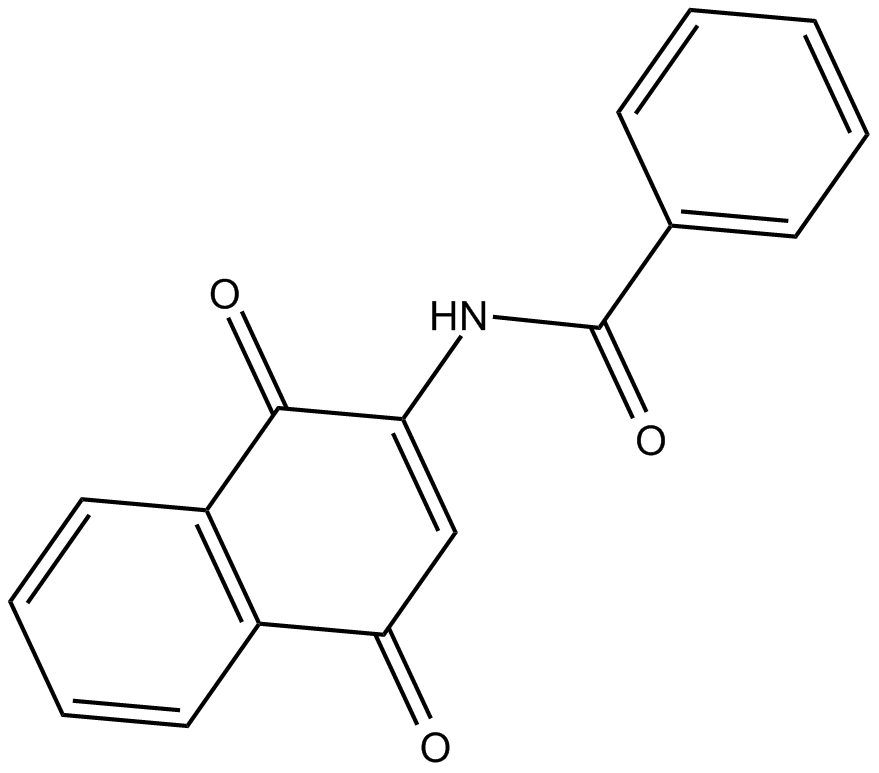 C4074 PPM-18Summary: NF-κB inhibitor
C4074 PPM-18Summary: NF-κB inhibitor -
 C4161 (S)-LisofyllineSummary: inactive optical enantiomer of (R)-LSF, an anti-inflammatory agent
C4161 (S)-LisofyllineSummary: inactive optical enantiomer of (R)-LSF, an anti-inflammatory agent -
