β-Pompilidotoxin
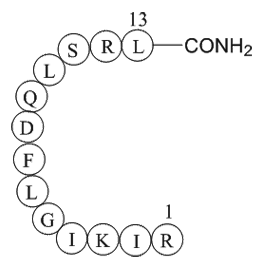
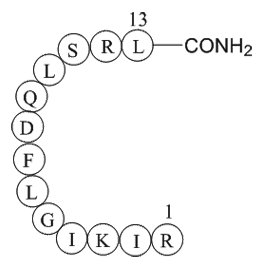
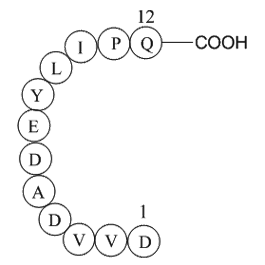
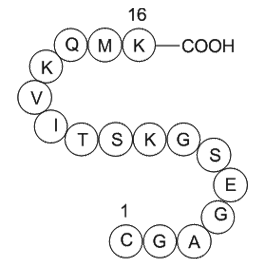
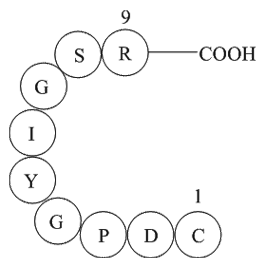
β-Pompilidotoxin, (C71H124N22O17), a peptide with the sequence H2N-Arg
-Ile-Lys-Ile-Gly-Leu-Phe-Asp-Gln-Leu-Ser-Arg-Leu-amide, MW= 1557.88. Pompilidotoxin is a toxin from the venom of spider wasps that slows the inactivation of Na+channels. α-Pompilidotoxin (α-PMTX) can be extracted from the venom of a solitary wasp, Anopolis samariensis. β-Pompilidotoxin (β-PMTX) originates from the venom of another wasp, Batozonellus maculifrons(1). Homology α-PMTX has no structural homology with other toxins. It lacks disulfide bonds which are known to be present in other toxins acting on sodium channels, such as sea anemone toxins or scorpion toxins(2). Both α- and β-PMTX slow the inactivation of neuronal sodium channels (but not heart sodium channels), possibly by binding to the neurotoxin receptor site 3 on the extracellular surface of the sodium channel(3). β-PMTX has higher potency than α-PMTX. By slowing down the inactivation of sodium channels, PMTXs can potentiate synaptic transmission in the lobster neuromuscular endplate.
Figure1 Formula of β-Pompilidotoxin
Ref:
1. Konno K, Hisada M, Itagaki Y, Naoki H, Kawai N, Miwa A, Yasuhara T, Takayama H (1998). "Isolation and structure of pompilidotoxins, novel peptide neurotoxins in solitary wasp venoms". Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 250 (3): 612–6.
2. Sahara Y, Gotoh M, Konno K, Miwa A, Tsubokawa H, Robinson HP, Kawai N (2000). "A new class of neurotoxin from wasp venom slows inactivation of sodium current". Eur J Neurosci. 12 (6): 1961–70.
3. Kawai N, Konno K (2004). "Molecular determinants of two neurotoxins that regulate sodium current inactivation in rat hippocampal neurons". Neurosci Lett. 361 (1-3): 44–6.
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 1557.9 |
| Cas No. | 216064-36-7 |
| Formula | C71H124N22O17 |
| Synonyms | Arg-Ile-Lys-Ile-Gly-Leu-Phe-Asp-Gln-Leu-Ser-Arg-Leu |
| Solubility | ≥155.8 mg/mL in DMSO; insoluble in EtOH; ≥22.05 mg/mL in H2O |
| Chemical Name | β-Pompilidotoxin |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | CCC(C)C(C(=O)NC(CCCCN)C(=O)NC(C(C)CC)C(=O)NCC(=O)NC(CC(C)C)C(=O)NC(CC1=CC=CC=C1)C(=O)NC(CC(=O)O)C(=O)NC(CCC(=O)N)C(=O)NC(CC(C)C)C(=O)NC(CO)C(=O)NC(CCCN=C(N)N)C(=O)NC(CC(C)C)C(=O)N)NC(=O)C(CCCN=C(N)N)N |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure