Immunology/Inflammation

The adaptive immune system consists of B and T lymphocytes which mediate humoral immunity (e.g. antibody response) and cell-mediated immunity, respectively. B cell receptor and T cell receptor signaling is responsible for activation of Src family tyrosine kinases, such as Blk, Fyn, and Lyn in B cells and Fyn and Lck in T cells, resulting phosphorylation of the receptor-associated ITAM motifs. Phosphorylated ITAMs serve as the docking sites for Syk family tyrosine kinases, e.g. Syk in B cells and Zap-70 in T cells. Activated Syk kinases then propagate the signals via phosphorylation of downstream proteins. Furthermore, lymphocyte receptor signaling facilitates B and T cell development, differentiation, proliferation and survival.
-
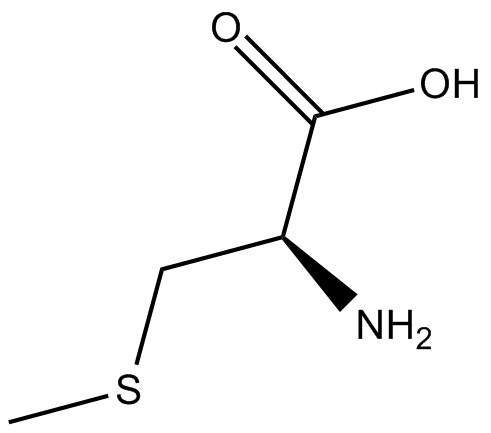 C7066 S-Methyl-L-cysteine
C7066 S-Methyl-L-cysteine -
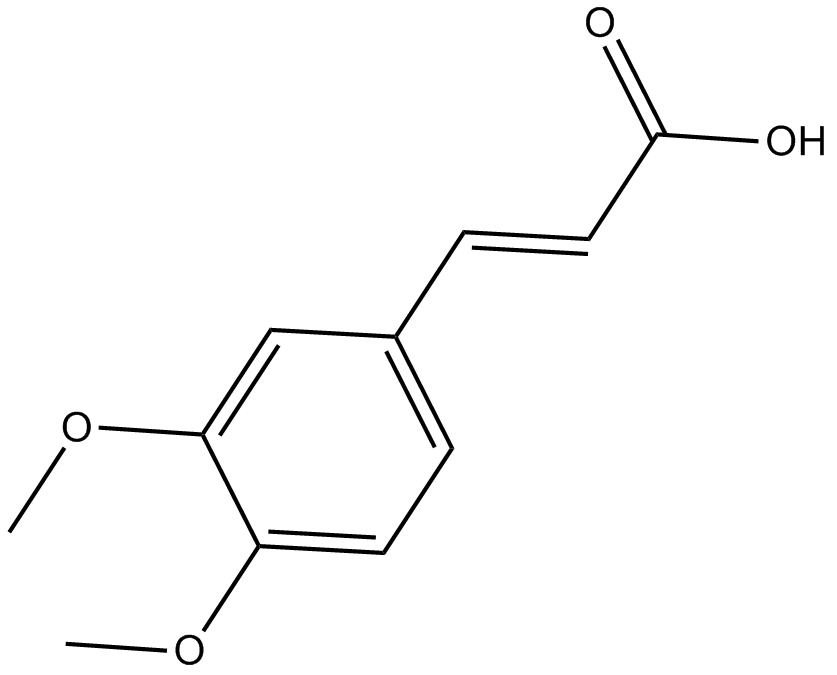 C7120 3,4-Dimethoxycinnamic acid
C7120 3,4-Dimethoxycinnamic acid -
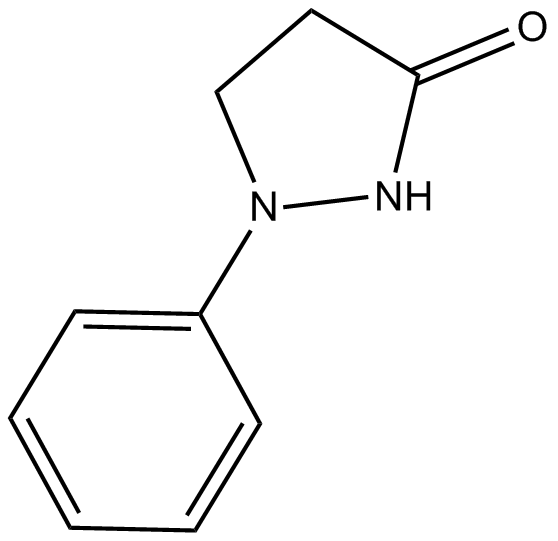 C7140 Phenidone
C7140 Phenidone -
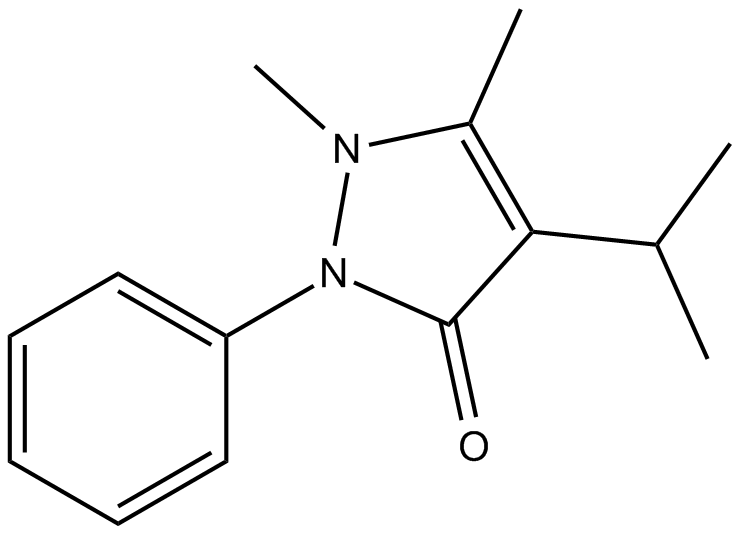 C7195 Propyphenazone (4-Isopropylantipyrine)
