Membrane Transporter/Ion Channel

Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins which allow the flow of ions across the membrane. The ion channels can be broadly grouped into six families including calcium channels, chloride channels, potassium channels, sodium channels, gap junction proteins and porins. Not all ion channels are gated, such as certain type of K+ and Cl– channels, transient receptor potential superfamily of cation channels, the ryanodine receptors and the IP3 receptors, but most Na+, K+, Ca2+ and some Cl– channels are all gated by voltage. Ligand-gated channels are regulated in response to ligand binding (e.g. neurotransmitters signaling). These ligand-gated neurotransmitter receptors are known as ionotropic receptors. Various neurotransmitters couple to ionotropic receptors such as glutamate, acetylcholine, glycine, GABA, and serotonin.
-
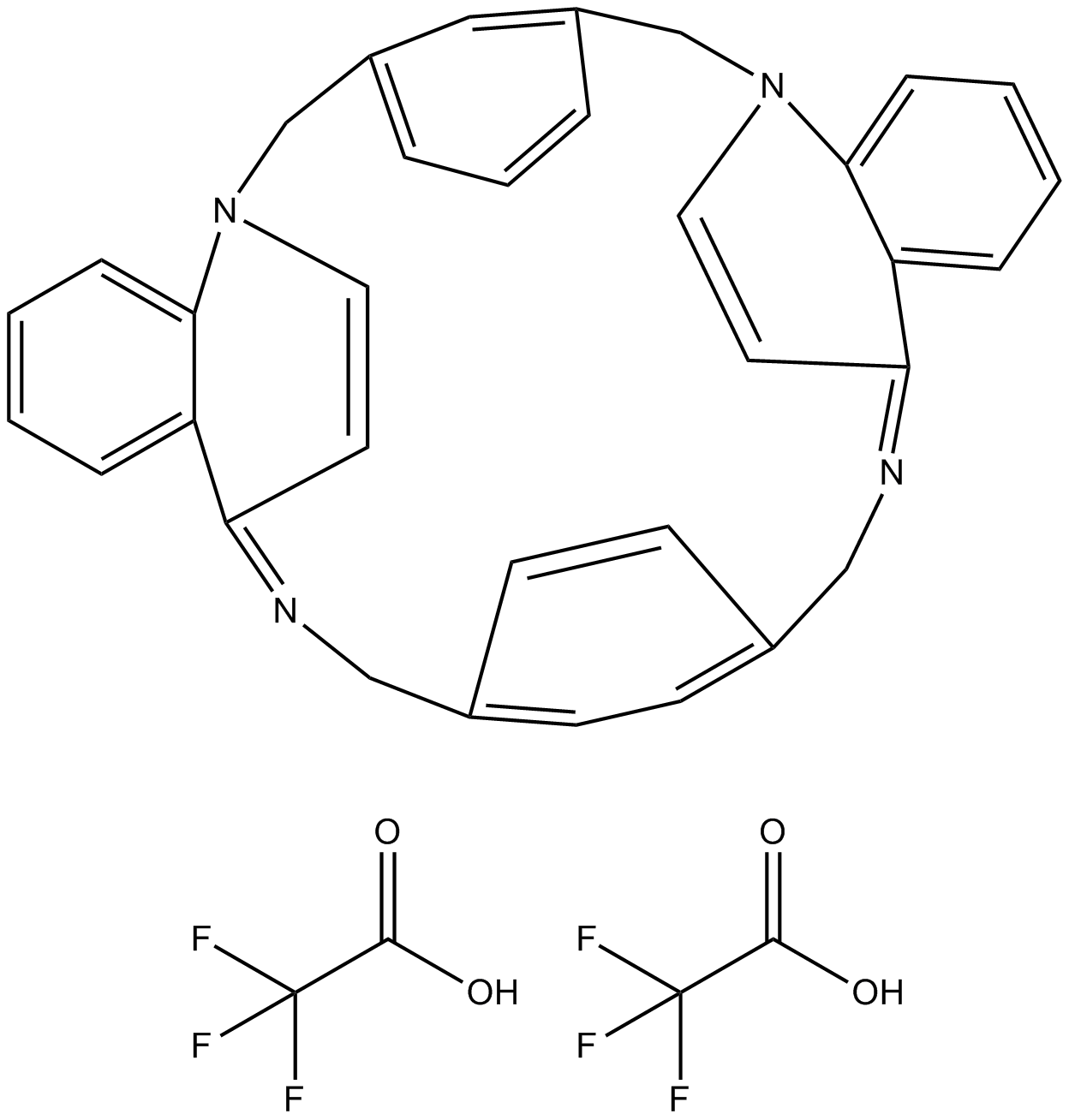 B6683 UCL 1684Summary: apamin-sensitive Ca2+-activated K+ channel (KCa2.1) blocker
B6683 UCL 1684Summary: apamin-sensitive Ca2+-activated K+ channel (KCa2.1) blocker -
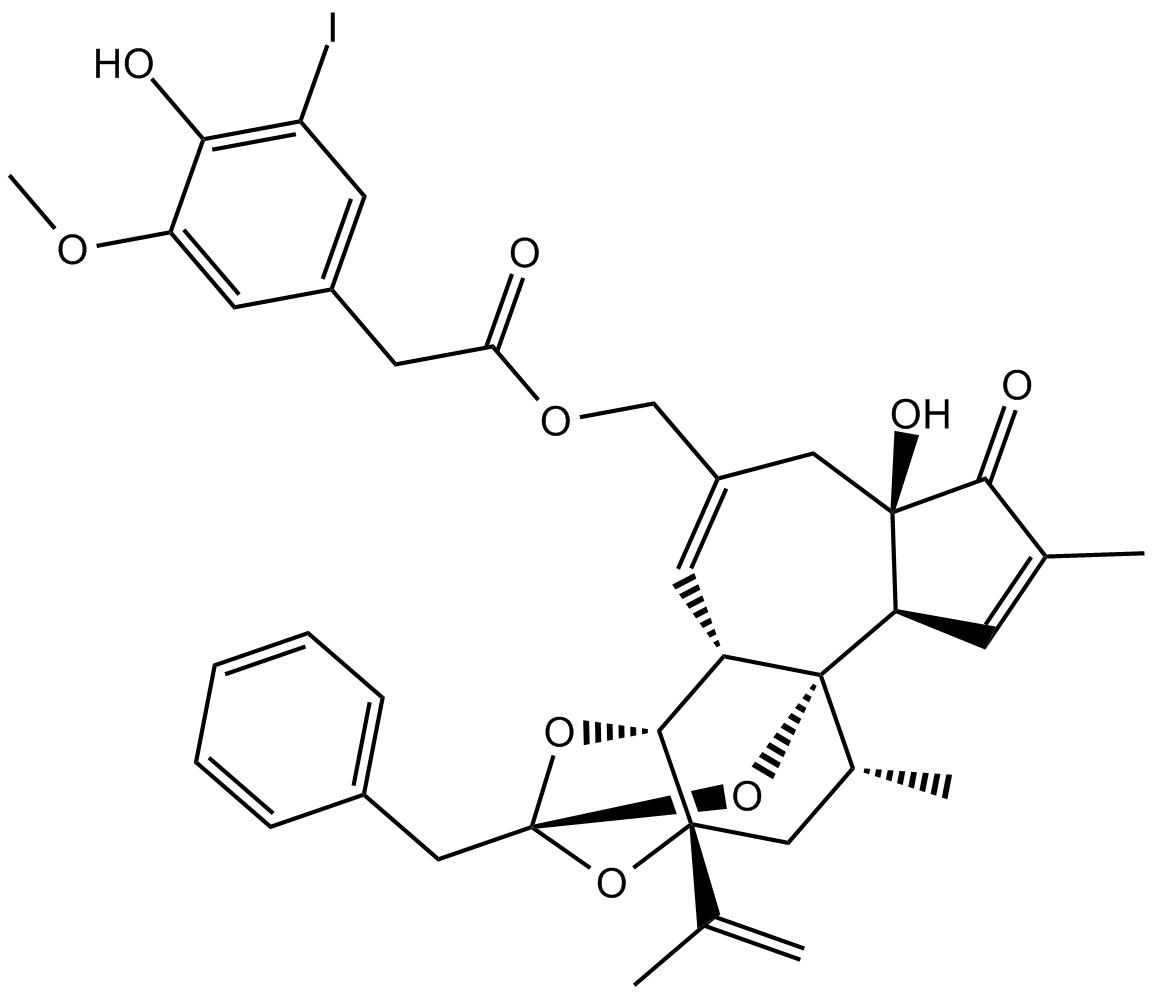 B6704 5'-IodoresiniferatoxinSummary: TRPV1 (VR1) receptor antagonist
B6704 5'-IodoresiniferatoxinSummary: TRPV1 (VR1) receptor antagonist -
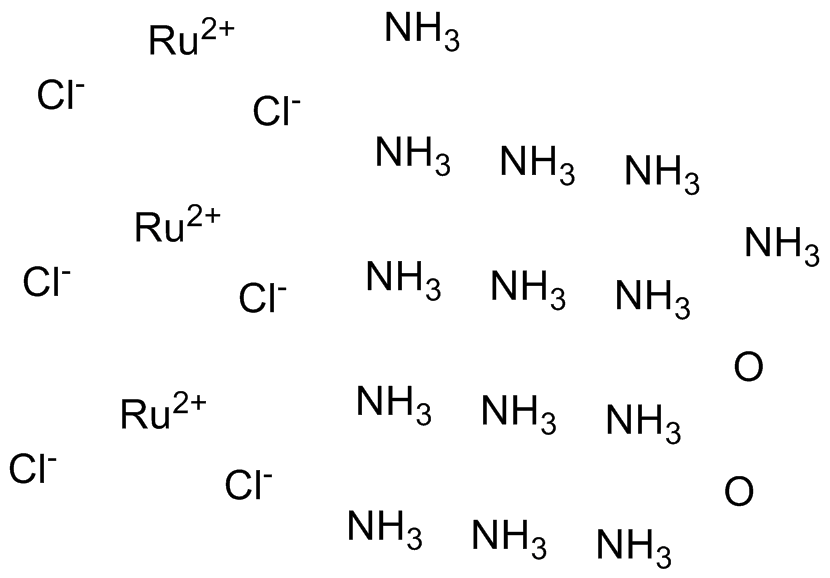 B6740 Ruthenium RedSummary: Blocks Ca2+ uptake and release, and voltage-sensitive Ca2+ channels
B6740 Ruthenium RedSummary: Blocks Ca2+ uptake and release, and voltage-sensitive Ca2+ channels -
