Cycloheximide
IC50: N/A
Cycloheximide is an inhibitor of protein biosynthesis in eukaryotic organisms widely used in biomedical research to inhibit protein synthesis in eukaryotic cells studied in vitro. Due to significant toxic side effects, including teratogenesis, DNA damage, and other reproductive effects, cycloheximide is generally used only in in vitro research applications, but not suitable for human use as a therapeutic compound.
In vitro: Cycloheximide blocks the movement of peptidyl-tRNA from acceptor site to the donor site on reticulocyte ribosomes. This translocation reaction is dependent on the transfer enzyme, TF-II, and GTP hydrolysis. Cycloheximide has no effect on the ribosome dependent GTPase activity of TF-II or peptidyl transferase reaction by which peptides on tRNA in the donor ribosomal site are transferred to an amino acid on tRNA in the acceptor site [1].
In vivo: Cycloheximide treatment was effective in attenuating rat brain injury within a 6 hr therapeutic window after hypoxia-ischemia in a newborn rat pup model. These data support the possibility that protein synthesis inhibitors, as well as other anti-apoptotic strategies, may have therapeutic utility in hypoxic-ischemic (HI) events of the developing newborn brain even when treatment is delayed for up to 6 hr after the primary asphyxial insult [2].
Clinical trial: Up to now, cycloheximide is still in the preclinical development stage.
References:
[1] McKeehan W, Hardesty B. The mechanism of cycloheximide inhibition of protein synthesis in rabbit reticulocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Aug 15;36(4):625-30.
[2] Park WS, Sung DK, Kang S, Koo SH, Kim YJ, Lee JH, Chang YS, Lee M. Therapeutic window for cycloheximide treatment after hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in neonatal rats. J Korean Med Sci. 2006 Jun;21(3):490-4.
- 1. Dongxiao Tang, Congyuan Cao, et al. "FTO-mediated demethylation of MTUS1/ATIP1 promotes tumor progression in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma." BMC Cancer 24, 1489 (2024).
- 2. Wang, Mengxue MD, Li, Xunjia MD, et al. "Loss of RPN1 Promotes Antitumor Immunity via PD-L1 Checkpoint Blockade in Triple-negative Breast Cancer——Experimental Studies." International Journal of Surgery December 20, 2024.
- 3. Wenwen Wang , Qi Li, et al. "RNF39 facilitates antiviral immune responses by promoting K63-linked ubiquitination of STING." Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Sep 9;142(Pt A):113091. PMID: 39255680
- 4. Dongqi Nan, Chenglong Rao, et al. "Burkholderia pseudomallei BipD modulates host mitophagy to evade killing." Nat Commun. 2024 Jun 4;15(1):4740. PMID: 38834545
- 5. Haiping Zhang, Lijun Jiang, et al. "The cGAS-Ku80 complex regulates the balance between two end joining subpathways." Cell Death Differ. 2024 Jun;31(6):792-803. PMID: 38664591
- 6. Ying Qin, Min Wang, et al. "ISGylation by HERCs facilitates STING activation." Cell Rep. 2024 May 28;43(5):114135. PMID: 38652662
- 7. Wenjie Shu, et al. "Maternal KLF17 controls zygotic genome activation by acting as a messenger for RNA Pol II recruitment in mouse embryos." Dev Cell. 2024 Mar 11;59(5):613-626.e6. PMID: 38325372
- 8. Zhengyi Zhen, Yu Chen, et al. "Nuclear cGAS restricts L1 retrotransposition by promoting TRIM41-mediated ORF2p ubiquitination and degradation." Nat Commun. 2023 Dec 12;14(1):8217. PMID: 38086852
- 9. Feiyu Tang, Can Lu, et al. "E3 ligase Trim35 inhibits LSD1 demethylase activity through K63-linked ubiquitination and enhances anti-tumor immunity in NSCLC." Cell Rep. 2023 Nov 17;42(12):113477. PMID: 37979167
- 10. Chengyue Wu, Mengdong Wang, et al. "TRIM26 facilitates PRV infection through NDP52-mediated MAVS autophagic degradation." Research Square. 02 Nov, 2023.
- 11. Qian Li, Dongqi Nan, et al. "Burkholderia pseudomallei BipD hijacks host KLHL9/KLHL13/CUL3 E3 ligase to ubiquitinate IMMT that initiates mitophagy to evade killing." Research Square. 15 Sep, 2023.
- 12. Meng Fang, Hong-Kun Wu, et al. "E3 ligase MG53 suppresses tumor growth by degrading cyclin D1." Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 Jul 7;8(1):263. PMID: 37414783
- 13. Shilong You, Jiaqi Xu, et al. "Down-regulation of WWP2 aggravates Type 2 diabetes mellitus-induced vascular endothelial injury through modulating ubiquitination and degradation of DDX3X." Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023 May 6;22(1):107. PMID: 37149668
- 14. Shiyue Du, Sheng Zeng, et al. "Functional characterization of novel NPRL3 mutations identified in three families with focal epilepsy." Sci China Life Sci. 2023 Sep;66(9):2152-2166. PMID: 37071290
- 15. Xiaoxiang Sun, Huanyin Tang, et al. "Loss of the receptors ER, PR and HER2 promotes USP15-dependent stabilization of PARP1 in triple-negative breast cancer." Nat Cancer. 2023 May;4(5):716-733. PMID: 37012401
- 16. Wenyi Zhang, Anran Wu, et al. "Ubiquitination of Ku70 by Parkin promotes apoptosis of lens epithelial cells." FEBS J. 2023 Aug;290(15):3828-3842. PMID: 37000041
- 17. Giridhar Sekar, Geetika Singh, et al. "Small molecule SJ572946 activates BAK to initiate apoptosis." iScience. 2022 Sep 6;25(10):105064. PMID: 36147946
- 18. Jingchun Du, Yougui Xiang, et al. "Cinobufagin induces acute promyelocytic leukaemia cell apoptosis and PML-RARA degradation in a caspase-dependent manner by inhibiting the β-catenin signalling pathway." Pharm Biol. 2022 Dec;60(1):1801-1811. PMID: 36121296
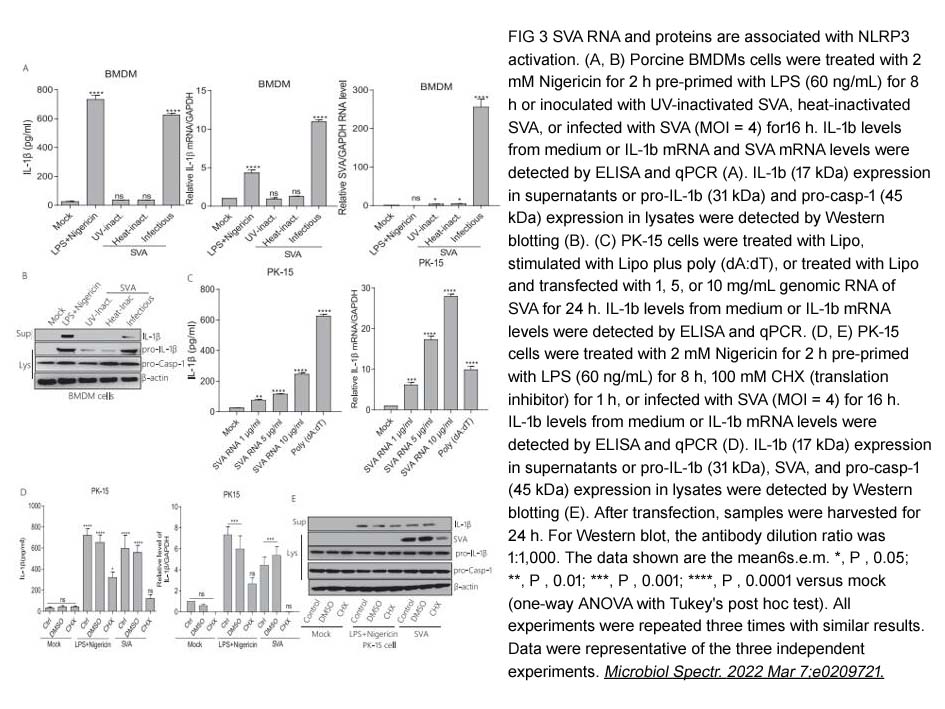
- 19. Sk Mohiuddin Choudhury, XuSheng Ma, et al. "Senecavirus a 3D Interacts with NLRP3 to Induce IL-1β Production by Activating NF-κB and Ion Channel Signals." Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Apr 27;10(2):e0209721. PMID: 35254168
- 20. Yong Bian, Gang Yin, et al. "Degradation of HIF-1α induced by curcumol blocks glutaminolysis and inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and invasion in colorectal cancer cells." Cell Biol Toxicol. 2022 Jan 27. PMID: 35083610
- 21. Jingchun Du, Yougui Xiang, et al. "RIPK1 dephosphorylation and kinase activation by PPP1R3G/PP1γ promote apoptosis and necroptosis." Nat Commun. 2021 Dec 3;12(1):7067. PMID: 34862394
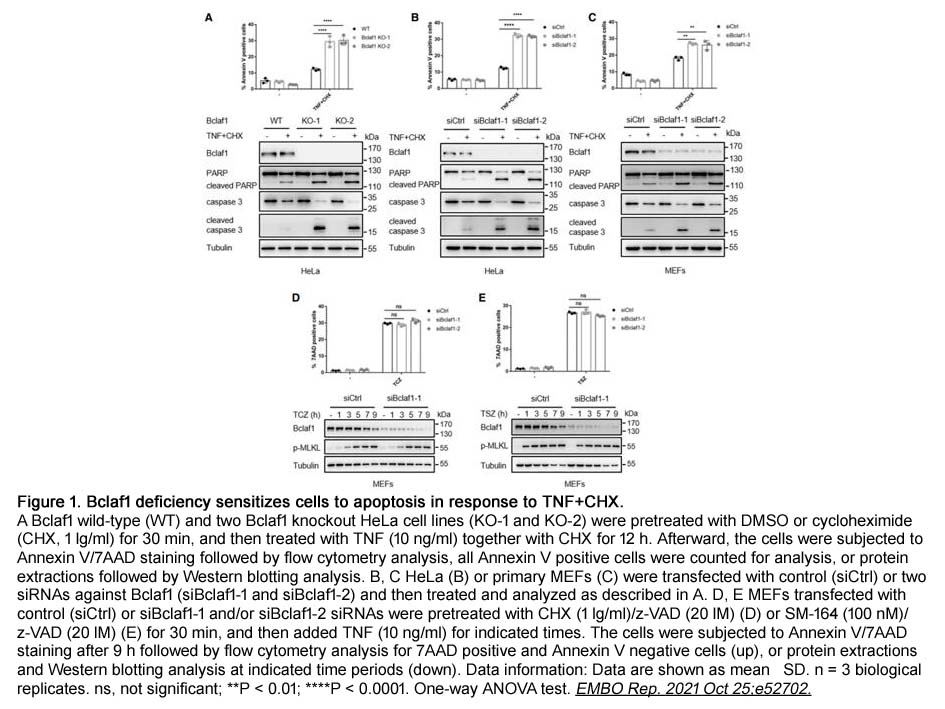
- 22. Rui Zhang, Teng Xue, et al. "Bclaf1 regulates c‐FLIP expression and protects cells from TNF‐induced apoptosis and tissue injury." EMBO Rep. 2021 Oct 25;e52702. PMID: 34693625
- 23. Yi-Xin Chen, Chen-Jing Wang, et al. "eIF3a R803K mutation mediates chemotherapy resistance by inducing cellular senescence in small cell lung cancer." Pharmacol Res. 2021 Dec;174:105934. PMID: 34648968
- 24. Wenwen Liu, Yang Zhou, et al. "Glutathione peroxidase 4-dependent glutathione high-consumption drives acquired platinum chemoresistance in lung cancer-derived brain metastasis." Clin Transl Med. 2021 Sep;11(9):e517. PMID: 34586745
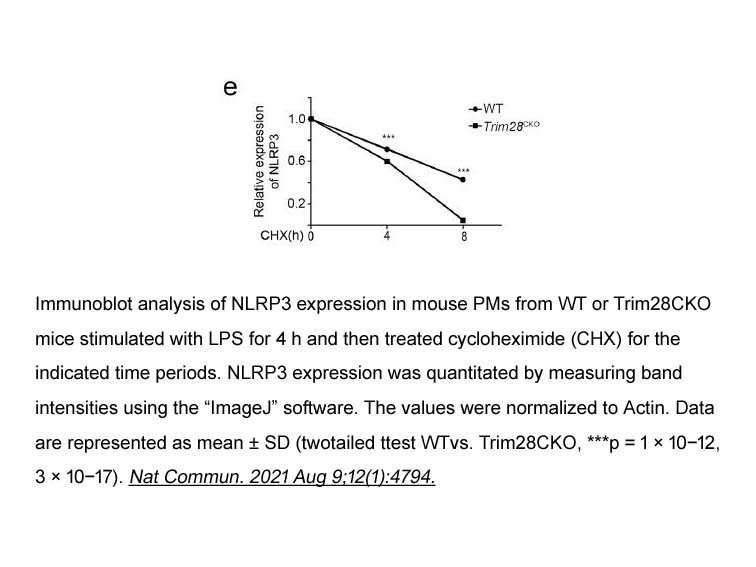
- 25. Ying Qin, Qi Li, et al. "TRIM28 SUMOylates and stabilizes NLRP3 to facilitate inflammasome activation." Nat Commun. 2021 Aug 9;12(1):4794. PMID: 34373456
- 26. Du Yu, Yundi Zhao, et al. "C19orf66 Inhibits Japanese Encephalitis Virus Replication by Targeting -1 PRF and the NS3 Protein." Virol Sin. 2021 Dec;36(6):1443-1455. PMID: 34309824
- 27. Shaojun Wu, Ying Zhang, et al. "Septin4 promotes cardiomyocytes apoptosis by enhancing the VHL-mediated degradation of HIF-1α." Cell Death Discov. 2021 Jul 6;7(1):172. PMID: 34230460
- 28. Jun Li, Yan Zhang, et al. "EBV-miR-BART12 inhibits cell migration and proliferation by targeting Snail expression in EBV-associated gastric cancer." Arch Virol. 2021 May;166(5):1313-1323. PMID: 33646408
- 29. Wenwen Wang, Ying Qin, et al. "Galectin-9 Targets NLRP3 for Autophagic Degradation to Limit Inflammation." J Immunol. 2021 Jun 1;206(11):2692-2699. PMID: 33963043
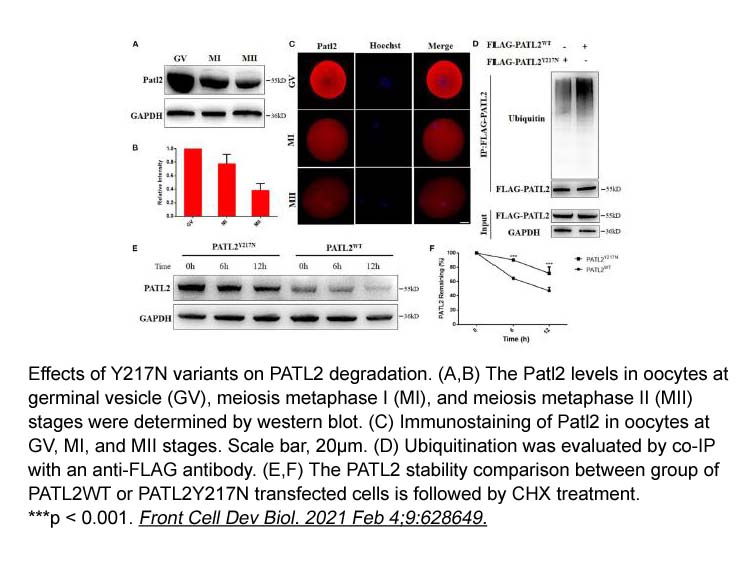
- 30. Qiqi Cao, Chun Zhao, et al. "The Recurrent Mutation in PATL2 Inhibits Its Degradation Thus Causing Female Infertility Characterized by Oocyte Maturation Defect Through Regulation of the Mos-MAPK Pathway." Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Feb 4;9:628649. PMID: 33614659
- 31. Xiaoli Liu, Yan Gu, et al. "Honokiol induces paraptosis-like cell death of acute promyelocytic leukemia via mTOR & MAPK signaling pathways activation." Apoptosis. 2021 Apr;26(3-4):195-208. PMID: 33550458
- 32. Lin Lv , Mingzhu Cao, et al. "PRV-encoded UL13 protein kinase acts as an antagonist of innate immunity by targeting IRF3-signaling pathways." Vet Microbiol. 2020 Nov;250:108860. PMID: 33045632
- 33. Shaojun Wu, Ying Zhang, et al. "Septin4 Aggravates Hypoxia-Induced Cardiomyocytes Injury by Promoting HIF-1α Ubiquitination and Degradation through VHL." Research Square. October 21st, 2020.