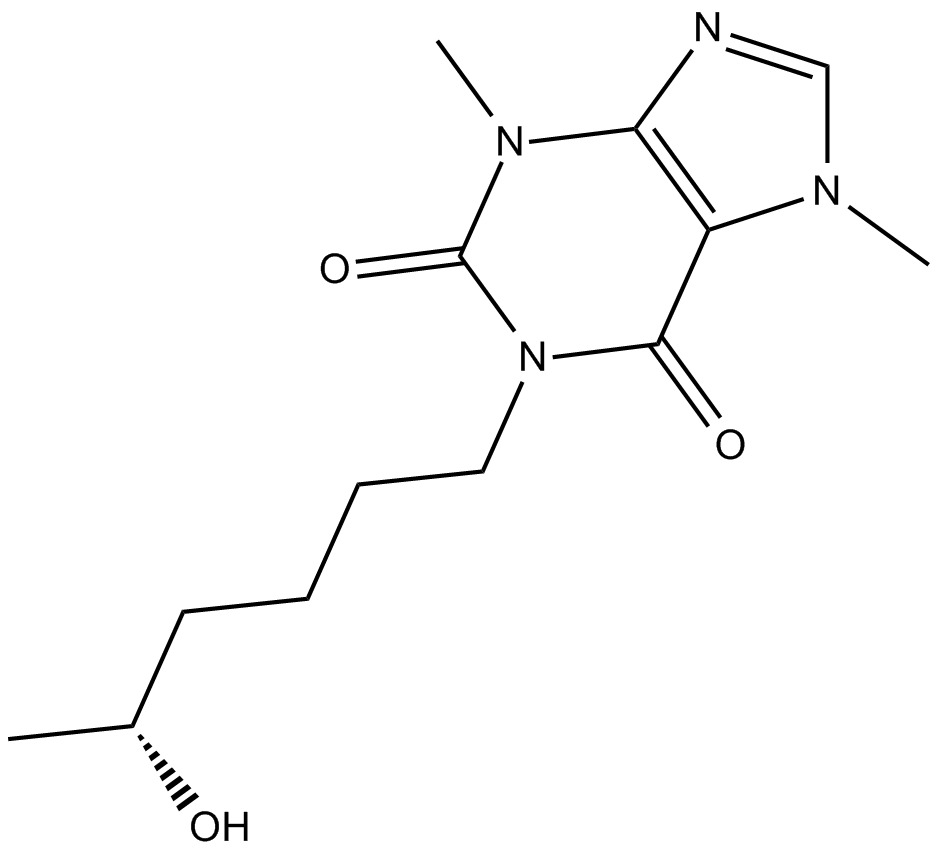 C4158 (R)-LisofyllineSummary: anti-inflammatory agent
C4158 (R)-LisofyllineSummary: anti-inflammatory agent -
 C4298 (±)-LisofyllineSummary: anti-inflammatory agent
C4298 (±)-LisofyllineSummary: anti-inflammatory agent -
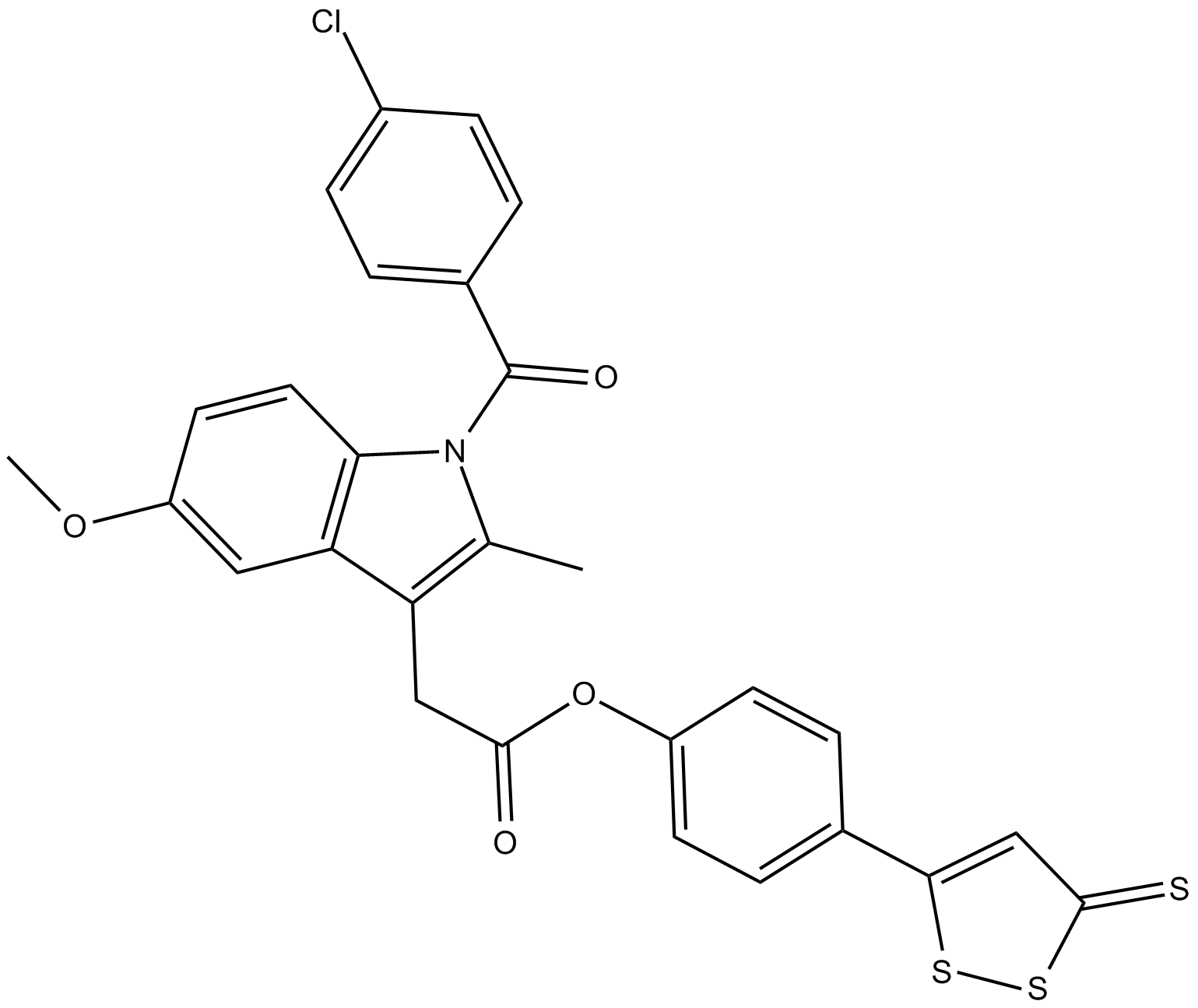 C4596 ATB-343Summary: hybrid molecule of an H2S donor and the NSAID indomethacin
C4596 ATB-343Summary: hybrid molecule of an H2S donor and the NSAID indomethacin -
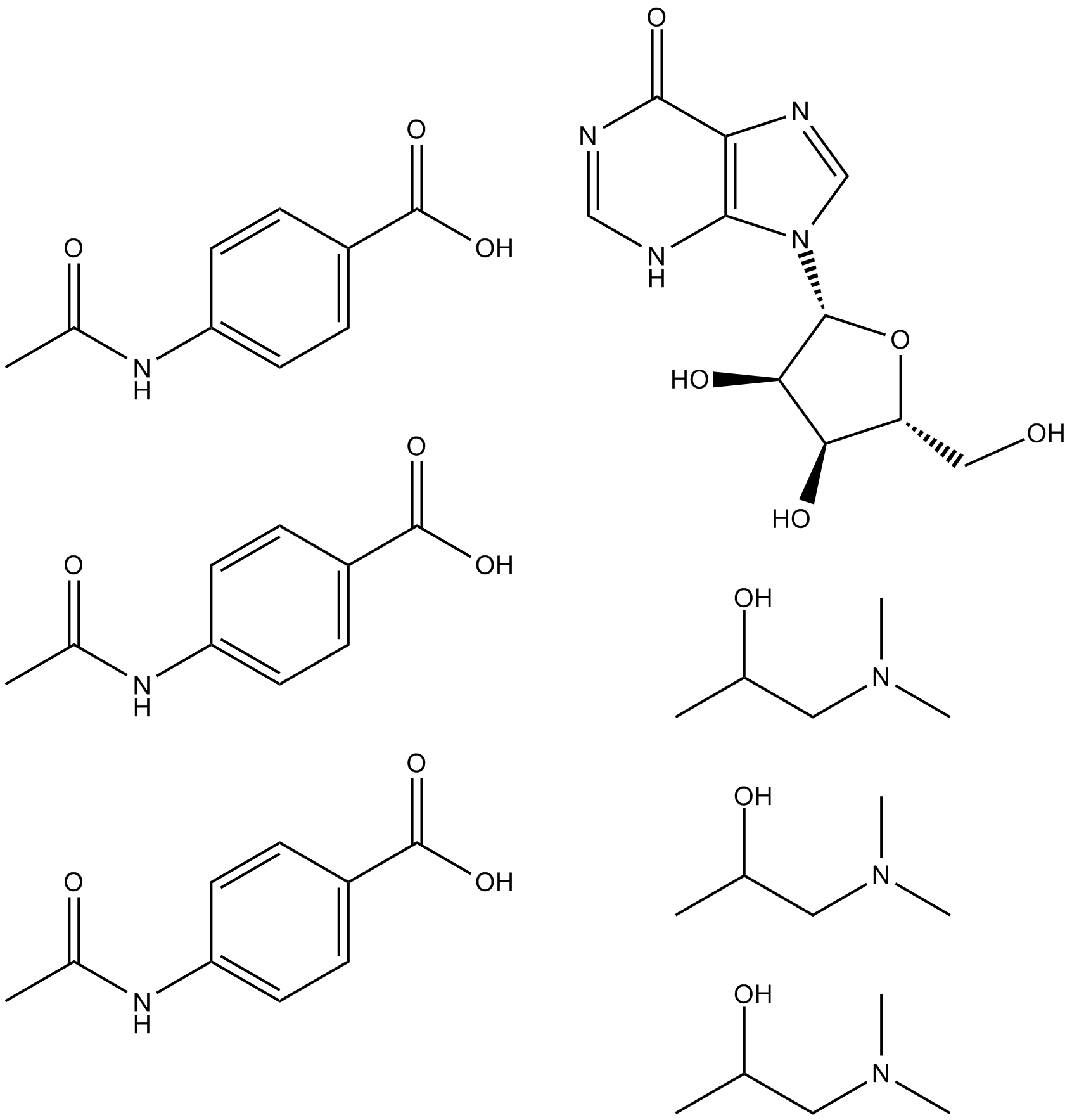 C4417 IsoprinosineSummary: immunomodulatory effects
C4417 IsoprinosineSummary: immunomodulatory effects -