C7195 Propyphenazone (4-Isopropylantipyrine) -
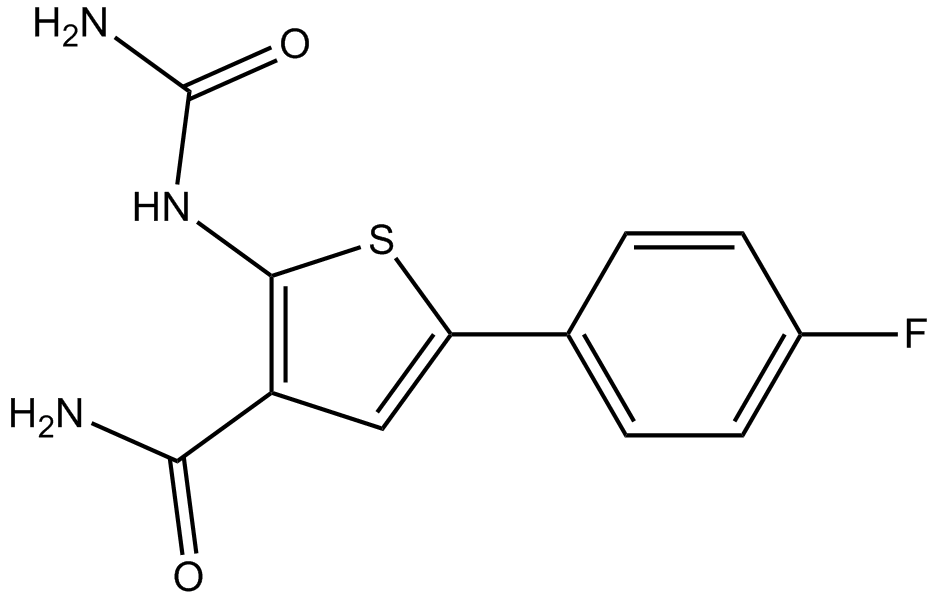 A4602 TPCA-12 CitationSummary: IKK-2 inhibitor,potent and selective
A4602 TPCA-12 CitationSummary: IKK-2 inhibitor,potent and selective -
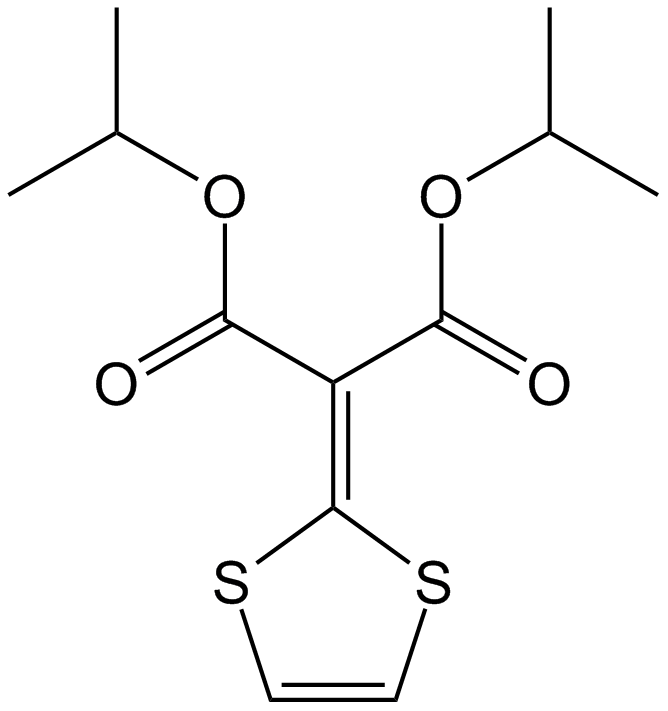 A2486 MalotilateSummary: Stimulates hepatocyte regeneration
A2486 MalotilateSummary: Stimulates hepatocyte regeneration -
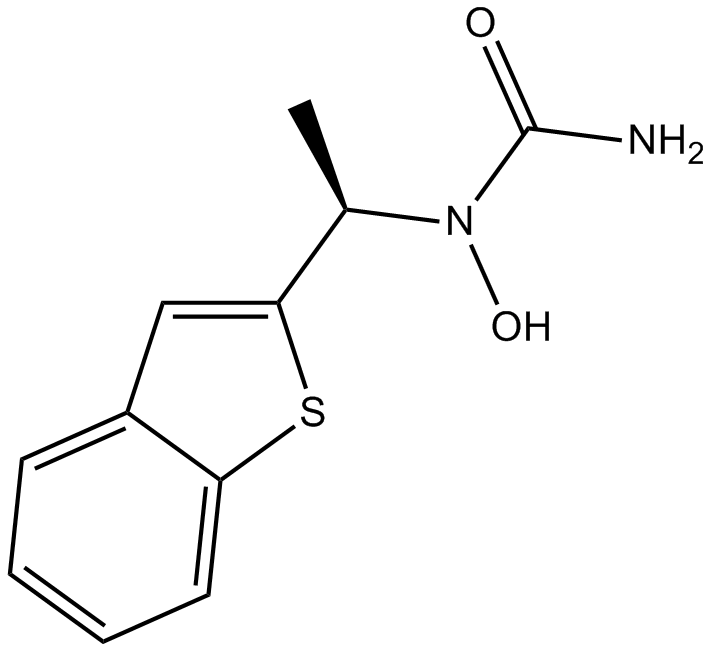 A5384 ZileutonSummary: 5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX) inhibitor, orally active
A5384 ZileutonSummary: 5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX) inhibitor, orally active -
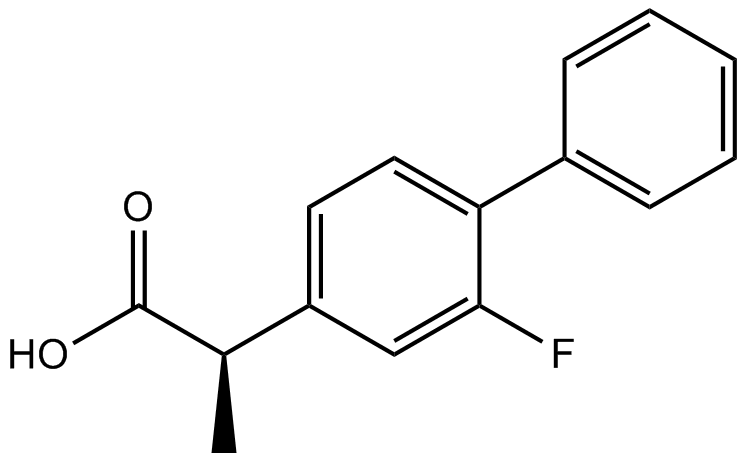 A8434 FlurbiprofenSummary: Cyclooxygenase inhibitors
A8434 FlurbiprofenSummary: Cyclooxygenase inhibitors -
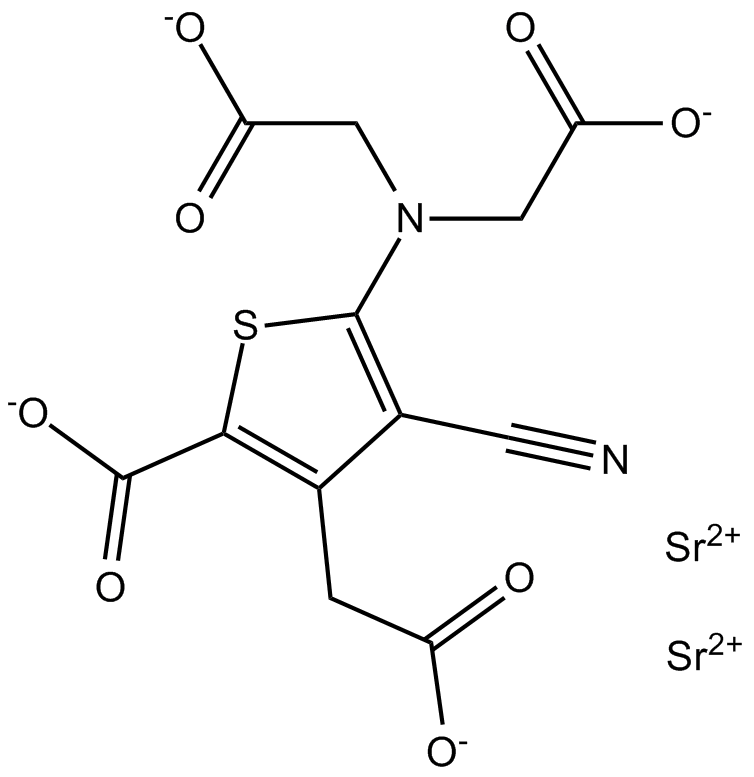 A8526 Strontium RanelateSummary: Calcium Channel activator
A8526 Strontium RanelateSummary: Calcium Channel activator -
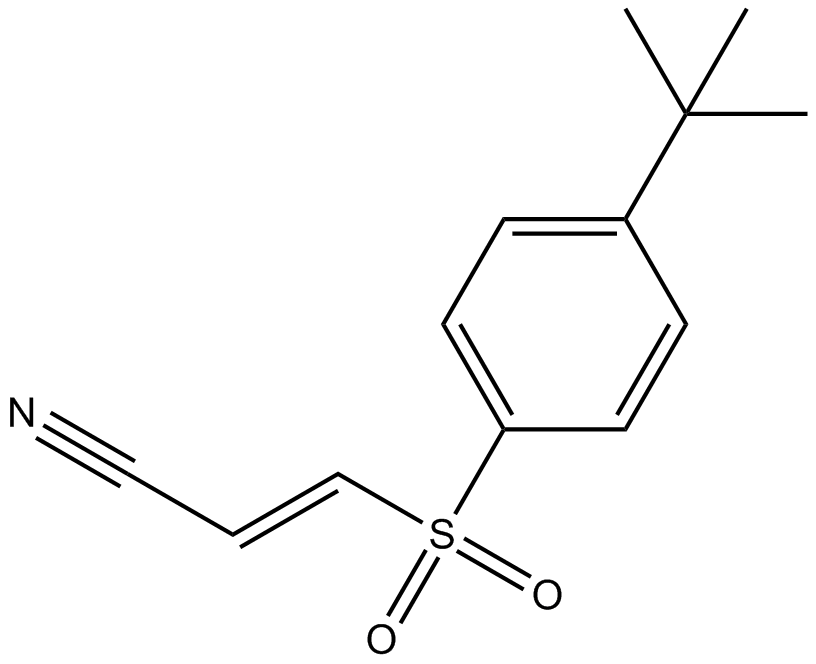 B3033 Bay 11-70851 CitationSummary: NK-κB activation inhibitor
B3033 Bay 11-70851 CitationSummary: NK-κB activation inhibitor