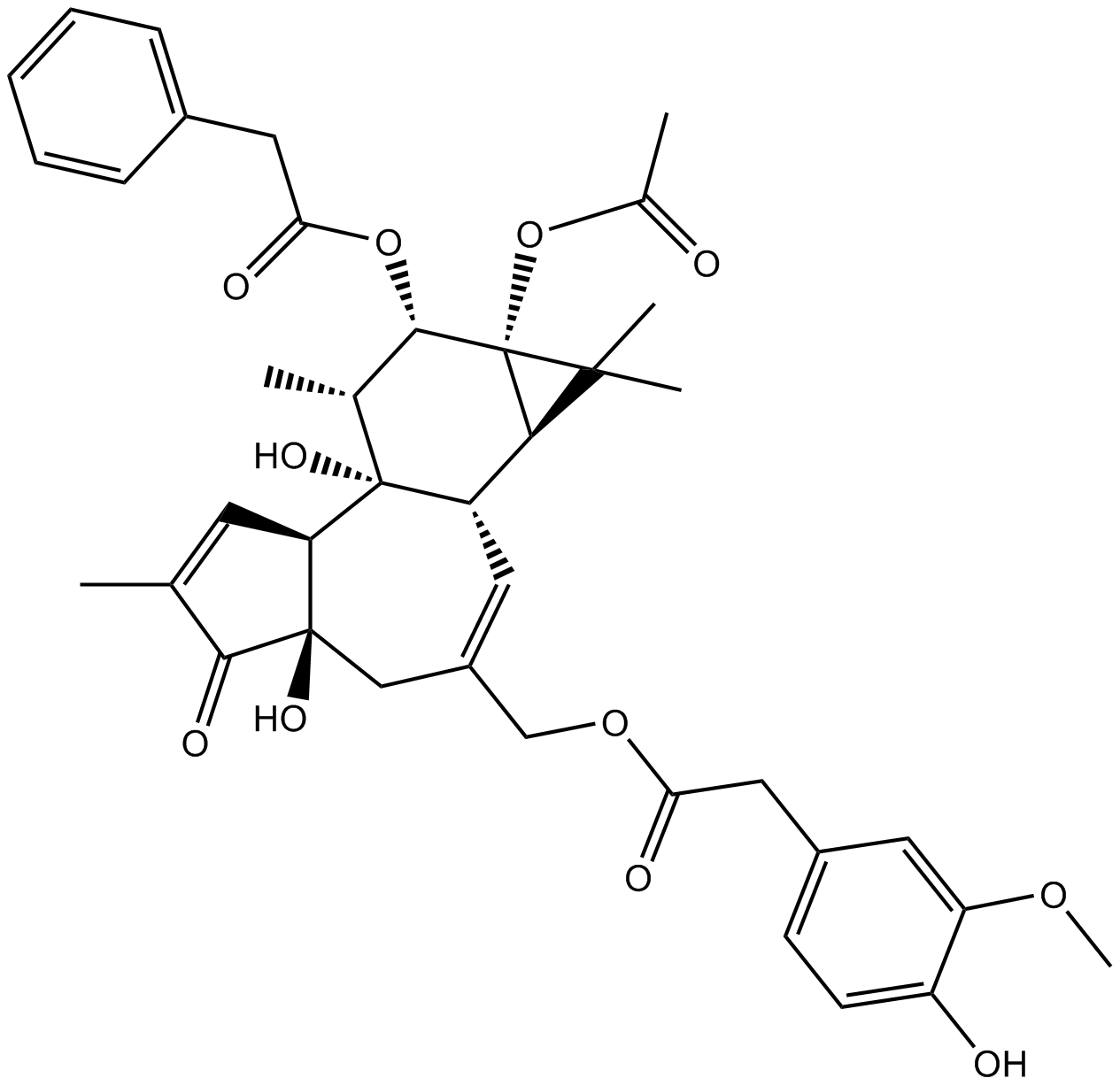 B6750 PPAHVSummary: vanilloid TRPV1 (VR1) receptor agonist
B6750 PPAHVSummary: vanilloid TRPV1 (VR1) receptor agonist -
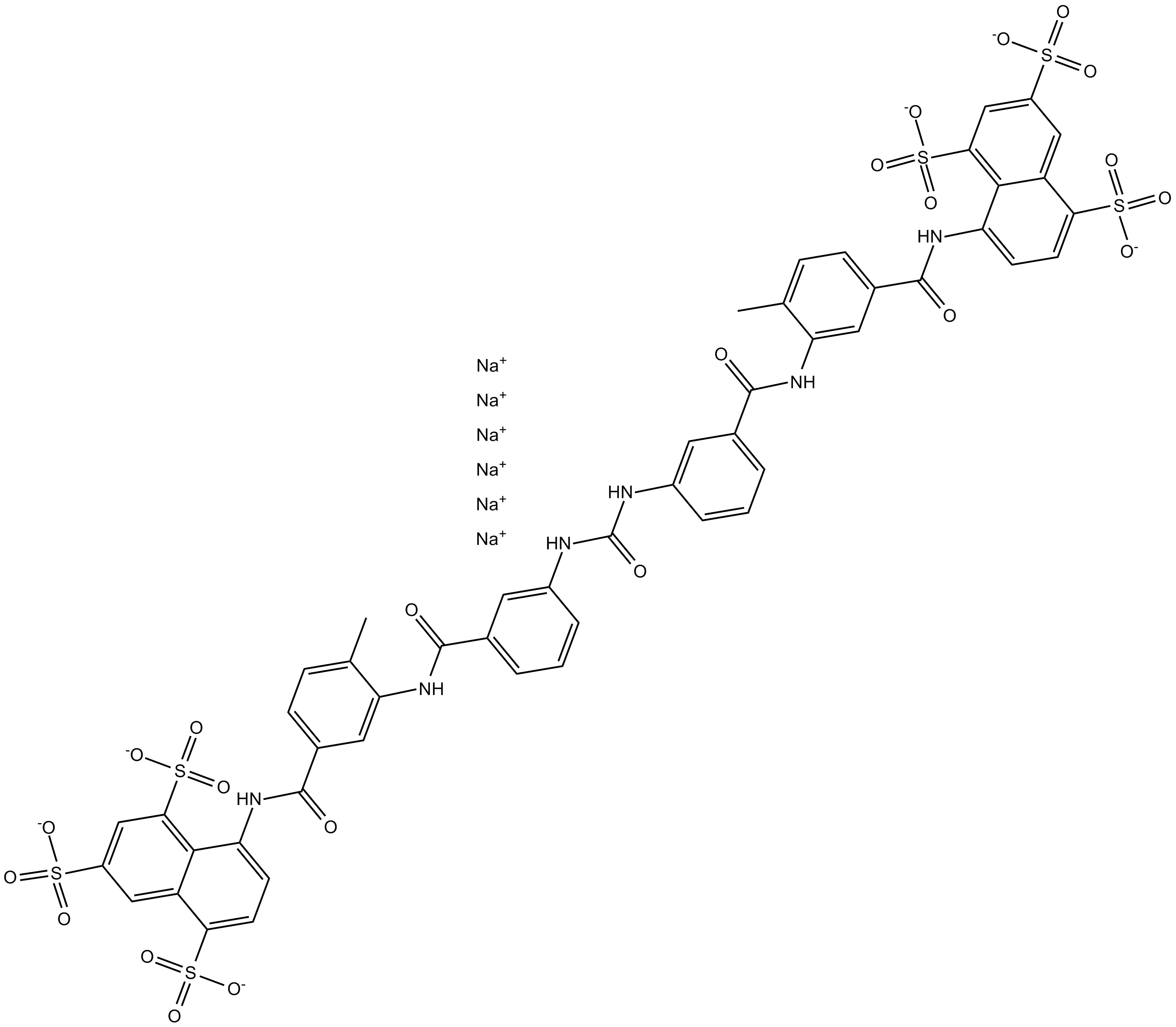 B6752 Suramin hexasodium saltSummary: DNA topoisomerase II inhibitor
B6752 Suramin hexasodium saltSummary: DNA topoisomerase II inhibitor -
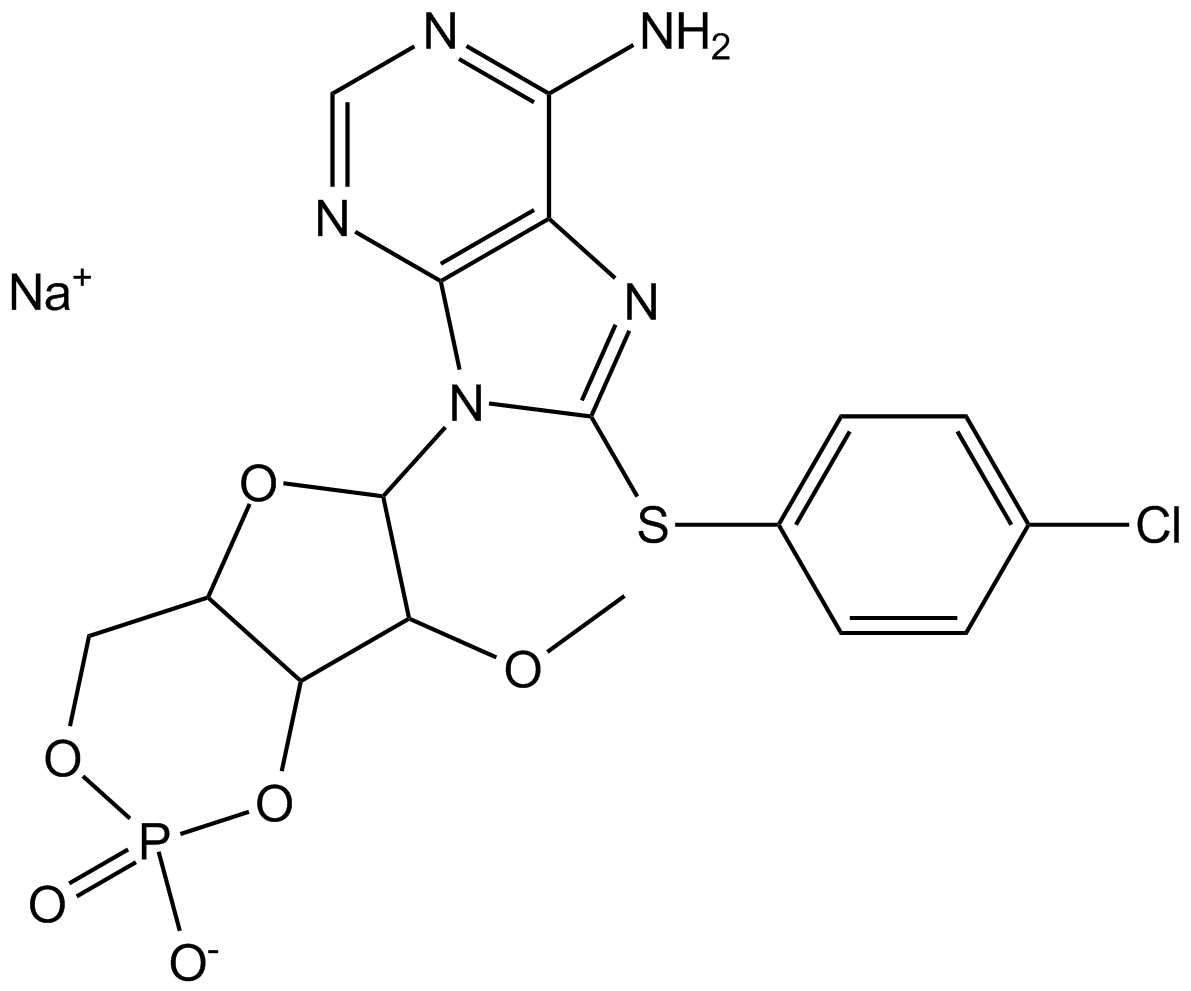 B6816 8-CPT-2Me-cAMP, sodium saltTarget: EpacSummary: EPAC activator, selective
B6816 8-CPT-2Me-cAMP, sodium saltTarget: EpacSummary: EPAC activator, selective -
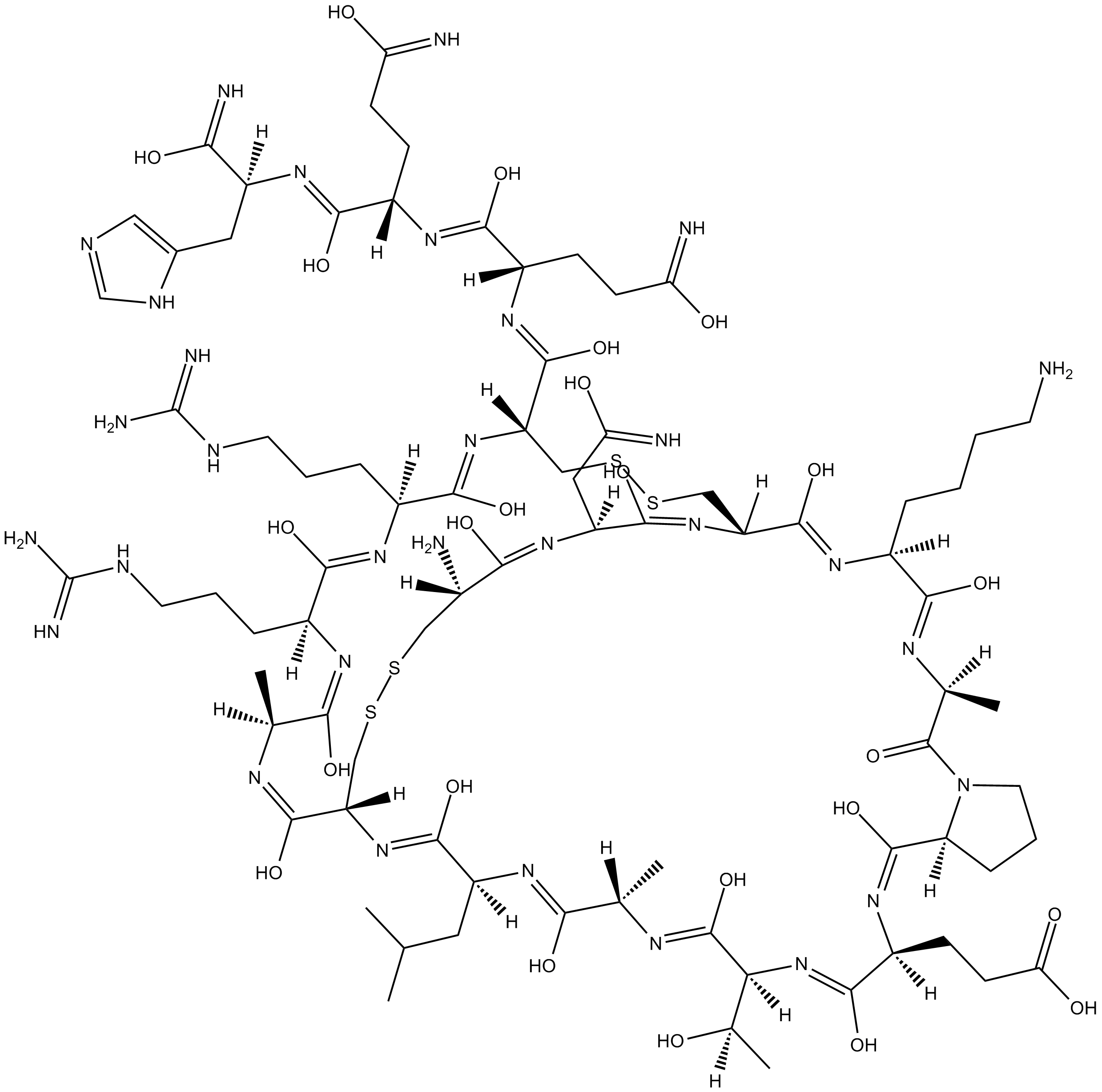 B6817 ApaminSummary: small-conductance Ca2+-activated K+-channel (KCa2, SK) inhibitor
B6817 ApaminSummary: small-conductance Ca2+-activated K+-channel (KCa2, SK) inhibitor -
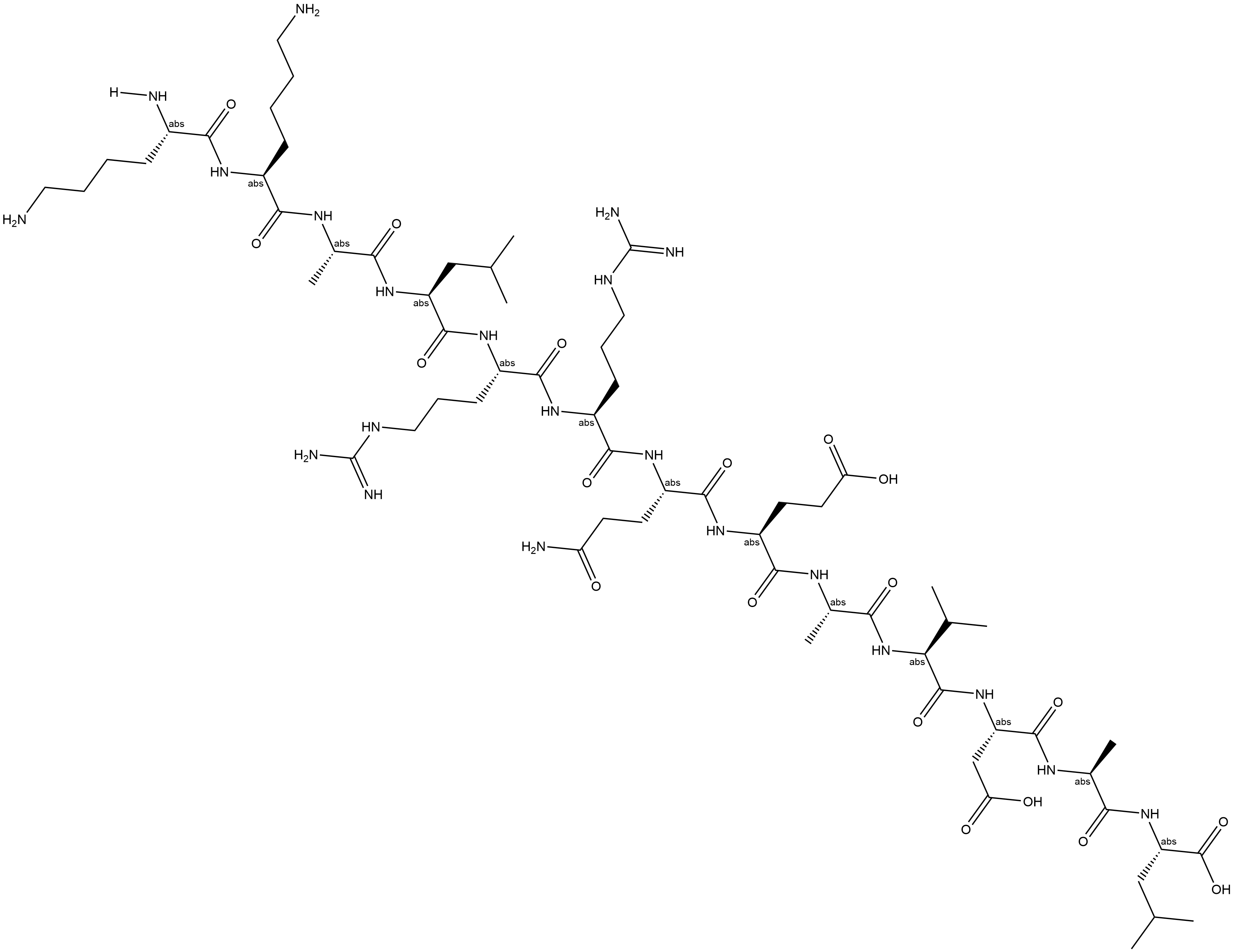 B6831 Autocamtide-2-related inhibitory peptideTarget: Ca2 /calmodulin-dependent protein kinases (CaMKs)Summary: inhibitor of calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaM-kinase II, CaMKII)
B6831 Autocamtide-2-related inhibitory peptideTarget: Ca2 /calmodulin-dependent protein kinases (CaMKs)Summary: inhibitor of calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaM-kinase II, CaMKII) -
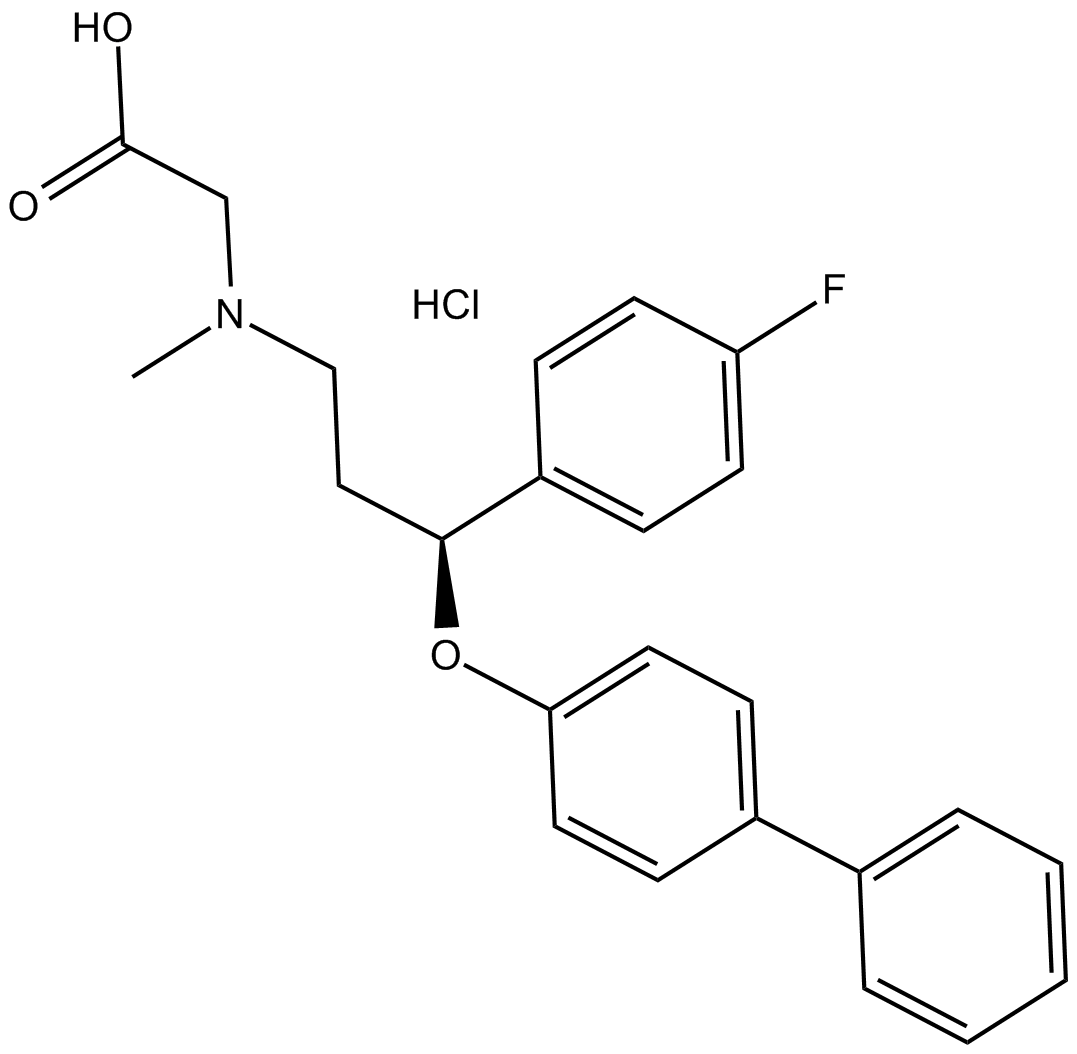 B6846 ALX 5407 hydrochlorideSummary: GlyT1 inhibitor,selective non-transportable
B6846 ALX 5407 hydrochlorideSummary: GlyT1 inhibitor,selective non-transportable -
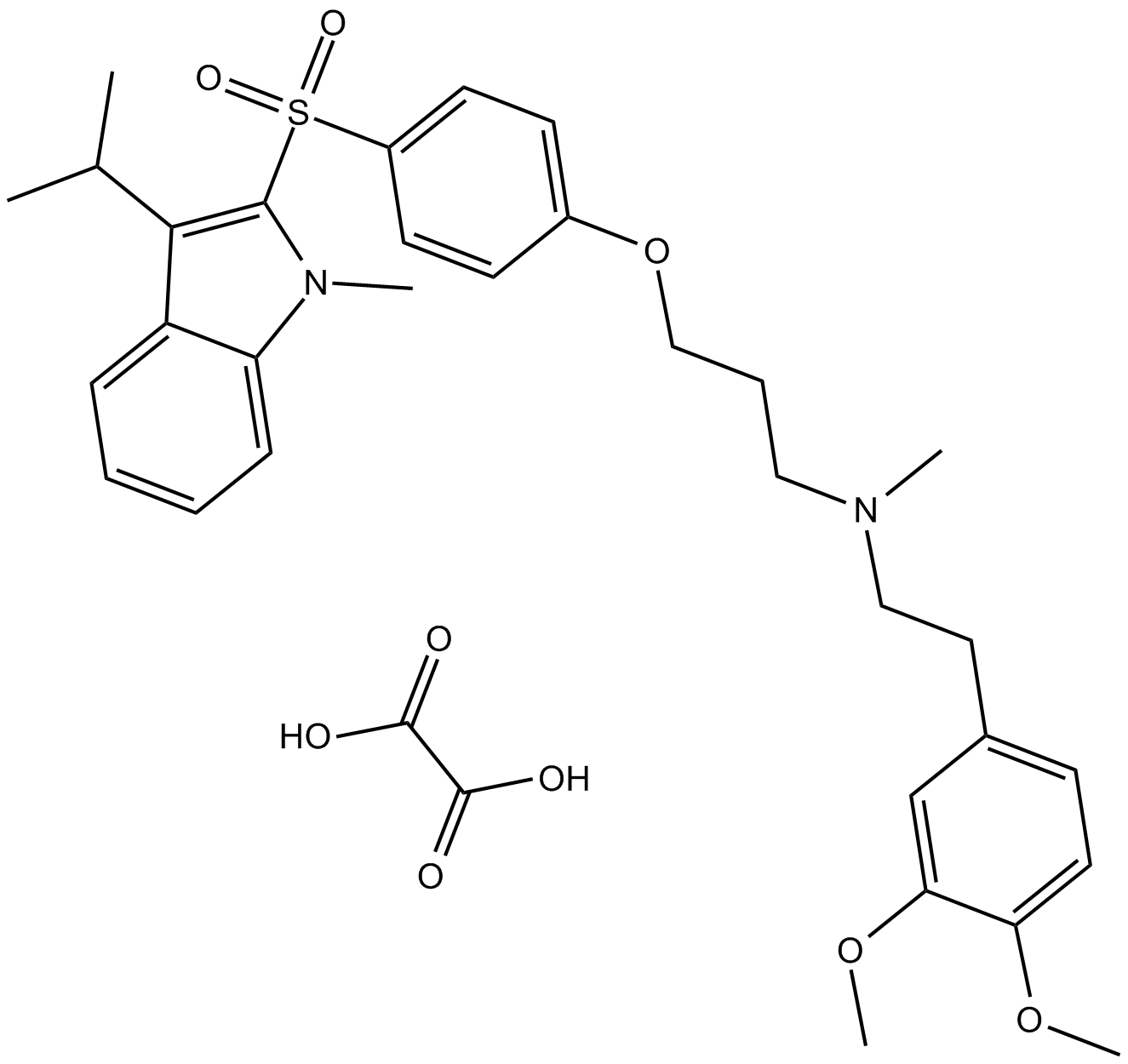 B6861 SR 33805 oxalateSummary: Ca2+ channel antagonist
B6861 SR 33805 oxalateSummary: Ca2+ channel antagonist