 C4277 ML351Summary: human reticulocyte 15-LO-1 inhibitor
C4277 ML351Summary: human reticulocyte 15-LO-1 inhibitor -
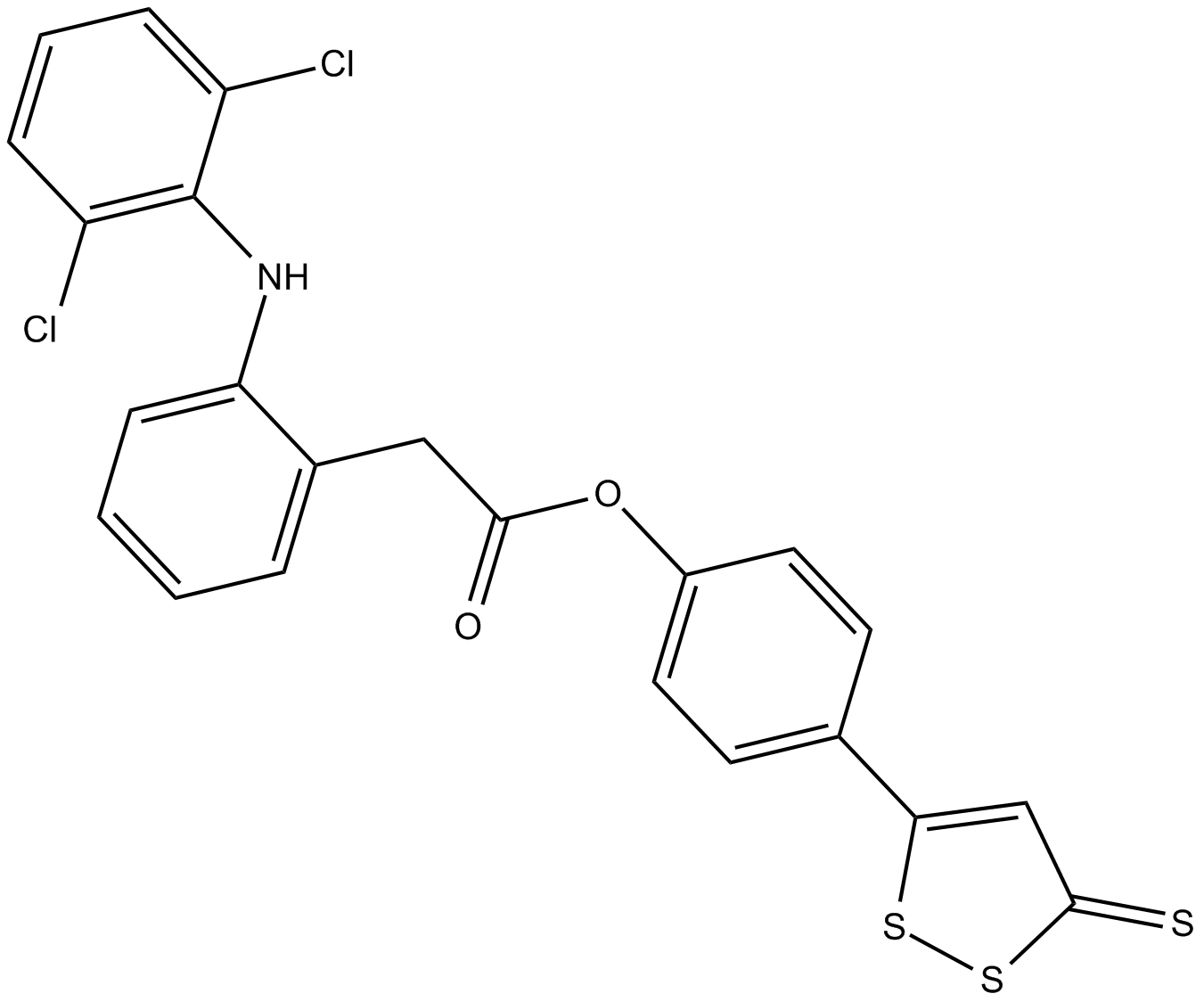 C4592 ATB-337Summary: hybrid molecule of an H2S donor and the NSAID diclofenac
C4592 ATB-337Summary: hybrid molecule of an H2S donor and the NSAID diclofenac