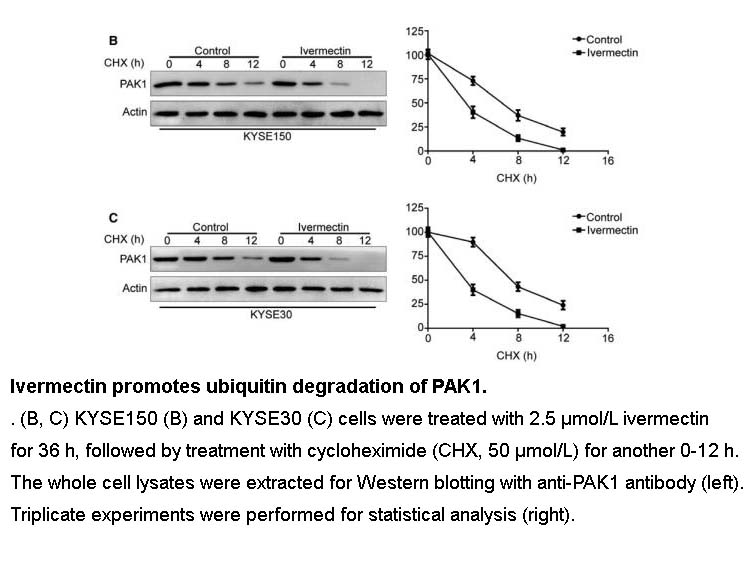
- 34. Chen L, Bi S, et al. "Ivermectin suppresses tumour growth and metastasis through degradation of PAK1 in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma." J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(9):5387-5401. PMID: 32237037
- 35. Dai J, Yang L, et al. "A Functional Synonymous Variant in PDGFRA Is Associated with Better Survival in Acral Melanoma." J Cancer. 2020;11(10):2945-2956. PMID: 32226509
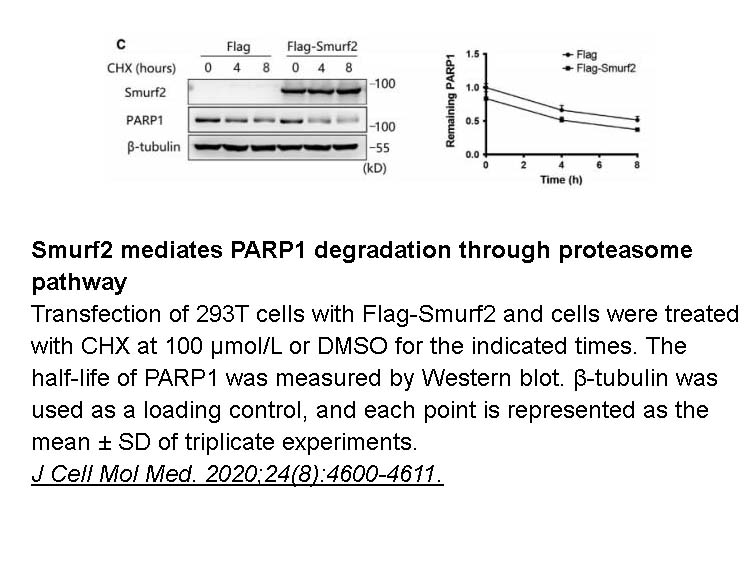
- 36. Qian H, Zhang N, et al. "The E3 ubiquitin ligase Smurf2 regulates PARP1 stability to alleviate oxidative stress-induced injury in human umbilical vein endothelial cells." J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(8):4600-4611. PMID: 32167680
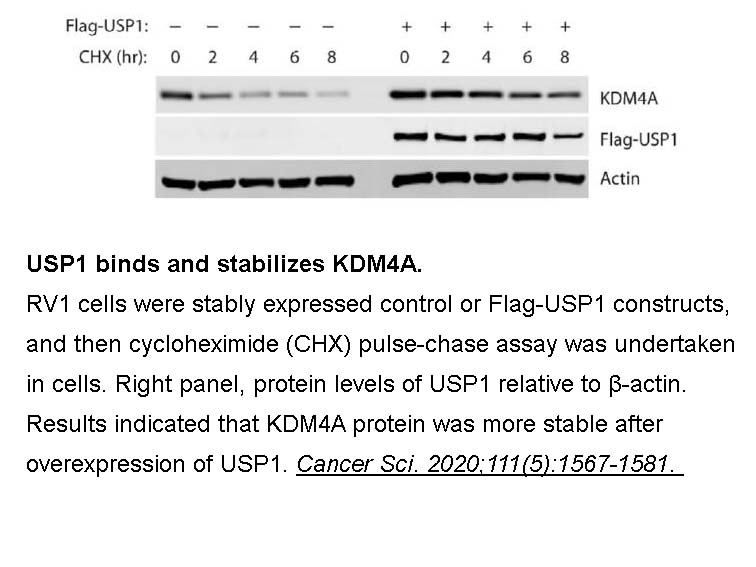
- 37. Cui SZ, Lei ZY, et al. "Targeting USP1-dependent KDM4A protein stability as a potential prostate cancer therapy." Cancer Sci. 2020;111(5):1567-1581. PMID: 32133742
- 38. Luo J, Xia Y, et al. "ATF4 destabilizes RET through nonclassical GRP78 inhibition to enhance chemosensitivity to bortezomib in human osteosarcoma." Theranostics. 2019 Aug 14;9(21):6334-6353. PMID: 31534554
- 39. Ji J, Xu R, et al. "Long noncoding RNA SChLAP1 forms a growth promoting complex with HNRNPL in human glioblastoma through stabilization of ACTN4 and activation of NF-κB signaling." Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Sep 6. pii: clincanres.0747.2019. PMID: 31492748
- 40. Zhao T, Bao Y, et al. "DNA methylation-regulated QPCT promotes sunitinib resistance by increasing HRAS stability in renal cell carcinoma." Theranostics. 2019 Aug 14;9(21):6175-6190.nbsp;PMID: 31534544
- 41. Shan F, Mei S, et al. "A telomerase subunit homolog La protein from Trypanosoma brucei plays an essential role in ribosomal biogenesis." FEBS J. 2019 Apr 16. PMID: 30993866
- 42. Song J, Yuan C, et al. "Novel flavagline-like compounds with potent Fli-1 inhibitory activity suppress diverse types of leukemia." FEBS J. 2018 Dec;285(24):4631-4645. PMID: 30387554
- 43. Xiao G, Li Y, et al. "FBXW7 suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition and chemo-resistance of non-small-cell lung cancer cells by targeting snai1 for ubiquitin-dependent degradation." Cell Prolif. 2018 Aug 9:e12473. PMID: 30094882
- 44. Bao Y, Yang F, et al. "Angiopoietin-like protein 3 blocks nuclear import of FAK and contributes to sorafenib response." Br J Cancer. 2018 Jul 23. PMID: 30033448
- 45. Ji J, Xu R, et al. "Actin like-6A promotes glioma progression through stabilization of transcriptional regulators YAP/TAZ."Cell Death Dis. 2018 May 3;9(5):517. PMID: 29725063
- 46. Cingöz O, Goff SP. "Cyclin-dependent kinase activity is required for type I interferon production." Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Mar 27;115(13):E2950-E2959. PMID: 29507205
- 47. Yu Z, Song H, et al. "USP1-UAF1 deubiquitinase complex stabilizes TBK1 and enhances antiviral responses." J Exp Med. 2017 Dec 4;214(12):3553-3563. PMID: 29138248
- 48. Wang L, Yu Z, et al. "Huaier aqueous extract protects against dextran sulfate sodium-induced experimental colitis in mice by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation." Oncotarget. 2017 May 16;8(20):32937-32945. PMID: 28380426
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
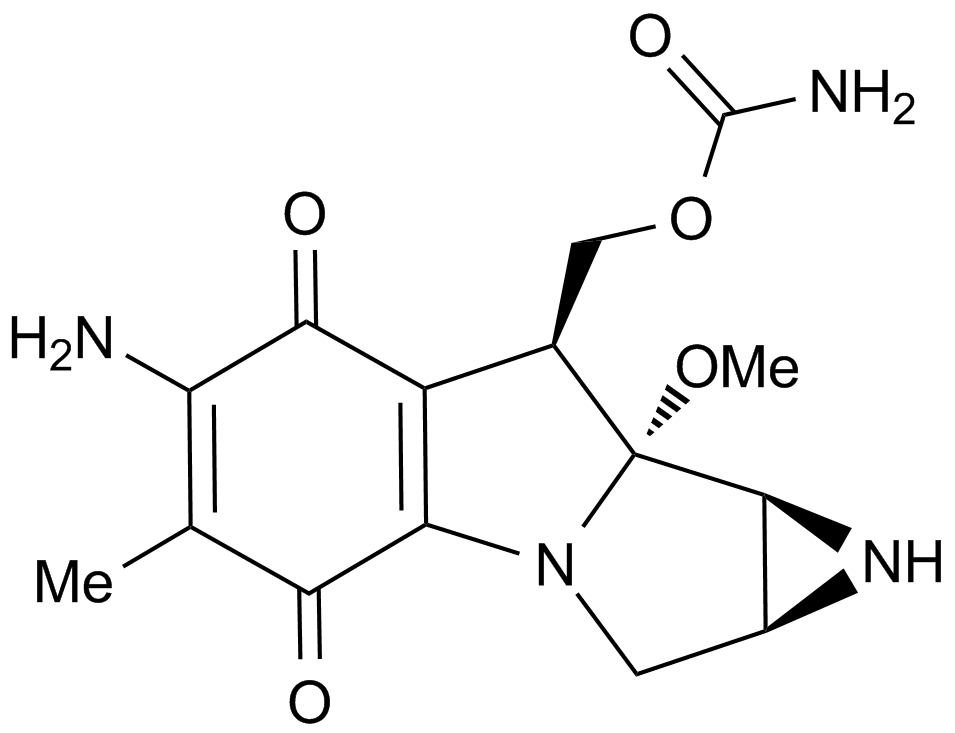
| M.Wt | 281.4 |
| Cas No. | 66-81-9 |
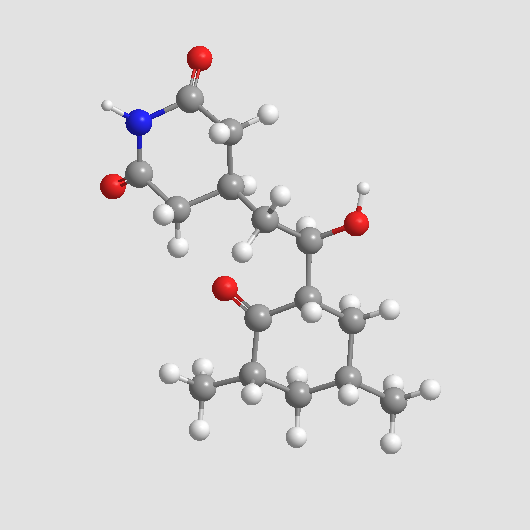
| Formula | C15H23NO4 |
| Synonyms | Naramycin A; Actidione; 3-[2-(3,5-Dimethyl-2-oxocyclohexyl)-2-hydroxyethyl]glutarimide |
| Solubility | ≥14.05 mg/mL in H2O with gentle warming and ultrasonic; ≥112.8 mg/mL in DMSO; ≥57.6 mg/mL in EtOH |
| Chemical Name | 4-[(2R)-2-[(1S,3S,5S)-3,5-dimethyl-2-oxocyclohexyl]-2-hydroxyethyl]piperidine-2,6-dione |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | O=C1[C@@H](C)C[C@H](C)C[C@@]1([H])[C@@H](CC2CC(NC(C2)=O)=O)O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment: [1] | |
|
Cell lines |
SGBS preadipocytes |
|
Preparation method |
The solubility of this compound in DMSO is >10 mM. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37 °C for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20°C for several months. |
|
Reaction Conditions |
10 μg/ml, 9 hours |
|
Applications |
Addition of CHX enhanced CD95-induced cleavage of caspase-8 into p43/p41 intermediate and p18 active fragments as well as proteolytic turnover of the proenzyme form of caspase-8 after 1, 3, 6, and 9 h. In addition, CHX increased cleavage of caspase-3 into the active p20/17 fragment at these time points. At later time points (24, 48, and 72 h), a decrease in the p55 pro-form of caspase-8 and the p35 pro-form of caspase-3 was observed. Interestingly, α-APO-1 alone induced caspase-8 and caspase-3 cleavage (3, 6, 9 h) although there is no induction of cell death after 24 h. Involvement of caspase-cleavage was confirmed by the use of the caspase inhibitor Z-VAD.fmk, which reduced CD95- and CHX-induced apoptosis. Apoptosis was rescued by ~50% pointing to a potential role of caspase-independent cell death in SGBS preadipocytes. |
| Animal experiment: [2] | |
|
Animal models |
Sprague Dawley rat pups |
|
Dosage form |
Intraperitoneal injection, 0.6 mg/kg, 0, 6, 12 or 24 hr |
|
Applications |
The hypoxia-ischemia model was set up using the rat pups. The hypoxia-ischemia control group (HI) and hypoxia-ischemia were treated with cycloheximide treatment group at 0, 6, 12, 24 and 24 hr after HI (HI_0, 6, 12, 24), respectively. Infarct volume, as measured by morphometric analysis of infarct areas with TTC, was significantly reduced by 92% and 61% when cycloheximide was given 0 or 6 hr after HI respectively, but showed an insignificant trend in infarct reduction if cycloheximide was administered 12 hr after HI compared to the HI control group, and no protective effect was observed when administration was delayed until 24 hr after HI. |
|
Other notes |
Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
|
References: [1] Fischer-Posovszky P, Keuper M, Nagel S, et al. Downregulation of FLIP by cycloheximide sensitizes human fat cells to CD95-induced apoptosis. Experimental cell research, 2011, 317(15): 2200-2209. [2] Park W S, Sung D K, Kang S, et al. Therapeutic window for cycloheximide treatment after hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in neonatal rats. Journal of Korean medical science, 2006, 21(3): 490-494. |
|
| Description | Cycloheximide is a highly effective antibiotic. | |||||
| Targets | bacteria protein synthesis | |||||
| IC50 | ||||||
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data